Magnetic resonance imaging: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
TimeForLunch (talk | contribs) Undid revision 789882315 by Special:Contributions/2405:204:7044:539C:4CF0:6E2B:BACF:E817 |
||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
===Liver and gastrointestinal imaging MRI=== |
===Liver and gastrointestinal imaging MRI=== |
||
[[Hepatobiliary system|Hepatobiliary]] . Focal or diffuse disorders of the liver may be evaluated using [[Diffusion MRI|diffusion-weighted]], opposed-phase imaging, and [[Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI|dynamic contrast enhancement]] sequences. Extracellular contrast agents are used widely in liver MRI and newer hepatobiliary contrast agents also provide the opportunity to perform functional biliary imaging. Anatomical imaging of the bile ducts is achieved by using a heavily T2-weighted sequence in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Functional imaging of the pancreas is performed following administration of [[secretin]]. MR enterography provides non-invasive assessment of inflammatory bowel disease and small bowel tumors. MR-colonography may play a role in the detection of large polyps in patients at increased risk of colorectal cancer.<ref name="FrydrychowiczLubner2012">{{cite journal | author = Frydrychowicz A | author2 = Lubner MG | author3 = Brown JJ | author4 = Merkle EM | author5 = Nagle SK | author6 = Rofsky NM | author7 = Reeder SB | title = Hepatobiliary MR imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents | journal = J Magn Reson Imaging | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 492–511 | date = 2012 | pmid = 22334493 | pmc = 3281562 | doi = 10.1002/jmri.22833 }}</ref><ref name="SandrasegaranLin2010">{{cite journal | author = Sandrasegaran K | author2 = Lin C | author3 = Akisik FM| author4 = Tann M | title = State-of-the-art pancreatic MRI | journal = AJR Am J Roentgenol | volume = 195 | issue = 1 | pages = 42–53 | date = 2010 | pmid = 20566796 | doi = 10.2214/ajr.195.3_supplement.0s42 }}</ref><ref name="MasselliGualdi2012">{{cite journal | author = Masselli G | author2 = Gualdi G | title = MR imaging of the small bowel | journal = Radiology | volume = 264 | issue = 2 | pages = 333–48 | date = 2012 | pmid = 22821694 | doi = 10.1148/radiol.12111658 }}</ref><ref name="ZijtaBipat2009">{{cite journal | author = Zijta FM | author2 = Bipat S | author3 = Stoker J | title = Magnetic resonance (MR) colonography in the detection of colorectal lesions: a systematic review of prospective studies | journal = Eur Radiol | volume = 20 | issue = 5 | pages = 1031–46 | date = 2010 | pmid = 19936754 | pmc = 2850516 | doi = 10.1007/s00330-009-1663-4 }}</ref> |
[[Hepatobiliary system|Hepatobiliary]] MR is used to detect and characterize lesions of the [[liver]], [[pancreas]], and [[bile duct]]s. Focal or diffuse disorders of the liver may be evaluated using [[Diffusion MRI|diffusion-weighted]], opposed-phase imaging, and [[Dynamic Contrast Enhanced MRI|dynamic contrast enhancement]] sequences. Extracellular contrast agents are used widely in liver MRI and newer hepatobiliary contrast agents also provide the opportunity to perform functional biliary imaging. Anatomical imaging of the bile ducts is achieved by using a heavily T2-weighted sequence in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Functional imaging of the pancreas is performed following administration of [[secretin]]. MR enterography provides non-invasive assessment of inflammatory bowel disease and small bowel tumors. MR-colonography may play a role in the detection of large polyps in patients at increased risk of colorectal cancer.<ref name="FrydrychowiczLubner2012">{{cite journal | author = Frydrychowicz A | author2 = Lubner MG | author3 = Brown JJ | author4 = Merkle EM | author5 = Nagle SK | author6 = Rofsky NM | author7 = Reeder SB | title = Hepatobiliary MR imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents | journal = J Magn Reson Imaging | volume = 35 | issue = 3 | pages = 492–511 | date = 2012 | pmid = 22334493 | pmc = 3281562 | doi = 10.1002/jmri.22833 }}</ref><ref name="SandrasegaranLin2010">{{cite journal | author = Sandrasegaran K | author2 = Lin C | author3 = Akisik FM| author4 = Tann M | title = State-of-the-art pancreatic MRI | journal = AJR Am J Roentgenol | volume = 195 | issue = 1 | pages = 42–53 | date = 2010 | pmid = 20566796 | doi = 10.2214/ajr.195.3_supplement.0s42 }}</ref><ref name="MasselliGualdi2012">{{cite journal | author = Masselli G | author2 = Gualdi G | title = MR imaging of the small bowel | journal = Radiology | volume = 264 | issue = 2 | pages = 333–48 | date = 2012 | pmid = 22821694 | doi = 10.1148/radiol.12111658 }}</ref><ref name="ZijtaBipat2009">{{cite journal | author = Zijta FM | author2 = Bipat S | author3 = Stoker J | title = Magnetic resonance (MR) colonography in the detection of colorectal lesions: a systematic review of prospective studies | journal = Eur Radiol | volume = 20 | issue = 5 | pages = 1031–46 | date = 2010 | pmid = 19936754 | pmc = 2850516 | doi = 10.1007/s00330-009-1663-4 }}</ref> |
||
===Functional MRI=== |
===Functional MRI=== |
||
Revision as of 10:31, 10 July 2017
| Magnetic resonance imaging | |
|---|---|
Para-sagittal MRI of the head, with aliasing artifacts (nose and forehead appear at the back of the head) | |
| Synonyms | nuclear magnetic resonance imaging (NMRI), magnetic resonance tomography (MRT) |
| ICD-9-CM | 88.91 |
| MeSH | D008279 |
| MedlinePlus | 003335 |
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a medical imaging technique used in radiology to form pictures of the anatomy and the physiological processes of the body in both health and disease. MRI scanners use strong magnetic fields, radio waves, and field gradients to generate images of the organs in the body.
MRI does not involve x-rays, which distinguishes it from computed tomography (CT or CAT). While the hazards of x-rays are now well-controlled in most medical contexts, MRI still may be seen as superior to CT in this regard.
MRI often may yield different diagnostic information compared with CT. There may be risks and discomfort associated with MRI scans. Compared with CT, MRI scans typically take greater time, are louder, and usually require that the subject go into a narrow, confined tube. In addition, people with some medical implants or other non-removable metal inside the body may be unable to undergo an MRI examination safely.
MRI is based upon the science of nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR). Certain atomic nuclei are able to absorb and emit radio frequency energy when placed in an external magnetic field. In clinical and research MRI, hydrogen atoms are most-often used to generate a detectable radio-frequency signal that is received by antennas in close proximity to the anatomy being examined. Hydrogen atoms exist naturally in people and other biological organisms in abundance, particularly in water and fat. For this reason, most MRI scans essentially map the location of water and fat in the body. Pulses of radio waves excite the nuclear spin energy transition, and magnetic field gradients localize the signal in space. By varying the parameters of the pulse sequence, different contrasts may be generated between tissues based on the relaxation properties of the hydrogen atoms therein.
Since its early development in the 1970s and 1980s, MRI has proven to be a highly versatile imaging technique. While MRI is most prominently used in diagnostic medicine and biomedical research, it also may be used to form images of non-living objects. MRI scans are capable of producing a variety of chemical and physical data, in addition to detailed spatial images.
MRI is widely used in hospitals and clinics for medical diagnosis, staging of disease and follow-up without exposing the body to ionizing radiation.
Medical uses
MRI has a wide range of applications in medical diagnosis and more than 25,000 scanners are estimated to be in use worldwide.[1] MRI affects diagnosis and treatment in many specialties although the effect on improved health outcomes is uncertain.[2] Since MRI does not use any ionizing radiation, its use generally is favored in preference to CT when either modality could yield the same information.[3] (In certain cases, MRI is not preferred as it may be more expensive, time-consuming, and claustrophobia-exacerbating).
MRI is in general a safe technique, although injuries may occur as a result of failed safety procedures or human error.[4] Contraindications to MRI include most cochlear implants and cardiac pacemakers, shrapnel, and metallic foreign bodies in the eyes. The safety of MRI during the first trimester of pregnancy is uncertain, but it may be preferable to other options.[5] The sustained increase in demand for MRI within the healthcare industry has led to concerns about cost effectiveness and overdiagnosis.[6][7]
Neuroimaging

MRI is the investigative tool of choice for neurological cancers, as it has better resolution than CT and offers better visualization of the posterior fossa. The contrast provided between grey and white matter makes MRI the best choice for many conditions of the central nervous system, including demyelinating diseases, dementia, cerebrovascular disease, infectious diseases, and epilepsy.[8] Since many images are taken milliseconds apart, it shows how the brain responds to different stimuli, enabling researchers to study both the functional and structural brain abnormalities in psychological disorders.[9] MRI also is used in mri-guided stereotactic surgery and radiosurgery for treatment of intracranial tumors, arteriovenous malformations, and other surgically treatable conditions using a device known as the N-localizer.[10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17][18] [19][20][21][22][23]
Cardiovascular

Cardiac MRI is complementary to other imaging techniques, such as echocardiography, cardiac CT, and nuclear medicine. Its applications include assessment of myocardial ischemia and viability, cardiomyopathies, myocarditis, iron overload, vascular diseases, and congenital heart disease.[24]
Musculoskeletal
Applications in the musculoskeletal system include spinal imaging, assessment of joint disease, and soft tissue tumors.[25]
Liver and gastrointestinal imaging MRI
Hepatobiliary MR is used to detect and characterize lesions of the liver, pancreas, and bile ducts. Focal or diffuse disorders of the liver may be evaluated using diffusion-weighted, opposed-phase imaging, and dynamic contrast enhancement sequences. Extracellular contrast agents are used widely in liver MRI and newer hepatobiliary contrast agents also provide the opportunity to perform functional biliary imaging. Anatomical imaging of the bile ducts is achieved by using a heavily T2-weighted sequence in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP). Functional imaging of the pancreas is performed following administration of secretin. MR enterography provides non-invasive assessment of inflammatory bowel disease and small bowel tumors. MR-colonography may play a role in the detection of large polyps in patients at increased risk of colorectal cancer.[26][27][28][29]
Functional MRI
Functional MRI (fMRI) is used to understand how different parts of the brain respond to external stimuli or passive activity in a resting state. Blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) fMRI measures the hemodynamic response to transient neural activity resulting from a change in the ratio of oxyhemoglobin and deoxyhemoglobin. Researchers use statistical methods to construct a 3-D parametric map of the brain indicating the regions of the cortex that demonstrate a significant change in activity in response to the task. fMRI has applications in behavioral and cognitive research, and in planning neurosurgery of eloquent brain areas.[30][31]
Oncology
MRI is the investigation of choice in the preoperative staging of rectal and prostate cancer and, has a role in the diagnosis, staging, and follow-up of other tumors.[32]
Phase contrast MRI
Phase contrast MRI (PC-MRI) is used to measure flow velocities in the body. It is used mainly to measure blood flow in the heart and throughout the body. PC-MRI may be considered a method of magnetic resonance velocimetry. Since modern PC-MRI typically is time-resolved, it also may be referred to as 4-D imaging (three spatial dimensions plus time).[33]
Safety
Structure and certification
In an effort to standardize the roles and responsibilities of MRI professionals, an international consensus document, written and endorsed by major MRI and medical physics professional societies from around the globe, has been published formally. The document outlines specific responsibilities for the following positions:
- MR Medical Director / Research Director (MRMD) - This individual is the supervising physician who has oversight responsibility for the safe use of MRI services.
- MR Safety Officer (MRSO) - Roughly analogous to a radiation safety officer, the MRSO acts on behalf of, and on the instruction of, the MRMD to execute safety procedures and practices at the point of care.
- MR Safety Expert (MRSE) - This individual serves in a consulting role to both the MRMD and MRSO, assisting in the investigation of safety questions that may include the need for extrapolation, interpolation, or quantification to approximate the risk of a specific study.
The American Board of Magnetic Resonance Safety (ABMRS) provides testing and board certification for each of the three positions, MRMD, MRSO, and MRSE. As most MRI accidents and injuries are directly attributable to decisions at the point of care, testing and certification of MRI professionals seeks to reduce the rates of MRI accidents and improve patient safety through the establishment of safety competency levels for MRI professionals.
Implants
All patients are reviewed for contraindications prior to MRI scanning. Medical devices and implants are categorized as MR Safe, MR Conditional or MR Unsafe:[34]
- MR-Safe – The device or implant is completely non-magnetic, non-electrically conductive, and non-RF reactive, eliminating all of the primary potential threats during an MRI procedure.
- MR-Conditional – A device or implant that may contain magnetic, electrically conductive, or RF-reactive components that is safe for operations in proximity to the MRI, provided the conditions for safe operation are defined and observed (such as 'tested safe to 1.5 teslas' or 'safe in magnetic fields below 500 gauss in strength').
- MR-Unsafe – Objects that are significantly ferromagnetic and pose a clear and direct threat to persons and equipment within the magnet room.
The MRI environment may cause harm in patients with MR-Unsafe devices such as cochlear implants, aneurysm clips, and many permanent pacemakers. In November 1992, a patient with an undisclosed cerebral aneurysm clip was reported to have died shortly after an MRI exam.[35] Several deaths have been reported in patients with pacemakers who have undergone MRI scanning without appropriate precautions.[36] Increasingly, MR-conditional pacemakers are available for selected patients.[37]
Ferromagnetic foreign bodies such as shell fragments, or metallic implants such as surgical prostheses and ferromagnetic aneurysm clips also are potential risks. Interaction of the magnetic and radio frequency fields with such objects may lead to heating or torque of the object during an MRI.[38]
Titanium and its alloys are safe from attraction and torque forces produced by the magnetic field, although there may be some risks associated with Lenz effect forces acting on titanium implants in sensitive areas within the subject, such as stapes implants in the inner ear.
Projectile risk
The very high strength of the magnetic field may cause projectile effect (or "missile-effect") accidents, where ferromagnetic objects are attracted to the center of the magnet. Pennsylvania reported 27 cases of objects becoming projectiles in the MRI environment between 2004 and 2008.[39] There have been incidents of injury and death.[40][41] In one case, a six-year-old boy died during a MRI exam, after a metal oxygen tank was pulled across the room and crushed the child's head.[42] To reduce the risk of projectile accidents, ferromagnetic objects and devices typically, are prohibited near the MRI scanner, and patients undergoing MRI examinations must remove all metallic objects, often by changing into a gown or scrubs. Some radiology departments use ferromagnetic detection devices to ensure that no ferromagnetic objects enter the scanner room.[43][44]
MRI-EEG
In research settings, structural MRI or functional MRI (fMRI) may be combined with EEG (electroencephalography) under the condition that the EEG equipment is MR-compatible. Although EEG equipment (electrodes, amplifiers, and peripherals) are either approved for research or clinical use, the same MR Safe, MR Conditional and MR Unsafe terminology applies. With the growth of the use of MR technology, the U.S. Food & Drug Administration [FDA] recognized the need for a consensus on standards of practice, and the FDA sought out ASTM International [ASTM] to achieve them. Committee F04 [45] of ASTM developed F2503, Standard Practice for Marking Medical Devices and Other Items for Safety in the Magnetic Resonance Environment.[46]
Genotoxic effects
There is no proven risk of biological harm from any aspect of a MRI scan, including very powerful static magnetic fields, gradient magnetic fields, or radio frequency waves.[47][48] Some studies have suggested possible genotoxic (i.e., potentially carcinogenic) effects of MRI scanning through micronuclei induction and DNA double strand breaks in vivo and in vitro,[49][50][51] however, in most, if not all cases, others have not been able to repeat or validate the results of these studies,[47][48] and the majority of research shows no genotoxic, or otherwise harmful, effects caused by any part of MRI.[47] A recent study confirmed that MRI at some of the most potentially-risky parameters tested to date (7-tesla static magnetic field, 70 mT/m gradient magnetic field, and maximum strength radio frequency waves), did not cause any DNA damage in vitro.[52]
Peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS)
The rapid switching on and off of the magnetic field gradients is capable of causing nerve stimulation. Volunteers report a twitching sensation when exposed to rapidly switched fields, particularly in their extremities.[53][54] The reason the peripheral nerves are stimulated is that the changing field increases with distance from the center of the gradient coils (which more or less coincides with the center of the magnet).[55] Although PNS was not a problem for the slow, weak gradients used in the early days of MRI, the strong, rapidly switched gradients used in techniques such as EPI, fMRI, diffusion MRI, etc. are capable of inducing PNS. American and European regulatory agencies insist that manufacturers stay below specified dB/dt limits (dB/dt is the change in magnetic field strength per unit time), or else prove that no PNS is induced for any imaging sequence. As a result of dB/dt limitation, commercial MRI systems cannot use the full rated power of their gradient amplifiers.
Heating caused by absorption of radio waves
Every MRI scanner has a powerful radio transmitter that generates the electromagnetic field that excites the spins. If the body absorbs the energy, heating occurs. For this reason, the transmitter rate at which energy is absorbed by the body must be limited (see Specific absorption rate). It has been claimed that tattoos made with iron-containing dyes may lead to burns on the subject's body.[56][57] Cosmetics are very unlikely to undergo heating, as well as body lotions, since the outcome of the reactions between those with the radio waves is unknown. The best option for clothing is 100% cotton. The MRI system must attend to periodic maintenance from the manufacturer. Gradients and RF transmit must attend factory specifications. In some systems there are parts responsible for the measurement of the power absorption limiter that must be replaced periodically with new ones (or be re-calibrated in the factory).
There are several positions strictly forbidden during measurement such as crossing arms and legs, and the patient's body may not create loops of any kind for the RF during the measurement.
Unusual patient heating cases must be reported to the appropriate regulatory agency for further investigation.
Acoustic noise
Switching of field gradients causes a change in the Lorentz force experienced by the gradient coils, producing minute expansions and contractions of the coil. As the switching typically is in the audible frequency range, the resulting vibration produces loud noises (clicking, banging, or beeping). This is most marked with high-field machines,[58] and rapid-imaging techniques in which sound pressure levels may reach 120 dB(A) (equivalent to a jet engine at take-off),[59] and therefore, appropriate ear protection is essential for anyone inside the MRI scanner room during the examination.[60]
Radio frequency in itself does not cause audible noises (at least for human beings), since modern systems are using frequencies of 8.5 MHz (0.2 T system) or higher.[61]
Cryogens
As described in the Physics of magnetic resonance imaging article, many MRI scanners rely on cryogenic liquids to enable the superconducting capabilities of the electromagnetic coils within. Although the cryogenic liquids used are non-toxic, their physical properties present specific hazards.[62]
An unintentional shut-down of a superconducting electromagnet, an event known as "quench", involves the rapid boiling of liquid helium from the device. If the rapidly expanding helium cannot be dissipated through an external vent, sometimes referred to as a 'quench pipe', it may be released into the scanner room where it may cause displacement of the oxygen and present a risk of asphyxiation.[63]
Oxygen deficiency monitors usually are used as a safety precaution. Liquid helium, the most commonly used cryogen in MRI, undergoes near explosive expansion as it changes from a liquid to gaseous state. The use of an oxygen monitor is important to ensure that oxygen levels are safe for patients and physicians. Rooms built for superconducting MRI equipment should be equipped with pressure relief mechanisms [64] and an exhaust fan, in addition to the required quench pipe.
Because a quench results in rapid loss of cryogens from the magnet, recommissioning the magnet is expensive and time-consuming. Spontaneous quenches are uncommon, but a quench also may be triggered by an equipment malfunction, an improper cryogen fill technique, contaminants inside the cryostat, or extreme magnetic or vibrational disturbances.[65][66]
Pregnancy
No effects of MRI on the fetus have been demonstrated.[67] In particular, MRI avoids the use of ionizing radiation, to which the fetus is particularly sensitive. As a precaution, however, many guidelines recommend pregnant women only undergo MRI when essential, especially during the first trimester.[68] The concerns in pregnancy are the same as for MRI in general, but the fetus may be more sensitive to the effects—particularly to heating and to noise. The use of gadolinium-based contrast media in pregnancy is an off-label indication and may be administered only in the lowest dose required to provide essential diagnostic information.[69]
Despite these concerns, MRI is rapidly growing in importance as a way of diagnosing and monitoring congenital defects of the fetus because it is able to provide more diagnostic information than ultrasound and it lacks the ionizing radiation of CT. MRI without contrast agents is the imaging mode of choice for pre-surgical, in-utero diagnosis and evaluation of fetal tumors, primarily teratomas, facilitating open fetal surgery, other fetal interventions, and planning for procedures (such as the EXIT procedure) to safely deliver and treat babies whose defects would otherwise be fatal.[70][71]
Claustrophobia and discomfort
Although painless, MRI scans may be unpleasant for those who are claustrophobic or otherwise uncomfortable with the imaging device surrounding them. Older closed bore MRI systems have a fairly long tube or tunnel. The part of the body being imaged must lie at the center of the magnet, which is at the absolute center of the tunnel. Because scan times on these older scanners may be long (occasionally up to 40 minutes for the entire procedure), people with even mild claustrophobia are sometimes unable to tolerate an MRI scan without management. Some modern scanners have larger bores (up to 70 cm) and scan times are shorter. A 1.5 T wide short bore scanner increases the examination success rate in patients with claustrophobia and substantially reduces the need for anesthesia-assisted MRI examinations even when claustrophobia is severe.[72]
Alternative scanner designs, such as open or upright systems, may be helpful where these are available. Although open scanners have increased in popularity, they produce inferior scan quality because they operate at lower magnetic fields than closed scanners. Commercial 1.5-tesla open systems have become available recently, however, providing much better image quality than previous lower field strength open models.[73]
Mirror glasses may be used to help create the illusion of openness. The mirrors are angled at 45 degrees, allowing the patient to look down their body and out the end of the imaging area. The appearance is of an open tube pointing upward (as seen when lying in the imaging area). Even though one is able to see around the glasses and the proximity of the device is very evident, this illusion is quite persuasive and relieves the claustrophobic feeling.
For babies and other young children, chemical sedation or general anesthesia are the norm, as these subjects cannot be expected or instructed to hold still during the scanning session. Also, children frequently are sedated because they are frightened by the unfamiliar procedure and the loud noises. To reduce anxiety, some hospitals have specially designed child-friendly approaches that pretend the MRI machine is a spaceship or another fun experience.[74]
Obese patients and pregnant women may find the MRI machine a tight fit. Pregnant women in the third trimester also may have difficulty lying on their backs for an hour or more without moving.
MRI versus CT
MRI and computed tomography (CT) are complementary imaging technologies and each has advantages and limitations for particular applications. CT is more widely used than MRI in OECD countries with a mean of 132 vs. 46 exams per 1000 population performed respectively.[75] A concern is the potential for CT to contribute to radiation-induced cancer and in 2007 it was estimated that 0.4% of current cancers in the United States were due to CTs performed in the past, and that in the future this figure may rise to 1.5–2% based on historical rates of CT usage.[76] An Australian study found that one in every 1800 CT scans was associated with an excess cancer.[77] An advantage of MRI is that no ionizing radiation is used and so it is recommended over CT when either approach could yield the same diagnostic information.[3] Although the cost of MRI has fallen, making it more competitive with CT, there are not many common imaging scenarios in which MRI can simply replace CT, however, this substitution has been suggested for the imaging of liver disease.[78] The effect of low doses of radiation on carcinogenesis also are disputed.[79] Although MRI is associated with biological effects, these have not been proven to cause measurable harm.[80]
Iodinated contrast medium is routinely used in CT and the main adverse events are anaphylactoid reactions and nephrotoxicity.[81] Commonly used MRI contrast agents have a good safety profile, but linear non-ionic agents in particular have been implicated in nephrogenic systemic fibrosis in patients with severely impaired renal function.[82]
MRI is contraindicated in the presence of MR-unsafe implants, and although these patients may be imaged with CT, beam hardening artefact from metallic devices, such as pacemakers and implantable cardioverter-defibrillators, also may affect image quality.[83] MRI is a longer investigation than CT and an exam may take between 20 and 40 minutes depending on complexity.[84]
Guidance
Safety issues, including the potential for biostimulation device interference, movement of ferromagnetic bodies, and incidental localized heating, have been addressed in the American College of Radiology's White Paper on MR Safety, which originally was published in 2002 and expanded in 2004. The ACR White Paper on MR Safety has been rewritten and was released early in 2007 under the new title ACR Guidance Document for Safe MR Practices.
In December 2007, the Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency (MHRA), a UK healthcare regulatory body, issued their Safety Guidelines for Magnetic Resonance Imaging Equipment in Clinical Use. In February 2008, the Joint Commission, a U.S. healthcare accrediting organization, issued a Sentinel Event Alert #38, their highest patient safety advisory, on MRI safety issues. In July 2008, the United States Veterans Administration, a federal governmental agency serving the healthcare needs of former military personnel, issued a substantial revision to their MRI Design Guide,[85] that includes physical and facility safety considerations.
The European Directive on electromagnetic fields
This Directive (2013/35/EU - electromagnetic fields) [86] covers all known direct biophysical effects and indirect effects caused by electromagnetic fields within the EU and repealed the 2004/40/EC directive. The deadline for implementation of the new directive was 1 July 2016. Article 10 of the directive sets out the scope of the derogation for MRI, stating that the exposure limits may be exceeded during "the installation, testing, use, development, maintenance of or research related to magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) equipment for patients in the health sector, provided that certain conditions are met." Uncertainties remain regarding the scope and conditions of this derogation.[87]
Procedure
To perform a study, the person is positioned within an MRI scanner that forms a strong magnetic field around the area to be imaged. In most medical applications, protons (hydrogen atoms) in tissues containing water molecules create a signal that is processed to form an image of the body. First, energy from an oscillating magnetic field temporarily is applied to the patient at the appropriate resonance frequency. The excited hydrogen atoms emit a radio frequency signal, which is measured by a receiving coil. The radio signal may be made to encode position information by varying the main magnetic field using gradient coils. As these coils are rapidly switched on and off they create the characteristic repetitive noise of an MRI scan. The contrast between different tissues is determined by the rate at which excited atoms return to the equilibrium state. Exogenous contrast agents may be given intravenously, orally, or intra-articularly.[88]
MRI requires a magnetic field that is both strong and uniform. The field strength of the magnet is measured in teslas – and while the majority of systems operate at 1.5 T, commercial systems are available between 0.2–7 T. Most clinical magnets are superconducting magnets, which require liquid helium. Lower field strengths can be achieved with permanent magnets, which are often used in "open" MRI scanners for claustrophobic patients.[89] Recently, MRI has been demonstrated also at ultra-low fields, i.e., in the microtesla-to-millitesla range, where sufficient signal quality is made possible by prepolarization (on the order of 10-100 mT) and by measuring the Larmor precession fields at about 100 microtesla with highly sensitive superconducting quantum interference devices (SQUIDs).[90][91][92]
Contrast


Image contrast may be weighted to demonstrate different anatomical structures or pathologies. Each tissue returns to its equilibrium state after excitation by the independent processes of T1 (spin-lattice) and T2 (spin-spin) relaxation. To create a T1-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to recover before measuring the MR signal by changing the repetition time (TR). This image weighting is useful for assessing the cerebral cortex, identifying fatty tissue, characterizing focal liver lesions and in general for obtaining morphological information, as well as for post-contrast imaging. To create a T2-weighted image, magnetization is allowed to decay before measuring the MR signal by changing the echo time (TE). This image weighting is useful for detecting edema and inflammation, revealing white matter lesions and assessing zonal anatomy in the prostate and uterus.
Contrast agents
MRI for imaging anatomical structures or blood flow do not require contrast agents as the varying properties of the tissues or blood provide natural contrasts. However, for more specific types of imaging the most commonly used intravenous contrast agents are based on chelates of gadolinium.[93] In general, these agents have proved safer than the iodinated contrast agents used in X-ray radiography or CT. Anaphylactoid reactions are rare, occurring in approx. 0.03–0.1%.[94] Of particular interest is the lower incidence of nephrotoxicity, compared with iodinated agents, when given at usual doses—this has made contrast-enhanced MRI scanning an option for patients with renal impairment, who would otherwise not be able to undergo contrast-enhanced CT.[95]
Although gadolinium agents have proved useful for patients with renal impairment, in patients with severe renal failure requiring dialysis there is a risk of a rare but serious illness, nephrogenic systemic fibrosis, which may be linked to the use of certain gadolinium-containing agents. The most frequently linked is gadodiamide, but other agents have been linked too.[96] Although a causal link has not been definitively established, current guidelines in the United States are that dialysis patients should only receive gadolinium agents where essential, and that dialysis should be performed as soon as possible after the scan to remove the agent from the body promptly.[97][98] In Europe, where more gadolinium-containing agents are available, a classification of agents according to potential risks has been released.[99][100] Recently, a new contrast agent named gadoxetate, brand name Eovist (US) or Primovist (EU), was approved for diagnostic use: this has the theoretical benefit of a dual excretion path.[101]
Interpretation
The standard display of MRI images is to represent fluid characteristics in black and white images, where different tissues turn out as follows:
| T1-weighted | T2-weighted | |
|---|---|---|
| Bright |
|
|
| Inter- mediate | Gray matter darker than white matter[104] | White matter darker than grey matter[104] |
| Dark |
|
|
History
Magnetic resonance imaging was invented by Paul C. Lauterbur in September 1971; he published the theory behind it in March 1973.[105][106] The factors leading to image contrast (differences in tissue relaxation time values) had been described nearly 20 years earlier by Erik Odeblad (physician and scientist) and Gunnar Lindström.[107][108][109][110]
In 1950, spin echoes were first detected by Erwin Hahn[111] and in 1952, Herman Carr produced a one-dimensional NMR spectrum as reported in his Harvard PhD thesis.[112][113][114] In the Soviet Union, Vladislav Ivanov filed (in 1960) a document with the USSR State Committee for Inventions and Discovery at Leningrad for a Magnetic Resonance Imaging device,[115][116][117] although this was not approved until the 1970s.[118]
By 1959, Jay Singer had studied blood flow by NMR relaxation time measurements of blood in living humans.[119][120] Such measurements were not introduced into common medical practice until the mid-1980s, although a patent for a whole-body NMR machine to measure blood flow in the human body was already filed by Alexander Ganssen in early 1967.[109][120][121][122][123]
In the 1960s and 1970s the results of a very large amount of work on relaxation, diffusion, and chemical exchange of water in cells and tissues of all sorts appeared in the scientific literature.[109] In 1967, Ligon reported the measurement of NMR relaxation of water in the arms of living human subjects.[109] In 1968, Jackson and Langham published the first NMR signals from a living animal.[109][124]

In a March 1971 paper in the journal Science,[125] Raymond Damadian, an Armenian-American physician and professor at the Downstate Medical Center State University of New York (SUNY), reported that tumors and normal tissue can be distinguished in vivo by nuclear magnetic resonance ("NMR"). He suggested that these differences could be used to diagnose cancer, though later research would find that these differences, while real, are too variable for diagnostic purposes. Damadian's initial methods were flawed for practical use,[126] relying on a point-by-point scan of the entire body and using relaxation rates, which turned out not to be an effective indicator of cancerous tissue.[127] While researching the analytical properties of magnetic resonance, Damadian created a hypothetical magnetic resonance cancer-detecting machine in 1972. He filed the first patent for such a machine, U.S. patent 3,789,832 on March 17, 1972, which was later issued to him on February 5, 1974.[128] Zenuemon Abe and his colleagues applied the patent for targeted NMR scanner, U.S. patent 3,932,805 on 1973.[129] They published this technique in 1974.[109][120][130]
Damadian claims to have invented the MRI.[131]
The US National Science Foundation notes "The patent included the idea of using NMR to 'scan' the human body to locate cancerous tissue."[132] However, it did not describe a method for generating pictures from such a scan or precisely how such a scan might be done.[133][134] Meanwhile, Paul Lauterbur at Stony Brook University expanded on Carr's technique and developed a way to generate the first MRI images, in 2D and 3D, using gradients. In 1973, Lauterbur published the first nuclear magnetic resonance image[105][135] and the first cross-sectional image of a living mouse in January 1974.[136] In the late 1970s, Peter Mansfield, a physicist and professor at the University of Nottingham, England, developed the echo-planar imaging (EPI) technique that would lead to scans taking seconds rather than hours and produce clearer images than Lauterbur had.[137] Damadian, along with Larry Minkoff and Michael Goldsmith, obtained an image of a tumor in the thorax of a mouse in 1976.[138] They also performed the first MRI body scan of a human being on July 3, 1977,[139][140] studies they published in 1977.[138][141] In 1979, Richard S. Likes filed a patent on k-space U.S. patent 4,307,343.

During the 1970s a team led by John Mallard built the first full-body MRI scanner at the University of Aberdeen.[142] On 28 August 1980 they used this machine to obtain the first clinically useful image of a patient's internal tissues using MRI, which identified a primary tumour in the patient's chest, an abnormal liver, and secondary cancer in his bones.[143] This machine was later used at St Bartholomew's Hospital, in London, from 1983 to 1993. Mallard and his team are credited for technological advances that led to the widespread introduction of MRI.[144]
In 1975, the University of California, San Francisco Radiology Department founded the Radiologic Imaging Laboratory (RIL).[145] With the support of Pfizer, Diasonics, and later Toshiba America MRI, the lab developed new imaging technology and installed systems in the US and worldwide.[146] In 1981 RIL researchers, including Leon Kaufman and Lawrence Crooks, published Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Medicine. In the 1980s the book was considered the definitive introductory textbook to the subject.[147]
In 1980 Paul Bottomley joined the GE Research Center in Schenectady, NY. His team ordered the highest field-strength magnet then available — a 1.5 T system — and built the first high-field device, overcoming problems of coil design, RF penetration and signal-to-noise ratio to build the first whole-body MRI/MRS scanner.[148] The results translated into the highly successful 1.5 T MRI product-line, with over 20,000 systems in use today[when?]. In 1982, Bottomley performed the first localized MRS in the human heart and brain. After starting a collaboration on heart applications with Robert Weiss at Johns Hopkins, Bottomley returned to the university in 1994 as Russell Morgan Professor and director of the MR Research Division.[149] Although MRI is most commonly performed at 1.5 T, higher fields such as 3 T are gaining more popularity because of their increased sensitivity and resolution. In research laboratories, human studies have been performed at up to 9.4 T[150] and animal studies have been performed at up to 21.1 T.[151]
2003 Nobel Prize
Reflecting the fundamental importance and applicability of MRI in medicine, Paul Lauterbur of the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign and Sir Peter Mansfield of the University of Nottingham were awarded the 2003 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for their "discoveries concerning magnetic resonance imaging". The Nobel citation acknowledged Lauterbur's insight of using magnetic field gradients to determine spatial localization, a discovery that allowed rapid acquisition of 2D images. Mansfield was credited with introducing the mathematical formalism and developing techniques for efficient gradient utilization and fast imaging. The actual research that won the prize was done almost 30 years before while Paul Lauterbur was a professor in the Department of Chemistry at Stony Brook University in New York.[105]
Economics
In the UK, the price of a clinical 1.5-tesla MRI scanner is around £920,000/US$1.4 million, with the lifetime maintenance cost broadly similar to the purchase cost.[152] In the Netherlands, the average MRI scanner costs around €1 million,[153] with a 7-T MRI having been taken in use by the UMC Utrecht in December 2007, costing €7 million.[154] Construction of MRI suites could cost up to US$500,000/€370.000 or more, depending on project scope. Pre-polarizing MRI (PMRI) systems using resistive electromagnets have shown promise as a low-cost alternative and have specific advantages for joint imaging near metal implants, however they are likely unsuitable for routine whole-body or neuroimaging applications.[155][156]
MRI scanners have become significant sources of revenue for healthcare providers in the US. This is because of favorable reimbursement rates from insurers and federal government programs. Insurance reimbursement is provided in two components, an equipment charge for the actual performance and operation of the MRI scan and a professional charge for the radiologist's review of the images and/or data. In the US Northeast, an equipment charge might be $3,500/€2.600 and a professional charge might be $350/€260,[157] although the actual fees received by the equipment owner and interpreting physician are often significantly less and depend on the rates negotiated with insurance companies or determined by the Medicare fee schedule. For example, an orthopedic surgery group in Illinois billed a charge of $1,116/€825 for a knee MRI in 2007, but the Medicare reimbursement in 2007 was only $470.91/€350.[158] Many insurance companies require advance approval of an MRI procedure as a condition for coverage.
In the US, the Deficit Reduction Act of 2005 significantly reduced reimbursement rates paid by federal insurance programs for the equipment component of many scans, shifting the economic landscape. Many private insurers have followed suit.[citation needed]
In the United States, an MRI of the brain with and without contrast billed to Medicare Part B entails, on average, a technical payment of US$403/€300 and a separate payment to the radiologist of US$93/€70.[159] In France, the cost of an MRI exam is approximately €150/US$205. This covers three basic scans including one with an intravenous contrast agent as well as a consultation with the technician and a written report to the patient's physician. [citation needed] In Japan, the cost of an MRI examination (excluding the cost of contrast material and films) ranges from US$155/€115 to US$180/€133, with an additional radiologist professional fee of US$17/€12.50.[160] In India, the cost of an MRI examination including the fee for the radiologist's opinion comes to around Rs 3000–4000 (€37–49/US$50–60), excluding the cost of contrast material. In the UK the retail price for an MRI scan privately ranges between £350 and £700 (€405–810).[161]
Overuse
Medical societies issue guidelines for when physicians should use MRI on patients and recommend against overuse. MRI can detect health problems or confirm a diagnosis, but medical societies often recommend that MRI not be the first procedure for creating a plan to diagnose or manage a patient's complaint. A common case is to use MRI to seek a cause of low back pain; the American College of Physicians, for example, recommends against this procedure as unlikely to result in a positive outcome for the patient.[162][163]
Specialized applications
Diffusion MRI

Diffusion MRI measures the diffusion of water molecules in biological tissues.[164] Clinically, diffusion MRI is useful for the diagnoses of conditions (e.g., stroke) or neurological disorders (e.g., multiple sclerosis), and helps better understand the connectivity of white matter axons in the central nervous system.[165] In an isotropic medium (inside a glass of water for example), water molecules naturally move randomly according to turbulence and Brownian motion. In biological tissues however, where the Reynolds number is low enough for laminar flow, the diffusion may be anisotropic. For example, a molecule inside the axon of a neuron has a low probability of crossing the myelin membrane. Therefore, the molecule moves principally along the axis of the neural fiber. If it is known that molecules in a particular voxel diffuse principally in one direction, the assumption can be made that the majority of the fibers in this area are parallel to that direction.
The recent development of diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)[166] enables diffusion to be measured in multiple directions, and the fractional anisotropy in each direction to be calculated for each voxel. This enables researchers to make brain maps of fiber directions to examine the connectivity of different regions in the brain (using tractography) or to examine areas of neural degeneration and demyelination in diseases like multiple sclerosis.
Another application of diffusion MRI is diffusion-weighted imaging (DWI). Following an ischemic stroke, DWI is highly sensitive to the changes occurring in the lesion.[167] It is speculated that increases in restriction (barriers) to water diffusion, as a result of cytotoxic edema (cellular swelling), is responsible for the increase in signal on a DWI scan. The DWI enhancement appears within 5–10 minutes of the onset of stroke symptoms (as compared to computed tomography, which often does not detect changes of acute infarct for up to 4–6 hours) and remains for up to two weeks. Coupled with imaging of cerebral perfusion, researchers can highlight regions of "perfusion/diffusion mismatch" that may indicate regions capable of salvage by reperfusion therapy.
Like many other specialized applications, this technique is usually coupled with a fast image acquisition sequence, such as echo planar imaging sequence.
Magnetic resonance angiography

Magnetic resonance angiography (MRA) generates pictures of the arteries to evaluate them for stenosis (abnormal narrowing) or aneurysms (vessel wall dilatations, at risk of rupture). MRA is often used to evaluate the arteries of the neck and brain, the thoracic and abdominal aorta, the renal arteries, and the legs (called a "run-off"). A variety of techniques can be used to generate the pictures, such as administration of a paramagnetic contrast agent (gadolinium) or using a technique known as "flow-related enhancement" (e.g., 2D and 3D time-of-flight sequences), where most of the signal on an image is due to blood that recently moved into that plane, see also FLASH MRI. Techniques involving phase accumulation (known as phase contrast angiography) can also be used to generate flow velocity maps easily and accurately. Magnetic resonance venography (MRV) is a similar procedure that is used to image veins. In this method, the tissue is now excited inferiorly, while the signal is gathered in the plane immediately superior to the excitation plane—thus imaging the venous blood that recently moved from the excited plane.[168]
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy
Magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS) is used to measure the levels of different metabolites in body tissues. The MR signal produces a spectrum of resonances that corresponds to different molecular arrangements of the isotope being "excited". This signature is used to diagnose certain metabolic disorders, especially those affecting the brain,[169] and to provide information on tumor metabolism.[170]
Magnetic resonance spectroscopic imaging (MRSI) combines both spectroscopic and imaging methods to produce spatially localized spectra from within the sample or patient. The spatial resolution is much lower (limited by the available SNR), but the spectra in each voxel contains information about many metabolites. Because the available signal is used to encode spatial and spectral information, MRSI requires high SNR achievable only at higher field strengths (3 T and above).[citation needed]
Functional MRI
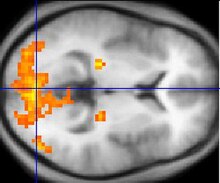
Functional MRI (fMRI) measures signal changes in the brain that are due to changing neural activity. Compared to anatomical T1W imaging, the brain is scanned at lower spatial resolution but at a higher temporal resolution (typically once every 2–3 seconds). Increases in neural activity cause changes in the MR signal via T*
2 changes;[171] this mechanism is referred to as the BOLD (blood-oxygen-level dependent) effect. Increased neural activity causes an increased demand for oxygen, and the vascular system actually overcompensates for this, increasing the amount of oxygenated hemoglobin relative to deoxygenated hemoglobin. Because deoxygenated hemoglobin attenuates the MR signal, the vascular response leads to a signal increase that is related to the neural activity. The precise nature of the relationship between neural activity and the BOLD signal is a subject of current research. The BOLD effect also allows for the generation of high resolution 3D maps of the venous vasculature within neural tissue.
While BOLD signal analysis is the most common method employed for neuroscience studies in human subjects, the flexible nature of MR imaging provides means to sensitize the signal to other aspects of the blood supply. Alternative techniques employ arterial spin labeling (ASL) or weighting the MRI signal by cerebral blood flow (CBF) and cerebral blood volume (CBV). The CBV method requires injection of a class of MRI contrast agents that are now in human clinical trials. Because this method has been shown to be far more sensitive than the BOLD technique in preclinical studies, it may potentially expand the role of fMRI in clinical applications. The CBF method provides more quantitative information than the BOLD signal, albeit at a significant loss of detection sensitivity.[citation needed]
Real-time MRI
Real-time MRI refers to the continuous monitoring ("filming") of moving objects in real time. While many different strategies have been developed over the past two decades, a recent development reported a real-time MRI technique based on radial FLASH and iterative reconstruction that yields a temporal resolution of 20 to 30 milliseconds for images with an in-plane resolution of 1.5 to 2.0 mm. The new method promises to add important information about diseases of the joints and the heart. In many cases MRI examinations may become easier and more comfortable for patients.[172]
Interventional MRI
The lack of harmful effects on the patient and the operator make MRI well-suited for interventional radiology, where the images produced by an MRI scanner guide minimally invasive procedures. Such procedures must be done with no ferromagnetic instruments.
A specialized growing subset of interventional MRI is intraoperative MRI, in which doctors use an MRI in surgery. Some specialized MRI systems allow imaging concurrent with the surgical procedure. More typical, however, is that the surgical procedure is temporarily interrupted so that MRI can verify the success of the procedure or guide subsequent surgical work.[citation needed]
Magnetic resonance guided focused ultrasound
In MRgFUS therapy, ultrasound beams are focused on a tissue—guided and controlled using MR thermal imaging—and due to the significant energy deposition at the focus, temperature within the tissue rises to more than 65 °C (150 °F), completely destroying it. This technology can achieve precise ablation of diseased tissue. MR imaging provides a three-dimensional view of the target tissue, allowing for precise focusing of ultrasound energy. The MR imaging provides quantitative, real-time, thermal images of the treated area. This allows the physician to ensure that the temperature generated during each cycle of ultrasound energy is sufficient to cause thermal ablation within the desired tissue and if not, to adapt the parameters to ensure effective treatment.[173]
Multinuclear imaging
Hydrogen is the most frequently imaged nucleus in MRI because it is present in biological tissues in great abundance, and because its high gyromagnetic ratio gives a strong signal. However, any nucleus with a net nuclear spin could potentially be imaged with MRI. Such nuclei include helium-3, lithium-7, carbon-13, fluorine-19, oxygen-17, sodium-23, phosphorus-31 and xenon-129. 23Na and 31P are naturally abundant in the body, so can be imaged directly. Gaseous isotopes such as 3He or 129Xe must be hyperpolarized and then inhaled as their nuclear density is too low to yield a useful signal under normal conditions. 17O and 19F can be administered in sufficient quantities in liquid form (e.g. 17O-water) that hyperpolarization is not a necessity.[citation needed]
Moreover, the nucleus of any atom that has a net nuclear spin and that is bonded to a hydrogen atom could potentially be imaged via heteronuclear magnetization transfer MRI that would image the high-gyromagnetic-ratio hydrogen nucleus instead of the low-gyromagnetic-ratio nucleus that is bonded to the hydrogen atom.[174] In principle, hetereonuclear magnetization transfer MRI could be used to detect the presence or absence of specific chemical bonds.[175][176]
Multinuclear imaging is primarily a research technique at present. However, potential applications include functional imaging and imaging of organs poorly seen on 1H MRI (e.g., lungs and bones) or as alternative contrast agents. Inhaled hyperpolarized 3He can be used to image the distribution of air spaces within the lungs. Injectable solutions containing 13C or stabilized bubbles of hyperpolarized 129Xe have been studied as contrast agents for angiography and perfusion imaging. 31P can potentially provide information on bone density and structure, as well as functional imaging of the brain. Multinuclear imaging holds the potential to chart the distribution of lithium in the human brain, this element finding use as an important drug for those with conditions such as bipolar disorder.[citation needed]
Molecular imaging by MRI
MRI has the advantages of having very high spatial resolution and is very adept at morphological imaging and functional imaging. MRI does have several disadvantages though. First, MRI has a sensitivity of around 10−3 mol/L to 10−5 mol/L, which, compared to other types of imaging, can be very limiting. This problem stems from the fact that the population difference between the nuclear spin states is very small at room temperature. For example, at 1.5 teslas, a typical field strength for clinical MRI, the difference between high and low energy states is approximately 9 molecules per 2 million. Improvements to increase MR sensitivity include increasing magnetic field strength, and hyperpolarization via optical pumping or dynamic nuclear polarization. There are also a variety of signal amplification schemes based on chemical exchange that increase sensitivity.[citation needed]
To achieve molecular imaging of disease biomarkers using MRI, targeted MRI contrast agents with high specificity and high relaxivity (sensitivity) are required. To date, many studies have been devoted to developing targeted-MRI contrast agents to achieve molecular imaging by MRI. Commonly, peptides, antibodies, or small ligands, and small protein domains, such as HER-2 affibodies, have been applied to achieve targeting. To enhance the sensitivity of the contrast agents, these targeting moieties are usually linked to high payload MRI contrast agents or MRI contrast agents with high relaxivities.[177] A new class of gene targeting MR contrast agents (CA) has been introduced to show gene action of unique mRNA and gene transcription factor proteins.[178][179] This new CA can trace cells with unique mRNA, microRNA and virus; tissue response to inflammation in living brains.[180] The MR reports change in gene expression with positive correlation to TaqMan analysis, optical and electron microscopy.[181]
Other specialized sequences
New methods and variants of existing methods are often published when they are able to produce better results in specific fields. Examples of these recent improvements are T*
2-weighted turbo spin-echo (T2 TSE MRI), double inversion recovery MRI (DIR-MRI) or phase-sensitive inversion recovery MRI (PSIR-MRI), all of them able to improve imaging of brain lesions.[182][183] Another example is MP-RAGE (magnetization-prepared rapid acquisition with gradient echo),[184] which improves images of multiple sclerosis cortical lesions.[185]
Magnetization transfer MRI
Magnetization transfer (MT) is a technique to enhance image contrast in certain applications of MRI.
Bound protons are associated with proteins and as they have a very short T2 decay they do not normally contribute to image contrast. However, because these protons have a broad resonance peak they can be excited by a radiofrequency pulse that has no effect on free protons. Their excitation increases image contrast by transfer of saturated spins from the bound pool into the free pool, thereby reducing the signal of free water. This homonuclear magnetization transfer provides an indirect measurement of macromolecular content in tissue. Implementation of homonuclear magnetization transfer involves choosing suitable frequency offsets and pulse shapes to saturate the bound spins sufficiently strongly, within the safety limits of specific absorption rate for MRI.[88]
The most common use of this technique is for suppression of background signal in time of flight MR angiography.[186] There are also applications in neuroimaging particularly in the characterization of white matter lesions in multiple sclerosis.[187]
T1rho MRI
T1ρ (T1rho): Molecules have a kinetic energy that is a function of the temperature and is expressed as translational and rotational motions, and by collisions between molecules. The moving dipoles disturb the magnetic field but are often extremely rapid so that the average effect over a long time-scale may be zero. However, depending on the time-scale, the interactions between the dipoles do not always average away. At the slowest extreme the interaction time is effectively infinite and occurs where there are large, stationary field disturbances (e.g., a metallic implant). In this case the loss of coherence is described as a "static dephasing". T2* is a measure of the loss of coherence in an ensemble of spins that includes all interactions (including static dephasing). T2 is a measure of the loss of coherence that excludes static dephasing, using an RF pulse to reverse the slowest types of dipolar interaction. There is in fact a continuum of interaction time-scales in a given biological sample, and the properties of the refocusing RF pulse can be tuned to refocus more than just static dephasing. In general, the rate of decay of an ensemble of spins is a function of the interaction times and also the power of the RF pulse. This type of decay, occurring under the influence of RF, is known as T1ρ. It is similar to T2 decay but with some slower dipolar interactions refocused, as well as static interactions, hence T1ρ≥T2.[188]
Proton density weighted
Proton density (PD) weighted images are created by having a long repetition time (TR) and a short echo time (TE).[189] On images of the brain, this sequence has a more pronounced distinction between gray matter (bright) and white matter (darker gray), but with little contrast between brain and CSF.[189]
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR)
Fluid attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR)[190] is an inversion-recovery pulse sequence used to nullify the signal from fluids. For example, it can be used in brain imaging to suppress cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) so as to bring out periventricular hyperintense lesions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS) plaques. By carefully choosing the inversion time TI (the time between the inversion and excitation pulses), the signal from any particular tissue can be suppressed.
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI)
Susceptibility weighted imaging (SWI) is a new type of contrast in MRI different from spin density, T1, or T2 imaging. This method exploits the susceptibility differences between tissues and uses a fully velocity compensated, three dimensional, RF spoiled, high-resolution, 3D gradient echo scan. This special data acquisition and image processing produces an enhanced contrast magnitude image very sensitive to venous blood, hemorrhage and iron storage. It is used to enhance the detection and diagnosis of tumors, vascular and neurovascular diseases (stroke and hemorrhage), multiple sclerosis,[191] Alzheimer's, and also detects traumatic brain injuries that may not be diagnosed using other methods.[192]
Neuromelanin imaging
This method exploits the paramagnetic properties of neuromelanin and can be used to visualize the substantia nigra and the locus coeruleus. It is used to detect the atrophy of these nuclei in Parkinson's disease and other parkinsonisms, and also detects signal intensity changes in major depressive disorder and schizophrenia.[193]
See also
- Earth's field NMR (EFNMR)
- Electron-spin resonance (spin physics)
- High definition fiber tracking
- History of brain imaging
- International Society of Magnetic Resonance in Medicine
- Jemris (open source MRI simulator)
- Magnetic immunoassay
- Magnetic particle imaging (MPI)
- Magnetic resonance elastography
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (journal)
- Magnetic resonance microscopy
- Magnetic resonance (quantum mechanics) for physical & mathematical understanding
- Medical imaging
- Molecular breast imaging
- MRI RF shielding
- Nephrogenic fibrosing dermopathy
- Neuroimaging software
- Nobel Prize controversies
- Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR)
- Relaxation (NMR)
- Robinson oscillator
- Rabi cycle
- Sodium MRI
- Virtopsy
References
- ^ "Magnetic Resonance, a critical peer-reviewed introduction". European Magnetic Resonance Forum. Retrieved 17 November 2014.
- ^ Hollingworth W; Todd CJ; Bell MI; Arafat Q; Girling S; Karia KR; Dixon AK (2000). "The diagnostic and therapeutic impact of MRI: an observational multi-centre study". Clin Radiol. 55 (11): 825–31. doi:10.1053/crad.2000.0546. PMID 11069736.
- ^ a b "iRefer". Royal College of Radiologists. Retrieved 10 November 2013.
- ^ Watson, Robert E. (2015-10-01). "Lessons Learned from MRI Safety Events". Current Radiology Reports. 3 (10): 37. doi:10.1007/s40134-015-0122-z. ISSN 2167-4825.
- ^ Wang PI; Chong ST; Kielar AZ; Kelly AM; Knoepp UD; Mazza MB; Goodsitt MM (2012). "Imaging of pregnant and lactating patients: part 1, evidence-based review and recommendations". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 198 (4): 778–84. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7405. PMID 22451541.
- ^ Smith-Bindman R; Miglioretti DL; Johnson E; Lee C; Feigelson HS; Flynn M; Greenlee RT; Kruger RL; Hornbrook MC; et al. (2012). "Use of diagnostic imaging studies and associated radiation exposure for patients enrolled in large integrated health care systems, 1996-2010". JAMA. 307 (22): 2400–9. doi:10.1001/jama.2012.5960. PMC 3859870. PMID 22692172.
- ^ "Health at a glance 2009 OECD indicators". Health at a Glance. Health at a Glance. OECD. 2009. doi:10.1787/health_glance-2009-en. ISBN 9789264061538. ISSN 1995-3992.
- ^ American Society of Neuroradiology (2013). "ACR-ASNR Practice Guideline for the Performance and Interpretation of Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) of the Brain" (PDF).
- ^ Nolen-Hoeksema, Susan (2014). Abnormal Psychology (Sixth ed.). New York, NY: McGraw-Hill Education. p. 67.
- ^ Galloway, RL Jr. (2015). "Introduction and Historical Perspectives on Image-Guided Surgery". In Golby, AJ (ed.). Image-Guided Neurosurgery. Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 3–4.
- ^ Tse, VCK; Kalani, MYS; Adler, JR (2015). "Techniques of Stereotactic Localization". In Chin, LS; Regine, WF (eds.). Principles and Practice of Stereotactic Radiosurgery. New York: Springer. p. 28.
- ^ Saleh, H; Kassas, B (2015). "Developing Stereotactic Frames for Cranial Treatment". In Benedict, SH; Schlesinger, DJ; Goetsch, SJ; Kavanagh, BD (eds.). Stereotactic Radiosurgery and Stereotactic Body Radiation Therapy. Boca Raton: CRC Press. pp. 156–159.
- ^ Khan, FR; Henderson, JM (2013). "Deep Brain Stimulation Surgical Techniques". In Lozano, AM; Hallet, M (eds.). Brain Stimulation: Handbook of Clinical Neurology. Vol. 116. Amsterdam: Elsevier. pp. 28–30.
- ^ Arle, J (2009). "Development of a Classic: the Todd-Wells Apparatus, the BRW, and the CRW Stereotactic Frames". In Lozano, AM; Gildenberg, PL; Tasker, RR (eds.). Textbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. Berlin: Springer-Verlag. pp. 456–461.
- ^ Sharan, AD; Andrews, DW (2003). "Stereotactic Frames: Technical Considerations". In Schulder, M; Gandhi, CD (eds.). Handbook of Stereotactic and Functional Neurosurgery. New York: Marcel Dekker. pp. 16–17.
- ^ Apuzzo, MLJ; Fredericks, CA (1988). "The Brown-Roberts-Wells System". In Lunsford, LD (ed.). Modern Stereotactic Neurosurgery. Boston: Martinus Nijhoff Publishing. pp. 63–77.
- ^ Brown RA; Nelson JA (2012). "Invention of the N-localizer for stereotactic neurosurgery and its use in the Brown-Roberts-Wells stereotactic frame". Neurosurgery. 70 (2 Supplement Operative): 173–176. doi:10.1227/NEU.0b013e318246a4f7. PMID 22186842.
- ^ Brown RA, Nelson JA (2016). "The invention and early history of the N-localizer for stereotactic neurosurgery". Cureus. 8 (6): e642. doi:10.7759/cureus.642. PMC 4959822. PMID 27462476.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Brown RA (2015). "The mathematics of three N-localizers used together for stereotactic neurosurgery". Cureus. 7 (10): e341. doi:10.7759/cureus.341. PMC 4636133. PMID 26594605.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Brown RA (2015). "The mathematics of four or more N-localizers for stereotactic neurosurgery". Cureus. 7 (10): e349. doi:10.7759/cureus.349. PMC 4641741. PMID 26623204.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Leksell L; Leksell D; Schwebel J (1985). "Stereotaxis and nuclear magnetic resonance". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 48 (1): 14–18. doi:10.1136/jnnp.48.1.14. PMC 1028176. PMID 3882889.
- ^ Thomas DG; Davis CH; Ingram S; Olney JS; Bydder GM; Young IR (1986). "Stereotaxic biopsy of the brain under MR imaging control". AJNR American Journal of Neuroradiology. 7 (1): 161–163. PMID 3082131.
- ^ Heilbrun MP; Sunderland PM; McDonald PR; Wells TH Jr.; Cosman E; Ganz E (1987). "Brown-Roberts-Wells stereotactic frame modifications to accomplish magnetic resonance imaging guidance in three planes". Applied Neurophysiology. 50 (1–6): 143–152. doi:10.1159/000100700. PMID 3329837.
- ^ "ACCF/ACR/SCCT/SCMR/ASNC/NASCI/SCAI/SIR 2006 Appropriateness Criteria for Cardiac Computed Tomography and Cardiac Magnetic Resonance Imaging". Journal of the American College of Radiology. 3 (10): 751–771. 2006. doi:10.1016/j.jacr.2006.08.008. ISSN 1546-1440.
- ^ Helms, C (2008). Musculoskeletal MRI. Saunders. ISBN 1416055347.
- ^ Frydrychowicz A; Lubner MG; Brown JJ; Merkle EM; Nagle SK; Rofsky NM; Reeder SB (2012). "Hepatobiliary MR imaging with gadolinium-based contrast agents". J Magn Reson Imaging. 35 (3): 492–511. doi:10.1002/jmri.22833. PMC 3281562. PMID 22334493.
- ^ Sandrasegaran K; Lin C; Akisik FM; Tann M (2010). "State-of-the-art pancreatic MRI". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 195 (1): 42–53. doi:10.2214/ajr.195.3_supplement.0s42. PMID 20566796.
- ^ Masselli G; Gualdi G (2012). "MR imaging of the small bowel". Radiology. 264 (2): 333–48. doi:10.1148/radiol.12111658. PMID 22821694.
- ^ Zijta FM; Bipat S; Stoker J (2010). "Magnetic resonance (MR) colonography in the detection of colorectal lesions: a systematic review of prospective studies". Eur Radiol. 20 (5): 1031–46. doi:10.1007/s00330-009-1663-4. PMC 2850516. PMID 19936754.
- ^ Giussani C; Roux FE; Ojemann J; Sganzerla EP; Pirillo D; Papagno C (2010). "Is preoperative functional magnetic resonance imaging reliable for language areas mapping in brain tumor surgery? Review of language functional magnetic resonance imaging and direct cortical stimulation correlation studies". Neurosurgery. 66 (1): 113–20. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000360392.15450.C9. PMID 19935438.
- ^ Heeger DJ; Ress D (2002). "What does fMRI tell us about neuronal activity?". Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 3 (2): 142–51. doi:10.1038/nrn730. PMID 11836522.
- ^ Husband, J (2008). Recommendations for Cross-Sectional Imaging in Cancer Management: Computed Tomography - CT Magnetic Resonance Imaging - MRI Positron Emission Tomography - PET-CT (PDF). Royal College of Radiologists. ISBN 1 905034 13 X.
- ^ Stankovic, Zoran; Allen, Bradley D.; Garcia, Julio; Jarvis, Kelly B.; Markl, Michael (2014). "4D flow imaging with MRI". Cardiovascular diagnosis and therapy. 4 (2): 173–192. doi:10.3978/j.issn.2223-3652.2014.01.02.
- ^ ASTM International (2005). "American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) International, Designation: F2503-05. Standard Practice for Marking Medical Devices and Other Items for Safety in the Magnetic Resonance Environment".
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ "MRI-Related Death of Patient With Aneurysm Clip". Food and Drug Administration. 25 November 1992. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
FDA has learned of a fatal injury sustained by a patient with a cerebral aneurysm clip while she was being prepared for an MRI procedure. It was reported that upon exposure to the magnetic field in the room, the clip moved and lacerated the patient's middle cerebral artery. Subsequently, the explanted device was shown to be magnetically active. This particular style or clip, which was implanted in 1978, was listed in several articles and recent medical texts as non-deflecting in a magnetic field.
- ^ "Physics of magnetic resonance imaging". My-MS.org. Retrieved 27 April 2012.
- ^ Colletti, P.M.; Shinbane, J; S, Shellock; F. G. (2011). "MR-conditional" pacemakers: the radiologist's role in multidisciplinary management". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 197 (4): 1024. doi:10.2214/AJR.11.7120.
- ^ "Magnetic resonance safety policy of ucsf". University of California, San Francisco. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
- ^ "Safety in the MR Environment: Ferromagnetic Projectile Objects in the MRI Scanner Room". Pa Patient Saf Advis. 6 (2). Pennsylvania Patient Safety Authority: 56–62. June 2009. Retrieved 4 February 2015.
- ^ Randal C. Archibold, "Hospital Details Failures Leading to M.R.I. Fatality," The New York Times, August 22, 2001
- ^ Donald G. McNeil Jr, "M.R.I.'s Strong Magnets Cited in Accidents," The New York Times, August 19, 2005.
- ^ Hartwig, Valentina; Giovannetti, Giulio; Vanello, Nicola; Lombardi, Massimo; Landini, Luigi; Simi, Silvana (2009). "Biological Effects and Safety in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Review". International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 6 (6): 1778–1798. doi:10.3390/ijerph6061778. ISSN 1660-4601. PMC 2705217. PMID 19578460.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "ACR Guidance Document for Safe MR Practices: 2007". Retrieved 2 August 2010.
- ^ "MRI Design Guide" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 14 July 2011. Retrieved 2 August 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Committee F04 on Medical and Surgical Materials and Devices." Committee F04
- ^ ASTM Standard F2503 - 13, 2013, "Standard Practice for Marking Medical Devices and Other Items for Safety in the Magnetic Resonance Environment," ASTM International, West Conshohocken, PA, 2003, doi:10.1520/C0033-03, Standards F2503.
- ^ a b c Formica D; Silvestri S (April 2004). "Biological effects of exposure to magnetic resonance imaging: an overview". Biomed Eng Online. 3: 11. doi:10.1186/1475-925X-3-11. PMC 419710. PMID 15104797.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Hartwig, V.; Giovannetti, G.; Vanello, N.; Lombardi, M.; Landini, L.; Simi, S. (2009). "Biological Effects and Safety in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Review". Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health. 6 (6): 1778–1798. doi:10.3390/ijerph6061778. PMC 2705217. PMID 19578460.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Lee JW; Kim MS; Kim YJ; Choi YJ; Lee Y; Chung HW. (2011). "Genotoxic effects of 3 T magnetic resonance imaging in cultured human lymphocytes". Bioelectromagnetics. 32 (7): 535–42. doi:10.1002/bem.20664. PMID 21412810.
- ^ Simi S; Ballardin M; Casella M; De Marchi D; Hartwig V; Giovannetti G; Vanello N; Gabbriellini S; Landini L; Lombardi M (2008). "Is the genotoxic effect of magnetic resonance negligible? Low persistence of micronucleus frequency in lymphocytes of individuals after cardiac scan". Mutat. Res. 645 (1–2): 39–43. doi:10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2008.08.011. PMID 18804118.
- ^ Suzuki Y; Ikehata M; Nakamura K; Nishioka M; Asanuma K; Koana T; Shimizu H (2001). "Induction of micronuclei in mice exposed to static magnetic fields" (PDF). Mutagenesis. 16 (6): 499–501. doi:10.1093/mutage/16.6.499. PMID 11682641.
- ^ Fatahi M; Reddig A; Vijayalaxmi, Friebe B; Hartig R; Prihoda TJ; Ricke J; Roggenbuck D; Reinhold D; Speck O (March 16, 2016). "DNA double-strand breaks and micronuclei in human blood lymphocytes after repeated whole body exposures to 7T Magnetic Resonance Imaging". NeuroImage. 133: 288–293. doi:10.1016/j.neuroimage.2016.03.023. PMID 26994830.
- ^ Cohen MS; Weisskoff RM; Rzedzian RR; Kantor HL (May 1990). "Sensory stimulation by time-varying magnetic fields". Magn Reson Med. 14 (2): 409–14. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910140226. PMID 2345521.
- ^ Budinger TF; Fischer H; Hentschel D; Reinfelder HE; Schmitt F (1991). "Physiological effects of fast oscillating magnetic field gradients". J Comput Assist Tomogr. 15 (6): 909–14. doi:10.1097/00004728-199111000-00001. PMID 1939767.
- ^ Reilly JP (March 1989). "Peripheral nerve stimulation by induced electric currents: exposure to time-varying magnetic fields". Med Biol Eng Comput. 27 (2): 101–10. doi:10.1007/BF02446217. PMID 2689806.
- ^ James R. Ross, MD; Matthew J. Matava, MD. "Tattoo-Induced Skin "Burn" During Magnetic Resonance Imaging in a Professional Football Player". Sports Health. 3 (5): 431–434. doi:10.1177/1941738111411698. PMC 3445217. PMID 23016039.
- ^ Rose Eveleth (March 6, 2014). "Some Tattoo Inks Can Burn You During an MRI".
- ^ "The Evolution of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: 3T MRI in Clinical Applications", Terry Duggan-Jahns, www.eradimaging.com
- ^ Price DL; De Wilde JP; Papadaki AM; Curran JS; Kitney RI (February 2001). "Investigation of acoustic noise on 15 MRI scanners from 0.2 T to 3 T". J Magn Reson Imaging. 13 (2): 288–93. doi:10.1002/1522-2586(200102)13:2<288::AID-JMRI1041>3.0.CO;2-P. PMID 11169836.
- ^ The Open University 2007: Understanding Cardiovascular Diseases, course book for the lesson SK121 Understanding cardiovascular diseases, printed by Cambridge University Press, ISBN 978-0-7492-2677-0 (can be found at OUW), pages 220 and 224.
- ^ "Introduction to MRI Physics, Page 4". www.simplyphysics.com. Retrieved 2017-06-09.
- ^ "Safety data sheet Nitrogen, refrigerated, liquid" (PDF). BOC. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2013-10-19. Retrieved 2014-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Kanal E; Barkovich AJ; Bell C; Borgstede JP; Bradley WG; Froelich JW; Gilk T; Gimbel JR; Gosbee J; et al. (2007). "ACR guidance document for safe MR practices: 2007". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 188 (6): 1447–74. doi:10.2214/AJR.06.1616. PMID 17515363.
- ^ International Electrotechnical Commission 2008: Medical Electrical Equipment – Part 2-33: Particular requirements for basic safety and essential performance of magnetic resonance equipment for medical diagnosis, manufacturers' trade standards [1], published by International Electrotechnical Commission, ISBN 2-8318-9626-6 (can be found for purchase at [2]).
- ^ "Cryogen Awareness Quenching and MRI Safety Training". Falck Productions. Retrieved 10 July 2012.
- ^ "GE Health Care" (PDF). GE. Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 January 2013. Retrieved 10 July 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Alorainy IA; Albadr FB; Abujamea AH (2006). "Attitude towards MRI safety during pregnancy". Ann Saudi Med. 26 (4): 306–9. PMID 16885635.
- ^ Coakley, F; Glenn, O; Qayyum, A; Barkovich, A; Goldstein, R; Filly, R (2004). "Fetal MRI: A Developing Technique for the Developing Patient". American Journal of Roentgenology. 182: 243–252. doi:10.2214/ajr.182.1.1820243. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ Webb JA; Thomsen HS (2013). "Gadolinium contrast media during pregnancy and lactation". Acta Radiol. 54 (6): 599–600. doi:10.1177/0284185113484894. PMID 23966544.
- ^ Kathary, N; Bulas, D; Newman, K; Schonberg, R (October 2001). "MRI imaging of fetal neck masses with airway compromise: utility in delivery planning". Pediatric Radiology. 31 (10): 727–731. doi:10.1007/s002470100527. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
- ^ Mota, Raquel; Ramalho, Carla; Monteiro, Joaquim; Correia-Pinto, Jorge; Rodrigues, Manuela; Guimarães, Hercília; Spratley, Jorge; Macedo, Filipe; Matias, Alexandra; Montenegro, Nuno (27 November 2006). "Evolving Indications for the EXIT Procedure: The Usefulness of Combining Ultrasound and Fetal MRI". Fetal Diagnosis and Therapy. 22 (2): 107–111. doi:10.1159/000097106. Retrieved 19 October 2016.
Our two cases stress once more the importance of combining fetal ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging in the characterization of cervical masses and its usefulness in programming the procedure with a multidisciplinary team.
- ^ Hunt CH; Wood CP; Lane JI; Bolster BD; Bernstein MA; Witte RJ (2011). "Wide, short bore magnetic resonance at 1.5 t: reducing the failure rate in claustrophobic patients". Clin Neuroradiol. 21 (3): 141–4. doi:10.1007/s00062-011-0075-4. PMID 21598040.
- ^ "Siemens Introduces First 1.5 Tesla Open Bore MRI". Medical.siemens.com. 2004-07-29. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ Tom Kelley; David Kelley (18 October 2013). "Kids Were Terrified of Getting MRIs. Then One Man Figured Out a Better Way". Slate.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Health at a Glance 2011". Health at a Glance. OECD. 2011. doi:10.1787/health_glance-2011-en. ISSN 1995-3992.
- ^ Brenner DJ; Hall EJ (November 2007). "Computed tomography--an increasing source of radiation exposure". N. Engl. J. Med. 357 (22): 2277–84. doi:10.1056/NEJMra072149. PMID 18046031.
- ^ Mathews JD; Forsythe AV; Brady Z; Butler MW; Goergen SK; Byrnes GB; Giles GG; Wallace AB; Anderson PR; et al. (2013). "Cancer risk in 680,000 people exposed to computed tomography scans in childhood or adolescence: data linkage study of 11 million Australians". BMJ. 346: f2360. doi:10.1136/bmj.f2360. PMC 3660619. PMID 23694687.
- ^ Semelka RC; Armao DM; Elias J; Huda W (2007). "Imaging strategies to reduce the risk of radiation in CT studies, including selective substitution with MRI". J Magn Reson Imaging. 25 (5): 900–9. doi:10.1002/jmri.20895. PMID 17457809.
- ^ Health risks from exposure to low levels of ionizing radiation : BEIR VII Phase. Washington, D.C.: National Academies Press. 2006. ISBN 978-0-309-09156-5.
- ^ Formica D; Silvestri S (2004). "Biological effects of exposure to magnetic resonance imaging: an overview". Biomed Eng Online. 3: 11. doi:10.1186/1475-925X-3-11. PMC 419710. PMID 15104797.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bettmann MA (2004). "Frequently asked questions: iodinated contrast agents". Radiographics. 24 (Suppl 1): S3–10. doi:10.1148/rg.24si045519. PMID 15486247.
- ^ "Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis" (PDF). ACR Manual on Contrast Material. American College of Radiology. Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ Mak GS; Truong QA (2012). "Cardiac CT: Imaging of and Through Cardiac Devices". Curr Cardiovasc Imaging Rep. 5 (5): 328–336. doi:10.1007/s12410-012-9150-8. PMC 3636997. PMID 23626865.
- ^ "MRI procedure". Royal College of Radiologists. Retrieved 17 November 2013.
- ^ "MRI Design Guide". United States Department of Veterans Affairs. April 2008. Retrieved 12 October 2012.
- ^ "Directive 2013/35/EU of the European Parliament and of the Council. Official Journal of the European Union 2004 L179/1".
- ^ Keevil SF; Lomas DJ (2013). "The European Union physical agents (electromagnetic fields) directive: an update for the MRI community". Br J Radiol. 86 (1032): 20130492. doi:10.1259/bjr.20130492. PMID 24096591.
- ^ a b McRobbie, Donald W. (2007). MRI from picture to proton. Cambridge, UK ; New York: Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-68384-X.
- ^ Sasaki M; Ehara S; Nakasato T; Tamakawa Y; Kuboya Y; Sugisawa M; Sato T (April 1990). "MR of the shoulder with a 0.2-T permanent-magnet unit". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 154 (4): 777–8. doi:10.2214/ajr.154.4.2107675. PMID 2107675.
- ^ McDermott, Robert; et al. "Microtesla MRI with a superconducting quantum interference device" (PDF). Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 101: 7857–7861. doi:10.1073/pnas.0402382101.
- ^ Zotev, Vadim; et al. "SQUID-based instrumentation for ultra-low-field MRI" (PDF).
- ^ Vesanen, Panu; et al. "Hybrid ultra-low-field MRI and magnetoencephalography system based on a commercial whole-head neuromagnetometer". Magnetic Resonance in Medicine. 69: 1795–1804. doi:10.1002/mrm.24413.
- ^ "MR Contrast Agents". 2014.
- ^ Murphy KJ; Brunberg JA; Cohan RH (October 1996). "Adverse reactions to gadolinium contrast media: a review of 36 cases". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 167 (4): 847–9. doi:10.2214/ajr.167.4.8819369. PMID 8819369.
- ^ "ACR guideline". guideline.gov. 2005.
- ^ Thomsen HS; Morcos SK; Dawson P (November 2006). "Is there a causal relation between the administration of gadolinium based contrast media and the development of nephrogenic systemic fibrosis (NSF)?". Clin Radiol. 61 (11): 905–6. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2006.09.003. PMID 17018301.
- ^ "FDA Drug Safety Communication: New warnings for using gadolinium-based contrast agents in patients with kidney dysfunction". Information on Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agents. U.S. Food and Drug Administration. 23 December 2010. Retrieved 12 March 2011.
- ^ "FDA Public Health Advisory: Gadolinium-containing Contrast Agents for Magnetic Resonance Imaging". fda.gov. Archived from the original on 2006-09-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ [3] Archived January 17, 2013, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "ismrm.org MRI Questions and Answers" (PDF). Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ "Response to the FDA's May 23, 2007, Nephrogenic Systemic Fibrosis Update1 — Radiology". Radiology.rsna.org. 2007-09-12. Retrieved 2010-08-02.
- ^ a b c d e f g h "Magnetic Resonance Imaging". University of Wisconsin. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Keith A. Johnson. "Basic proton MR imaging. Tissue Signal Characteristics". Harvard Medical School. Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- ^ a b Tushar Patil. "MRI sequences". Retrieved 2016-03-14.
- ^ a b c Lauterbur PC (1973). "Image Formation by Induced Local Interactions: Examples of Employing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance". Nature. 242 (5394): 190–1. Bibcode:1973Natur.242..190L. doi:10.1038/242190a0.
- ^ Rinck PA (2014). "The history of MRI". Magnetic Resonance in Medicine (8th ed.).
- ^ Odeblad E; Lindström G (1955). "Some preliminary observations on the proton magnetic resonance in biological samples". Acta Radiologica. 43: 469–76. doi:10.3109/00016925509172514.
- ^ Erik Odeblad; Baidya Nath Bhar; Gunnar Lindström (July 1956). "Proton magnetic resonance of human red blood cells in heavy water exchange experiments". Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics. 63 (1): 221–225. doi:10.1016/0003-9861(56)90025-X.
- ^ a b c d e f History of MRI
- ^ Europe celebrates the forgotten pioneer of MRI: Dr. Erik Odeblad
- ^ Hahn, E.L. (1950). "Spin echoes". Physical Review. 80: 580–594. Bibcode:1950PhRv...80..580H. doi:10.1103/PhysRev.80.580.
- ^ Carr, Herman (1952). Free Precession Techniques in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (PhD thesis). Cambridge, MA: Harvard University. OCLC 76980558.[page needed]
- ^ Carr, Herman Y. (July 2004). "Field Gradients in Early MRI". Physics Today. 57 (7). American Institute of Physics: 83. Bibcode:2004PhT....57g..83C. doi:10.1063/1.1784322.
- ^ Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Vol. 1. Hoboken, NJ: Wiley and Sons. 1996. p. 253 https://books.google.com/?id=-OBvMgEACAAJ&dq=Encyclopedia%20of%20Nuclear%20Magnetic%20Resonance.
{{cite encyclopedia}}: Missing or empty|title=(help) - ^ MacWilliams B (November 2003). "Russian claims first in magnetic imaging". Nature. 426 (6965): 375. Bibcode:2003Natur.426..375M. doi:10.1038/426375a. PMID 14647349.
- ^ ПРИВЕТ НОБЕЛЮ ОТ ИВАНОВА
- ^ Patents by Ivan Vladislav
- ^ "Best Regards to Alfred Nobel". Archived from the original on 2009-12-13. Retrieved 2009-10-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Singer RJ (1959). "Blood-flow rates by NMR measurements". Science. 130: 1652–1653. doi:10.1126/science.130.3389.1652. PMID 17781388.
- ^ a b c "A SHORT HISTORY OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FROM A EUROPEAN POINT OF VIEW". emrf.org. Archived from the original on 2007-04-13. Retrieved 2016-08-08.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ de 1566148
- ^ First MAGNETOM scanner in the USA in 1983
- ^ Nachruf auf Alexander Ganssen
- ^ Jackson JA; Langham WH (April 1968). "Whole-body NMR spectrometer". Review of Scientific Instruments. 39 (4): 510–513. doi:10.1063/1.1683420. PMID 5641806.
- ^ Damadian R (March 1971). "Tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance". Science. 171 (3976): 1151–3. Bibcode:1971Sci...171.1151D. doi:10.1126/science.171.3976.1151. PMID 5544870.
- ^ "The man who did not win". Sydney Morning Herald. 2003-10-17. Retrieved 2007-08-04.
- ^ "Scan and Deliver". Wall Street Journal. 2002-06-14. Retrieved 2007-08-04.
- ^ "Apparatus And Method For Detecting Cancer In Tissue". United States Patent and Trademark Office.
- ^ Abe Z [in Japanese]; Tanaka K; Hotta M (1971). "Non-invasive measurements of biological information with application of NMR". 北海道大学応用電気研究所 報告. 23 (11).
- ^ Tanaka K; Yamada T; Shimizu T; Sano F; Abe Z [in Japanese] (1974). "Fundamental investigations (in vitro) for a non-invasive method of tumor detection by nuclear magnetic resonance". Biotelemetry. 1: 337–350.
- ^ "The Inventor of the MRI on Real Science Radio". kgov.com. Retrieved 2016-09-25.
- ^ "NSF history". Sri.com. Archived from the original on 2012-01-03. Retrieved 2011-11-28.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Scientist Claims Exclusion From Nobel Prize for MRI". Los Angeles Times. 2003-11-08. Retrieved 2013-02-13.
- ^ "Does Dr. Raymond Damadian Deserve the Nobel Prize for Medicine?". The Armenian Reporter. 2003-11-08. Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ Filler A (October 2009). "Magnetic resonance neurography and diffusion tensor imaging: origins, history, and clinical impact of the first 50,000 cases with an assessment of efficacy and utility in a prospective 5000-patient study group". Neurosurgery. 65 (4 Suppl): A29–43. doi:10.1227/01.NEU.0000351279.78110.00. PMC 2924821. PMID 19927075.
- ^ Lauterbur PC (1974). "Magnetic resonance zeugmatography". Pure and Applied Chemistry. 40: 149–57. doi:10.1351/pac197440010149.
- ^ Mansfield P; Grannell, P (1975). "Diffraction and microscopy in solids and liquids by NMR". Physical Review B. 12 (9): 3618–3634. Bibcode:1975PhRvB..12.3618M. doi:10.1103/physrevb.12.3618.
- ^ a b Damadian R; Minkoff L; Goldsmith M; Stanford M; Koutcher J (1976). "Field focusing nuclear magnetic resonance (FONAR): visualization of a tumor in a live animal". Science. 194 (4272): 1430–2. Bibcode:1976Sci...194.1430D. doi:10.1126/science.1006309. PMID 1006309.
- ^ "First MRI and ultrasound scanning". Benjamin S. Beck. Archived from the original on 2011-11-20.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "The "Indomitable" MRI". Smithsonian Institution. Archived from the original on 2012-09-09.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hinshaw WS; Bottomley PA; Holland GN (1977). "Radiographic thin-section image of the human wrist by nuclear magnetic resonance". Nature. 270 (5639): 722–3. Bibcode:1977Natur.270..722H. doi:10.1038/270722a0. PMID 593393.
- ^ University of Aberdeen. "Celebrated scientist donates medal collection".
- ^ "JOHN MALLARD".
- ^ "Science Museum". sciencemuseum.org.uk.
- ^ "UCSF Library". ucsf.edu.
- ^ http://www.oac.cdlib.org/findaid/ark:/13030/kt3199s1qf/admin/#ref732 Lawrence Crooks Radiologic Imaging Laboratory Records
- ^ "JAMA Network - JAMA - Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Imaging". jamanetwork.com. 17 February 1984.
- ^ Sijbers J; Scheunders P; Bonnet N; Van Dyck D; Raman E (1996). "Quantification and improvement of the signal-to-noise ratio in a magnetic resonance image acquisition procedure". Magn Reson Imaging. 14 (10): 1157–63. doi:10.1016/S0730-725X(96)00219-6. PMID 9065906.
- ^ "BIOGRAPHICAL SKETCH" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on July 4, 2010. Retrieved May 20, 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)[full citation needed] - ^ Vaughan T; DelaBarre L; Snyder C; Tian J; Akgun C; Shrivastava D; Liu W; Olson C; Adriany G; et al. (December 2006). "9.4T human MRI: preliminary results". Magn Reson Med. 56 (6): 1274–82. doi:10.1002/mrm.21073. PMC 4406343. PMID 17075852.
- ^ Qian C; Masad IS; Rosenberg JT; Elumalai M; Brey WW; Grant SC; Gor'kov PL (August 2012). "A volume birdcage coil with an adjustable sliding tuner ring for neuroimaging in high field vertical magnets: ex and in vivo applications at 21.1T". J. Magn. Reson. 221: 110–6. Bibcode:2012JMagR.221..110Q. doi:10.1016/j.jmr.2012.05.016. PMC 4266482. PMID 22750638.
- ^ "Managing high value capital equipment in the NHS in England" (PDF). National Audit Office (United Kingdom). Retrieved 30 November 2013.
- ^ "MRI-scanner big financial success for Philips (Dutch)". Eindhovens Dagblad (ED). Retrieved 18 February 2009.
- ^ "MRI scanner of €7 million in use(Dutch)". Medisch Contact. Retrieved 5 December 2007.
- ^ Morgan P; Conolly S; Scott G; Macovski A (1996). "A readout magnet for prepolarized MRI". Magn Reson Med. 36 (4): 527–36. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910360405. PMID 8892203.
- ^ Blamire AM (2008). "The technology of MRI--the next 10 years?". Br J Radiol. 81 (968): 601–17. doi:10.1259/bjr/96872829. PMID 18628329.
- ^ Stamford Hospital price quotation October 2008, Stamford CT US
- ^ Goldstein, Wayne M.; Gordon, Alexander C.; Branson, Jill Jasperson; Simmons, Christopher; Berland, Kimberly; Willsey, Daniel S.; Andrews, Amanda L. (March 5–9, 2008). Over-Utilization of MRI in the Osteoarthritis Patient (PDF). Annual Meeting AAOS. San Francisco.
- ^ Current Procedural Terminology code #70553 "2010 Medicare Part B National Summary Data File". Data.gov, An Official Website of the United States Government.
- ^ Ehara S; Nakajima Y; Matsui O (August 2008). "Radiology in Japan in 2008". AJR Am J Roentgenol. 191 (2): 328–9. doi:10.2214/AJR.07.3940. PMID 18647897.
- ^ "Private MRI Scan". Fairfield.org.uk. Fairfield Independent Hospital. Retrieved 2017-03-28.
- ^ Consumer Reports; American College of Physicians. "Five Things Physicians and Patients Should Question" (PDF). Choosing Wisely. presented by ABIM Foundation. Consumer Reports. Archived from the original (PDF) on June 24, 2012. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Consumer Reports; American College of Physicians (April 2012). "Imaging tests for lower-back pain: Why you probably don't need them" (PDF). High Value Care. presented by Annals of Internal Medicine. Consumer Reports. Retrieved August 14, 2012.
- ^ Le Bihan D; Breton E; Lallemand D; Grenier P; Cabanis E; Laval-Jeantet M (November 1986). "MR imaging of intravoxel incoherent motions: application to diffusion and perfusion in neurologic disorders". Radiology. 161 (2): 401–7. doi:10.1148/radiology.161.2.3763909. PMID 3763909.
- ^ "Diffusion Inaging". Stanford University. Archived from the original on 24 December 2011. Retrieved 28 April 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Filler A (2009). "The History, Development and Impact of Computed Imaging in Neurological Diagnosis and Neurosurgery: CT, MRI, and DTI". Nature Precedings. doi:10.1038/npre.2009.3267.5.
- ^ Moseley ME; Cohen Y; Mintorovitch J; Chileuitt L; Shimizu H; Kucharczyk J; Wendland MF; Weinstein PR (May 1990). "Early detection of regional cerebral ischemia in cats: comparison of diffusion- and T2-weighted MRI and spectroscopy". Magn Reson Med. 14 (2): 330–46. doi:10.1002/mrm.1910140218. PMID 2345513.
- ^ Haacke, E Mark; Brown, Robert F; Thompson, Michael; Venkatesan, Ramesh (1999). Magnetic resonance imaging: Physical principles and sequence design. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-35128-8.[page needed]
- ^ Rosen Y; Lenkinski RE (July 2007). "Recent advances in magnetic resonance neurospectroscopy". Neurotherapeutics. 4 (3): 330–45. doi:10.1016/j.nurt.2007.04.009. PMID 17599700.
- ^ Golder W (June 2004). "Magnetic resonance spectroscopy in clinical oncology". Onkologie. 27 (3): 304–9. doi:10.1159/000077983. PMID 15249722.
- ^ Thulborn KR; Waterton JC; Matthews PM; Radda GK (February 1982). "Oxygenation dependence of the transverse relaxation time of water protons in whole blood at high field". Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 714 (2): 265–70. doi:10.1016/0304-4165(82)90333-6. PMID 6275909.
- ^ I Uyanik, P Lindner, D Shah, N Tsekos I Pavlidis (2013) Applying a Level Set Method for Resolving Physiologic Motions in Free-Breathing and Non-gated Cardiac MRI. FIMH, 2013, [4]
- ^ Cline HE; Schenck JF; Hynynen K; Watkins RD; Souza SP; Jolesz FA (1992). "MR-guided focused ultrasound surgery". J Comput Assist Tomogr. 16 (6): 956–65. doi:10.1097/00004728-199211000-00024. PMID 1430448.
- ^ Hurd RE; John BK (February 1991). "Gradient-enhanced proton-detected heteronuclear multiple-quantum coherence spectroscopy". Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A. 91 (3): 648–653. Bibcode:1991JMagR..91..648H. doi:10.1016/0022-2364(91)90395-a.
- ^ Brown RA; Venters RA; Tang PPPZ; Spicer LD (March 1995). "A test for scalar coupling between heteronuclei using gradient-enhanced proton-detected HMQC spectroscopy". Journal of Magnetic Resonance, Series A. 113 (1): 117–119. Bibcode:1995JMagR.113..117B. doi:10.1006/jmra.1995.1064.
- ^ Miller AF; Egan LA; Townsend CA (March 1997). "Measurement of the degree of isotopic enrichment of different positions in an antibiotic peptide by NMR" (PDF). Journal of Magnetic Resonance. 125 (1): 120–131. Bibcode:1997JMagR.125..120M. doi:10.1006/jmre.1997.1107. PMID 9245367.
- ^ Xue S; Qiao J; Pu F; Cameron M; Yang JJ (2013). "Design of a novel class of protein-based magnetic resonance imaging contrast agents for the molecular imaging of cancer biomarkers". Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 5 (2): 163–79. doi:10.1002/wnan.1205. PMID 23335551.
- ^ Liu CH; Kim YR; Ren JQ; Eichler F; Rosen BR; Liu PK (2007). "Imaging cerebral gene transcripts in live animals". J. Neurosci. 27 (3): 713–22. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4660-06.2007. PMC 2647966. PMID 17234603.
- ^ Liu CH; Ren J; Liu CM; Liu PK (2014). "Intracellular gene transcription factor protein-guided MRI by DNA aptamers in vivo". FASEB J. 28 (1): 464–73. doi:10.1096/fj.13-234229. PMID 24115049.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Liu CH; You Z; Liu CM; Kim YR; Whalen MJ; Rosen BR; Liu PK (2009). "Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging reversal by gene knockdown of matrix metalloproteinase-9 activities in live animal brains". J. Neurosci. 29 (11): 3508–17. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5332-08.2009. PMC 2726707. PMID 19295156.
- ^ Liu CH; Yang J; Ren JQ; Liu CM; You Z; Liu PK (2013). "MRI reveals differential effects of amphetamine exposure on neuroglia in vivo". FASEB J. 27 (2): 712–24. doi:10.1096/fj.12-220061. PMC 3545538. PMID 23150521.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Wattjes MP; Lutterbey GG; Gieseke J; Träber F; Klotz L; Schmidt S; Schild HH (January 2007). "Double inversion recovery brain imaging at 3T: diagnostic value in the detection of multiple sclerosis lesions". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28 (1): 54–9. PMID 17213424.
- ^ Nelson F; Poonawalla AH; Hou P; Huang F; Wolinsky JS; Narayana PA (October 2007). "Improved identification of intracortical lesions in multiple sclerosis with phase-sensitive inversion recovery in combination with fast double inversion recovery MR imaging". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 28 (9): 1645–9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A0645. PMID 17885241.
- ^ Nelson F; Poonawalla A; Hou P; Wolinsky JS; Narayana PA (November 2008). "3D MPRAGE improves classification of cortical lesions in multiple sclerosis". Mult. Scler. 14 (9): 1214–9. doi:10.1177/1352458508094644. PMC 2650249. PMID 18952832.
- ^ Brant-Zawadzki M; Gillan GD; Nitz WR (March 1992). "MP RAGE: a three-dimensional, T1-weighted, gradient-echo sequence--initial experience in the brain". Radiology. 182 (3): 769–75. doi:10.1148/radiology.182.3.1535892. PMID 1535892.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Wheaton AJ; Miyazaki M (2012). "Non-contrast enhanced MR angiography: physical principles". J Magn Reson Imaging. 36 (2): 286–304. doi:10.1002/jmri.23641. PMID 22807222.
- ^ Filippi M; Rocca MA; De Stefano N, Enzinger C; Fisher E; Horsfield MA; Inglese M; Pelletier D; Comi G (2011). "Magnetic Resonance Techniques in Multiple Sclerosis". Archives of Neurology. 68 (12): 1514–20. doi:10.1001/archneurol.2011.914. ISSN 0003-9942. PMID 22159052.
- ^ Borthakur A; Mellon E; Niyogi S; Witschey W; Kneeland JB; Reddy R (November 2006). "Sodium and T1rho MRI for molecular and diagnostic imaging of articular cartilage". NMR Biomed. 19 (7): 781–821. doi:10.1002/nbm.1102. PMC 2896046. PMID 17075961.
- ^ a b "Structural MRI Imaging". UC San Diego School of Medicine. Retrieved 2017-01-01.
- ^ De Coene B; Hajnal JV; Gatehouse P; Longmore DB; White SJ; Oatridge A; Pennock JM; Young IR; Bydder GM (1992). "MR of the brain using fluid-attenuated inversion recovery (FLAIR) pulse sequences". AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 13 (6): 1555–64. PMID 1332459.
- ^ Wiggermann C; Hernandez-Torres E; Vavasour I; Moore W; Laule C; MacKay A; Li D; Traboulsee A; Rauscher A (June 2013). "Magnetic resonance frequency shifts during acute MS lesion formation". Neurology. 81 (3): 211–218. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e31829bfd63. PMC 3770162. PMID 23761621.
- ^ Reichenbach JR; Venkatesan R; Schillinger DJ; Kido DK; Haacke EM (July 1997). "Small vessels in the human brain: MR venography with deoxyhemoglobin as an intrinsic contrast agent". Radiology. 204 (1): 272–7. doi:10.1148/radiology.204.1.9205259. PMID 9205259.[permanent dead link]
- ^ Sasaki M; Shibata E; Tohyama K; Takahashi J; Otsuka K; Tsuchiya K; Takahashi S; Ehara S; Terayama Y; Sakai A (July 2006). "Neuromelanin magnetic resonance imaging of locus ceruleus and substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease". NeuroReport. 17 (11): 1215–8. doi:10.1097/01.wnr.0000227984.84927.a7. PMID 16837857.
Further reading
- TRTF/EMRF: The history of MRI (Peter A. Rinck, ed). url = http://www.magnetic-resonance.org/ch/20-01.html
- Guadalupe Portal; Aliosvi Rodriguez Whole body magnetic resonance imaging in early diagnosis in Trinidad BMJ (2010) ISSN 1756-1833 url = http://www.bmj.com/rapid-response/2011/12/19/re-whole-body-magnetic-resonance-imaging
- Ian L. Pykett (May 1, 1982). "NMR Imaging in Medicine" (PDF). Scientific American. 246 (5): 78–88. doi:10.1038/scientificamerican0582-78. Archived from the original (PDF) on March 10, 2016.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - Simon, Merrill; Mattson, James S (1996). The pioneers of NMR and magnetic resonance in medicine: The story of MRI. Ramat Gan, Israel: Bar-Ilan University Press. ISBN 0-9619243-1-4.
- Haacke, E Mark; Brown, Robert F; Thompson, Michael; Venkatesan, Ramesh (1999). Magnetic resonance imaging: Physical principles and sequence design. New York: J. Wiley & Sons. ISBN 0-471-35128-8.
- Lee SC; Kim K; Kim J; Lee S; Han Yi J; Kim SW; Ha KS; Cheong C (June 2001). "One micrometer resolution NMR microscopy". J. Magn. Reson. 150 (2): 207–13. Bibcode:2001JMagR.150..207L. doi:10.1006/jmre.2001.2319. PMID 11384182.
- Perry Sprawls (2000). Magnetic Resonance Imaging Principles, Methods, and Techniques. Medical Physics Publishing. ISBN 9780944838976.
- P Mansfield (1982). NMR Imaging in Biomedicine: Supplement 2 Advances in Magnetic Resonance. Elsevier. ISBN 9780323154062.
- Eiichi Fukushima (1989). NMR in Biomedicine: The Physical Basis. Springer Science & Business Media. ISBN 9780883186091.
- Bernhard Blümich; Winfried Kuhn (1992). Magnetic Resonance Microscopy: Methods and Applications in Materials Science, Agriculture and Biomedicine. Wiley. ISBN 9783527284030.
- Peter Blümer (1998). Peter Blümler; Bernhard Blümich; Robert E. Botto; Eiichi Fukushima (eds.). Spatially Resolved Magnetic Resonance: Methods, Materials, Medicine, Biology, Rheology, Geology, Ecology, Hardware. Wiley-VCH. ISBN 9783527296378.
- Zhi-Pei Liang; Paul C. Lauterbur (1999). Principles of Magnetic Resonance Imaging: A Signal Processing Perspective. Wiley. ISBN 9780780347236.
- Franz Schmitt; Michael K. Stehling; Robert Turner (1998). Echo-Planar Imaging: Theory, Technique and Application. Springer Berlin Heidelberg. ISBN 9783540631941.
- Vadim Kuperman (2000). Magnetic Resonance Imaging: Physical Principles and Applications. Academic Press. ISBN 9780080535708.
- Bernhard Blümich (2000). NMR Imaging of Materials. Clarendon Press. ISBN 9780198506836.
- Jianming Jin (1998). Electromagnetic Analysis and Design in Magnetic Resonance Imaging. CRC Press. ISBN 9780849396939.
- Imad Akil Farhat; P. S. Belton; Graham Alan Webb; Royal Society of Chemistry (Great Britain) (2007). Magnetic Resonance in Food Science: From Molecules to Man. Royal Society of Chemistry. ISBN 9780854043408.
External links
- MRI: A Peer-Reviewed, Critical Introduction. European Magnetic Resonance Forum (EMRF)/The Round Table Foundation (TRTF); Peter A. Rinck (editor)
- A Guided Tour of MRI: An introduction for laypeople National High Magnetic Field Laboratory
- The Basics of MRI. Underlying physics and technical aspects.
- Video: What to Expect During Your MRI Exam from the Institute for Magnetic Resonance Safety, Education, and Research (IMRSER)
- Royal Institution Lecture – MRI: A Window on the Human Body
- A SHORT HISTORY OF MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING FROM A EUROPEAN POINT OF VIEW
- Animal Imaging Database (AIDB)
- How MRI works explained simply using diagrams
- Real-time MRI videos: Biomedizinische NMR Forschungs GmbH.



