Quadruplanar inversor: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
MichaelFrey (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
MichaelFrey (talk | contribs) No edit summary |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
== Gallery == |
== Gallery == |
||
<gallery caption="Example 1"> |
<gallery caption="Example 1"> |
||
File:Quadruplanar invesor.gif |
|||
File:Quadruplanar invesor.svg |
|||
</gallery> |
|||
<gallery caption="Example 2"> |
|||
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe.gif |
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe.gif |
||
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe.svg |
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe.svg |
||
</gallery> |
</gallery> |
||
<gallery caption="Example |
<gallery caption="Example 3"> |
||
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe Alternate.gif |
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe Alternate.gif |
||
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe Alternate.svg |
File:Quadruplanar invesor of Sylvester and Kempe Alternate.svg |
||
Revision as of 05:20, 24 November 2016
This article provides insufficient context for those unfamiliar with the subject. (November 2016) |
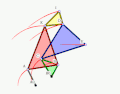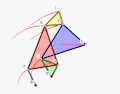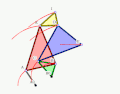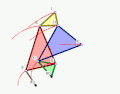
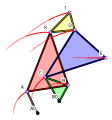
The Quadruplanar inversor of Sylvester and Kempe is a generalization[1] of Hart's inversor. Like Hart's inversor, is a mechanism that provides a perfect straight line motion without sliding guides.
The mechanism was described in 1875 by James Joseph Sylvester (1814-1897) in the journal Nature.
Gallery
- Example 1
- Example 2
- Example 3
-
Description
References
External links
Wikimedia Commons has media related to Invesor of Sylvester and Kempe.
- [2]
- A strong relationship between new and old inversion mechanisms Dijksman, E.A., Published in: Journal of Engineering for Industry : Transactions of the ASME, Published: 01/01/1971
- http://americanhistory.si.edu/collections/search/object/nmah_1214012
- http://alexandria.tue.nl/repository/freearticles/605221.pdf