Cluster headache: Difference between revisions
m Reverted edits by 113.210.226.8 (talk): addition of unsourced content (HG) (3.3.2) |
Add citation |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
<!--Treatment and prevention --> |
<!--Treatment and prevention --> |
||
Recommended management includes lifestyle changes such as avoiding potential triggers.<ref name=AFP2013/> Treatments for acute attacks include [[oxygen]] or a fast acting [[triptan]].<ref name=AFP2013>{{cite journal |pmid=23939643 |url=http://www.aafp.org/link_out?pmid=23939643 |year=2013 |author1=Weaver-Agostoni |first1=J |title=Cluster headache |journal=American Family Physician |volume=88 |issue=2 |pages=122–8 }}</ref><ref name=Rob2016/> Measures recommended to decrease the frequency of attacks include [[steroid injections]], [[civamide]], or [[verapamil]].<ref name=Rob2016/> [[Nerve stimulation]] or surgery may occasionally be used if other measures are not effective.<ref name=AFP2013/> |
Recommended management includes lifestyle changes such as avoiding potential triggers.<ref name=AFP2013/> Treatments for acute attacks include [[oxygen]] or a fast acting [[triptan]].<ref name=AFP2013>{{cite journal |pmid=23939643 |url=http://www.aafp.org/link_out?pmid=23939643 |year=2013 |author1=Weaver-Agostoni |first1=J |title=Cluster headache |journal=American Family Physician |volume=88 |issue=2 |pages=122–8 }}</ref><ref name=Rob2016/> Measures recommended to decrease the frequency of attacks include [[steroid injections]]<ref name="Gaul11">{{cite journal |last1=Gaul |first1=C |last2=Diener |first2=H |last3=Müller |first3=OM |year=2011 |title=Cluster Headache Clinical Features and Therapeutic Options |journal=Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. Review |volume=108 |issue=33 |pages=543-549 |publisher= |doi=10.3238/arztebl.2011.0543 |url=https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21912573 |accessdate=12 January 2018}}</ref>, [[civamide]], or [[verapamil]].<ref name=Rob2016/> [[Nerve stimulation]] or surgery may occasionally be used if other measures are not effective.<ref name=AFP2013/> |
||
<!-- Epidemiology, history, and culture --> |
<!-- Epidemiology, history, and culture --> |
||
Revision as of 01:33, 2 February 2018
| Cluster headache | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Trigeminal nerve | |
| Specialty | Neurology |
| Symptoms | Recurrent, severe headaches on one side of the head, eye watering, stuffy nose[1] |
| Usual onset | 20 to 40 years old[2] |
| Duration | 15 min to 3 hrs[2] |
| Types | Episodic, chronic[2] |
| Causes | Unknown[2] |
| Risk factors | Tobacco smoke, family history[2] |
| Diagnostic method | Based on symptoms[2] |
| Differential diagnosis | Migraine, trigeminal neuralgia,[2] other trigeminal autonomic cephalgias[3] |
| Prevention | Steroid injections, civamide, verapamil[4] |
| Treatment | Oxygen therapy, triptans[2][4] |
| Frequency | ~0.1% at some point in time[5] |
Cluster headache (CH) is a neurological disorder characterized by recurrent, severe headaches on one side of the head, typically around the eye.[1] There is often accompanying eye watering, nasal congestion, or swelling around the eye, on the affected side.[1] These symptoms typically last 15 minutes to 3 hours.[2] Attacks often occur in clusters which typically last for weeks or months and occasionally more than a year.[2]
The cause is unknown.[2] Risk factors include a history of exposure to tobacco smoke and a family history of the condition.[2] Exposures which may trigger attacks include alcohol and nitroglycerin.[2] They are a primary headache disorder of the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias type.[2] Diagnosis is based on symptoms.[2]
Recommended management includes lifestyle changes such as avoiding potential triggers.[2] Treatments for acute attacks include oxygen or a fast acting triptan.[2][4] Measures recommended to decrease the frequency of attacks include steroid injections[6], civamide, or verapamil.[4] Nerve stimulation or surgery may occasionally be used if other measures are not effective.[2]
The condition affects about 0.1% of the general population at some point in their life and 0.05% in any given year.[5] The condition usually first occurs between 20 and 40 years of age.[2] Men are affected about four times more often than women.[5] Cluster headaches are named for the occurrence of groups of headache attacks (clusters).[1] They have also been referred to as "suicide headaches".[2]
Signs and symptoms
Cluster headaches are recurring bouts of excruciating unilateral headache attacks[7] of extreme intensity.[8] The duration of a typical CH attack ranges from about 15 to 180 minutes.[2] Most untreated attacks (about 75%) last less than 60 minutes.[9]
The onset of an attack is rapid and most often without preliminary signs that are characteristic in migraine. Preliminary sensations of pain in the general area of attack, referred to as "shadows", may signal an imminent CH, or these symptoms may linger after an attack has passed, or even between attacks.[10] Though CH is strictly unilateral, there are some documented cases of "side-shift" between cluster periods,[11] or, extremely rarely, simultaneous (within the same cluster period) bilateral cluster headaches.[12]
Pain
The pain occurs only on one side of the head (unilateral), around the eye (orbital), particularly above the eye (supraorbital), in the temple (temporal), or in any combination. The pain of CH attack is remarkably greater than in other headache conditions, including severe migraine. The pain is typically described as burning, stabbing, boring or squeezing, and may be located near or behind the eye.[13] As a result of the pain, those with cluster headaches may experience suicidal thoughts during an attack (giving the alternative name "suicide headache" or "suicidal headache").[14][15] It is reported as one of the most painful conditions.[16]
Other symptoms
The typical symptoms of cluster headache include grouped occurrence and recurrence (cluster) of headache attack, severe unilateral orbital, supraorbital and/or temporal pain. If left untreated, attack frequency may range from one attack every two days to eight attacks per day.[2][17] Cluster headache attack is accompanied by at least one of the following autonomic symptoms: drooping eyelid, pupil constriction, redness of the conjunctiva, tearing, runny nose, and less commonly, facial blushing, swelling, or sweating, typically appearing on the same side of the head as the pain.[17]
Restlessness (for example, pacing or rocking back and forth) may occur. Similar to a migraine, sensitivity to light (photophobia) or noise (phonophobia) may occur during a CH. Nausea is a rare symptom, although it has been reported.[7] Secondary effects may include inability to organize thoughts and plans, physical exhaustion, confusion, agitation, aggressiveness, depression and anxiety.[14]
People with CH may dread facing another headache and adjust their physical or social activities around a possible future occurrence. Likewise they may seek assistance to accomplish what would otherwise be normal tasks. They may hesitate to make plans because of the regularity, or conversely, the unpredictability of the pain schedule. These factors can lead to generalized anxiety disorders, panic disorder,[14] serious depressive disorders,[18] social withdrawal and isolation.[19]
Recurrence
Cluster headaches may occasionally be referred to as "alarm clock headache" because of the regularity of their recurrence. CH attacks often awaken individuals from sleep. Both individual attacks and the cluster grouping can have a metronomic regularity; attacks typically striking at a precise time of day each morning or night. The recurrence of headache cluster grouping may occur more often around solstices, or seasonal changes, sometimes showing circannual periodicity. Conversely, attack frequency may be highly unpredictable, showing no periodicity at all. These observations have prompted researchers to speculate an involvement, or dysfunction of the hypothalamus. The Hypothalamus controls the body's "biological clock" and circadian rhythm.[20][21]
In episodic cluster headache, attacks occur once or more daily, often at the same time each day for a period of several weeks, followed by a headache-free period lasting weeks, months, or years. Approximately 10–15% of cluster headaches are chronic, with multiple headaches occurring every day for years, sometimes without any remission.
This article needs additional citations for verification. (January 2014) |
In accordance with the International Headache Society (IHS) diagnostic criteria, cluster headaches occurring in two or more cluster periods, lasting from 7 to 365 days with a pain-free remission of one month or longer between the headache attacks, may be classified as episodic. If headache attacks occur for more than a year without pain-free remission of at least one month, the condition is classified as chronic.[17] Chronic CH both occurs and recurs without any remission periods between cycles; there may be variation in cycles, meaning the frequency and severity of attacks may change without predictability for a period of time. The frequency, severity and duration of headache attacks experienced by people during these cycles varies between individuals and does not demonstrate complete remission of the episodic form. The condition may change unpredictably, from chronic to episodic and from episodic to chronic.[22]
Causes
 |
 |
 |
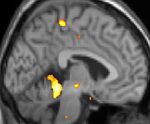
| Positron emission tomography (PET) shows brain areas being activated during pain | ||
 |
 |
 |
| Voxel-based morphometry (VBM) shows brain area structural differences | ||
The cause of cluster headache is unknown.[23] Cluster headaches were historically described as vascular headaches, with the belief that intense pain was caused by dilation of blood vessels which in turn, was thought to create pressure on the trigeminal nerve. The vascular theory now holds less credence,[24] and other mechanisms are being considered.[25] The Third Edition of the Internal Classification of Headache disorders classifies CH as belonging to the trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias.[26]
Genetics
Cluster headache may, but rarely, run in some families in an autosomal dominant inheritance pattern.[23] People with a first degree relative with the condition are about 14–48 times more likely to develop it themselves,[1] and between 1.9 and 20% of persons with CH have a positive family history.[23] Possible genetic factors warrant further research, current evidence for genetic inheritance is limited.[23]
Tobacco smoking
About 65% of persons with CH are, or have been, tobacco smokers.[1] Stopping smoking does not lead to improvement of the condition and CH also occurs in those who have never smoked (e.g. children);[1] it is thought unlikely that smoking is a cause.[1] People with CH may be predisposed to certain traits, including smoking or other lifestyle habits.[27]
Hypothalamus
A review suggests that the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus, which is the major biological clock in the human body, may be involved in cluster headaches, because CH occurs with diurnal and seasonal rhythmicity.[28] A drop in RBC choline levels has also been reported during an attack.[29]
Positron emission tomography (PET) scans indicate the brain areas which are activated during attack only, compared to pain free periods. These pictures show brain areas which are active during pain in yellow/orange color (called "pain matrix"). The area in the center (in all three views) is specifically activated during CH only. The bottom row voxel-based morphometry (VBM) shows structural brain differences between individuals with and without CH; only a portion of the hypothalamus is different.[30]
Diagnosis
Cluster headaches are often misdiagnosed, mismanaged, or undiagnosed for many years; they may be confused with migraine, "cluster-like" headache (or mimics), CH subtypes, other TACs ( trigeminal autonomic cephalalgias), or other types of primary or secondary headache syndrome.[31] Cluster-like head pain may be diagnosed as secondary headache rather than cluster headache.[17]
A detailed oral history aids practitioners in correct differential diagnosis, as there are no confirmatory tests for CH. A headache diary can be useful in tracking when and where pain occurs, how severe it is, and how long the pain lasts. A record of coping strategies used may help distinguish between headache type; data on frequency, severity and duration of headache attacks are a necessary tool for initial and correct differential diagnosis in headache conditions.[32]
Correct diagnosis presents a challenge as the first CH attack may present where staff are not trained in the diagnosis of rare or complex chronic disease.[9] Although experienced ER staff are sometimes trained to detect headache types,[33] CH attacks themselves are not directly life-threatening, they are linked to an increased risk of suicide.[14][34]
Individuals with CH typically experience diagnostic delay before correct diagnosis.[31][35] People are often misdiagnosed due to reported neck, tooth, jaw, and sinus symptoms and may unnecessarily endure many years of referral to ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialists for investigation of sinuses; dentists for tooth assessment; chiropractors and manipulative therapists for treatment; or psychiatrists, psychologists, and other medical disciplines before their headaches are correctly diagnosed.[36] Under-recognition of CH by health care professionals is reflected in consistent findings in Europe and the United States that the average time to diagnosis is around seven years.[37] Medical students receive little training in differential diagnoses and management of headaches.[38]
Differential
Cluster headache may be misdiagnosed as migraine or sinusitis.[37] Other types of headache are sometimes mistaken for, or may mimic closely, CH. Incorrect terms like "cluster migraine" confuse headache types, confound differential diagnosis and are often the cause of unnecessary diagnostic delay,[39] ultimately delaying appropriate specialist treatment.
Headaches that may be confused with CH include:
- Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania (CPH) is a unilateral headache condition, without the male predominance usually seen in CH. Paroxysmal hemicrania may also be episodic but the episodes of pain seen in CPH are usually shorter than those seen with cluster headaches. CPH typically responds "absolutely" to treatment with the anti-inflammatory drug indomethacin[17] where in most cases CH typically shows no positive indomethacin response, making "Indomethacin response" an important diagnostic tool for specialist practitioners seeking correct differential diagnosis between the conditions.[40][41]
- Short-lasting unilateral neuralgiform headache with conjunctival injection and tearing (SUNCT) is a headache syndrome belonging to the group of TACs.[17][42]
- Trigeminal neuralgia is a unilateral headache syndrome,[36] or "cluster-like" headache.[43]
Prevention
Preventive treatments are used to reduce or eliminate cluster headache attacks; they are generally used in combination with abortive and transitional techniques.[7]
Verapamil
The recommended first-line preventive therapy is verapamil, a calcium channel blocker.[2][44] Verapamil was previously underused in people with cluster headache.[7]
Steroids
There is little evidence to support a long-term benefit from steroids,[2] but they may be used until other medications take effect as they appear to be effective at three days.[2] They are generally discontinued after 8–10 days of treatment.[7]
Surgery
Nerve stimulators may be an option in the small number of people who do not improve with medications.[45][46] Two procedures, deep brain stimulation or occipital nerve stimulation, may be useful;[2] early experience shows a benefit in about 60% of cases.[47] It typically takes weeks or months for this benefit to appear.[46] A non-invasive method using transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) is being studied.[46]
A number of surgical procedures, such as a rhizotomy or microvascular decompression, may also be considered,[46] but evidence to support them is limited and there are cases of people whose symptoms worsen after these procedures.[46]
Other
Lithium, methysergide, and topiramate are recommended alternative treatments,[44][48] although there is little evidence supporting the use of topiramate or methysergide.[2][49] This is also true for tianeptine, melatonin, and ergotamine.[2] Valproate, sumatriptan, and oxygen are not recommended as preventive measures.[2] Botulinum toxin injections have shown limited success.[50] Evidence for baclofen, botulinum toxin, and capsaicin is unclear.[49]
Management
Treatment for cluster headache is divided into three primary categories: abortive, transitional, and preventative.[51] There are two primary treatments for acute CH: oxygen and triptans,[2] but they are underused due to misdiagnosis of the syndrome.[7] During bouts of headaches, triggers such as alcohol, nitroglycerine and naps during the day should be avoided.[9]
Oxygen
Oxygen therapy may help people with CH, but it does not help prevent future episodes.[2] Typically it is given via a non-rebreather mask at 12–15 liters per minute for 15–20 minutes.[2] One review found about 70% improve within 15 minutes.[9] The evidence for effectiveness of 100% oxygen, however, is weak.[9][52] Hyperbaric oxygen at pressures of ~2 times greater than atmospheric pressure may relieve cluster headache.[52]
Triptans
The other primarily recommended treatment of acute attacks is subcutaneous or intranasal sumatriptan.[44] Sumatriptan and zolmitriptan have both been shown to improve symptoms during an attack with sumatriptan being superior.[53] Because of the vasoconstrictive side-effect of triptans, they may be contraindicated in people with ischemic heart disease.[2]
Opioids
The use of opioid medication in management of CH is not recommended[54] and may make headache syndromes worse.[55][56] Long-term opioid use is associated with well known dependency, addiction, and withdrawal syndromes.[57] Prescription of opioid medication may additionally lead to further delay in differential diagnosis, undertreatment, and mismanagement.[54]
Other
The vasoconstrictor ergot compounds may be useful,[9] but have not been well studied in acute attacks.[53] Octreotide administered subcutaneously has been demonstrated to be more effective than placebo for the treatment of acute attacks.[58]
Epidemiology
Cluster headache affects about 0.1% of the general population at some point in their life.[5] Males are affected about four times more often than females.[5] The condition usually starts between the ages of 20 and 50 years, although it can occur at any age.[1] About one in five of adults reports the onset of cluster headache between 10 and 19 years.[59]
History
The first complete description of cluster headache was given by the London neurologist Wilfred Harris in 1926, who named the disease migrainous neuralgia.[60][61][62] Descriptions of CH date to 1745 and probably earlier.[63]
The condition was originally named Horton's cephalalgia after Bayard Taylor Horton, a US neurologist who postulated the first theory as to their pathogenesis. His original paper describes the severity of the headaches as being able to take normal men and force them to attempt or complete suicide; his 1939 paper said:
"Our patients were disabled by the disorder and suffered from bouts of pain from two to twenty times a week. They had found no relief from the usual methods of treatment. Their pain was so severe that several of them had to be constantly watched for fear of suicide. Most of them were willing to submit to any operation which might bring relief."[64]
CH has alternately been called erythroprosopalgia of Bing, ciliary neuralgia, erythromelalgia of the head, Horton's headache, histaminic cephalalgia, petrosal neuralgia, sphenopalatine neuralgia, vidian neuralgia, Sluder's neuralgia, Sluder's syndrome, and hemicrania angioparalyticia.[65]
Society and culture
Robert Shapiro, a professor of neurology, says that while cluster headaches are about as common as multiple sclerosis with a similar disability level, as of 2013, the US National Institutes of Health had spent $1.872 billion on research into multiple sclerosis in one decade, but less than $2 million on CH research in 25 years.[66] Due to an occasional association with suicidal thoughts, cluster headaches have been colloquially named "suicide headaches."[14]
As of July 2015[update] there are no approved medicines for the prevention of cluster headache in the United States.[67]
Research directions
Some controversial case reports suggest that ingesting tryptamines such as LSD, psilocybin, or DMT can reduce pain and interrupt cluster headache cycles.[68][69] A 2006 interview/survey of 53 individuals with CH said that psilocybin extended remission periods in 10% cases.[69] The survey was not a blinded or controlled study, and was "limited by recall and selection bias".[68]
Fremanezumab, a humanized monoclonal antibody directed against calcitonin gene-related peptides alpha and beta, is in phase 3 clinical trials for CH.[70][71]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Nesbitt, A. D.; Goadsby, P. J. (2012). "Cluster headache". BMJ. 344: e2407. doi:10.1136/bmj.e2407. PMID 22496300.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa ab ac ad ae af ag Weaver-Agostoni, J (2013). "Cluster headache". American Family Physician. 88 (2): 122–8. PMID 23939643.
- ^ Rizzoli, P; Mullally, WJ (20 September 2017). "Headache". The American Journal of Medicine. 131: 17–24. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.09.005. PMID 28939471.
- ^ a b c d Robbins, Matthew S.; Starling, Amaal J.; Pringsheim, Tamara M.; Becker, Werner J.; Schwedt, Todd J. (2016). "Treatment of Cluster Headache: The American Headache Society Evidence-Based Guidelines". Headache. 56 (7): 1093–106. doi:10.1111/head.12866. PMID 27432623.
- ^ a b c d e Fischera, M; Marziniak, M; Gralow, I; Evers, S (2008). "The Incidence and Prevalence of Cluster Headache: A Meta-Analysis of Population-Based Studies". Cephalalgia. 28 (6): 614–8. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2008.01592.x. PMID 18422717.
- ^ Gaul, C; Diener, H; Müller, OM (2011). "Cluster Headache Clinical Features and Therapeutic Options". Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. Review. 108 (33): 543–549. doi:10.3238/arztebl.2011.0543. Retrieved 12 January 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f Beck E, Sieber WJ, Trejo R (February 2005). "Management of cluster headache". Am Fam Physician (Review). 71 (4): 717–24. PMID 15742909. Archived from the original on 13 November 2015.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Capobianco, David; Dodick, David (2006). "Diagnosis and Treatment of Cluster Headache". Seminars in Neurology. 26 (2): 242–59. doi:10.1055/s-2006-939925. PMID 16628535.
- ^ a b c d e f Friedman, Benjamin Wolkin; Grosberg, Brian Mitchell (2009). "Diagnosis and Management of the Primary Headache Disorders in the Emergency Department Setting". Emergency Medicine Clinics of North America. 27 (1): 71–87, viii. doi:10.1016/j.emc.2008.09.005. PMC 2676687. PMID 19218020.
- ^ Marmura, Michael J; Pello, Scott J; Young, William B (2010). "Interictal pain in cluster headache". Cephalalgia. 30 (12): 1531–4. doi:10.1177/0333102410372423. PMID 20974600.
- ^ Meyer, Eva Laudon; Laurell, Katarina; Artto, Ville; Bendtsen, Lars; Linde, Mattias; Kallela, Mikko; Tronvik, Erling; Zwart, John-Anker; Jensen, Rikke M.; Hagen, Knut (2009). "Lateralization in cluster headache: A Nordic multicenter study". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 10 (4): 259–63. doi:10.1007/s10194-009-0129-z. PMC 3451747. PMID 19495933.
- ^ Bahra, A; May, A; Goadsby, PJ (2002). "Cluster headache: A prospective clinical study with diagnostic implications". Neurology. 58 (3): 354–61. doi:10.1212/wnl.58.3.354. PMID 11839832. Archived from the original on 9 February 2017.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Noshir Mehta; George E. Maloney; Dhirendra S. Bana; Steven J. Scrivani (20 September 2011). Head, Face, and Neck Pain Science, Evaluation, and Management: An Interdisciplinary Approach. John Wiley & Sons. pp. 199–. ISBN 978-1-118-20995-0. Archived from the original on 14 February 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e Robbins, Matthew S. (2013). "The Psychiatric Comorbidities of Cluster Headache". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 17 (2): 313. doi:10.1007/s11916-012-0313-8. PMID 23296640.
- ^ The 5-Minute Sports Medicine Consult (2 ed.). Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. 2012. p. 87. ISBN 9781451148121. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Matharu, Manjit S; Goadsby, Peter J (2014). "Cluster headache: Focus on emerging therapies". Expert Review of Neurotherapeutics. 4 (5): 895–907. doi:10.1586/14737175.4.5.895. PMID 15853515.
- ^ a b c d e f "IHS Classification ICHD-II 3.1 Cluster headache". The International Headache Society. Archived from the original on 3 November 2013. Retrieved 3 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Liang, Jen-Feng; Chen, Yung-Tai; Fuh, Jong-Ling; Li, Szu-Yuan; Liu, Chia-Jen; Chen, Tzeng-Ji; Tang, Chao-Hsiun; Wang, Shuu-Jiun (2012). "Cluster headache is associated with an increased risk of depression: A nationwide population-based cohort study". Cephalalgia. 33 (3): 182–9. doi:10.1177/0333102412469738. PMID 23212294.
- ^ Jensen, RM; Lyngberg, A; Jensen, RH (2016). "Burden of Cluster Headache". Cephalalgia. 27 (6): 535–41. doi:10.1111/j.1468-2982.2007.01330.x. PMID 17459083.
- ^ Pringsheim, Tamara (2014). "Cluster Headache: Evidence for a Disorder of Circadian Rhythm and Hypothalamic Function". The Canadian Journal of Neurological Sciences. 29 (1): 33–40. doi:10.1017/S0317167100001694. PMID 11858532.
- ^ Dodick, David W.; Eross, Eric J.; Parish, James M. (2003). "Clinical, Anatomical, and Physiologic Relationship Between Sleep and Headache". Headache: the Journal of Head and Face Pain. 43 (3): 282–92. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2003.03055.x. PMID 12603650.
- ^ Torelli, Paola; Manzoni, Gian Camillo (2002). "What predicts evolution from episodic to chronic cluster headache?". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 6 (1): 65–70. doi:10.1007/s11916-002-0026-5. PMID 11749880.
- ^ a b c d Pinessi, L.; Rainero, I.; Rivoiro, C.; Rubino, E.; Gallone, S. (2005). "Genetics of cluster headache: An update". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 6 (4): 234–6. doi:10.1007/s10194-005-0194-x. PMC 3452030. PMID 16362673.
- ^ Goadsby, Peter J. (2009). "The vascular theory of migraine—a great story wrecked by the facts". Brain. 132 (Pt 1): 6–7. doi:10.1093/brain/awn321. PMID 19098031.
- ^ Leone, Massimo; Cecchini, Alberto Proietti; Tullo, Vincenzo; Curone, Marcella; Di Fiore, Paola; Bussone, Gennaro (2013). "Cluster headache: What has changed since 1999?". Neurological Sciences. 34 (1): 71–4. doi:10.1007/s10072-013-1365-1. PMID 22193419.
- ^ Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The International Classification of Headache Disorders, 3rd edition (beta version). Cephalalgia 33(9) 629–808
- ^ Schürks, Markus; Diener, Hans-Christoph (2008). "Cluster headache and lifestyle habits". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 12 (2): 115–21. doi:10.1007/s11916-008-0022-5. PMID 18474191.
- ^ Pringsheim T. Cluster headache: evidence for a disorder of circadian rhythm and hypothalamic function.Canadian J Neurol Sciences. 2002 Feb;29(1):33-40.
- ^ de Belleroche J, Clifford Rose F, Das I, Cook GE. (1984). "Metabolic abnormality in cluster headache". Headache, 1984 Nov;24(6):310-312. 24: 310–2. PMID 6519980.
{{cite journal}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|journal=(help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ Dasilva, Alexandre F. M.; Goadsby, Peter J.; Borsook, David (2007). "Cluster headache: A review of neuroimaging findings". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 11 (2): 131–6. doi:10.1007/s11916-007-0010-1. PMID 17367592.
- ^ a b Van Vliet, J A (2003). "Features involved in the diagnostic delay of cluster headache". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 74 (8): 1123–5. doi:10.1136/jnnp.74.8.1123. PMC 1738593. PMID 12876249.
- ^ "Headache diary: helping you manage your headache" (PDF). NPS.org.au. Archived from the original (PDF) on 21 September 2013. Retrieved 2 January 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Clarke, C E (2005). "Ability of a nurse specialist to diagnose simple headache disorders compared with consultant neurologists". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 76 (8): 1170–2. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2004.057968. PMC 1739753. PMID 16024902.
- ^ "Cluster headache". MedlinePlus Medical Encyclopedia. 2 November 2012. Archived from the original on 5 April 2014. Retrieved 5 April 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Bahra, A.; Goadsby, P. J. (2004). "Diagnostic delays and mis-management in cluster headache". Acta Neurologica Scandinavica. 109 (3): 175–9. doi:10.1046/j.1600-0404.2003.00237.x. PMID 14763953.
- ^ a b Van Alboom, E; Louis, P; Van Zandijcke, M; Crevits, L; Vakaet, A; Paemeleire, K (2009). "Diagnostic and therapeutic trajectory of cluster headache patients in Flanders". Acta neurologica Belgica. 109 (1): 10–7. PMID 19402567.
- ^ a b Tfelt-Hansen, Peer C.; Jensen, Rigmor H. (2012). "Management of Cluster Headache". CNS Drugs. 26 (7): 571–80. doi:10.2165/11632850-000000000-00000. PMID 22650381.
- ^ Ahmed F (2012). "Headache disorders: differentiating and managing the common subtypes". British Journal of Pain. 6 (3): 124–32. doi:10.1177/2049463712459691. PMC 4590146. PMID 26516483.
- ^ Klapper, Jack A.; Klapper, Amy; Voss, Tracy (2000). "The Misdiagnosis of Cluster Headache: A Nonclinic, Population-Based, Internet Survey". Headache. 40 (9): 730–5. doi:10.1046/j.1526-4610.2000.00127.x. PMID 11091291.
- ^ Prakash, Sanjay; Shah, Nilima D; Chavda, Bhavna V (2010). "Cluster headache responsive to indomethacin: Case reports and a critical review of the literature". Cephalalgia. 30 (8): 975–82. doi:10.1177/0333102409357642. PMID 20656709.
- ^ Sjaastad, O; Vincent, M (2010). "Indomethacin responsive headache syndromes: Chronic paroxysmal hemicrania and Hemicrania continua. How they were discovered and what we have learned since". Functional neurology. 25 (1): 49–55. PMID 20626997.
- ^ Rizzoli, P; Mullally, WJ (September 2017). "Headache". American Journal of Medicine (Review). S0002-9343 (17): 30932–4. doi:10.1016/j.amjmed.2017.09.005. PMID 28939471.
- ^ Benoliel, Rafael (2012). "Trigeminal autonomic cephalgias". British Journal of Pain. 6 (3): 106–23. doi:10.1177/2049463712456355. PMC 4590147. PMID 26516482.
- ^ a b c May, A.; Leone, M.; Áfra, J.; Linde, M.; Sándor, P. S.; Evers, S.; Goadsby, P. J. (2006). "EFNS guidelines on the treatment of cluster headache and other trigeminal-autonomic cephalalgias". European Journal of Neurology. 13 (10): 1066–77. doi:10.1111/j.1468-1331.2006.01566.x. PMID 16987158.
- ^ Magis, Delphine; Schoenen, Jean (2011). "Peripheral Nerve Stimulation in Chronic Cluster Headache". Peripheral Nerve Stimulation. Progress in Neurological Surgery. Vol. 24. pp. 126–32. doi:10.1159/000323045. ISBN 978-3-8055-9489-9. PMID 21422783.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b c d e Martelletti, Paolo; Jensen, Rigmor H; Antal, Andrea; Arcioni, Roberto; Brighina, Filippo; De Tommaso, Marina; Franzini, Angelo; Fontaine, Denys; Heiland, Max; Jürgens, Tim P; Leone, Massimo; Magis, Delphine; Paemeleire, Koen; Palmisani, Stefano; Paulus, Walter; May, Arne (2013). "Neuromodulation of chronic headaches: Position statement from the European Headache Federation". The Journal of Headache and Pain. 14: 86. doi:10.1186/1129-2377-14-86.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Bartsch, Thorsten; Paemeleire, Koen; Goadsby, Peter J (2009). "Neurostimulation approaches to primary headache disorders". Current Opinion in Neurology. 22 (3): 262–8. doi:10.1097/wco.0b013e32832ae61e. PMID 19434793.
- ^ Evers, Stefan (2010). "Pharmacotherapy of cluster headache". Expert Opinion on Pharmacotherapy. 11 (13): 2121–7. doi:10.1517/14656566.2010.496454. PMID 20569084.
- ^ a b Matharu M (9 February 2010). "Cluster headache". Clinical evidence (Review). 2010. PMC 2907610. PMID 21718584.
- ^ Ailani, Jessica; Young, William B. (2009). "The role of nerve blocks and botulinum toxin injections in the management of cluster headaches". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 13 (2): 164–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-009-0028-7. PMID 19272284.
- ^ Nalini Vadivelu; Alan David Kaye; Jack M. Berger (28 November 2012). Essentials of palliative care. New York, NY: Springer. p. 335. ISBN 9781461451648. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Bennett, Michael H; French, Christopher; Schnabel, Alexander; Wasiak, Jason; Kranke, Peter; Weibel, Stephanie (2015). "Normobaric and hyperbaric oxygen therapy for the treatment and prevention of migraine and cluster headache". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. pp. CD005219. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD005219.pub3. PMID 26709672.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ a b Law, Simon; Derry, Sheena; Moore, R Andrew (2013). "Triptans for acute cluster headache". Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews. doi:10.1002/14651858.cd008042.pub3.
- ^ a b Paemeleire, Koen; Evers, Stefan; Goadsby, Peter J. (2008). "Medication-overuse headache in patients with cluster headache". Current Pain and Headache Reports. 12 (2): 122–7. doi:10.1007/s11916-008-0023-4. PMID 18474192.
- ^ Johnson, Jacinta L; Hutchinson, Mark R; Williams, Desmond B; Rolan, Paul (2012). "Medication-overuse headache and opioid-induced hyperalgesia: A review of mechanisms, a neuroimmune hypothesis and a novel approach to treatment". Cephalalgia. 33 (1): 52–64. doi:10.1177/0333102412467512. PMID 23144180.
- ^ Watkins, Linda R.; Hutchinson, Mark R.; Rice, Kenner C.; Maier, Steven F. (2009). "The "Toll" of Opioid-Induced Glial Activation: Improving the Clinical Efficacy of Opioids by Targeting Glia". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 30 (11): 581–91. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2009.08.002. PMC 2783351. PMID 19762094.
- ^ Saper, Joel R.; Da Silva, Arnaldo Neves (2013). "Medication Overuse Headache: History, Features, Prevention and Management Strategies". CNS Drugs. 27 (11): 867–77. doi:10.1007/s40263-013-0081-y. PMID 23925669.
- ^ Matharu, M (2010). "Cluster headache". BMJ clinical evidence. 2010. PMC 2907610. PMID 21718584.
- ^ Ishaq Abu-Arafeh; Aynur Özge (2016). Headache in Children and Adolescents: A Case-Based Approach. Springer International Publishing Switzerland. pp. 62–. ISBN 978-3-319-28628-0. Archived from the original on 10 September 2017.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Harris W.: Neuritis and Neuralgia. p. 307-12. Oxford: Oxford University Press 1926.
- ^ Bickerstaff E (1959). "The periodic migrainous neuralgia of Wilfred Harris". The Lancet. 273 (7082): 1069–71. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(59)90651-8. PMID 13655672.
- ^ Boes, CJ; Capobianco, DJ; Matharu, MS; Goadsby, PJ (2016). "Wilfred Harris' Early Description of Cluster Headache". Cephalalgia. 22 (4): 320–6. doi:10.1046/j.1468-2982.2002.00360.x. PMID 12100097.
- ^ Pearce, J M S (2007). "Gerardi van Swieten: Descriptions of episodic cluster headache". Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry. 78 (11): 1248–9. doi:10.1136/jnnp.2007.123091. PMC 2117620. PMID 17940171.
- ^ Horton BT, MacLean AR, Craig WM (1939). "A new syndrome of vascular headache: results of treatment with histamine: preliminary report". Mayo Clinic Proceedings. 14: 257.
- ^ Silberstein SD, Lipton RB, Goadsby PJ (2002). Headache in Clinical Practice (Second ed.). Taylor & Francis.[page needed]
- ^ Johnson, Tim (16 May 2013). "Researcher works to unlock mysteries of migraines". USA Today. Archived from the original on 17 May 2013. Retrieved 4 January 2013.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Lilly's investigational medicine for prevention of migraine met primary endpoint in a Phase 2b study". Archived from the original on 18 June 2015. Retrieved 18 June 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)[full citation needed] - ^ a b Sun-Edelstein, Christina; Mauskop, Alexander (2011). "Alternative Headache Treatments: Nutraceuticals, Behavioral and Physical Treatments". Headache. 51 (3): 469–83. doi:10.1111/j.1526-4610.2011.01846.x. PMID 21352222.
- ^ a b Vollenweider, Franz X.; Kometer, Michael (2010). "The neurobiology of psychedelic drugs: Implications for the treatment of mood disorders". Nature Reviews Neuroscience. 11 (9): 642–51. doi:10.1038/nrn2884. PMID 20717121.
- ^ A Study Comparing the Efficacy and Safety of TEV-48125 (Fremanezumab) for the Prevention of Chronic Cluster Headache (CCH)
- ^ A Study to Evaluate the Efficacy and Safety of TEV-48125 (Fremanezumab) for the Prevention of Episodic Cluster Headache (ECH)
