Cadder: Difference between revisions
AndrasSkot (talk | contribs) |
AndrasSkot (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
In antiquity, Cadder was the site of a [[Castra|Roman fort]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://canmore.org.uk/site/45247/cadder|title=Cadder|accessdate=2017-11-18 |last= |first= |work=[[CANMORE]] |publisher=[[Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland]]}}</ref> on the route of the [[Antonine Wall]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://canmore.org.uk/site/45239/antonine-wall-wilderness-plantation-easter-cawder-cadder|title= |
In antiquity, Cadder was the site of a [[Castra|Roman fort]]<ref>{{cite web |url=https://canmore.org.uk/site/45247/cadder|title=Cadder|accessdate=2017-11-18 |last= |first= |work=[[CANMORE]] |publisher=[[Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland]]}}</ref> on the route of the [[Antonine Wall]].<ref>{{cite web |url=https://canmore.org.uk/site/45239/antonine-wall-wilderness-plantation-easter-cawder-cadder|title= |
||
Antonine Wall: Wilderness Plantation - Easter Cawder - Cadder |
Antonine Wall: Wilderness Plantation - Easter Cawder - Cadder |
||
|accessdate=2017-11-18 |last= |first= |work=[[CANMORE]] |publisher=[[Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland]]}}</ref> Its neighbouring forts are [[Balmuildy]] to the west and [[Kirkintilloch]] to the east although there are intermediate [[Castellum|fortlets]] at [[Wilderness Plantation]] to the west and [[Glasgow Bridge, Kirkintilloch|Glasgow Bridge]] to the east.<ref>{{cite web|title=OS 25 inch map 1892-1949, with Bing opacity slider|url=http://maps.nls.uk/geo/explore/#zoom=16&lat=55.9263&lon=-4.2142&layers=168&b=1|website=National Library of Scotland|publisher=Ordnance Survey|accessdate=12 October 2017}}</ref> John Clarke of the Glasgow Archaeological Society excavated the remains in the 1930s.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Journal of Roman Studies (Volume 24, Issue 1, 1934, pp. 104-105)|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-roman-studies/article/clarke-john-the-roman-fort-at-cadder-near-glasgow-being-an-account-of-excavations-conducted-under-the-auspices-of-the-glasgow-archaeological-society-glasgow-jackson-wylie-and-co-1933-pp-xii-93-with-10-plates-and-19-figures-12s-6d/42906508EB598FC52B667A844FCBFB38|website=Cambridge University Press|accessdate=29 April 2018}}</ref> The site was destroyed by sand quarrying in the 1940s.<ref>{{cite web|title=CADDER: FORT|url=http://www.antoninewall.org/system/files/documents/Cadder-%20Fort.pdf|website=Frontiers of the Roman Wall|accessdate=25 November 2017}}</ref> A sketch of the medieval motte made by Skinner still survives.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Rohl|first1=Darrell, Jesse|title=More than a Roman Monument: A Place-centred Approach to the Long-term History and Archaeology of the Antonine Wall|url=http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/9458/1/DarrellRohl_PhDThesis_2014.pdf?DDD6+#page=308|website=Durham Theses|publisher=Durham University. Available at Durham E-Theses Online ref: 9458|accessdate=14 October 2017}}</ref> One find at Cadder was an oil lamp which is associated with the bath house of the fort.<ref>{{cite web|title=Oil Lamp, Cadder|url=https://vimeo.com/134602884|accessdate=12 November 2017}}</ref> Before the Reformation the lands of Cadder and the kirk belonged to the Bishops of Glasgow.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Brotchie|first1=T.C.F.|title=Some Sylvan Scenes near Glasgow|date=1921|publisher=Aird & Coghill|location=Glasgow|pages=35–38|url=https://archive.org/stream/somesylvanscenesbrot#page/36/mode/2up|accessdate=3 December 2017}}</ref> In the 18th century James Dunlop of [[Garnkirk]] being a wealthy landowner opposed [[Thomas Muir of Huntershill|Thomas Muir]] and the congregation at Cadder over who appointed their minister.<ref>{{cite news|title=Thomas Muir - new evidence unearthed|url=https://www.gla.ac.uk/news/archiveofnews/2016/december/headline_504475_en.html|accessdate=24 February 2018|agency=University news|publisher=Glasgow University|date=14 December 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Miller|first1=Phil|title=Newly discovered papers unveil further details about the life of Thomas Muir, 'Father of Democracy'|url=http://www.heraldscotland.com/news/14965475.Newly_discovered_papers_unveil_further_details_about_the_life_of_Thomas_Muir__Scottish_political_reformer/|accessdate=24 February 2018|agency=The Herald|date=14 December 2016}}</ref> Cadder Parish Church was described in the 19th century as a neat modern Gothic church.<ref>{{cite book|last1=M'Donald|first1=Hugh|title=Rambles Round Glasgow|date=1856|publisher=Thomas Murray and Son|location=Glasgow|page=376|edition=2nd|url=https://archive.org/stream/ramblesroundgla00mdogoog#page/n386/mode/2up|accessdate=30 November 2017}}</ref> Cadder House was a property held by the [[Clan Stirling|Stirling family]] for generations.<ref>[http://gdl.cdlr.strath.ac.uk/smihou/smihou014.htm Glasgow Digital Library "Cadder House"]</ref> |
|accessdate=2017-11-18 |last= |first= |work=[[CANMORE]] |publisher=[[Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland]]}}</ref> Its neighbouring forts are [[Balmuildy]] to the west and [[Kirkintilloch]] to the east although there are intermediate [[Castellum|fortlets]] at [[Wilderness Plantation]] to the west and [[Glasgow Bridge, Kirkintilloch|Glasgow Bridge]] to the east.<ref>{{cite web|title=OS 25 inch map 1892-1949, with Bing opacity slider|url=http://maps.nls.uk/geo/explore/#zoom=16&lat=55.9263&lon=-4.2142&layers=168&b=1|website=National Library of Scotland|publisher=Ordnance Survey|accessdate=12 October 2017}}</ref> The [[Second Legion Augusta|Second Legion]] may have been responsible for building the fort.<ref>{{cite web|title=RIB 2188. Building inscription of the Second Legion Augusta|url=https://romaninscriptionsofbritain.org/inscriptions/2188|website=Roman Inscriptions of Britain|accessdate=18 November 2017}}</ref> John Clarke of the Glasgow Archaeological Society excavated the remains in the 1930s.<ref>{{cite web|title=The Journal of Roman Studies (Volume 24, Issue 1, 1934, pp. 104-105)|url=https://www.cambridge.org/core/journals/journal-of-roman-studies/article/clarke-john-the-roman-fort-at-cadder-near-glasgow-being-an-account-of-excavations-conducted-under-the-auspices-of-the-glasgow-archaeological-society-glasgow-jackson-wylie-and-co-1933-pp-xii-93-with-10-plates-and-19-figures-12s-6d/42906508EB598FC52B667A844FCBFB38|website=Cambridge University Press|accessdate=29 April 2018}}</ref> The site was destroyed by sand quarrying in the 1940s.<ref>{{cite web|title=CADDER: FORT|url=http://www.antoninewall.org/system/files/documents/Cadder-%20Fort.pdf|website=Frontiers of the Roman Wall|accessdate=25 November 2017}}</ref> A sketch of the medieval motte made by Skinner still survives.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Rohl|first1=Darrell, Jesse|title=More than a Roman Monument: A Place-centred Approach to the Long-term History and Archaeology of the Antonine Wall|url=http://etheses.dur.ac.uk/9458/1/DarrellRohl_PhDThesis_2014.pdf?DDD6+#page=308|website=Durham Theses|publisher=Durham University. Available at Durham E-Theses Online ref: 9458|accessdate=14 October 2017}}</ref> One find at Cadder was an oil lamp which is associated with the bath house of the fort.<ref>{{cite web|title=Oil Lamp, Cadder|url=https://vimeo.com/134602884|accessdate=12 November 2017}}</ref> Before the Reformation the lands of Cadder and the kirk belonged to the Bishops of Glasgow.<ref>{{cite book|last1=Brotchie|first1=T.C.F.|title=Some Sylvan Scenes near Glasgow|date=1921|publisher=Aird & Coghill|location=Glasgow|pages=35–38|url=https://archive.org/stream/somesylvanscenesbrot#page/36/mode/2up|accessdate=3 December 2017}}</ref> In the 18th century James Dunlop of [[Garnkirk]] being a wealthy landowner opposed [[Thomas Muir of Huntershill|Thomas Muir]] and the congregation at Cadder over who appointed their minister.<ref>{{cite news|title=Thomas Muir - new evidence unearthed|url=https://www.gla.ac.uk/news/archiveofnews/2016/december/headline_504475_en.html|accessdate=24 February 2018|agency=University news|publisher=Glasgow University|date=14 December 2016}}</ref><ref>{{cite news|last1=Miller|first1=Phil|title=Newly discovered papers unveil further details about the life of Thomas Muir, 'Father of Democracy'|url=http://www.heraldscotland.com/news/14965475.Newly_discovered_papers_unveil_further_details_about_the_life_of_Thomas_Muir__Scottish_political_reformer/|accessdate=24 February 2018|agency=The Herald|date=14 December 2016}}</ref> Cadder Parish Church was described in the 19th century as a neat modern Gothic church.<ref>{{cite book|last1=M'Donald|first1=Hugh|title=Rambles Round Glasgow|date=1856|publisher=Thomas Murray and Son|location=Glasgow|page=376|edition=2nd|url=https://archive.org/stream/ramblesroundgla00mdogoog#page/n386/mode/2up|accessdate=30 November 2017}}</ref> Cadder House was a property held by the [[Clan Stirling|Stirling family]] for generations.<ref>[http://gdl.cdlr.strath.ac.uk/smihou/smihou014.htm Glasgow Digital Library "Cadder House"]</ref> |
||
Cadder has a large [[cemetery]], is also the site of Strathkelvin Retail Park and [[Low Moss (HM Prison)]].<ref>[http://www.glasgowguide.co.uk/images_cadder_cemetery.html Glasgow Guide Cadder Cemetery]</ref> |
Cadder has a large [[cemetery]], is also the site of Strathkelvin Retail Park and [[Low Moss (HM Prison)]].<ref>[http://www.glasgowguide.co.uk/images_cadder_cemetery.html Glasgow Guide Cadder Cemetery]</ref> |
||
Revision as of 12:01, 29 April 2018
Cadder
| |
|---|---|
 Cadder parish church erected in 1830[1] | |
Location within East Dunbartonshire | |
| OS grid reference | NS6172 |
| Council area | |
| Country | Scotland |
| Sovereign state | United Kingdom |
| Police | Scotland |
| Fire | Scottish |
| Ambulance | Scottish |
| UK Parliament | |
| Scottish Parliament | |
Cadder (Scottish Gaelic: Coile Dobhair) is a district of the town of Bishopbriggs, East Dunbartonshire, Scotland. It is located 7 km north of Glasgow city centre, 0.5 km south of the River Kelvin, and approximately 1.5 km north-east of Bishopbriggs town centre, sited on the route of the Forth and Clyde Canal. There is a Glasgow council housing scheme of a similar name, generally pronounced Cawder, in the district of Lambhill some 4 km to the west along the Canal, which was built in the early 1950s. Similarly, within Cadder, there is also Cawder Golf Club, which also uses that alternative spelling.
History
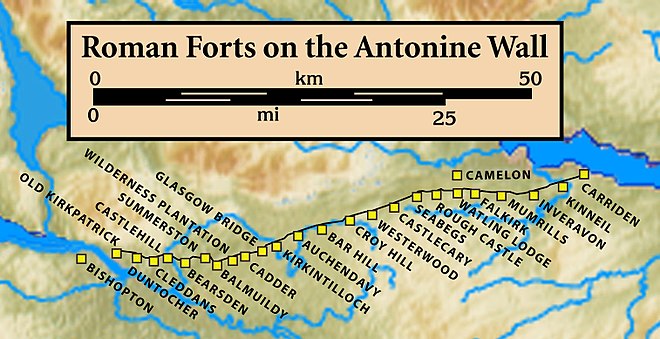
In antiquity, Cadder was the site of a Roman fort[2] on the route of the Antonine Wall.[3] Its neighbouring forts are Balmuildy to the west and Kirkintilloch to the east although there are intermediate fortlets at Wilderness Plantation to the west and Glasgow Bridge to the east.[4] The Second Legion may have been responsible for building the fort.[5] John Clarke of the Glasgow Archaeological Society excavated the remains in the 1930s.[6] The site was destroyed by sand quarrying in the 1940s.[7] A sketch of the medieval motte made by Skinner still survives.[8] One find at Cadder was an oil lamp which is associated with the bath house of the fort.[9] Before the Reformation the lands of Cadder and the kirk belonged to the Bishops of Glasgow.[10] In the 18th century James Dunlop of Garnkirk being a wealthy landowner opposed Thomas Muir and the congregation at Cadder over who appointed their minister.[11][12] Cadder Parish Church was described in the 19th century as a neat modern Gothic church.[13] Cadder House was a property held by the Stirling family for generations.[14]
Cadder has a large cemetery, is also the site of Strathkelvin Retail Park and Low Moss (HM Prison).[15]
Gallery
-
watchhouse and iron mortsafe at Cadder Parish Church
-
Cadder stables
-
Strathkelvin retail park
-
Cadder Road sign

References
- ^ Wilson, John Marius (1882). The gazetteer of Scotland. Edinburgh: W. & A.K. Johnston. p. 65. Retrieved 27 February 2018.
- ^ "Cadder". CANMORE. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. Retrieved 2017-11-18.
- ^ "Antonine Wall: Wilderness Plantation - Easter Cawder - Cadder". CANMORE. Royal Commission on the Ancient and Historical Monuments of Scotland. Retrieved 2017-11-18.
- ^ "OS 25 inch map 1892-1949, with Bing opacity slider". National Library of Scotland. Ordnance Survey. Retrieved 12 October 2017.
- ^ "RIB 2188. Building inscription of the Second Legion Augusta". Roman Inscriptions of Britain. Retrieved 18 November 2017.
- ^ "The Journal of Roman Studies (Volume 24, Issue 1, 1934, pp. 104-105)". Cambridge University Press. Retrieved 29 April 2018.
- ^ "CADDER: FORT" (PDF). Frontiers of the Roman Wall. Retrieved 25 November 2017.
- ^ Rohl, Darrell, Jesse. "More than a Roman Monument: A Place-centred Approach to the Long-term History and Archaeology of the Antonine Wall" (PDF). Durham Theses. Durham University. Available at Durham E-Theses Online ref: 9458. Retrieved 14 October 2017.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ^ "Oil Lamp, Cadder". Retrieved 12 November 2017.
- ^ Brotchie, T.C.F. (1921). Some Sylvan Scenes near Glasgow. Glasgow: Aird & Coghill. pp. 35–38. Retrieved 3 December 2017.
- ^ "Thomas Muir - new evidence unearthed". Glasgow University. University news. 14 December 2016. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ^ Miller, Phil (14 December 2016). "Newly discovered papers unveil further details about the life of Thomas Muir, 'Father of Democracy'". The Herald. Retrieved 24 February 2018.
- ^ M'Donald, Hugh (1856). Rambles Round Glasgow (2nd ed.). Glasgow: Thomas Murray and Son. p. 376. Retrieved 30 November 2017.
- ^ Glasgow Digital Library "Cadder House"
- ^ Glasgow Guide Cadder Cemetery





