Greater sac: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
GreenC bot (talk | contribs) m Rescued 1 archive link; reformat 1 link. Wayback Medic 2.1 |
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead. #IABot (v1.6beta3) |
||
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
* {{NormanAnatomy|peritoneum}} |
* {{NormanAnatomy|peritoneum}} |
||
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20070313152543/http://iws.ccccd.edu/mweis/Images/Models/2402%20Models/digestive%20models/labeled%20gi%20models/gi_abd_omentum_organs_torso_labeled.png Diagram at ccccd.edu] |
* [https://web.archive.org/web/20070313152543/http://iws.ccccd.edu/mweis/Images/Models/2402%20Models/digestive%20models/labeled%20gi%20models/gi_abd_omentum_organs_torso_labeled.png Diagram at ccccd.edu] |
||
* [http://137.222.110.150/calnet/abdpel1/page8.htm Dissection video at University of Bristol] |
* [https://archive.is/20030129154420/http://137.222.110.150/calnet/abdpel1/page8.htm Dissection video at University of Bristol] |
||
{{Peritoneum}} |
{{Peritoneum}} |
||
Revision as of 06:23, 23 October 2017
| Greater sac | |
|---|---|
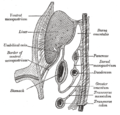
 The greater sac or general cavity (red) and lesser sac, or omental bursa (blue). | |
 Horizontal disposition of the peritoneum in the upper part of the abdomen. | |
| Anatomical terminology |
In human anatomy, the greater sac, also known as the general cavity (of the abdomen) or peritoneum of the peritoneal cavity proper, is the cavity in the abdomen that is inside the peritoneum but outside the lesser sac.
It is connected with the lesser sac via the omental foramen, also known as the foramen of Winslow or epiploic foramen, which is anteriorly bounded by the portal triad – portal vein, hepatic artery, and common bile duct.
Additional images
-
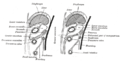
Schematic figure of the bursa omentalis, etc. Human embryo of eight weeks.
-
Diagrams to illustrate the development of the greater omentum and transverse mesocolon.
See also
External links
- "Greater sac". Medcyclopaedia. GE. Archived from the original on 2012-02-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - peritoneum at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University)
- Diagram at ccccd.edu
- Dissection video at University of Bristol