Brussels: Difference between revisions
→Folklore: DAB Project: Fixed erroneous disambiguation page link Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
Typo Tags: Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{About|the Brussels-Capital Region|the |
{{About|the Brussels-Capital Region|the state within it and the official capital of Belgium|City of Brussels}} |
||
{{Other places}} |
{{Other places}} |
||
{{pp-move-indef}} |
{{pp-move-indef}} |
||
Revision as of 05:39, 12 November 2017
Brussels (Template:Lang-fr, [bʁysɛl] ; Template:Lang-nl, [ˈbrɵsəl] ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region[6][7] (Template:Lang-fr, Template:Lang-nl),[8] is a region of Belgium comprising 19 municipalities, including the City of Brussels, which is the de jure capital of Belgium.[9] The Brussels-Capital Region is located in the central portion of the country and is a part of both the French Community of Belgium[10] and the Flemish Community, but is separate from the region of Flanders (in which it forms an enclave) or Wallonia.[11][12] Compared to most regions in Europe, Brussels has a relatively small territory, with an area of 161 km2 (62.31 sq mi). The region has a population of 1.2 million and a metropolitan area with a population of over 2.1 million, the largest agglomeration in Belgium.[13][14][15] Brussels is also part of a large conurbation which extends between Brussels, Antwerp, Ghent, Leuven and Walloon Brabant and is home to over 5 million people.
Brussels has grown from a small rural settlement on the river Senne to become an important city-region in Europe. Since the end of the Second World War, Brussels has been a major centre for international politics and has become the home of numerous international organisations, politicians, diplomats and civil servants.[16] Brussels is the de facto capital of the European Union, as it hosts a number of principal EU institutions (the other administrative centres are Luxembourg and Strasbourg).[17][18][19] The name Brussels is sometimes used metonymically to describe the EU and its institutions.[20][21] The secretariat of the Benelux and the headquarters of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) are also located in Brussels.[22][23] Today, it is classified as an Alpha global city.[24]
Historically a Dutch-speaking city, Brussels has seen a language shift to French from the late 19th century onwards. Today, the majority language is French, and the Brussels-Capital Region is an officially bilingual enclave within the Flemish Region. All road signs, street names, and many advertisements and services are shown in both languages.[25] Brussels is increasingly becoming multilingual, being home to many international institutions. English is spoken as a second language by nearly a third of the population, while a large number of migrants and expatriates speak other languages, namely Arabic, Spanish, German and Italian.[26]
Toponymy
Etymology
The most common theory of the origin of the name Brussels is that it derives from the Old Dutch Bruocsella, Broekzele or Broeksel, meaning marsh (bruoc / broek) and home (sella / zele / sel) or "home in the marsh".[27] Saint Vindicianus, the bishop of Cambrai made the first recorded reference to the place Brosella in 695[28], when it was still a hamlet. The names of all the municipalities in the Brussels-Capital Region are also of Dutch origin, except for Evere, which is of Celtic origin.
Pronunciation
In French, Bruxelles is pronounced [bʁy.sɛl] (the x is pronounced [s] (ss), like in English) and in Dutch, Brussel is pronounced [bry.s(ɘ)l] or [brɘ.s(ɘ)l]. Inhabitants of Brussels are known in French as Bruxellois and in Dutch as Brusselaars. In the Brabantian dialect of Brussels, they are called Brusseleers or Brusseleirs.
Originally, the written x noted the group /ks/. In the Belgian French pronunciation as well as in Dutch, the k eventually disappeared and z became s, as reflected in the current Dutch spelling, whereas in the more conservative French form, the spelling remained. The pronunciation [ks] in French only dates from the 18th century, but this modification did not affect the traditional Brussels usage. In France, the pronunciation [bʁyk.sɛl] and [bʁyk.sɛlwa] is often heard, but it is rather rare in Belgium.
History
- See also: History of Brussels (in French)

Early history
The history of Brussels is closely linked to that of Western Europe. Traces of human settlement go back to the Stone age, with vestiges and place-names related to the civilisation of megaliths, dolmens and standing stones (Plattesteen, Tomberg). During Antiquity, the region was home to Roman occupation, as attested by archaeological evidence discovered near the centre.[29][30] Following the decline of the Western Roman Empire, the region was incorporated into the Frankish Empire.
The origin of the settlement which was to become Brussels lies in Saint Gaugericus' construction of a chapel on an island in the river Senne around 580.[31] The official founding of Brussels is usually situated around 979, when Duke Charles of Lower Lotharingia transferred the relics of Saint Gudula from Moorsel to the Saint Gaugericus chapel. Charles would construct the first permanent fortification in the city, doing so on that same island.
Middle Ages
Lambert I of Leuven, Count of Leuven, gained the County of Brussels around 1000, by marrying Charles' daughter. Because of its location on the shores of the Senne, on an important trade route between Bruges and Ghent, and Cologne, Brussels became a commercial centre, specialised in the textile trade. The town grew quite rapidly and extended towards the upper town (Treurenberg, Coudenberg and Sablon areas), where there was a smaller risk of floods. As it grew to a population of around 30,000, the surrounding marshes were drained to allow for further expansion. Around this time, work began on the Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula (1225), replacing an older Romanesque church. In 1183, the Counts of Leuven became Dukes of Brabant. Brabant, unlike the county of Flanders, was not fief of the king of France but was incorporated into the Holy Roman Empire. In the early 13th century, the city got its first walls.[32] After the construction of the city walls, Brussels grew significantly. To let the city expand, a second set of walls was erected, between 1356 and 1383. Today, traces of it can still be seen, mostly because the small ring, a series of roadways in downtown Brussels, bounding the historic city centre, follows its former course.
Early modern


In the 15th century, by means of the wedding of heiress Margaret III of Flanders with Philip the Bold, Duke of Burgundy, a new Duke of Brabant emerged from the House of Valois (namely Antoine, their son). In 1477, the Burgundian duke Charles the Bold perished in the Battle of Nancy. Through the marriage of his daughter Mary of Burgundy (who was born in Brussels) to Holy Roman Emperor Maximilian I, the Low Countries fell under Habsburg sovereignty. Brabant had lost its independence, but Brussels became the Princely Capital of the prosperous Burgundian Netherlands, also known as the Seventeen Provinces, and flourished. After the death of Mary in 1482, her son Philip the Handsome succeeded as the Duke of Brabant. In 1506, he became King of Castile, and hence the period of the Spanish Netherlands began.
In 1516, Charles V, who had been heir of the Low Countries since 1506, was declared King of Spain in Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula of Brussels. Upon the death of his grandfather Maximilian I, Holy Roman Emperor in 1519, Charles became the new ruler of the Habsburg Empire and was subsequently elected Holy Roman Emperor. It was in the Palace complex at Coudenberg that Charles V abdicated in 1555. This impressive palace, famous all over Europe, had greatly expanded since it had first become the seat of the Dukes of Brabant, but it was destroyed by fire in 1731. In the 17th century, the city was a capital of the lace industry.
In 1695, during the Nine Years' War, King Louis XIV of France sent troops to bombard Brussels with artillery. Together with the resulting fire, it was the most destructive event in the entire history of Brussels. The Grand Place was destroyed, along with 4,000 buildings – a third of all the buildings in the city. The reconstruction of the city centre, effected during subsequent years, profoundly changed the appearance of the city and left numerous traces still visible today.
Following the Treaty of Utrecht in 1713, the Spanish sovereignty over the Southern Netherlands was transferred to the Austrian branch of the House of Habsburg. This event started the era of the Austrian Netherlands. The city was captured by France in 1746, during the War of the Austrian Succession, but was handed back to Austria three years later. Brussels remained with Austria until 1795, when the Southern Netherlands were captured and annexed by France. Brussels became the capital of the department of the Dyle. The French rule ended in 1815, with the defeat of Napoleon on the battlefield of Waterloo, which is located south of today's Brussels-Capital Region. With the Congress of Vienna, the Southern Netherlands joined the United Kingdom of the Netherlands, under William I of Orange. The former Dyle department became the province of South Brabant, with Brussels as its capital.
Late modern


In 1830, the Belgian revolution took place in Brussels, after a performance of Auber's opera La Muette de Portici at La Monnaie theatre. Brussels became the capital and seat of government of the new nation. South Brabant was renamed simply Brabant, with Brussels as its capital. On 21 July 1831, Leopold I, the first King of the Belgians, ascended the throne, undertaking the destruction of the city walls and the construction of many buildings.
Following independence, the city underwent many more changes. Brussels became a financial centre, thanks to the dozens of companies put into orbit by the Société Générale de Belgique. The Industrial Revolution and the building of the Brussels-Charleroi Canal brought prosperity to the city through commerce and manufacturing. The Free University of Brussels was established in 1834. In 1835, the first passenger railway built outside England linked Brussels (Molenbeek) with Mechelen.
During the 19th century, the population of Brussels grew considerably; from about 80,000 to more than 625,000 people for the city and its surroundings. The Senne had become a serious health hazard, and from 1867 to 1871, under the tenure of mayor Jules Anspach, its entire course through the urban area was completely covered over. This allowed urban renewal and the construction of modern buildings of hausmannien style along central boulevards, characteristic of downtown Brussels today. Buildings such as the Brussels Stock Exchange (1873), the Palace of Justice (1883) and Saint Mary's Royal Church (1885) date from this period. This development continued throughout the reign of King Leopold II. The International Exposition of 1897 contributed to the promotion of the infrastructure. Among other things, the Colonial Palace (today's Royal Museum for Central Africa), in the suburb of Tervuren, was connected to the capital by the construction of an 11-km long grand alley.
20th century

During the 20th century, the city hosted various fairs and conferences, including the Solvay Conference on Physics and on Chemistry, and two world fairs: the Brussels International Exposition of 1935 and the Expo '58. During World War I, Brussels was an occupied city, but German troops did not cause much damage. During World War II, the city was again occupied, and was spared major damage during its occupation by German forces, before it was liberated by the British Guards Armoured Division, on 3 September 1944. The Brussels Airport, in the suburb of Zaventem, dates from the occupation.
After the war, Brussels underwent extensive modernisation. The construction of the North–South connection, linking the main railway stations in the city, was completed in 1952, while the first Brussels premetro was finished in 1969, and the first line of the Brussels Metro was opened in 1976. Starting from the early 1960s, Brussels became the de facto capital of what would become the European Union, and many modern buildings were built. Development was allowed to proceed with little regard to the aesthetics of newer buildings, and many architectural landmarks were demolished to make way for newer buildings that often clashed with their surroundings, giving name to the process of Brusselisation.
Contemporary
The Brussels-Capital Region was formed on 18 June 1989, after a constitutional reform in 1988. It has bilingual status and it is one of the three federal regions of Belgium, along with Flanders and Wallonia.[6][7] The yellow iris is the emblem of the region (referring to the presence of these flowers on the original site of the city) and a stylised version in shown on the official flag of the Brussels region.[33]
In recent years, Brussels has become an important venue for international events. In 2000, Brussels, along with eight other European cities, was named European Capital of Culture.[34] In 2014, Brussels hosted the 40th G7 summit.[35] It is among the cities which will host the UEFA Euro 2020.
On 22 March 2016, three coordinated nail bombings were detonated by ISIL in Brussels – two at Brussels Airport in Zaventem, and one at Maalbeek/Maelbeek metro station, – resulting in 32 victims and three suicide bombers killed, and 330 people were injured. It was the deadliest act of terrorism in Belgium.
Geography

Location and topography
Brussels lies in the north-central part of Belgium, about 110 km (68 mi) from the Belgian coast and about 180 km (111 mi) from the southern tip of Belgium. It is located in the heartland of the Brabantian Plateau, about 45 km (28 mi) south of Antwerp (Flanders), and 50 km (31 mi) north of Charleroi (Wallonia). Its average elevation is 57 metres (187 ft) above sea level, varying from a low point in the valley of the almost completely covered Senne, which cuts the region from east to west, up to high points in the Sonian Forest, at the southeastern side. In addition to the Senne, tributary streams such as the Maalbeek and the Woluwe, to the east of the region, account for significant elevation differences. Brussels' central boulevards are 15 metres above sea level.[36] The highest point lies at a height of about 108 metres (354 ft), near Place de l'Altitude Cent/Hoogte Honderdplein, in Forest.
Climate
Under the Köppen climate classification, Brussels experiences an oceanic climate (Cfb). Brussels' proximity to coastal areas influences the area's climate by sending marine air masses from the Atlantic Ocean. Nearby wetlands also ensure a maritime temperate climate. On average (based on measurements over the last 100 years), there are approximately 200 days of rain per year in the Brussels-Capital Region, the second highest amount of any European capital, after Dublin (Ireland).[37] Snowfall is infrequent, averaging 24 days per year. In Brussels, there are often violent thunderstorms.
| Climate data for Brussels | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Month | Jan | Feb | Mar | Apr | May | Jun | Jul | Aug | Sep | Oct | Nov | Dec | Year |
| Record high °C (°F) | 15.3 (59.5) |
20.0 (68.0) |
24.2 (75.6) |
28.7 (83.7) |
34.1 (93.4) |
38.8 (101.8) |
37.1 (98.8) |
36.5 (97.7) |
34.9 (94.8) |
27.8 (82.0) |
20.6 (69.1) |
16.7 (62.1) |
38.8 (101.8) |
| Mean daily maximum °C (°F) | 5.7 (42.3) |
6.6 (43.9) |
10.4 (50.7) |
14.2 (57.6) |
18.1 (64.6) |
20.6 (69.1) |
23.0 (73.4) |
22.6 (72.7) |
19.0 (66.2) |
14.7 (58.5) |
9.5 (49.1) |
6.1 (43.0) |
14.2 (57.6) |
| Daily mean °C (°F) | 3.3 (37.9) |
3.7 (38.7) |
6.8 (44.2) |
9.8 (49.6) |
13.6 (56.5) |
16.2 (61.2) |
18.4 (65.1) |
18.0 (64.4) |
14.9 (58.8) |
11.1 (52.0) |
6.8 (44.2) |
3.9 (39.0) |
10.5 (51.0) |
| Mean daily minimum °C (°F) | 0.7 (33.3) |
0.7 (33.3) |
3.1 (37.6) |
5.3 (41.5) |
9.2 (48.6) |
11.9 (53.4) |
14.0 (57.2) |
13.6 (56.5) |
10.9 (51.6) |
7.8 (46.0) |
4.1 (39.4) |
1.6 (34.9) |
6.9 (44.4) |
| Record low °C (°F) | −21.1 (−6.0) |
−18.3 (−0.9) |
−13.6 (7.5) |
−5.7 (21.7) |
−2.2 (28.0) |
0.3 (32.5) |
4.4 (39.9) |
3.9 (39.0) |
0.0 (32.0) |
−6.8 (19.8) |
−12.8 (9.0) |
−17.7 (0.1) |
−21.1 (−6.0) |
| Average precipitation mm (inches) | 76.1 (3.00) |
63.1 (2.48) |
70.0 (2.76) |
51.3 (2.02) |
66.5 (2.62) |
71.8 (2.83) |
73.5 (2.89) |
79.3 (3.12) |
68.9 (2.71) |
74.5 (2.93) |
76.4 (3.01) |
81.0 (3.19) |
852.4 (33.56) |
| Average precipitation days | 19.2 | 16.3 | 17.8 | 15.9 | 16.2 | 15.0 | 14.3 | 14.5 | 15.7 | 16.6 | 18.8 | 19.3 | 199.6 |
| Average snowy days | 5.2 | 5.9 | 3.2 | 2.4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2.4 | 4.6 | 24.1 |
| Average relative humidity (%) | 86.6 | 82.5 | 78.5 | 72.5 | 73.2 | 74.1 | 74.3 | 75.5 | 80.9 | 84.6 | 88.2 | 88.8 | 80 |
| Mean monthly sunshine hours | 59 | 77 | 114 | 159 | 191 | 188 | 201 | 190 | 143 | 113 | 66 | 45 | 1,546 |
| Source: KMI/IRM[38] | |||||||||||||
Brussels as a capital

Despite what its name suggests, the Brussels-Capital Region is not the capital of Belgium in itself. Article 194 of the Belgian Constitution establishes that the capital of Belgium is the City of Brussels, the municipality within the capital region that once was the city's core.[9]
The City of Brussels is the location of many national institutions. The Royal Palace, where the King of Belgium exercises his prerogatives as head of state, is situated alongside the Brussels Park (not to be confused with the Royal Castle of Laeken, the official home of the Belgian Royal Family). The Palace of the Nation is located on the opposite side of this park, and is the seat of the Belgian Federal Parliament. The office of the Prime Minister of Belgium, colloquially called Law Street 16 (Dutch: Wetstraat 16, French: 16, rue de la Loi), is located adjacent to this building. This is also the place where the Council of Ministers holds its meetings. The Court of Cassation, Belgium's main court, has its seat in the Palace of Justice. Other important institutions in the City of Brussels are the Constitutional Court, the Council of State, the Court of Audit, the Royal Belgian Mint and the National Bank of Belgium.
The City of Brussels is also the capital of both the French Community of Belgium[10] and the Flemish Community.[11] The Flemish Parliament and Flemish Government have their seats in Brussels,[39] as do the Parliament of the French Community and the Government of the French Community.
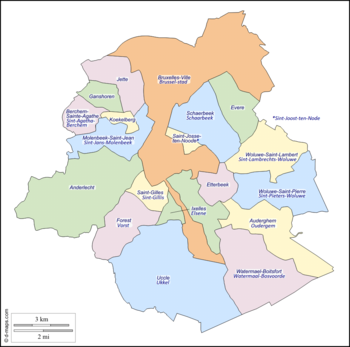
Municipalities
| French name | Dutch name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anderlecht | Anderlecht | rowspan=19 style="padding:20px; Template:Linear-gradient" | | ||
| Auderghem | Oudergem | |||
| Berchem-Sainte-Agathe | Sint-Agatha-Berchem | |||
| Bruxelles-Ville | Stad Brussel | |||
| Etterbeek | Etterbeek | |||
| Evere | Evere | |||
| Forest | Vorst | |||
| Ganshoren | Ganshoren | |||
| Ixelles | Elsene | |||
| Jette | Jette | |||
| Koekelberg | Koekelberg | |||
| Molenbeek-Saint-Jean | Sint-Jans-Molenbeek | |||
| Saint-Gilles | Sint-Gillis | |||
| Saint-Josse-ten-Noode | Sint-Joost-ten-Node | |||
| Schaerbeek | Schaarbeek | |||
| Uccle | Ukkel | |||
| Watermael-Boitsfort | Watermaal-Bosvoorde | |||
| Woluwe-Saint-Lambert | Sint-Lambrechts-Woluwe | |||
| Woluwe-Saint-Pierre | Sint-Pieters-Woluwe | |||

The 19 municipalities (communes) of the Brussels-Capital Region are political subdivisions with individual responsibilities for the handling of local level duties, such as law enforcement and the upkeep of schools and roads within its borders.[40][41] Municipal administration is also conducted by a mayor, a council, and an executive.[41]
In 1831, Belgium was divided into 2,739 municipalities, including the 19 in the Brussels-Capital Region.[42] Unlike most of the municipalities in Belgium, the ones located in the Brussels-Capital Region were not merged with others during mergers occurring in 1964, 1970, and 1975.[42] However, several municipalities outside of the Brussels-Capital Region have been merged with the City of Brussels throughout its history, including Laeken, Haren, and Neder-Over-Heembeek, which were merged into the City of Brussels in 1921.[43]
The largest and most populous of the municipalities is the City of Brussels, covering 32.6 square kilometres (12.6 sq mi) and with 145,917 inhabitants. The least populous is Koekelberg with 18,541 inhabitants, while the smallest in area is Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, which is only 1.1 square kilometres (0.4 sq mi). Despite being the smallest municipality, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode has the highest population density of the 19, with 20,822 inhabitants per square kilometre (53,930/sq mi).
A lot of controversy exists concerning the division of 19 municipalities for a highly urbanised region, which is considered as (half of) one city by most people. Some politicians mock the '19 baronies' and want to merge the municipalities under one city council and one mayor.[44][45] This would lower the number of politicians needed to govern Brussels, and centralise the power over the city to make decisions easier, thus reduce the overall running costs. The current municipalities could be transformed into districts with limited responsibilities, similar to the current structure of Antwerp or to structures of other capitals like the boroughs in London or arrondissements in Paris, to keep politics close enough to the citizen.[46]
The commune of Molenbeek has gained a reputation as a safe haven for Jihadists in relation to the support shown by some residents towards the bombers who carried out the Paris and Brussels attacks.[47][48][49][50][51]
- Municipalities of Brussels
Brussels-Capital Region

Political status
The Brussels-Capital Region is one of the three federated regions of Belgium, alongside the Walloon Region and the Flemish Region. Geographically and linguistically, it is a bilingual enclave in the monolingual Flemish Region. Regions are one component of Belgium's institutions, the three communities being the other component: Brussels' inhabitants deal with either the French Community or the Flemish Community for matters such as culture and education, as well as a Common Community for competencies which do not belong exclusively to either Community, such as healthcare and assistance to individuals.
Since the splitting of Brabant in 1995, the Brussels Region does not belong to any of the provinces of Belgium, nor is it subdivided into provinces itself. Within the Region, 99% of the areas of provincial jurisdiction are assumed by the Brussels regional institutions and community commissions. Remaining is only the governor of Brussels-Capital and some aides, analogously to provinces. Its status is roughly akin to that of a federal district.
Institutions

The Brussels-Capital Region is governed by a parliament of 89 members (72 French-speaking, 17 Dutch-speaking – parties are organised on a linguistic basis) and an eight-member regional cabinet consisting of a minister-president, four ministers and three state secretaries. By law, the cabinet must comprise two French-speaking and two Dutch-speaking ministers, one Dutch-speaking secretary of state and two French-speaking secretaries of state. The minister-president does not count against the language quota, but in practice every minister-president has been a bilingual francophone. The regional parliament can enact ordinances (French: ordonnances, Dutch: ordonnanties), which have equal status as a national legislative act.
19 of the 72 French-speaking members of the Brussels Parliament are also members of the Parliament of the French Community of Belgium, and, until 2004, this was also the case for six Dutch-speaking members, who were at the same time members of the Flemish Parliament. Now, people voting for a Flemish party have to vote separately for 6 directly elected members of the Flemish Parliament.
Agglomeration of Brussels
Before the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, regional competences in the 19 municipalities were performed by the Brussels Agglomeration. The Brussels Agglomeration was an administrative division established in 1971. This decentralised administrative public body also assumed jurisdiction over areas which, elsewhere in Belgium, were exercised by municipalities or provinces.[52]
The Brussels Agglomeration had a separate legislative council, but the by-laws enacted by it did not have the status of a legislative act. The only election of the council took place on 21 November 1971. The working of the council was subject to many difficulties caused by the linguistic and socio-economic tensions between the two communities.
After the creation of the Brussels-Capital Region, the Brussels Agglomeration was never formally abolished, although it no longer has a purpose.
French and Flemish communities

The French Community and the Flemish Community exercise their powers in Brussels through two community-specific public authorities: the French Community Commission (French: Commission communautaire française or COCOF) and the Flemish Community Commission (Dutch: Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie or VGC). These two bodies each have an assembly composed of the members of each linguistic group of the Parliament of the Brussels-Capital Region. They also have a board composed of the ministers and secretaries of state of each linguistic group in the Government of the Brussels-Capital Region.
The French Community Commission has also another capacity: some legislative powers of the French Community have been devolved to the Walloon Region (for the French language area of Belgium) and to the French Community Commission (for the bilingual language area).[53] The Flemish Community, however, did the opposite; it merged the Flemish Region into the Flemish Community.[54] This is related to different conceptions in the two communities, one focusing more on the Communities and the other more on the Regions, causing an asymmetrical federalism. Because of this devolution, the French Community Commission can enact decrees, which are legislative acts.
Common Community Commission
A bi-communitarian public authority, the Common Community Commission (French: Commission communautaire commune, COCOM, Dutch: Gemeenschappelijke Gemeenschapscommissie, GGC) also exists. Its assembly is composed of the members of the regional parliament, and its board are the ministers – not the secretaries of state – of the region, with the minister-president not having the right to vote. This Commission has two capacities: it is a decentralised administrative public body, responsible for implementing cultural policies of common interest. It can give subsidies and enact by-laws. In another capacity, it can also enact ordinances, which have equal status as a national legislative act, in the field of the welfare powers of the communities: in the Brussels-Capital Region, both the French Community and the Flemish Community can exercise powers in the field of welfare, but only in regard to institutions that are unilingual (for example, a private French-speaking retirement home or the Dutch-speaking hospital of the Vrije Universiteit Brussel). The Common Community Commission is responsible for policies aiming directly at private persons or at bilingual institutions (for example, the centres for social welfare of the 19 municipalities). Its ordinances have to be enacted with a majority in both linguistic groups. Failing such a majority, a new vote can be held, where a majority of at least one third in each linguistic group is sufficient.
International institutions
Brussels has, since World War II, become the administrative centre of many international organisations. The European Union (EU) and the North Atlantic Treaty Organisation (NATO) have their main institutions in the city, along with many other international organisations such as the World Customs Organization and EUROCONTROL as well as international corporations. Brussels is third in the number of international conferences it hosts[55] also becoming one of the largest convention centres in the world.[56] The presence of the EU and the other international bodies has, for example, led to there being more ambassadors and journalists in Brussels than in Washington D.C.[57] International schools have also been established to serve this presence.[56] The "international community" in Brussels numbers at least 70,000 people.[58] In 2009, there were an estimated 286 lobbying consultancies known to work in Brussels.[59]
European Union
Brussels serves as de facto capital of the European Union, hosting the major political institutions of the Union.[17] The EU has not declared a capital formally, though the Treaty of Amsterdam formally gives Brussels the seat of the European Commission (the executive branch of government) and the Council of the European Union (a legislative institution made up from executives of member states).[60][61] It locates the formal seat of European Parliament in the French city of Strasbourg, where votes take place, with the Council, on the proposals made by the Commission. However, meetings of political groups and committee groups are formally given to Brussels, along with a set number of plenary sessions. Three quarters of Parliament sessions now take place at its Brussels hemicycle.[62] Between 2002 and 2004, the European Council also fixed its seat in the city.[63] In 2014, the Union hosted a G7 summit in the city.[35]
Brussels, along with Luxembourg and Strasbourg, began to host European institutions in 1957, soon becoming the centre of activities, as the Commission and Council based their activities in what has become the European Quarter, in the east of the city.[60] Early building in Brussels was sporadic and uncontrolled, with little planning. The current major buildings are the Berlaymont building of the Commission, symbolic of the quarter as a whole, the Justus Lipsius building of the Council and the Espace Léopold of the Parliament.[61] Today, the presence has increased considerably, with the Commission alone occupying 865,000 m2 within the European Quarter (a quarter of the total office space in Brussels[17]). The concentration and density has caused concern that the presence of the institutions has created a ghetto effect in that part of the city.[64] However, the European presence has contributed significantly to the importance of Brussels as an international centre.[57]
Eurocontrol

The European Organisation for the Safety of Air Navigation, commonly known as Eurocontrol, is an international organisation which is tasked to monitor the European aviation by flight. Eurocontrol coordinates and plans air traffic control across European airspace. The corporation was founded in 1960 and currently has 41 member states. Its headquarters are located in Haren, on the northeast perimeter of the City of Brussels.
North Atlantic Treaty Organisation

The Treaty of Brussels, which was signed on 17 March 1948 between Belgium, France, Luxembourg, the Netherlands and the United Kingdom, was a prelude to the establishment of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO), an intergovernmental military alliance,[65] and was a preview of the western European defense against communism[citation needed].
Today, the alliance consists of 29 independent member countries across North America and Europe. Several countries also have diplomatic missions to NATO through embassies in Belgium. Since 1949, a number of NATO Summits have been held in the city.[66] The most recent NATO summit took place in Brussels in May 2017.[67]
The organisation's headquarters are located on Boulevard Léopold III/Leopold III-laan in Haren, Brussels.[68] A new €750 million headquarters building begun in 2010 and was completed in 2017.[69]
Demographics
Population

Brussels is located in one of the most urbanised regions of Europe, between Paris, London, the Rhine-Ruhr (Germany), and the Randstad (Netherlands). The Brussels-Capital Region has a population of around 1.2 million and has witnessed, in recent years, a remarkable increase in its population. In general, the population of Brussels is younger than the national average, and the gap between rich and poor is wider.[70]
| 01-07-2004[71] | 01-07-2005[71] | 01-07-2006[71] | 01-01-2008[71] | 01-01-2015[71] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brussels-Capital Region[71] | 1.004.239 | 1.012.258 | 1.024.492 | 1.048.491 | 1.181.272 |
| -- of which legal immigrants[71] | 262.943 | 268.009 | 277.682 | 295.043 | 385.381 |
Nationalities
| Largest groups of foreign residents[72] | |
| Nationality | Population (2016) |
|---|---|
| 62,507 | |
| 38,690 | |
| 38,274 | |
| 32,322 | |
| 28,042 | |
| 26,399 | |
| 19,791 | |
| 11,371 | |
| 10,527 | |
| 8,846 | |
Brussels is home to a large number of immigrants. At the last Belgian census in 1991, 63.7% of inhabitants in Brussels-Capital Region answered that they were Belgian citizens, born as such in Belgium. However, there have been numerous individual or familial migrations towards Brussels since the end of the 18th century, including political refugees (Karl Marx, Victor Hugo, Pierre Joseph Proudhon, Léon Daudet, for example), from neighbouring or more distant countries, as well as labour migrants, former foreign students or expatriates, and many Belgian families in Brussels can claim at least one foreign grandparent.
Brussels has a large concentration of immigrants from other countries, and their children, including many of Moroccan (Riffian, Berber) and Turkish ancestry, together with French-speaking black Africans from former Belgian colonies, such as the Democratic Republic of the Congo, Rwanda and Burundi.
People of foreign origin make up nearly 70%[73] of the population of Brussels, most of whom have been naturalised following the great 1991 reform of the naturalisation process. About 32% of city residents are of non-Belgian European origin, and 36% are of another background, mostly from Morocco, Turkey and Sub-Saharan Africa. Among all major migrant groups from outside the EU, a majority of the permanent residents have acquired Belgian nationality.[74]
Languages

Since the founding of the Kingdom of Belgium in 1830, Brussels has transformed from being almost entirely Dutch-speaking (Brabantian dialect to be exact), to being a multilingual city with French (specifically Belgian French) as the majority language and lingua franca. This language shift, the Francisation of Brussels, is rooted in the 18th century and accelerated after Belgium became independent and Brussels expanded past its original boundaries.[76][77]

French-speaking immigration contributed to the Frenchification of Brussels; both Walloons and expatriates from other countries – mainly France – came to Brussels in great numbers. However, a more important cause for the Frenchification was the language change over several generations from Dutch to French that was carried out, in Brussels, by the Flemish people themselves. The main reason for this was a political, administrative and social pressure, partly based on the low social prestige of the Dutch language in Belgium at the time; this made French the only language of administration, law, politics and education in Belgium, and thus necessary for social mobility.[78] From 1880 on, faced with the necessity of using French in dealing with such institutions, more and more Dutch-speakers became bilingual, and a rise in the number of monolingual French-speakers was seen after 1910. Halfway through the 20th century, the number of monolingual French-speakers surpassed the number of mostly bilingual Flemish inhabitants.[79]
Only since the 1960s, after the fixation of the Belgian language border, and after the socio-economic development of Flanders was in full effect, could Dutch stem the tide of increasing French use.[80] Through immigration, a further number of formerly Dutch-speaking municipalities in surrounding Brussels became majoritively French-speaking in the second half of the 20th century.[81][82][83] This phenomenon is, together with the future of Brussels, one of the most controversial topics in all of Belgian politics.[84][85]

Given its Dutch-speaking origins and the role that Brussels plays as the capital city in a bilingual country, the administration of the entire Brussels-Capital Region is fully bilingual, including its subdivisions and public services. Nevertheless, some communautarian issues remain. Flemish political parties demanded, for decades, that the Flemish part of Brussels-Halle-Vilvoorde arrondissement be separated from the Brussels Region (which made Halle-Vilvoorde a monolingual Flemish arrondissement). BHV was divided mid 2012. The French-speaking population regards the language border as artificial[86] and demands the extension of the bilingual region to at least all six municipalities with language facilities in the surroundings of Brussels.[87] Flemish politicians have strongly rejected these proposals.[88][89][90]
The original Dutch dialect of Brussels (Brussels) is a form of Brabantic (the variant of Dutch spoken in the ancient Duchy of Brabant) with a significant number of loanwords from French, and still survives among a minority of inhabitants called Brusseleers, many of them quite bi- and multilingual, or educated in French and not writing in Dutch. Brussels and its suburbs have evolved from a Dutch-dialect-speaking town to a mainly French-speaking town. The ethnic and national self-identification of the inhabitants is quite different along ethnic lines.
For their French-speaking Bruxellois, it can vary from Belgian, Francophone Belgian, Bruxellois (like the Memellanders in interwar ethnic censuses in Memel), Walloon (for people who migrated from the Wallonia Region at an adult age); for Flemings living in Brussels, it is mainly either Flemish or Brusselaar (Dutch for an inhabitant), and often both. For the Brusseleers, many simply consider themselves as belonging to Brussels. For the many rather recent immigrants from other countries, the identification also includes all the national origins: people tend to call themselves Moroccans or Turks rather than an American-style hyphenated version.
The two largest foreign groups come from two francophone countries: France and Morocco.[91] The first language of roughly half of the inhabitants is not an official one of the Capital Region.[92] Nevertheless, about three out of four residents are Belgian nationals.[93][94][95]
In recent decades, owing to migration and the city's international role, Brussels is home to a growing number of foreign language speakers. In 2013, figures cited in the Marnix Plan show that 63.2% of Brussels inhabitants are native speakers of French, while less than 20% are native Dutch speakers. Just 2.5% speak English as their mother tongue, but 29.7% of people living in the city claim to speak English well or very well.[96] Even though some people want English to be used as an unofficial compromise language between Dutch and French, French remains the lingua franca. And laws still require Dutch and French translations in most cases. The acceptance of English as a language for communication with the city's public servants depends entirely on their knowledge of this language, though they must accept questions in French and Dutch.[97]
The migrant communities, as well as rapidly growing communities of EU-nationals from other EU-member states, speak many languages like French, Turkish, Arabic, Berber, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Polish, German, and (increasingly) English. The degree of linguistic integration varies widely within each migrant group.
Religions
Religion in Brussels-Capital Region (2016)[98]
Historically, Brussels has been predominantly Roman Catholic, especially since the expulsion of Protestants in the 16th century. This is clear from the large number of historical churches around the area, particularly in the City of Brussels. The pre-eminent Catholic cathedral in Brussels is the Cathedral of Saint Michael and Saint Gudula, which serves as the co-cathedral of the Archdiocese of Mechelen-Brussels. On the northwestern side of the city, the National Basilica of the Sacred Heart is the 14th largest church building in the world. The Church of Our Lady of Laeken holds the tombs of many members of the Belgian royal family, including all the former Kings of Belgium, within the Royal Crypt.
Nowadays, most residents of Brussels are nonreligious, with only about 10% of Catholics regularly attending church services.[citation needed] In reflection of its multicultural makeup, Brussels hosts a variety of religious communities, as well as large numbers of atheists and agnostics. Minority faiths include Islam, Anglicanism, Eastern Orthodoxy, Judaism, and Buddhism.
Recognised religions and Laïcité enjoy public funding and school courses. It was once the case that every pupil in an official school from 6 years old to 18 had to choose 2 hours per week of compulsory religion – or Laïcité – inspired morals. However, in 2015, the Belgian Constitutional court ruled religious studies could no longer be required in the primary and secondary education system.[99]
Brussels has a large concentration of Muslims, mostly of Moroccan and Turkish ancestry. Belgium does not collect statistics by ethnic background, so exact figures are unknown. It was estimated that, in 2005, people of Muslim background living in the Brussels Region numbered 256,220 and accounted for 25.5% of the city's population, a much higher concentration than those of the other regions of Belgium.[100][better source needed] The Great Mosque of Brussels, located in the Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark, is the oldest mosque in Brussels.
In 2016, 40% of residents of Brussels declared themselves Catholics (12% were practising Catholics and 28% were non-practising Catholics), 30% were non-religious, 23% were Muslim (19% practising, 4% non-practising), 3% were Protestants, 4% were of another religion.[98]
| Regions of Belgium[100] (1 January 2016) | Total population | People of Muslim origin | % of Muslims |
|---|---|---|---|
| Belgium | 11,371,928 | 603,642 | 5.3% |
| Brussels-Capital Region | 1 180 531 | 212,495 | 18% |
| Wallonia | 3,395,942 | 149,421 | 4.4% |
| Flanders | 6,043,161 | 241,726 | 4.0% |
Culture
Architecture
The architecture in Brussels is diverse, and spans from the clashing combination of Gothic, Baroque, and Louis XIV styles on the Grand Place to the postmodern buildings of the EU institutions.[101]
Very little medieval architecture is preserved in Brussels. Buildings from this period are mostly to be found in the historic centre (called Îlot Sacré), Saint Géry and Sainte-Catherine/Sint Katelijne neighbourhoods. The Brabantine Gothic Cathedral of St. Michael and St. Gudula is still a prominent feature in the skyline of downtown Brussels. Isolated portions of the first city walls were saved from destruction and can be seen to this day. One of the only remains of the second walls is the Halle Gate. The Grand Place is the main attraction in the city centre and has been a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 1998.[102] The square is dominated by the 15th century Flamboyant Town Hall (French: Hôtel de Ville, Dutch: Stadhuis), the Neo-Gothic Breadhouse (French: Maison du Roi, Dutch: Broodhuis) and the Baroque guildhalls of the Guilds of Brussels. The Manneken Pis, a fountain containing a small bronze sculpture of a urinating youth, is a tourist attraction and symbol of the city.[103]

The neoclassical style of the 18th and 19th centuries is represented in the Royal Quarter/Coudenberg area, around the Brussels Park and Royal Square. Examples include the Royal Palace, the Church of Saint Jacques-sur-Coudenberg, the Palace of the Nation (Parliament building), the Academy Palace, the Palace of Charles of Lorraine, the Egmont Palace, etc. Other uniform neoclassical ensembles can be found around Martyrs' Square and Barricades' Square. Some other landmarks, in the centre, are the Galeries Royales Saint-Hubert (1847), one of the oldest covered shopping arcades in Europe; the Congress Column (1859); the Brussels Stock Exchange building (1873) (French: Bourse, Dutch: Beurs); and the Palace of Justice (1883), designed by Joseph Poelaert, in eclectic style, and reputed to be the largest building constructed in the 19th century.[104]
Also particularly striking are the buildings in the Art Nouveau style, most famously by the Belgian architects Victor Horta, Paul Hankar and Henry Van de Velde.[105][106] Some of Brussels districts were developed during the heyday of Art Nouveau, and many buildings are in this style. Good examples can be found in Schaerbeek, Etterbeek, Ixelles, and Saint-Gilles. The Major Town Houses of the Architect Victor Horta – Hôtel Tassel (1893), Hôtel Solvay (1894), Hôtel van Eetvelde (1895) and the Horta Museum (1901) – have been listed as a UNESCO World Heritage Site since 2000.[107] Another example of Brussels Art Nouveau is the Stoclet Palace (1911), by the Viennese architect Josef Hoffmann, designated a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in June 2009.[108]
- Art Nouveau in Brussels
-
Stairway of Hôtel Tassel by Victor Horta (1893)
-
Hôtel Ciamberlani by Paul Hankar (1897)
-
Former Old England department store by Paul Saintenoy (1899)
-
Saint Cyr house by Gustave Strauven (1903)
-
Cauchie house, with sgraffiti by Paul Cauchie (1905)
-
Stoclet Palace by Josef Hoffmann (1911)
Art Deco structures in Brussels include the Résidence Palace (1927) (now part of the Europa building), the Centre for Fine Arts (1928), the Villa Empain (1934), the Town Hall of Forest (1938), and the former House of the Radio building on Flagey Square (1935–1938) in Ixelles. Some religious buildings from the interwar era were also constructed in that style, such as the Church of St John the Baptist (1932) in Molenbeek and the Church of Saint Augustine (1935) in Forest. Completed only in 1969, and combining Art Deco with Neo-Byzantine elements, the Basilica of the Sacred Heart in Koekelberg is one of the largest Roman Catholic basilicas by area in the world, and its cupola provides a panoramic view of Brussels and its outskirts. Another example are the exhibition halls of the Centenary Palace (Brussels Expo), built for the 1935 World Fair on the Heysel Plateau in northern Brussels.[109]

Since the second half of the 20th century, modern office towers have been built in Brussels (Madou Tower, Rogier Tower, Proximus Towers, Finance Tower, the World Trade Center, among others). There are some thirty towers, mostly concentrated in the city's main business district: the Northern Quarter (also called Little Manhattan), near Brussels-North railway station. The South Tower, standing adjacent to Brussels-South railway station, is the tallest building in Belgium, at 148 m. Along the North-South connection, is the State Administrative City (French: Cité administrative de l'État, Dutch: Rijksadministratief Centrum), an administrative complex in the International Style. The postmodern buildings of the Espace Léopold complete the picture.
Located outside the centre, in a greener environment, are the Cinquantenaire park with its triumphal arch and nearby museums, and in Laeken, the Royal Castle of Laeken and the Royal Domain with its large greenhouses, as well as the Museums of the Far East.

The Atomium is a symbolic 103-metre (338 ft) tall structure, located on the Heysel Plateau, which was originally built for the 1958 World's Fair (Expo '58). It consists of nine steel spheres connected by tubes, and forms a model of an iron crystal (specifically, a unit cell), magnified 165 billion times. The architect A. Waterkeyn devoted the building to science. It is now considered a landmark of Brussels.[110][111] Next to the Atomium, is the Mini-Europe park, with 1:25 scale maquettes of famous buildings from across Europe.
The city's embrace of modern architecture translated into an ambivalent approach towards historic preservation, leading to the destruction of notable architectural landmarks, most famously the Maison du Peuple by Victor Horta, a process known as Brusselisation.
Arts

Brussels contains over 80 museums.[112] The Royal Museums of Fine Arts has an extensive collection of various painters, such as Flemish old masters like Bruegel, Rogier van der Weyden, Robert Campin, Anthony van Dyck, Jacob Jordaens, and Peter Paul Rubens. The Magritte Museum houses the world's largest collection of the works of the surrealist René Magritte. Museums dedicated to the national history of Belgium include the BELvue Museum, the Royal Museums of Art and History, and the Royal Museum of the Armed Forces and Military History. The Musical Instruments Museum (MIM), housed in the splendid Old England building, is part of the Royal Museums for Art and History and is internationally renowned for its collection of over 8,000 instruments.

The city has had a distinguished artist scene for many years. The famous Belgian surrealists René Magritte and Paul Delvaux, for instance, studied and lived in Brussels, as did the avant-garde dramatist Michel de Ghelderode. The city was also home of the impressionist painter Anna Boch from the Artist Group Les XX, and includes others famous Belgian painters such as Léon Spilliaert and Guy Huygens. The city is also a capital of the comic strip;[2] some treasured Belgian characters are Tintin, Lucky Luke, The Smurfs, Spirou, Gaston, Marsupilami, Blake and Mortimer, Boule et Bill and Cubitus. Throughout the city, walls are painted with large motifs of comic book characters; these murals taken together are known as the Brussels' Comic Book Route. Also, the interiors of some Metro stations are designed by artists. The Belgian Comic Strip Center combines two artistic leitmotifs of Brussels, being a museum devoted to Belgian comic strips, housed in the former Waucquez department store, designed by Victor Horta in the Art Nouveau style.
Brussels is well known for its performing arts scene, with the Kunstenfestivaldesarts, the Kaaitheater and La Monnaie among the most notable institutions. The King Baudouin Stadium is a concert and competition facility with a 50,000 seat capacity, the largest in Belgium. The site was formerly occupied by the Heysel Stadium. Furthermore, the Center for Fine Arts (often referred to as Bozar), a multi-purpose centre for theatre, cinema, music, literature and art exhibitions, is home to the National Orchestra of Belgium and to the annual Queen Elisabeth Competition for classical singers and instrumentalists, one of the most challenging and prestigious competitions of the kind. The Studio 4 in Flagey cultural centre hosts the Brussels Philharmonic. Other concert venues include Forest National/Vorst Nationaal, the Ancienne Belgique, the Cirque Royal, the Botanique and Palais 12.
Folklore

Brussels’ identity owes much to its rich folklore and traditions, among the liveliest in the country:
- The Ommegang, a folkloric costumed procession, commemorating the Joyous Entry of Emperor Charles V in the city in 1549, takes place every year in July. The colourful parade includes floats, traditional giant puppets, such as Saint Michael and Saint Gudula, and scores of folkloric groups, either on foot or on horseback, dressed in medieval garb. The parade ends in a pageant on the Grand Place.
- The planting of the Meyboom is an even older folk tradition of Brussels (1308), celebrating the May tree – in fact, a bad translation of the Dutch tree of joy – which takes place paradoxically on 9 August. After parading a young beech in the city, it is planted in a joyful spirit involving lots of music, Brusseleir songs, and giant puppets. It was recognised as an expression of intangible cultural heritage by UNESCO, as part of the binational inscription 'Processional giants and dragons in Belgium and France'.[113][114] The celebration is reminiscent of the town's long-standing (folkloric) feud with Leuven, which dates back to the Middle Ages.
- Another good introduction to the Brusseleir local dialect and way of life can be obtained at the Théâtre Royal de Toone, a folkloric theatre of marionettes, located a stone throw away from the Grand Place.
Cultural events and festivals
Many events are organised or hosted in Brussels throughout the year. In addition, a large number of festivals animate the Brussels scene.
- The Iris Festival, the festival of the Brussels-Capital Region, is held every year in spring.
- The International Fantastic Film Festival of Brussels (BIFFF), is held during the Easter holidays.
- The Festival of Europe, an open day and activities in and around the institutions of the European Union, is celebrated on 9 May.
- The Zinneke Parade, a colourful, multicultural parade through the city, has been held every two years since 2000 in May.
- The KunstenFESTIVALdesArts, a festival of international contemporary art, is organised in May.
- The Couleur Café Festival, a festival of world and urban music takes place each year around the end of June or early July.
- Brussels Beach (French: Bruxelles les Bains, Dutch: Brussel Bad); in summer, the banks of the canal are turned into an urban beach.
- The Brussels Fair (French: Foire du Midi, Dutch: Zuidfoor), the most important fair in Brussels, takes place every year during the months of July and August and lasts more than a month.
- The Flower Carpet at the Grand Place is held every two years in August.
- The Brussels Summer Festival (BSF), a music festival held in August.
- The Heritage Days are held on the third weekend of September and are a good opportunity to discover the wealth of buildings, institutions and real estate in Brussels.
- The Saint-Verhaegen (often shortened to St V), a folkloric student procession celebrating the anniversary of the founding of the Université libre de Bruxelles and the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, is held on 20 November.
- The Plaisirs d'Hiver animate the heart of Brussels in December. These winter activities were launched in Brussels in 2001.
Cuisine

Brussels is known for its local waffle, its chocolate, its French fries and its numerous types of beers. The Brussels sprout, which has long been popular in Brussels, and may have originated there, is also named after the city.[115]
The gastronomic offer includes approximately 1,800 restaurants, and a number of high quality bars. Belgian cuisine is known among connoisseurs as one of the best in Europe. In addition to the traditional restaurants, there are a large number of cafés, bistros, and the usual range of international fast food chains. The cafés are similar to bars, and offer beer and light dishes; coffee houses are called salons de thé. Also widespread are brasseries, which usually offer a large number of beers and typical national dishes.
Belgian cuisine is characterised by the combination of French cuisine with the more hearty Flemish fare. Notable specialities include Brussels waffles (gaufres) and mussels (usually as moules-frites, served with fries). The city is a stronghold of chocolate and pralines manufacturers with renowned companies like Neuhaus, Leonidas and Godiva. Pralines were first introduced in 1912, by Jean Neuhaus II, a Belgian chocolatier of Swiss origin, in the Galeries Royales Saint-Hubert, in central Brussels.[116] Numerous friteries are spread throughout the city, and in tourist areas, fresh hot waffles are also sold on the street.
In addition to the regular selection of Belgian beer, the famous lambic style of beer is predominately brewed in and around Brussels, and the yeasts have their origin in the Senne valley. Kriek, a cherry lambic, enjoys outstanding popularity, as it does in the rest of Belgium. Kriek is available in almost every bar or restaurant.
Brussels is known as the birthplace of the Belgian Endive (Dutch: witloof or witlof ("white leaf"), French: chicon). The technique for growing blanched endives was accidentally discovered in the 1850s at the Botanical Garden of Brussels in Saint-Josse-ten-Noode, Brussels.[117]
Shopping

Famous shopping areas include the pedestrian-only Rue Neuve (Dutch: Nieuwstraat), the second busiest shopping street in Belgium (after the Meir, in Antwerp) with a weekly average of 230,000 visitors[118][119]; Chaussée d’Ixelles in the Matongé district; Avenue Louise lined with high-end fashion stores and boutiques; the Galeries Royales Saint-Hubert; as well as the neighbourhood around Antoine Dansaert Street, which has become, in recent years, a focal point for fashion and design.[120] This main street and its side streets also feature Belgium’s young and most happening artistic talent.[121]
In addition, Brussels ranks as one of Europe’s best capital cities for flea market shopping. The Old Market (French: Vieux Marché, Dutch: Vlooienmarkt), on the Place du Jeu de Balle/Vossenplein, in the Marollen neighbourhood, is particularly renowned.[122] The nearby Sablon area is home to many of Brussels' antique dealers.[123] The Midi Market around Brussels-South station and Boulevard du Midi is reputed to be one of the largest markets in Europe.[124]
Sports
Sport in Brussels is under the responsibility of the Communities. The Administration de l'Éducation Physique et du Sport (ADEPS) is responsible for recognising the various French-speaking sports federations and also runs three sports centres in the Brussels-Capital Region.[125] Its Dutch-speaking counterpart is Sport Vlaanderen (formerly called BLOSO).[126]
The King Baudouin Stadium (formerly Heysel Stadium) is the largest in the country and home to the national teams in football and rugby union.[127] It hosted the final of the 1972 UEFA European Football Championship, and the opening game of the 2000 edition. Several European club finals have been held at the ground, including the 1985 European Cup Final which saw 39 deaths due to hooliganism and structural collapse.[128] The King Baudouin Stadium is also home of the annual Memorial Van Damme athletics event, Belgium's foremost track and field competition, which is part of the IAAF Diamond League. Other important athletics events are the Brussels Marathon and the 20 km of Brussels.
Cycling
In cycling, the city is the arrival location of the Brussels Cycling Classic, formerly known as Paris–Brussels, which is one of the oldest semi classic bicycle races on the international calendar. From Word War I until the early 1970s, the Six Days of Brussels was organised regularly. In the last decades of the 20th century, the Grand Prix Eddy Merckx was also held in Brussels.
Association football

R.S.C. Anderlecht, based in the Constant Vanden Stock Stadium in the Anderlecht municipality, is the most successful Belgian football club in the Belgian Pro League, with 34 titles.[129] It has also won the most major European tournaments for a Belgian side, with 6 European titles.
Brussels is also home to Union Saint-Gilloise, the most successful Belgian club before World War II, with 11 titles[130] The club was founded in Saint-Gilles but is based in the nearby Forest municipality and currently plays in Second Division. White Star Bruxelles is another football club that plays in second division. Racing White Daring Molenbeek, based in the Sint-Jans-Molenbeek municipality and often referred to as RWDM, was a very popular football club until it was dissolved in 2002. Since 2015, its reincarnation RWDM47 is back playing in the fourth division.
Economy


Serving as the centre of administration for Belgium and Europe, Brussels' economy is largely service-oriented. It is dominated by regional and world headquarters of multinationals, by European institutions, by various local and federal administrations, and by related services companies, though it does have a number of notable craft industries, such as the Cantillon Brewery, a lambic brewery, founded in 1900.[131]
Brussels has a robust economy. The region contributes to one fifth of Belgium's GDP, and its 550,000 jobs account for 17.7% of Belgium’s employment.[132] Its GDP per capita is nearly double that of Belgium as a whole,[133] and it has the highest GDP per capita of any NUTS 1 region in the European Union, at €62,000 in 2011.[134] That being said, the GDP is boosted by a massive inflow of commuters from neighbouring regions; over half of those who work in Brussels live in Flanders or Wallonia, with 230,000 and 130,000 commuters per day respectively. Conversely, only 16.0% of people from Brussels work outside Brussels (68,827 (68.5%) of them in Flanders and 21,035 (31.5%) in Wallonia).[135] Not all of the wealth generated in Brussels remains in Brussels itself, and as of December 2013, the unemployment among residents of Brussels is 20.4%.[136]
There are approximately 50,000 businesses in Brussels, of which around 2,200 are foreign. This number is constantly increasing and can well explain the role of Brussels in the European subcontinent. The city’s infrastructure is very favourable in terms of starting up a new business. House prices have also increased in recent years, especially with the increase of young professionals settling down in Brussels, making it the most expensive city to live in Belgium.[137] In addition, Brussels holds more than 1,000 business conferences annually, making it the ninth most popular conference city in Europe.[138]
Brussels is rated as the seventh most important financial centre in the world. The Brussels Stock Exchange, abbreviated to BSE, now called Euronext Brussels, is part of the European stock exchange Euronext N.V., along with Paris Bourse, Lisbon Stock Exchange and Amsterdam Stock Exchange. Its benchmark stock market index is the BEL20.
Media
Many Belgian newspapers have their headquarters in Brussels, such as Le Soir, La Libre, De Morgen and the news agency Belga. The Belgian French-language public broadcaster RTBF, the Belgian Dutch-speaking public broadcaster VRT, the two regional channels BX1 (formerly Télé Bruxelles) and Bruzz (formerly TV Brussel), the encrypted BeTV channel and private channels RTL-TVI and VTM are also headquartered in the city.
Education

Tertiary education
There are several universities in Brussels. The two main universities are the Université Libre de Bruxelles, a French-speaking university, with about 20,000 students, in three campuses in the city (and two others outside),[139] and the Vrije Universiteit Brussel, a Dutch-speaking university, with about 10,000 students.[140] Both universities originate from a single ancestor university, founded in 1834, namely the Free University of Brussels, which was split in 1970, at about the same time the Flemish and French Communities gained legislative power over the organisation of higher education.[141]
Other universities include the Université Saint-Louis Bruxelles, with 4,000 students;[142] a campus of the Katholieke Universiteit Leuven,[143] (offering bachelor & master's degrees in economics & business, law, arts, and architecture, and counting a faculty in the city centre); the Royal Military Academy, a military college established in 1834 by a French colonel[144]; and two drama schools, founded in 1982: the French-speaking Conservatoire Royal and the Dutch-speaking Koninklijk Conservatorium.[145][146]
Still other universities have campuses in Brussels, such as the Université Catholique de Louvain, which has had its medical faculty in the city since 1973.[147] In addition, the University of Kent's Brussels School of International Studies is a specialised postgraduate school offering advanced international studies.
Primary and secondary education
Most of Brussels pupils between the ages of 3 and 18 go to schools organised by the Flemish Community or the French-speaking Community, with roughly 20% going to Dutch-speaking schools, and close to 80% to French-speaking schools. Due to the post-war international presence in the city, there are also a number of international schools, including the International School of Brussels, with 1,450 pupils, between the ages of 2½ and 18;[148] the British School of Brussels; and the four European Schools, which provide free education for the children of those working in the EU institutions. The combined student population of the four European Schools in Brussels is currently around 10,000.[149]
Libraries
Brussels has a number of public or private-owned libraries on its territory:[150]
- Royal Library of Belgium
- Library of the National Archives of Belgium
- Royal Belgian Film Archive (Cinematek)
- The PointCulture
- CERIA Francophone Central Library
- Scientific Library of the Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences
- Library and Photo Archive of the Royal Institute for Cultural Heritage
- Infotheque-Library of the Federal Public Service Finance
- Library of the National Botanical Garden of Belgium
- Central Library of the Federal Public Service Justice
- Library of the Royal Conservatory of Brussels
- Library of the Museum of Musical Instruments
- Libraries of the Royal Museum for Central Africa
- Libraries of the Royal Museums of Art and History
- Library and documentation center of the Royal Museums of Fine Arts of Belgium
- Library of the Royal Observatory of Belgium
- Archives and libraries of the Université Libre de Bruxelles
- Library of the Saint-Louis University, Brussels
- Erasmus Library
- Duden Library
Science and technology
Science and technology in Brussels is well developed with the presence of several universities and research institutes.
The Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences houses the world's largest hall completely dedicated to dinosaurs, with its collection of 30 fossilised Iguanodon skeletons.[151] The Planetarium of the Royal Observatory of Belgium is one of the largest in Europe.[152]
Healthcare

Brussels is home to a thriving pharmaceutical and health care industry which includes pioneering biotechnology research. The health sector employs 70,000 employees in 30,000 companies. There are 3,000 life sciences researchers in the city and two large science parks: Da Vinci Research Park and Erasmus Research Park. There are five university hospitals, a military hospital and more than 40 general hospitals and specialist clinics. Some examples include:[153]
- CHU Brugmann
- CHU Saint-Pierre
- Clinique Saint Jean
- Cliniques Universitaires Saint-Luc (university hospital of the Université catholique de Louvain)
- Erasmus Hospital (university hospital of the Université libre de Bruxelles)
- Saint Elisabeth Hospital and Saint Michel Hospital.
- Jules Bordet Institute
- IRIS Hospital Network
- Queen Fabiola Children's University Hospital
- UZ Brussel (university hospital of the Vrije Universiteit Brussel)
- Clinique Edith Cavell
Transport
Air

The Brussels Region does not have airports on its territory and its institutions do not manage any. The peculiarity of the Region is that it is served by two airports located outside its administrative territory. These are also the two main airports of Belgium:[154]
- Brussels-National Airport, located in the nearby Flemish municipality of Zaventem, 12 km east of the capital;
- Brussels South Charleroi Airport, located near Charleroi (Wallonia), some 50 km (30 mi) south-west of Brussels.
This particularity can be explained by the fact that the territory of the Region is in fact nearly entirely urbanised, and like most major cities of the world, it does not have an airport on its own territory.
Water

Since the 16th century, Brussels has had its own harbour, the port of Brussels. It has been enlarged throughout the centuries to become the second Belgian inland port. Historically situated near the Sainte-Catherine/Sint-Katelijne square, it lies today in the northwest of the city, on the Brussels-Scheldt Maritime Canal (commonly called Willebroek Canal), which connects Brussels to Antwerp via the Scheldt. Ships and large barges up to 4,500 tons can penetrate deep into the country, avoiding break-ups and load transfers between Antwerp and the centre of Brussels, hence reducing the cost for companies using the canal, which offers a competitive advantage.
Moreover, the connection of the Willebroek Canal with the Brussels-Charleroi Canal, in the very heart of the capital, creates a north-south link, by means of waterways, between the Netherlands, Flanders and the industrial zone of Hainaut (Wallonia). There, navigation can access the network of French canals, thanks to the important inclined plane of Ronquières and the lifts of Strépy-Bracquegnies.
The importance of river traffic in Brussels makes it possible to avoid the road equivalent of 740,000 trucks per year – almost 2,000 per day – which, in addition to easing traffic problems, represents an estimated carbon dioxide saving of 51,545 tonnes per year.[155]
Train
The Brussels Capital-Region has three main train stations: Brussels-South, Central and North, which are amongst the busiest of the country. Brussels-South is also served by direct high-speed rail links: to London by the Eurostar train via the Channel Tunnel (1hr 51 min); to Amsterdam by the Thalys and InterCity-Plus connections; to Amsterdam, Paris (1hr 50min, 1hr 25 min respectively) as of 6 April 2015, and Cologne by the Thalys; and to Cologne and Frankfurt by the German ICE (2hr 59 min–3hr 16min).
The train rails in Brussels go underground, near the centre, through the North–South connection, with the Brussels-Central station also being largely underground. The tunnel itself is only six tracks wide at its narrowest point, which often causes congestion and delays due to heavy use of the route.
The City has minor railway stations at Bockstael, Brussels-Chapel, Brussels-Congres, Brussels-Luxembourg, Brussels-Schuman, Brussels-West, Haren, Haren-South, Simonis.
In the Brussels Region, there are also railways stations at Berchem-Sainte-Agathe, Boitsfort, Boondael, Bordet (Evere), Etterbeek, Evere, Forest-East, Forest-South, Jette, Meiser (Schaarbeek), Moensberg (Uccle), Saint-Job (Uccle), Schaarbeek, Uccle-Calevoet, Uccle-Stalle, Vivier d'Oie-Diesdelle (Uccle), Merode and Watermael.
City public transport
The Brussels Intercommunal Transport Company STIB/MIVB is the local public transport operator in Brussels. It covers the 19 municipalities of the Brussels Capital-Region and some surface routes extend to the near suburbs in the other regions.
Metro

The Brussels Metro dates back to 1976,[156] but underground lines known as premetro have been serviced by tramways since 1968. The network consists of four conventional metro lines and three premetro lines. The metro-grade lines are M1, M2, M5, and M6, with some shared sections, covering a total of 40 kilometres (24.8 mi).[157] The metro is an important means of transport, connecting with six railway stations of the National Railway Company of Belgium, and many tram and bus stops operated by STIB/MIVB, and with Flemish De Lijn and Walloon TEC bus stops.
Trams and buses
A comprehensive bus and tram network covers the city. As of 2017, the Brussels tram system consists of 17 tram lines (three of which – lines T3, T4 and T7 – qualify as premetro lines). The total route length is 139 km (86.3 mi),[157] making it one of the largest tram networks in Europe. The Brussels bus network is complementary to the rail network. It consists of 50 bus routes and 11 night routes, spanning 445 km (276 mi).[157] Since April 2007, STIB/MIVB has been operating a night bus network called Noctis. On Fridays and Saturdays, 11 bus routes operate from midnight until 3 a.m. They run from the centre of Brussels to the outer reaches of the Brussels-Capital Region.[158]
Ticketing
An interticketing system means that a STIB/MIVB ticket holder can use the train or long-distance buses inside the city. A single journey can include multiple stages across the different modes of transport. The commuter services operated by De Lijn, TEC and NMBS/SNCB will, in the next few years,[when?] be augmented by the Brussels RER/GEN network, which will connect the capital and surrounding towns. Since August 2016, paper tickets have been discontinued in favour of electronic MoBIB cards.
Other public transport

Since 2003, Brussels has had a car-sharing service operated by the Bremen company Cambio, in partnership with the STIB/MIVB and local ridesharing company Taxi Stop. In 2006, a public bicycle-sharing programme was introduced. The scheme was subsequently taken over by Villo!. Since 2008, this night-time public transport service has been supplemented by Collecto, a shared taxi system, which operates on weekdays between 11 p.m. and 6 a.m. In 2012, the Zen Car electric car-sharing scheme was launched in the university and European areas.
Road network

In medieval times, Brussels stood at the intersection of routes running north-south (the modern Rue Haute/Hoogstraat) and east-west (Chaussée de Gand/Gentsesteenweg-Rue du Marché aux Herbes/Grasmarkt-Rue de Namur/Naamsestraat). The ancient pattern of streets, radiating from the Grand Place, in large part remains, but has been overlaid by boulevards built over the River Senne, over the city walls and over the railway connection between the North and South Stations.
Today, Brussels has the most congested traffic in North America and Europe, according to US traffic information platform INRIX.[159]
As one expects of a capital city, Brussels is the hub of a range of old national roads, the main ones being clockwise: the N1 (N to Breda), N2 (E to Maastricht), N3 (E to Aachen), N4 (SE to Luxembourg) N5 (S to Rheims), N6 (S to Maubeuge), N7 (SW to Lille), N8 (W to Koksijde) and N9 (NW to Ostend).[160] Usually named chaussées/steenwegen, these highways normally run in a straight line, but sometimes lose themselves in a maze of narrow shopping streets.
The town is skirted by the European route E19 (N-S) and the E40 (E-W), while the E411 leads away to the SE. Brussels has an orbital motorway, numbered R0 (R-zero) and commonly referred to as the Ring. It is pear-shaped, as the southern side was never built as originally conceived, owing to residents' objections.
The city centre, sometimes known as the pentagon, is surrounded by an inner ring road, the Small Ring (French: Petite Ceinture, Dutch: Kleine Ring), a sequence of boulevards formally numbered R20 or N0. These were built upon the site of the second set of city walls following their demolition. The metro line 2 runs under much of these. Since June 2015, a number of central boulevards inside the pentagon have become car-free, limiting transit traffic through the old city.[161]
On the eastern side of the city, the R21 or Greater Ring (French: Grande Ceinture, Dutch: Grote Ring) is formed by a string of boulevards that curves round from Laeken to Uccle. Some premetro stations (see Brussels Metro) were built on that route. A little further out, a stretch numbered R22 leads from Zaventem to Saint-Job.
Security and emergency services
Police

The Brussels police is responsible for the security in Brussels. The 19 municipalities of Brussels are divided into six police zones,[162] all bilingual (French-Dutch):
- 5339 Brussels Capital Ixelles: the City of Brussels and Ixelles
- 5340 Brussels West : Ganshoren, Jette, Koekelberg, Sint-Agatha-Berchem and Sint-Jans-Molenbeek
- 5341 South : Anderlecht, Forest and Saint-Gilles
- 5342 Uccle/Watermael-Boitsfort/Auderghem : Auderghem, Uccle and Watermael-Boitsfort
- 5343 Montgomery : Etterbeek, Woluwe-Saint-Lambert et Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
- 5344 Polbruno : Evere, Saint-Josse-ten-Noode et Schaerbeek
Fire department
The Brussels Fire and Emergency Medical Care Service, commonly known by its acronym SIAMU (DBDMH), operates in the 19 municipalities of Brussels.[163] It is a class X fire department and the largest fire service in Belgium in terms of annual operations, equipment, and personnel. It has 9 fire stations, spread over the entire Brussels-Capital Region, and employs about 1,000 professional firefighters. As well as preventing and fighting fires, SIAMU also provides emergency medical care services in Brussels via its centralised 100 number (and the single 112 emergency number for the 27 countries of the European Union). It is bilingual (French-Dutch).
Parks and green spaces
Brussels is one of the greenest capitals in Europe, with over 8,000 hectares of green spaces.[164] Vegetation cover and natural areas are higher in the outskirts, where they have limited the peri-urbanisation of the capital, but they decrease sharply towards the centre of Brussels; 10% in the central pentagon, 30% of the municipalities in the first ring, and 71% of the municipalities in the second ring are occupied by green spaces.
A multitude of parks and gardens, both public and privately owned, are scattered throughout the city. Examples include, in the City of Brussels:
- Brussels Park 11 ha (27 acres)
- Mont des Arts/Kunstberg 1.4 ha (3.5 acres)
- Egmont Park 1.5 ha (3.7 acres)
- Leopold Park 10 ha (25 acres)
- Osseghem Park 17 ha (42 acres)
- Laeken Park 30 ha (74 acres)
- Parc du Cinquantenaire/Jubelpark 30 ha (74 acres)
- Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos 122 ha (301 acres)
-
Brussels Park
-
Mont des Arts/Kunstberg
-
Parc du Cinquantenaire/ Jubelpark
-
Bois de la Cambre/Ter Kamerenbos
In the Brussels Capital-Region:
- Tenbosch 2 ha (2.5 acres) in Ixelles
- Ixelles Ponds 5 ha (12.3 acres) in Ixelles
- Forest Park 13 ha (32 acres) in Forest
- Rouge-Cloître Abbey 13 ha (32 acres) in Auderghem
- Elisabeth Park 21 ha (51 acres) in Koekelberg/Ganshoren
- Duden Park 24 ha (59 acres) in Forest
- Josaphat Park 30 ha (74 acres) in Schaerbeek
- Woluwe Park 69 ha (170 acres) in Woluwe-Saint-Pierre
- The Sonian Forest 4.421 ha (10.920 acres), stretching out over the three Belgian regions.
-
Ixelles Ponds
-
Royal Greenhouses of Laeken
-
Sonian Forest
Notable people
International relations
This section needs additional citations for verification. (June 2015) |
Twin towns and sister cities
Brussels is twinned with the following cities:
See also
References
- ^ "Brussels". City-Data.com. Retrieved 10 January 2008.
- ^ a b Herbez, Ariel (30 May 2009). "Bruxelles, capitale de la BD". Le Temps (in French). Switzerland. Retrieved 28 May 2010.
Plus que jamais, Bruxelles mérite son statut de capitale de la bande dessinée.
[dead link] - ^ "Cheap flights to Brussels". Easyjet. Retrieved 1 June 2010.
- ^ Population per municipality as of 1 January 2017 (XLS; 397 KB)
- ^ http://ec.europa.eu/eurostat/documents/2995521/7962764/1-30032017-AP-EN.pdf/4e9c09e5-c743-41a5-afc8-eb4aa89913f6
- ^ a b The Belgian Constitution (PDF). Brussels, Belgium: Belgian House of Representatives. May 2014. p. 5. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
Article 3: Belgium comprises three Regions: the Flemish Region, the Walloon Region and the Brussels Region. Article 4: Belgium comprises four linguistic regions: the Dutch-speaking region, the French-speaking region, the bilingual region of Brussels-Capital and the German-speaking region.
- ^ a b "Brussels-Capital Region: Creation". Centre d'Informatique pour la Région Bruxelloise (Brussels Regional Informatics Center). 2009. Archived from the original on 29 April 2009. Retrieved 5 June 2009.
Since 18 June 1989, the date of the first regional elections, the Brussels-Capital Region has been an autonomous region comparable to the Flemish and Walloon Regions.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) - ^ Dutch pronunciation: [ˈbrɵsəls ɦoːftˈsteːdələk xəˈʋɛst] . Gewest in isolation is pronounced [ɣəˈʋɛst].
- ^ a b The Belgian Constitution (PDF). Brussels, Belgium: Belgian House of Representatives. May 2014. p. 63. Retrieved 10 September 2015.
Article 194: The city of Brussels is the capital of Belgium and the seat of the Federal Government.
- ^ a b Décret instituant Bruxelles capitale de la Communauté française. Brussels, Belgium: Parliament of the French Community. 4 April 1984. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ a b Decreet betreffende de keuze van Brussel tot hoofdstad van de Vlaamse Gemeenschap (PDF). Brussels, Belgium: Flemish Parliament. 6 March 1984. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ "DE BELGISCHE GRONDWET". www.senate.be. Retrieved 24 October 2017.
- ^ "Statistics Belgium; Population de droit par commune au 1 janvier 2008 (excel-file)". Archived from the original on 17 September 2008. Retrieved 2008-09-17.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) Population of all municipalities in Belgium on 1 January 2008. Retrieved on 18 October 2008. - ^ "Statistics Belgium; De Belgische Stadsgewesten 2001 (pdf-file)" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 29 October 2008. Retrieved 2008-10-19.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) Definitions of metropolitan areas in Belgium. The metropolitan area of Brussels is divided into three levels. First, the central agglomeration (geoperationaliseerde agglomeratie) with 1,451,047 inhabitants (2008-01-01, adjusted to municipal borders). Adding the closest surroundings (suburbs, banlieue or buitenwijken) gives a total of 1,831,496. And, including the outer commuter zone (forensenwoonzone) the population is 2,676,701. Retrieved on 18 October 2008. - ^ http://www.demographia.com/db-worldua.pdf
- ^ "Europe | Country profiles | Country profile: Belgium". BBC News. 14 June 2010. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ a b c Demey, Thierry (2007). Brussels, capital of Europe. S. Strange (trans.). Brussels: Badeaux. ISBN 2-9600414-2-9.
- ^ "Protocol (No 6) on the location of the seats of the institutions and of certain bodies, offices, agencies and departments of the European Union, Consolidated version of the Treaty on the Functioning of the European Union, OJ C 83, 30.3.2010, p. 265–265". EUR-Lex. 30 March 2010. Retrieved 3 August 2010.
- ^ It should be noted that Brussels is not formally declared capital of the EU, though its position is spelled out in the Treaty of Amsterdam. See the section dedicated to this issue.
- ^ Editorial, Reuters. "Spain to ask Brussels for extra year to meet deficit target". Reuters UK. Retrieved 23 June 2017.
{{cite news}}:|first=has generic name (help) - ^ Rankin, Jennifer (13 June 2017). "Brussels plan could force euro clearing out of UK after Brexit". The Guardian. ISSN 0261-3077. Retrieved 23 June 2017.
- ^ http://www.benelux.int/fr/benelux-unie/introduction
- ^ http://www.nato.int/cps/en/natohq/topics_49284.htm
- ^ http://www.lboro.ac.uk/gawc/world2016t.html
- ^ Hughes, Dominic (15 July 2008). "Europe | Analysis: Where now for Belgium?". BBC News. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ http://www.marnixplan.org/MULTILINGUAL-BRUSSELS
- ^ Geert van Istendael Arm Brussel, uitgeverij Atlas, ISBN 90-450-0853-X
- ^ Jean Baptiste D'Hane; François Huet; P.A. Lenz; H.G. Moke (1837). Nouvelles archives historiques, philosophiques, et littéraires (in French). Vol. 1. Gent: C. Annoot- Braeckman. p. 405. Retrieved 11 September 2010.
- ^ "Bruxelles: des vestiges romains retrouvés sur le site de Tour et Taxis". RTBF Info (in French). 6 August 2015. Retrieved 28 April 2017.
- ^ "Les Romains de Tour & Taxis — Patrimoine – Erfgoed". patrimoine.brussels (in French). Retrieved 28 April 2017.
- ^ "Brussels History". City-data.com. Retrieved 5 July 2009.
- ^ Template:Nl icon Zo ontstond Brussel Archived 20 November 2007 at the Wayback Machine Vlaamse Gemeenschapscommissie – Commission of the Flemish Community in Brussels
- ^ "LOI – WET". www.ejustice.just.fgov.be. Retrieved 22 April 2017.
- ^ "Association of European Cities of Culture of the Year 2000 – KRAKOW THE OPEN CITY". www.krakow.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ a b "Brussels G7 summit, Brussels, 04-05/06/2014 – Consilium". www.consilium.europa.eu. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- ^ "Brussels in figures 1". visit.brussels. Retrieved 3 September 2017.
- ^ "Site de l'institut météorologique belge". Meteo.be. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ "Monthly normals for Uccle, Brussels". KMI/IRM. Retrieved 11 June 2012.
- ^ "Brussels, the capital of Flanders". Flemish Department of Foreign Affairs. Archived from the original on 10 June 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Communes". Centre d'Informatique pour la Région Bruxelloise. 2004. Archived from the original on 6 June 2004. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b "Managing across levels of government" (PDF). OECD. 1997. pp. 107, 110. Archived from the original (PDF) on 19 August 2008. Retrieved 5 August 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Picavet, Georges (29 April 2003). "Municipalities (1795-now)". Georges Picavet. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- ^ "Brussels Capital-Region". Georges Picavet. 4 June 2005. Retrieved 4 August 2008.
- ^ "Fusie van de 19 Brusselse gemeenten". Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ "De Brusselse Baronieën". Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ "Bruxelles vaut bien une messe?" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 12 August 2014. Retrieved 7 August 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Brussels attacks: Molenbeek's gangster jihadists". BBC. 24 March 2016. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ^ "The Belgian neighborhood indelibly linked to jihad". Washington Post. 15 November 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ^ "Beleaguered Molenbeek struggles to fend off jihadist recruiters". The Times of Israel. 3 April 2016. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ^ "Molenbeek: Inside Belgium's seething city of jihad where ISIS are heroes". Express. 25 November 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ^ "World points to "jihad Capital" Molenbeek". Het Niuewsblad. 16 November 2015. Retrieved 13 April 2016.
- ^ "Wet houdende organisatie van de agglomeraties en de federaties van gemeenten". Belgiëlex.be. FOD Justitie. Retrieved 11 September 2015.
- ^ Procedure contained in art. 138 of the Belgian Constitution
- ^ Procedure in art. 137 of the Belgian Constitution
- ^ Brussels, an international city and European capital Archived 3 August 2010 at the Wayback Machine Université Libre de Bruxelles
- ^ a b Brussels: home to international organisations diplomatie.be
- ^ a b E!Sharp magazine, January–February 2007 issue: Article "A tale of two cities".
- ^ Andrew Rettman. "Euobserver.com". Euobserver.com. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ Leigh Phillips. "Euobserver.com". Euobserver.com. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ a b European Navigator Seat of the European Commission
- ^ a b European Commission publication: Europe in Brussels 2007
- ^ Wheatley, Paul (2 October 2006). "The two-seat parliament farce must end". Café Babel. Archived from the original on 10 June 2007. Retrieved 16 July 2007.
- ^ Stark, Christine. "Evolution of the European Council: The implications of a permanent seat" (PDF). Dragoman.org. Archived from the original (PDF) on 9 July 2007. Retrieved 12 July 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Vucheva, Elitsa (5 September 2007). "EU quarter in Brussels set to grow". EU Observer. Retrieved 27 September 2007.
- ^ "Brussels.info – Brussels Pact". www.brussels.info. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ NATO. "Summit meetings". NATO. Retrieved 2 March 2017.
- ^ "NATO Summit 2017". www.state.gov. Retrieved 27 July 2017.
- ^ Isby & Kamps Jr. 1985, p. 13.
- ^ NATO. "New NATO Headquarters". NATO. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ^ "Très riches et très pauvres". Lalibre.be. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ a b c d e f g Institut National de Statistique
- ^ "Studies and statistics". Brussels Institute for Statistics and Analysis. Retrieved 11 November 2016.
- ^ "Non-Profit Data". Npdata.be. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ "Vreemde afkomst 01/01/2012". Npdata.be. Retrieved 12 March 2013.
- ^ Janssens, Rudi (2013). BRIO-taalbarometer 3: diversiteit als norm (PDF) (in Dutch) (Brussels Informatie-, Documentatie- en Onderzoekscentrum ed.). Retrieved 26 May 2015.
- ^ "Wallonie – Bruxelles, Le Service de la langue française" (in French). 19 May 1997. Archived from the original on 5 January 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Villes, identités et médias francophones: regards croisés Belgique, Suisse, Canada" (in French). University of Laval, Quebec. Archived from the original on 19 June 2009. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ G. Geerts. "Nederlands in België, Het Nederlands bedreigd en overlevend". Geschiedenis van de Nederlandse taal (in Dutch). M.C. van den Toorn, W. Pijnenburg, J.A. van Leuvensteijn and J.M. van der Horst. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ Template:Nl icon "Thuis in gescheiden werelden" – "De migratoire en sociale aspecten van verfransing te Brussel in het midden van de 19e eeuw", BTNG-RBHC, XXI, 1990, 3–4, pp. 383–412, Machteld de Metsenaere, Eerst aanwezend assistent en docent Vrije Universiteit Brussel
- ^ J. Fleerackers (1973). "De historische kracht van de Vlaamse beweging in België: de doelstellingen van gister, de verwezenlijkingen vandaag en de culturele aspiraties voor morgen". Digitale bibliotheek voor Nederlandse Letteren (in Dutch). Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Kort historisch overzicht van het OVV" (in Dutch). Overlegcentrum van Vlaamse Verenigingen. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Bisbilles dans le Grand Bruxelles" (in French). Le Monde. 2 October 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Sint-Stevens-Woluwe: een unicum in de Belgische geschiedenis" (in Dutch). Overlegcentrum van Vlaamse Verenigingen. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Brussels". Encyclopædia Britannica. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Bruxelles dans l'oeil du cyclone" (in French). France 2. 14 November 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "La Flandre ne prendra pas Bruxelles..." (in French). La Libre Belgique. 28 May 2006.
- ^ The six municipalities with language facilities around Brussels are Wemmel, Kraainem, Wezembeek-Oppem, Sint-Genesius-Rode, Linkebeek and Drogenbos.
- ^ "Une question: partir ou rester?" (in French). La Libre Belgique. 24 January 2005.
- ^ "Position commune des partis démocratiques francophones" (in French). Union des Francophones (UF), Province of Flemish Brabant. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "Bruxelles-capitale: une forte identité" (in French). France 2. 14 November 2007. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
- ^ "IS 2007 – Population (Tableaux)". Bruxelles.irisnet.be. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ^ "Van autochtoon naar allochtoon". De Standaard (newspaper) online (in Dutch). Retrieved 5 May 2007.
Meer dan de helft van de Brusselse bevolking is van vreemde afkomst. In 1961 was dat slechts 7 procent. (More than half of the Brussels' population is of foreign origin. In 1961 this was only 7 percent.)
- ^ Van Parijs, Philippe. "Belgium's new linguistic challenges" (PDF). KVS Express (supplement to newspaper De Morgen) March–April 2007: Article from original source (pdf 4.9 MB) pages 34–36 republished by the Belgian Federal Government Service (ministry) of Economy – Directorate–general Statistics Belgium. Archived from the original (pdf 0.7 MB) on 13 June 2007. Retrieved 5 May 2007.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|nopp=ignored (|no-pp=suggested) (help) – The linguistic situation in Belgium (and in particular various estimations of the population speaking French and Dutch in Brussels) is discussed in detail."Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 25 March 2009. Retrieved 2008-07-11.{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ The Brussels region's 56% residents of foreign origin include several percents of either Dutch people or native speakers of French, thus roughly half of the inhabitants do not speak either French or Dutch as primary language.
- ^ "Population et ménages" (pdf 1.4 MB) (in French). IBSA Cellule statistique – Min. Région Bruxelles-Capitale (Statistical cell – Ministry of the Brussels-Capital Region). Retrieved 5 May 2007.[dead link]
- ^ "English should be Brussels' official language, Flemish minister says". EurActiv. Retrieved 9 August 2014.
- ^ "Language usage in Brussels (nl)". Retrieved 26 August 2015.
- ^ a b lesoir.be (28 January 2016). "75% des francophones revendiquent une identité religieuse". lesoir.be. Retrieved 5 June 2017.
- ^ "Lessons in religion no longer obligatory in Belgium | Flanders Today". www.flanderstoday.eu. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ a b "In België wonen 628.751 moslims(*), 6,0% van de bevolking. In Brussel is dit 25,5%, in Wallonië 4,0%, in Vlaanderen 3,9%," BuG 100 – Bericht uit het Gewisse – 11 September 2008, http://www.npdata.be, (*)Berekend aantal – indicatief cijfer, zie methodologie hieronder
- ^ "Brussels.info - Brussels Architecture". www.brussels.info. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "La Grand-Place, Brussels". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 6 February 2017.
- ^ "Manneken Pis — Région bruxelloise – Brussels Gewest". be.brussels. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Le Palais de Justice de Bruxelles – UNESCO World Heritage Centre". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ^ "10 must-visit world-class Art Nouveau buildings in Brussels!". visit.brussels. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ Stambolic, Ana. "The Most Remarkable Art Nouveau Houses In Brussels". Culture Trip. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Major Town Houses of the Architect Victor Horta (Brussels)". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 14 February 2017.
- ^ Centre, UNESCO World Heritage. "Stoclet House". whc.unesco.org. Retrieved 8 January 2017.
- ^ "Top 10 of Art Deco buildings in Brussels". Brussleslife. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Atomium – the iron landmark of Brussels". www.beneluxguide.com. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
- ^ Germany, SPIEGEL ONLINE, Hamburg. "The Atomium: How Do You Clean a Massive Molecule? – SPIEGEL ONLINE – International". SPIEGEL ONLINE. Retrieved 3 February 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Museums in Brussels". Bruxelles.irisnet.be. Archived from the original on 6 June 2010. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Meyboom — Région bruxelloise – Brussels Gewest". be.brussels. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ "Processional giants and dragons in Belgium and France - intangible heritage - Culture Sector - UNESCO". ich.unesco.org. Retrieved 27 October 2017.
- ^ Oliver, Lynne (11 April 2011). "Food Timeline: Brussels sprouts". Retrieved 9 April 2012.
- ^ Thomas, Amy M. (22 December 2011). "Brussels: The Chocolate Trail". The New York Times. ISSN 0362-4331. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
- ^ "Food Museum, Belgium Endive". 29 July 2005. Archived from the original on 29 July 2005. Retrieved 4 February 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Rue Neuve most popular shopping street". www.xpats.com. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ bvb. "Meir klopt voor het eerst Nieuwstraat als drukste winkelstraat". De Standaard (in Flemish). Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Brussels Shopping Streets | Brussels.info". www.brussels.info. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ Foster, Nick (24 January 2014). "Why stylish Dansaert district stands out in downtown Brussels". Financial Times. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Flea Markets in Brussels – Flea Market InsidersFlea Market Insiders". www.fleamarketinsiders.com. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ "Sablon – City of Brussels". www.brussels.be. Retrieved 24 February 2017.
- ^ "Midi Market". Brusselslife. Retrieved 8 July 2017.
- ^ "Accueil - Portail du sport en Fédération Wallonie-Bruxelles". www.sport-adeps.be (in French). Retrieved 11 November 2017.
{{cite web}}: no-break space character in|title=at position 8 (help) - ^ Vlaanderen, Sport. "Doe aan sport". www.sport.vlaanderen (in Dutch). Retrieved 11 November 2017.
- ^ "Stade Roi Baudouin - Brussels - The Stadium Guide". www.stadiumguide.com. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ Alessandro Del Piero 'turned down Liverpool move due to Heysel' | Metro News. Metro.co.uk (6 September 2012). Retrieved on 12 August 2013.
- ^ Anderlecht clinch 34th league title. Rsssf.com. Retrieved on 12 August 2013.
- ^ Belgium – List of Champions. Rsssf.com. Retrieved on 19 February 2014.
- ^ "Cantillon – Museum". www.cantillon.be. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ "Brussels Economy and Business | Brussels.info". www.brussels.info. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ "Gross domestic product per resident, at current prices – Ratio in relation to the total of the Kingdom". National Bank of Belgium. Archived from the original on 8 August 2014. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Eurostat (27 February 2014). "GDP per capita in the EU in 2011: seven capital regions among the ten most prosperous" (PDF). Europa web portal. Archived from the original (PDF) on 7 March 2014. Retrieved 20 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "EURES – Labour market information – Région De Bruxelles-Capitale / Brussels Hoofdstedelijk Gewest – European Commission". ec.europa.eu. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ "Youth unemployment in Brussels falls under 30%". Flandersnews.be. 6 January 2014. Archived from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 23 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Cost of Living in Belgium". Expatistan, cost of living comparisons. Retrieved 26 March 2017.
- ^ "Cvent's Top 25 Meeting Destinations in the Europe". www.cvent.com. Retrieved 6 November 2017.
- ^ "Presentation of the Université libre de Bruxelles". Université Libre de Bruxelles. Archived from the original on 3 December 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "About the University: Culture and History". Vrije Universiteit Brussel. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
- ^ "About the University: Culture and History". www.vub.ac.be. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Institution: Historique". Facultés Universitaires Saint Louis. Archived from the original on 23 December 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "KU Leuven organisational chart: KU Leuven, Campus Brussels". Katholieke Universiteit Leuven. Retrieved 11 January 2015.
- ^ "What makes the RMA so special?". Belgian Royal Military Academy. Archived from the original on 28 December 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Petite histoire du Conservatoire royal de Bruxelles". Conservatoire Royal. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
- ^ "Koninklijk Conservatorium Brussel". Koninklijk Conservatorium. Archived from the original on 13 October 2006. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "L'histoire de l'UCL à Bruxelles". Université Catholique de Louvain. Archived from the original on 14 November 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "ISB Profile". International School of Brussels. Archived from the original on 17 October 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Background". Schola Europaea. Archived from the original on 31 December 2007. Retrieved 9 December 2007.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Public libraries — Région bruxelloise - Brussels Gewest". be.brussels. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Permanent Exhibition » Dinosaur Gallery | Royal Belgian Institute of Natural Sciences". www.naturalsciences.be. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Planetarium of Brussels – Brussels' Museums". www.brusselsmuseums.be. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ "Belgian Association of Hospitals". www.hospitals.be. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Brussels.info - Brussels Airports". www.brussels.info. Retrieved 18 October 2017.
- ^ "Port of Brussels". Port of Brussels. Retrieved 4 August 2017.
- ^ "Brussels Metro and Tram Network". Railway Technology. Retrieved 10 March 2016.
- ^ a b c "The network and vehicles". STIB-MIVB (in French). Retrieved 27 February 2017.
- ^ "Metro, tram and bus in Brussels – City of Brussels". www.brussels.be. Retrieved 27 February 2017.
- ^ "Brussels and Antwerp have worst traffic". Flanders Today. 27 June 2012. Retrieved 8 December 2013.
- ^ "Belgian N roads". Autosnelwegen.net. Retrieved 29 June 2010.
- ^ "Circulation plan". Retrieved 26 August 2015.[dead link]
- ^ "Zones de police". www.policelocale.be (in French). Retrieved 24 March 2017.
- ^ "SIAMU — Région bruxelloise – Brussels Gewest". be.brussels. Retrieved 24 March 2017.
- ^ "Parks and green spaces — Région bruxelloise – Brussels Gewest". be.brussels. Retrieved 10 February 2017.
- ^ "City of Atlanta, GA : List of Atlanta's 18 Sister Cities".
- ^ "Sister Cities". Beijing Municipal Government. Retrieved 23 September 2008.
- ^ "Berlin – City Partnerships". Der Regierende Bürgermeister Berlin. Archived from the original on 21 May 2013. Retrieved 17 September 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Brasilia Global Partners". Internacional.df.gov.br. Archived from the original on 28 February 2014. Retrieved 25 February 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Medmestno in mednarodno sodelovanje". Mestna občina Ljubljana (Ljubljana City) (in Slovenian). Archived from the original on 26 June 2013. Retrieved 27 July 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Mapa Mundi de las ciudades hermanadas". Ayuntamiento de Madrid. Archived from the original on 26 May 2012. Retrieved 22 July 2009.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Discover Montreal" (PDF). mliesl.com. Muskoka Language International. 2007. Retrieved 4 January 2017.
- ^ Foreign relations of Moscow[permanent dead link]
- ^ "Partnerská města HMP" [Prague – Twin Cities HMP]. Portál "Zahraniční vztahy" [Portal "Foreign Affairs"] (in Czech). 18 July 2013. Archived from the original on 25 June 2013. Retrieved 5 August 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Protocol and International Affairs". DC Office of the Secretary. Archived from the original on 13 May 2008. Retrieved 12 July 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)