Kirkintilloch: Difference between revisions
ClueBot NG (talk | contribs) m Reverting possible vandalism by 81.106.226.60 to version by AndrasSkot. Report False Positive? Thanks, ClueBot NG. (3255991) (Bot) |
Amended details for council hq, Kirkintilloch Town Hall and primary schools. |
||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
==Governance== |
==Governance== |
||
Kirkintilloch and Lenzie had their own burgh council until the 1975 abolition of the [[counties of Scotland]] when it became part of the [[Strathkelvin]] local government district within the region of [[Strathclyde]]. A second reorganisation in 1996 established [[East Dunbartonshire]] council from Strathkelvin and the adjacent district of [[Bearsden and Milngavie]]; Kirkintilloch is its administrative centre and the council's headquarters |
Kirkintilloch and Lenzie had their own burgh council until the 1975 abolition of the [[counties of Scotland]] when it became part of the [[Strathkelvin]] local government district within the region of [[Strathclyde]]. A second reorganisation in 1996 established [[East Dunbartonshire]] council from Strathkelvin and the adjacent district of [[Bearsden and Milngavie]]; with Kirkintilloch is its administrative centre and the council's headquarters at Tom Johnston House in the town, named after prominent early 20th century politician and Kirkintilloch native, [[Tom Johnston (Scottish politician)|Thomas Johnston]]. The council's headquarters moved to the William Patrick Library in August 2012, forming the local authority's first community hub.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk/news/new-era-for-kirkintilloch-landmark-as-community-hub-opens-1-2486879|title=New era for Kirkintilloch landmark as community hub opens|website=www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk|language=en|access-date=2018-01-24}}</ref> Tom Johnstone House was demolished in 2015.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk/news/bulldozers-move-in-to-demolish-landmark-1-3935992|title=Bulldozers move in to demolish landmark|website=www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk|language=en|access-date=2018-01-24}}</ref> |
||
==Geography== |
==Geography== |
||
| Line 57: | Line 57: | ||
==Culture== |
==Culture== |
||
[[Kirkintilloch Town Hall]] was opened in 1906, paid for by public subscription. Listed as a building of special architectural or historic interest, it was closed by East Dunbartonshire Council in June 2004, largely due to the anticipated expense of restoring a building constructed of notoriously crumbling soft sandstone. In response the Kirkintilloch Town Hall Preservation Trust was established as a registered charity to preserve the hall and restore it for community use. Work began on the redevelopment of the hall in early summer 2016, with |
[[Kirkintilloch Town Hall]] was opened in 1906, paid for by public subscription. Listed as a building of special architectural or historic interest, it was closed by East Dunbartonshire Council in June 2004, largely due to the anticipated expense of restoring a building constructed of notoriously crumbling soft sandstone. In response the Kirkintilloch Town Hall Preservation Trust was established as a registered charity to preserve the hall and restore it for community use. Work began on the redevelopment of the hall in early summer 2016, with major works completed in October 2017.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.eastdunbarton.gov.uk/news/major-works-complete-kirkintilloch-town-hall|title=Major works complete at Kirkintilloch Town Hall|last=Alan.Muir|date=2017-10-10|website=www.eastdunbarton.gov.uk|language=en|access-date=2018-01-24}}</ref> Kirkintilloch Town Hall will reopen in March 2018.<ref>{{Cite web|url=https://www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk/news/new-dawn-for-iconic-town-hall-building-1-4660104|title=New dawn for iconic town hall building|website=www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk|language=en|access-date=2018-01-24}}</ref> |
||
The town is served by the William Patrick Library, which moved from a converted private villa near Peel Park to a new building on West High Street in the 1990s. The titular William Patrick was a local minister whose brother donated funds to the local people to have a library founded in William's name. The neglected old library was sold by the council back into private ownership and returned to residential use after restoration works. William Patrick [[Library]] is the main library for East Dunbartonshire Council and also houses the reference department and other council offices including social services, planning and a new community hub. |
The town is served by the William Patrick Library, which moved from a converted private villa near Peel Park to a new building on West High Street in the 1990s. The titular William Patrick was a local minister whose brother donated funds to the local people to have a library founded in William's name. The neglected old library was sold by the council back into private ownership and returned to residential use after restoration works. William Patrick [[Library]] is the main library for East Dunbartonshire Council and also houses the reference department and other council offices including social services, planning and a new community hub. |
||
| Line 78: | Line 78: | ||
==Education== |
==Education== |
||
There are |
There are six [[primary school]]s in Kirkintilloch, which are Hillhead, Harestanes, Oxgang, Gartconner, Lairdsland and Holy Trinity. There are also two schools in the area for children with special needs, these being Merkland School in Hillhead and Campsie View School in Lenzie. |
||
The two [[secondary school]]s in the area are Kirkintilloch High School ([[Non-denominational]]) and St Ninian's High School ([[Catholic school|Roman Catholic]]) Both schools recently constructed new-build campuses, which were completed in August 2009. |
The two [[secondary school]]s in the area are Kirkintilloch High School ([[Non-denominational]]) and St Ninian's High School ([[Catholic school|Roman Catholic]]) Both schools recently constructed new-build campuses, which were completed in August 2009. |
||
Revision as of 14:58, 24 January 2018
Kirkintilloch
| |
|---|---|
 St Mary's Church in Kirkintilloch's Cowgate | |
Location within East Dunbartonshire | |
| Population | 19,700 |
| OS grid reference | NS655735 |
| Council area | |
| Lieutenancy area | |
| Country | Scotland |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Post town | Glasgow [2] |
| Postcode district | G66 |
| Dialling code | 0141 |
| Police | Scotland |
| Fire | Scottish |
| Ambulance | Scottish |
| UK Parliament | |
| Scottish Parliament | |
Kirkintilloch (/ˌkɜːrkɪnˈtɪləx/; Template:Lang-gd)[3][4] is a town and former royal burgh in East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It lies on the Forth and Clyde Canal and on the south side of Strathkelvin, about 8 miles (13 km) northeast of central Glasgow. Historically part of Dunbartonshire, the town is the administrative centre of the East Dunbartonshire council area, and its population in 2009 was estimated at 19,700.[5]
Toponymy
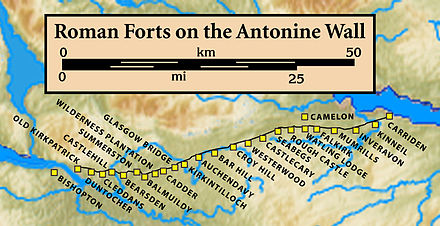


"Kirkintilloch" comes from the Gaelic Cair Cheann Tulaich or Cathair Cheann Tulaich, meaning "fort at the end of the hill". This, in turn, may come from a Cumbric name, Caer-pen-taloch, which has the same meaning.[6] A possible reference to the site is made in the 9th century Welsh text Historia Brittonum, in which the Antonine Wall is said to end at 'Caerpentaloch'. The fort referred to is the former Roman settlement on the wall and the hillock is the volcanic drumlin which would have offered a strategic viewpoint for miles to the West, North and East.[7] The etymology is sometimes taken literally as "Kirk in tilloch" ("church in the field"). Its long name is often shortened by locals to the colloquial Kirkie or Kirky,[8] as reflected in a number of business names in the town.
History
The first known settlement on the site of what is now Kirkintilloch was of Roman origin, a fort established in what is now the Peel Park area of the town in the mid-2nd century, one of the northernmost posts in Roman Britannia.[9] Through it the Antonine Wall was routed; its course continues through the centre of the town to this day, although little trace can now be seen above ground. There are many archeological artifacts found in Kirkintilloch on display at the Hunterian Museum[10] in Glasgow. There is no strong evidence of habitation on the site for the following thousand years until Clan Cumming established a castle (Motte and Bailey) and church there in the 12th century. A small settlement grew and was granted burgh status in 1211, becoming an important staging post for west-east journeys from Glasgow to eastern and north-eastern Scotland. From this time, a weekly market was held in the town, probably at the foot of Peel Brae (along with High Street and Cowgate, one of the three medieval thoroughfares in the town). The castle was of some importance during the wars of independence when an English garrison was stationed there, commanded by Sir Philip de Moubray, who was later to command Stirling Castle at the time of the Battle of Bannockburn. Soldiers from the castle were dispatched to arrest William Wallace at Robroyston in 1305 and escorted him to Dumbarton Castle. Later the same year, the garrison is recorded as having sent a petition to King Edward of England complaining of non-payment of wages. The castle was attacked by Scottish forces in 1306 under Bishop Wishart of Glasgow (using timber given to Glasgow diocese by the English for cathedral repairs), but the siege was unsuccessful. The castle is thought to have been destroyed on the orders of Robert Bruce later in the conflict, although the traces of a mot surrounded by a ditch can still be seen in the Peel Park.[11]
The original Cumming parish church, St Ninian's, was constructed around 1140 some distance to the east of the town (where some of the stones remain in the form of an 18th-century watchtower at the entrance to the Auld Aisle Cemetery) as Kirkintilloch was originally in the parish of Lenzie which stretched from Cumbernauld in the East to Kirkintilloch in the West. The establishment was part of the endowment of Cambuskenneth Abbey, and was accompanied by a grant of one oxgang of land (approximately 15 acres), the measurement that lent its name to the area near the church. A chapel to the Virgin Mary was established in the town itself, sometime before 1379, and was endowed with land at Duntiblae by Sir David Fleming. The move of the parish church to the site of the chapel at Kirkintilloch Cross (now the Auld Kirk Museum) in 1644 resulted in a split of the Parish into Easter and Wester Lenzie (later Cumbernauld and Kirkintilloch Parishes) The name Lenzie was later reused for Kirkintilloch's railway station on the main Glasgow to Edinburgh line, around which the later village of that name developed.
Following the Scottish victory in the wars of independence and the subsequent decline of Clan Cumming, the baronies of Kirkintilloch, Lenzie, and Cumbernauld were granted by Robert Bruce to Sir Malcolm Fleming, Sheriff of Dumbarton and a supporter of the Bruce faction in the war. Hitherto part of Stirlingshire, the area subsequently became a detached part of the county of Dumbarton, in which it remains today.
On 3 January 1746, the retreating Jacobite army of Charles Stuart made its way through Kirkintilloch, on its way back from Derby, and on the march to Falkirk and ultimately Culloden. One of the Highland army's stragglers was shot dead at the town cross by a man hidden in a barn at the Kiln Close (where the library now stands). On hearing of the murder, Charles halted his army on the Kilsyth road and threatened to turn back and burn the town. The town magistrates persuaded him to continue marching, in return for an unspecified payment, and the town was spared.[12]
The town was one of the hotbeds of the Industrial Revolution in Scotland, beginning with the emergence of a booming textile industry in the area. There were 185 weavers in Kirkintilloch by 1790, and in 1867 James Slimon's cotton mill at Kelvinside employed 200 women.[13] With the construction of the Forth and Clyde Canal through the town in 1773, and the establishment of the Monkland and Kirkintilloch Railway in 1826, Kirkintilloch developed further as an important transportation hub, inland port and production centre for iron, coal, nickel and even small ships. This industrial heritage lives on in the town's designation as the "Canal Capital of Scotland", and in the redevelopment of the canal and surrounding former industrial sites in the early 21st century.
By the 20th century, the principal employers in the town were the shipbuilders J & J Hay and Peter McGregor, and the Lion (1880–1984) and Star foundries, all of which produced goods for the domestic market and for export around the world.[13] Kirkintilloch's most famous exports were the distinctive red British postboxes and phoneboxes K2 to K6, produced in the town until 1984 and still to be found as far afield as Taiwan and Mississippi. Listed versions of these boxes still stand at the foot of Alexandra Street in the centre of Kirkintilloch.
Kirkintilloch was a "dry town" for much of its recent history, with the sale of alcohol on public premises banned from 1923 until 1967. The prohibition on the sale of alcohol had long been demanded by the Liberal Party and the temperance movement, both of which had a strong influence in the town in the early part of the 20th century, largely due to the perceived negative effects of alcohol on the town's inhabitants.
The 1960s development plan to redevelop inner city areas of Glasgow saw Kirkintilloch used as an overspill settlement for relocated Glaswegians in combination with the new towns of Livingston and Cumbernauld, offering employment in housebuilding and an increase to the local population to its current levels. Large numbers of new houses for owner occupation have been built since that time.[14]
Governance
Kirkintilloch and Lenzie had their own burgh council until the 1975 abolition of the counties of Scotland when it became part of the Strathkelvin local government district within the region of Strathclyde. A second reorganisation in 1996 established East Dunbartonshire council from Strathkelvin and the adjacent district of Bearsden and Milngavie; with Kirkintilloch is its administrative centre and the council's headquarters at Tom Johnston House in the town, named after prominent early 20th century politician and Kirkintilloch native, Thomas Johnston. The council's headquarters moved to the William Patrick Library in August 2012, forming the local authority's first community hub.[15] Tom Johnstone House was demolished in 2015.[16]
Geography
As well as the Forth and Clyde Canal the Luggie Water passes through Kirkintilloch, the canal crossing the Luggie on an aqueduct. The Luggie flows into the River Kelvin which in turn flows into the River Clyde in Glasgow.
Communities in and around Kirkintilloch include: Cleddans; Harestanes; Hayston; Hillhead; Oxgang; Rosebank; Langmuir; Greens; Fauldhead; Waterside; Westermains; Lenzie: Gallowhill: Whitegates; Back O' Loch; Woodilee; Broomhill etc.
Culture
Kirkintilloch Town Hall was opened in 1906, paid for by public subscription. Listed as a building of special architectural or historic interest, it was closed by East Dunbartonshire Council in June 2004, largely due to the anticipated expense of restoring a building constructed of notoriously crumbling soft sandstone. In response the Kirkintilloch Town Hall Preservation Trust was established as a registered charity to preserve the hall and restore it for community use. Work began on the redevelopment of the hall in early summer 2016, with major works completed in October 2017.[17] Kirkintilloch Town Hall will reopen in March 2018.[18]
The town is served by the William Patrick Library, which moved from a converted private villa near Peel Park to a new building on West High Street in the 1990s. The titular William Patrick was a local minister whose brother donated funds to the local people to have a library founded in William's name. The neglected old library was sold by the council back into private ownership and returned to residential use after restoration works. William Patrick Library is the main library for East Dunbartonshire Council and also houses the reference department and other council offices including social services, planning and a new community hub.
Kirkintilloch underwent significant population growth in the post-Second World War period, with several new amenities erected to cater for the growing population of the town and its surrounding villages. New shopping facilities were built in the Cowgate and Townhead areas, culminating in the opening, by Diana, Princess of Wales, of the Regent Centre shopping mall in the 1990s.[19]
The local swimming pool and Community Education Centre, built in the 1960s and '70s in Woodhead Park to the south of the town, were demolished in 1999 and 2005 respectively. Woodhead Park was once home to a petting zoo, bandstand, greenhouses, putting green and public toilets. All are now closed, although a new leisure centre was opened on the same spot as the old pool in July 2007, providing facilities for tennis, badminton, swimming, football and a gymnasium. A large new children's play area has been created near the site of the former putting green in the park.
The construction of the new leisure centre came in combination with a wider-ranging artistic, cultural and social regeneration project called Kirkintilloch's Initiative.[20] This includes the new link road largely funded by housebuilders developing on the site of the former Woodilee Hospital.
Kirkintilloch Learning Centre is located on Southbank Road, overlooking the Forth and Clyde Canal, an offshoot of Cumbernauld College.
Locally, a G66+ Live! Cultural festival offers a wide range of events from talks on history in local churches to musical events in the town's local bars, such as Bar Bliss, dramas and also entries from the schools in the G66 postcode area. G66+ Live! is annual festival taking place in June. Kirkintilloch's most successful musical ensemble is its brass band, the Kirkintilloch Band,[21] who were crowned Scottish Brass Band Champions in 2007 and who have had success in competitions both in Scotland and further afield. Each August the local Canal Festival takes place.
An amateur theatre group, the Kirkintilloch Players,[22] is based at the Turret Theatre in the Eastside area of Kirkintilloch, the former home of the town's Liberal Club.
The town has a pipe band of the same name, Kirkintilloch Pipe Band. Established on 12 November 1888 it is one of, if not the oldest civilian pipe band in the world.[citation needed] The band takes part in civic and private events in the local and surrounding areas and also takes part in competition. Its pipers and drummers are mostly from the local area and the band still practices weekly in the Hillhead Community Centre.
The town has a variety of eateries, bars and nightspots. The Kirky Puffer beat local rival bar the Antonine (now closed) to pub of the year in January 2006 and this is an accolade that the Puffer has been able to win year after year. Local nightclubs Club Bliss (formerly Babylon then Tantra) and Smith's Hotel (formerly Broadcroft Hotel) have been threatened with closure and have been forced into investing heavily in security and local alcohol awareness initiatives to help to discourage anti-social behaviour. [citation needed]
Education
There are six primary schools in Kirkintilloch, which are Hillhead, Harestanes, Oxgang, Gartconner, Lairdsland and Holy Trinity. There are also two schools in the area for children with special needs, these being Merkland School in Hillhead and Campsie View School in Lenzie.
The two secondary schools in the area are Kirkintilloch High School (Non-denominational) and St Ninian's High School (Roman Catholic) Both schools recently constructed new-build campuses, which were completed in August 2009.
In the Lenzie area primary schools include Lenzie Primary, Lenzie Meadow Primary, Millersneuk and Holy Family Primary. Holy Family is a Catholic school on the edge of Lenzie on the border with Kirkintilloch, and is a feeder to St Ninian's High School. The other three non-denomination schools in the area feed onto Lenzie Academy, along with Lairdsland Primary in Kirkintilloch and the nearby Auchinloch Primary.
Media
The Kirkintilloch Herald[23] is the local newspaper of record, established by town businessman Donald MacLeod in premises on the Cowgate in 1883.
Notable people
- Moira Anderson, singer[24]
- Alexander Bain (inventor), inventor of an electric clock, lived in Kirkintilloch in his latter days.}[citation needed]
- Archibald Scott Couper, chemist.[citation needed]
- Andrew Crumey, novelist[25]
- James Dalrymple Duncan Dalrymple FRSE (1852-1908), author and antiquarian[citation needed]
- John Davie (1918-1945), boy soprano who, as "Master Jackie Davie", in the 1930s recorded for HMV, gave concerts in the Glasgow area, won prizes at the Glasgow Music Festivals and broadcast on BBC radio; died on active service in Italy.[26]
- Joseph Devine, Roman Catholic bishop[27]
- Walter Dick, professional footballer who earned one cap for the United States[28]
- James Fletcher, industrialist[29]
- John Fletcher (New Zealand politician)
- Jimmy Gallagher, professional footballer who played for the United States[30]
- Alasdair Graham (1934–2016), concert pianist[31]
- David Gray, poet [32]
- Tom Johnston, Labour politician[33]
- David Lapsley, professional footballer[34]
- Tommy Lorne, comedian [35]
- Hugh McCartney, Labour politician[36]
- Ian McCartney, Labour politician[37]
- John Meikle, recipient of the Victoria Cross[citation needed]
- Macvey Napier, solicitor and editor of the Encyclopædia Britannica[38][39]
- Rita Taketsuru, (born Jessie Roberta Cowan), Japanese whisky pioneer.[40]
- Jim Watt (boxer)[41]
- John Ruddy, deaf international athlete for Great Britain [42]
Sport
The town has a small junior football club, Kirkintilloch Rob Roy F.C., thrice winners of the Scottish Junior Cup, who formerly played at Adamslie Park in the west of the town, and is also home to the amateur Harestanes A.F.C., twice winners of the Scottish Amateur Cup.
Lenzie rugby club is based in the town, playing their home games at Viewfield Avenue. They are in West regional league 1, the 4th tier of Scottish club rugby.[43]
After the town had been without such facilities for the better part of a decade a replacement swimming pool and gym finally opened in July 2007 at Woodhead Park. The town is also home to the "Kirkintilloch Olympians", a local athletics club.
Kirkintilloch is also the home of Aberdeen and former Rangers player Gregg Wylde and Celtic and Scotland player, Charlie Mulgrew.[44]
Lenzie Youth Club is a local football club founded in 1980 by Ian Stevenson which has sections from age 5 upwards. Famous ex Lenzie Youth Club players include Barry Bannan and Stephen Crainey.[citation needed]
Churches
There are a number of churches in Kirkintilloch. The four Church of Scotland congregations are: St Mary's, St David's Memorial Park, St Columba's and Hillhead. The Baptist Union of Scotland has churches at Townhead [45][46] and Harestanes. There are two Roman Catholic Churches - St Flannan's in Hillhead, and Holy Family and St Ninian's in the town centre. Jehovah's Witnesses have a congregation in Kirkintilloch which shares a Kingdom Hall with its sister congregation in Bishopbriggs.
The Edinburgh Gazette of 17 November 1896 announces "INTIMATION is hereby given that the Reverend THOMAS ANGUS MORRISON, Minister of the Parish of Kirkintilloch, in the Presbytery of Glasgow and County of Dumbarton, has, under and by virtue of "The Glebe Lands (Scotland) Act, 1866," presented a ; Petition to the Lords of Council and Session, Commissioners for the Plantation of Kirks and Valuation of Teinds, for authority to Feu the GLEBE OF KIRKINTILLOCH ; and that an Interlocutor has been pronounced therein in the following terms...." After depositing £400 with the "Lord of the Manor" or "Patron" T Angus Morrison becomes Minister of St Mary's. The original church was old and damp, T Angus Morrison built up his congregation and it was soon to outgrow the old church or kirk. Travelling throughout the UK T Angus Morrison worked with the Architect, George Bell of Glasgow. Thomas Angus Morrison was born in Motherwell, but for much of his youth he lived in Glasgow and attended school in Dennistoun. Commencing his ministerail career as an Assistant at the Plantation Church in Govan he was soon to move to St Mary's Church as assistant to the Reverened Mr Craven in 1890. T Angus Morrison was to marry a local girl, Mary Stewart Galloway Smillie, sole surviving child of James Smillie of Fearndean, a local Kirkintilloch family, tracing their family back to the town of the 1790s. T Angus Morrison and Mary were to have seven children, one of the sons, William Angus Galloway Morrison dying on the Siam Burmese Railway in World War Two. The Reverened T Angus Morrison was born in Shotts, near Motherwell in 1862, died suddenly in 1941 at the age of 79 having served St Mary's for 51 years. In addition to a long career as Presbyterian Minister, the Reverened T Angus Morrison was a Freemason and had become Provincial Grand Master to the Province of Dunbartonshire from 1921 until his death.
Twin Town
Yoichi, Hokkaido, Japan[47]
Photogallery
See also
References
- ^ "Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba - Gaelic Place-Names of Scotland - Database". Gaelicplacenames.org. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ^ Evox Facilities. "List of UK post towns". Evox Facilities. Archived from the original on 2012-02-19. Retrieved 2012-02-22.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba/Gaelic Place-Names of Scotland". Ainmean-Àite na h-Alba. Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ "Scottish Parliament: Placenames collected by Iain Mac an Tailleir" (PDF). Retrieved 13 October 2012.
- ^ "Town Centre Regeneration: TCRF Case Studies Report". Scotland.gov.uk. Retrieved 2012-02-21.
- ^ Origin of the Name - Peter Drummond
- ^ Tim. "The name Kirkintilloch " Senchus". Senchus.wordpress.com. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- ^ Published on Tue Jul 19 15:23:26 BST 2011. "Queue must be having a laugh – Kirky's cut off! - Local Headlines". Kirkintilloch Herald. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ "The Romans are here! - Local Headlines". Kirkintilloch Herald. 2012-02-21. Retrieved 2012-02-21.
- ^ "University of Glasgow - The Hunterian - Collections - Permanent Displays - The Antonine Wall". Gla.ac.uk. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ^ Published on Tue Apr 29 18:09:49 BST 2003. "Time Team invited to unearth Kirky's medieval secrets - Local Headlines". Kirkintilloch Herald. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ Kirkintilloch, town and parish - Thomas Watson - Google Book. Books.google.com. 2009-10-31. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- ^ a b "The rich history of Kirkintilloch". s1Kirkintilloch. Archived from the original on 2012-04-25. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ [1] Archived October 7, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "New era for Kirkintilloch landmark as community hub opens". www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk. Retrieved 2018-01-24.
- ^ "Bulldozers move in to demolish landmark". www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk. Retrieved 2018-01-24.
- ^ Alan.Muir (2017-10-10). "Major works complete at Kirkintilloch Town Hall". www.eastdunbarton.gov.uk. Retrieved 2018-01-24.
- ^ "New dawn for iconic town hall building". www.kirkintilloch-herald.co.uk. Retrieved 2018-01-24.
- ^ "Down Memory Lane – a trip back through time with the Herald". Kirkintilloch Herald. 2012-03-06. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ^ "Archived copy". Archived from the original on February 5, 2016. Retrieved 2016-08-03.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "出会い出陣 Kirkintilloch Band". Kirkintilloch-band.com. 2013-11-21. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ^ "Home of Kirkintilloch Players Amateur Drama Club". Kirkintillochplayers.co.uk. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- ^ "Kirkintilloch Herald". Kirkintilloch Herald. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- ^ [2]
- ^ "Award winning author Andrew Crumey - Local Headlines". Kirkintilloch Herald. 2008-06-24. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ Kirkintilloch Gazette 22 Sept. 1933; Kirkintilloch Herald 6 May 1931, 25 April 1945; memorial in Auld Aisle Cemertery, Kirkintilloch.
- ^ "Library : Sectarianism and Secularism: Bugbears for the Catholic Church in Scotland". Catholic Culture. 2008-03-11. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Archives | providencejournal.com | The Providence Journal". Pqasb.pqarchiver.com. 1989-07-25. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ James, Selwyn. "Fletcher, James - Biography - Te Ara Encyclopedia of New Zealand". Teara.govt.nz. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Soccer pioneers: The Scottish players that made it to the semi-finals in the first World Cup - Sport". Scotsman.com. 2010-05-29. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ Alasdair Graham, concert pianist – obituary The Daily Telegraph 15 August 2016. Retrieved 2017-02-04.
- ^ "Sense of Place event put the focus on town's proud past - Community". Kirkintilloch Herald. 2011-10-17. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Tom Johnston : Biography". Spartacus.schoolnet.co.uk. 1965-09-05. Archived from the original on 2012-05-20. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Alastair MacLachlan (2001-01-20). "David Lapsley". Herald Scotland. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "TGS - 1914 to 1950s - Personalities - Tommy Lorne". Theglasgowstory.com. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Hugh McCartney - Obituaries - News". The Independent. 2006-03-02. Archived from the original on 2012-11-11. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Abram remembers pit disaster victims - Local News". Wigan Today. 2008-08-20. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Macvey Napier". Electricscotland.com. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
- ^ "Catalogue". Archives.lib.ed.ac.uk. Archived from the original on 2010-09-24. Retrieved 2012-05-16.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "(Rita) Jessie Roberta Cowan Taketsuru". BBC. 2015-01-11. Retrieved 2016-08-03.
- ^ "The Sun". Thescottishsun.co.uk. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
- ^ "John's in the running for Deaflympics= Evening Times". 2012-09-25. Retrieved 2014-01-17.
- ^ "Location - Lenzie Rugby Club". Pitchero.com. 2013-04-29. Archived from the original on 2015-10-06. Retrieved 2015-10-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Published on Tue Jan 25 15:56:00 GMT 2011. "Ibrox winger is still Wylde about Rangers! - Football". Kirkintilloch Herald. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: numeric names: authors list (link) - ^ [3] Archived September 27, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^ "Kirkintilloch Baptist Church". Kirkiebaptist.com. Retrieved 2011-12-05.
- ^ "Town twinned since 1988". Kirkintilloch Herald. 2014-11-27. Retrieved 2016-08-03.
Bibliography
- Old Glasgow and It's Suburbs in their Celtic Gard: Also Parish of Baldernock - Kirkintilloch to Stirling - Robroyston by Neil Thomson with 80 pages. From a copy of Old Glasgow published by Coghill in 1907 with no ISBN
External links
- East Dunbartonshire Council
- G66 Festival
- Canal Festival website
- National Library of Scotland: SCOTTISH SCREEN ARCHIVE (selection of archive films about Kirkintilloch)



