User:Ellen00a/sandbox: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Geospeedometry''' is the science of measuring the timescales and/or temperatures of thermal events in the history of a [[metamorphic]] or [[Igneous rock|igneous]] rock using diffusion profiles of elements within individual minerals. "''Geospeedometry"'' refers to the ''speed'', or timescale, of thermal events in geologic materials. The term first appeared in the literature in 1983<ref>{{Cite book|url=http://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4612-5587-1_3|title=Kinetics and Equilibrium in Mineral Reactions|last=Lasaga|first=Antonio C.|date=1983-01-01|publisher=Springer New York|isbn=9781461255895|editor-last=Saxena|editor-first=Surendra K.|series=Advances in Physical Geochemistry|pages=81–114|language=en|doi=10.1007/978-1-4612-5587-1_3}}</ref>; prior [[Thermochronology|thermochronometric]] studies focused on diffusion of [[iron]] and [[magnesium]] in [[olivine]] provided the foundation for the field<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Buening|first=D. K.|last2=Buseck|first2=Peter R.|date=1973-10-10|title=Fe-Mg lattice diffusion in olivine|url=http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1029/JB078i029p06852/abstract|journal=Journal of Geophysical Research|language=en|volume=78|issue=29|pages=6852–6862|doi=10.1029/JB078i029p06852|issn=2156-2202}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Taylor|first=L. A.|last2=Onorato|first2=P. I. K.|last3=Uhlmann|first3=D. R.|date=1977-01-01|title=Cooling rate estimations based on kinetic modelling of Fe-Mg diffusion in olivine|url=http://adsabs.harvard.edu/abs/1977LPSC....8.1581T|volume=8|pages=1581–1592}}</ref><ref>{{Cite journal|last=Lehmann|first=J.|year=1983|title=Diffusion between Olivine and Spinel: application to geothermometry|url=|journal=Earth and Planetary Science Letters|volume=64|pages=123-138|via=Elsevier Science Direct}}</ref>. Geospeedometry has since developed rapidly as |
|||
'''Geospeedometry''' is the science of measuring the timescales and/or temperatures of thermal events in the history of a [[metamorphic]] or [[Igneous rock|igneous]] rock using diffusion profiles of elements within individual minerals. "''Geospeedometry"'' refers to the ''speed'', or timescale, of thermal events in geologic materials. |
|||
== Diffusion Theory == |
== Diffusion Theory == |
||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
where<blockquote>'''''D<sub>0</sub>''''' is the maximum diffusivity at infinite temperature; also known as the pre-exponential factor (m<sup>2</sup> s<sup>-1</sup>)</blockquote><blockquote>'''''E<sub>A</sub>''''' is the [[activation energy]] for diffusivity (J mol<sup>-1</sup> )</blockquote><blockquote>'''''R''''' is the [[gas constant]] (J mol<sup>-1</sup> K<sup>-1</sup>)</blockquote><blockquote>'''''T''''' is absolute temperature (K)</blockquote>Given an experimentally determined '''''D<sub>0</sub>''''' for a given element in a given substance, an empirical diffusion profile can be used to calculate the peak temperature or duration of a thermal pulse experienced by the substance. |
where<blockquote>'''''D<sub>0</sub>''''' is the maximum diffusivity at infinite temperature; also known as the pre-exponential factor (m<sup>2</sup> s<sup>-1</sup>)</blockquote><blockquote>'''''E<sub>A</sub>''''' is the [[activation energy]] for diffusivity (J mol<sup>-1</sup> )</blockquote><blockquote>'''''R''''' is the [[gas constant]] (J mol<sup>-1</sup> K<sup>-1</sup>)</blockquote><blockquote>'''''T''''' is absolute temperature (K)</blockquote>Given an experimentally determined '''''D<sub>0</sub>''''' for a given element in a given substance, an empirical diffusion profile can be used to calculate the peak temperature or duration of a thermal pulse experienced by the substance. |
||
== |
== Methodology == |
||
Geologists apply diffusion theory to natural minerals in order to understand the thermal histories of igneous and metamorphic systems. Diffusion profiles of a given element are measured between growth zones of a single mineral, or at the interface between two different minerals. In order to measure a diffusion profile in a single crystal, geologists measure one-dimesional transects using high spatial resolution instruments such as the [[scanning electron microscope]], [[electron microprobe]], [[secondary ion mass spectrometry]] or [[nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometry]]. |
[[File:Geospeedometry diffusion illustration.pdf|thumb|Schematic illustration of an initially sharp concentration gradient between mineral growth zones (blue dashed line) and subsequent measured diffusive gradient (red lines).]]Geologists apply diffusion theory to natural minerals in order to understand the thermal histories of igneous and metamorphic systems. Diffusion profiles of a given element are measured between growth zones of a single mineral, or at the interface between two different minerals. In order to measure a diffusion profile in a single crystal, geologists measure one-dimesional transects using high spatial resolution instruments such as the [[scanning electron microscope]], [[electron microprobe]], [[secondary ion mass spectrometry]] or [[nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometry]]. |
||
== Limitations == |
|||
[[File:Geospeedometry diffusion illustration.pdf|thumb|Schematic illustration of an initially sharp concentration gradient between mineral growth zones (blue dashed line) and subsequent measured diffusive gradient (red lines).]] |
|||
Because the solution to the diffusion equation requires a knowledge of both temperature and time duration of a thermal event, one must be independently constrained in order to measure the other. In geologic systems, neither the temperature nor time duration of thermal events is known [[A priori and a posteriori|a priori]]. An independent [[Geothermobarometry|geothermometer]] must be used to constrain peak temperature in order to use geospeedometry to calculate the duration of a thermal pulse. Conversely, the duration of heating must be constrained independently using [[geochronology]] to estimate maximum temperatures<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Barboni|first=Mélanie|last2=Boehnke|first2=Patrick|last3=Schmitt|first3=Axel K.|last4=Harrison|first4=T. Mark|last5=Shane|first5=Phil|last6=Bouvier|first6=Anne-Sophie|last7=Baumgartner|first7=Lukas|date=2016-12-06|title=Warm storage for arc magmas|url=http://www.pnas.org/content/113/49/13959|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|language=en|volume=113|issue=49|pages=13959–13964|doi=10.1073/pnas.1616129113|issn=0027-8424|pmc=PMC5150383|pmid=27799558}}</ref>. There is ongoing debate in the literature as to geospeedometry's utility to understand large scale magma storage and remobilization<ref>{{Cite journal|last=Miller|first=Calvin F.|date=2016-12-06|year=|title=Eruptible magma|url=http://www.pnas.org/content/113/49/13941|journal=Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences|language=en|volume=113|issue=49|pages=13941–13943|doi=10.1073/pnas.1617105113|issn=|pmc=|pmid=|via=}}</ref>. |
|||
Because the solution to the diffusion equation requires a knowledge of both temperature and time duration of a thermal event, one must be independently constrained in order to measure the other. As such |
|||
Revision as of 18:17, 28 February 2017
Geospeedometry is the science of measuring the timescales and/or temperatures of thermal events in the history of a metamorphic or igneous rock using diffusion profiles of elements within individual minerals. "Geospeedometry" refers to the speed, or timescale, of thermal events in geologic materials. The term first appeared in the literature in 1983[1]; prior thermochronometric studies focused on diffusion of iron and magnesium in olivine provided the foundation for the field[2][3][4]. Geospeedometry has since developed rapidly as
Diffusion Theory
Geospeedometry makes use of the temperature dependence of the chemical diffusion of elements between zones of a mineral grain. According to Fick's second law, the concentration of an element in one dimension across a diffusive interface is given by the partial differential equation
where
D is the diffusion coefficient, or diffusivity (m2 s-1) of the element in the medium
x is the position (length)
t is time
C is the concentration of the element; C(x,t) is a function dependent on both length and time.
For a one-dimensional interface at x = 0 with a fixed concentration C0,
where erfc is the complementary error function.
The diffusivity of an element in a medium is given by the temperature-dependent Arrhenius equation
where
D0 is the maximum diffusivity at infinite temperature; also known as the pre-exponential factor (m2 s-1)
EA is the activation energy for diffusivity (J mol-1 )
R is the gas constant (J mol-1 K-1)
T is absolute temperature (K)
Given an experimentally determined D0 for a given element in a given substance, an empirical diffusion profile can be used to calculate the peak temperature or duration of a thermal pulse experienced by the substance.
Methodology
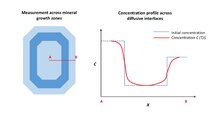
Geologists apply diffusion theory to natural minerals in order to understand the thermal histories of igneous and metamorphic systems. Diffusion profiles of a given element are measured between growth zones of a single mineral, or at the interface between two different minerals. In order to measure a diffusion profile in a single crystal, geologists measure one-dimesional transects using high spatial resolution instruments such as the scanning electron microscope, electron microprobe, secondary ion mass spectrometry or nanoscale secondary ion mass spectrometry.
Limitations
Because the solution to the diffusion equation requires a knowledge of both temperature and time duration of a thermal event, one must be independently constrained in order to measure the other. In geologic systems, neither the temperature nor time duration of thermal events is known a priori. An independent geothermometer must be used to constrain peak temperature in order to use geospeedometry to calculate the duration of a thermal pulse. Conversely, the duration of heating must be constrained independently using geochronology to estimate maximum temperatures[5]. There is ongoing debate in the literature as to geospeedometry's utility to understand large scale magma storage and remobilization[6].
- ^ Lasaga, Antonio C. (1983-01-01). Saxena, Surendra K. (ed.). Kinetics and Equilibrium in Mineral Reactions. Advances in Physical Geochemistry. Springer New York. pp. 81–114. doi:10.1007/978-1-4612-5587-1_3. ISBN 9781461255895.
- ^ Buening, D. K.; Buseck, Peter R. (1973-10-10). "Fe-Mg lattice diffusion in olivine". Journal of Geophysical Research. 78 (29): 6852–6862. doi:10.1029/JB078i029p06852. ISSN 2156-2202.
- ^ Taylor, L. A.; Onorato, P. I. K.; Uhlmann, D. R. (1977-01-01). "Cooling rate estimations based on kinetic modelling of Fe-Mg diffusion in olivine". 8: 1581–1592.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ Lehmann, J. (1983). "Diffusion between Olivine and Spinel: application to geothermometry". Earth and Planetary Science Letters. 64: 123–138 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ^ Barboni, Mélanie; Boehnke, Patrick; Schmitt, Axel K.; Harrison, T. Mark; Shane, Phil; Bouvier, Anne-Sophie; Baumgartner, Lukas (2016-12-06). "Warm storage for arc magmas". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (49): 13959–13964. doi:10.1073/pnas.1616129113. ISSN 0027-8424. PMC 5150383. PMID 27799558.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: PMC format (link) - ^ Miller, Calvin F. (2016-12-06). "Eruptible magma". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 113 (49): 13941–13943. doi:10.1073/pnas.1617105113.



