17α-Hydroxypregnenolone: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 72: | Line 72: | ||
{{Endogenous steroids}} |
{{Endogenous steroids}} |
||
{{ |
{{Xenobiotic-sensing receptor modulators}} |
||
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxypregnenolone, 17α-}} |
{{DEFAULTSORT:Hydroxypregnenolone, 17α-}} |
||
Revision as of 22:21, 31 August 2017
 | |
 | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
|---|---|
| Metabolism | Adrenal, Gonads |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ChEBI | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.239 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C21H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 332.48 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 268 °C (514 °F) |
| |
| |
| | |
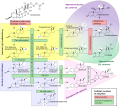
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone is a pregnane (C21) steroid that is obtained by hydroxylation of pregnenolone at the C17α position. This step is performed by the mitochondrial cytochrome P450 enzyme 17α-hydroxylase (CYP17A1) that is present in the adrenal and gonads. Peak levels are reached in humans at the end of puberty and then decline.[1] High levels are also achieved during pregnancy.
Prohormone
17α-Hydroxypregnenolone is considered a prohormone in the formation of dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA), itself a prohormone of the sex steroids.
This conversion is mediated by the enzyme 17,20 lyase. As such 17α-hydroxypregenolone represents an intermediary in the Δ5 pathway that leads from pregnenolone to DHEA. 17α-Hydroxypregneolone is also converted to 17α-hydroxyprogesterone, a prohormone for glucocorticosteroids and androstenedione through the activity of 3α-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase.
Clinical use
Measurements of 17α-hydroxypregnenolone are useful in the diagnosis of certain forms of congenital adrenal hyperplasia.[2] In patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 3β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase deficiency 17α-hydroxypregnenolone is increased, while in patients with congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 17α-hydroxylase deficiency levels are low to absent.
See also
Additional images
References
- ^ Hill, M; Lukác, D; Lapcík, O; Sulcová, J; Hampl, R; Pouzar, V; Stárka, L (1999). "Age relationships and sex differences in serum levels of pregnenolone and 17-hydroxypregnenolone in healthy subjects". Clinical chemistry and laboratory medicine : CCLM / FESCC. 37 (4): 439–47. doi:10.1515/CCLM.1999.072. PMID 10369116.
- ^ Riepe FG, Mahler P, Sippell, Partsch CJ. Longitudinal Study of Plasma Pregnenolone and 17-Hydroxypregnenolone in Full-Term and Preterm Neonates at Birth and during the Early Neonatal Period. The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism (2002) 87: 4301-4306 [1]