Optic vesicle: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
| GivesRiseTo = [[Human eye]]s |
| GivesRiseTo = [[Human eye]]s |
||
}} |
}} |
||
The [[Human eyes|eyes]] begin to develop as a pair of [[diverticula]] from the lateral aspects of the [[forebrain]]. These diverticula make their appearance before the closure of the anterior end of the [[neural tube]]; after the closure of the tube they are known as the '''optic vesicles'''. |
The [[Human eyes|eyes]] begin to develop as a pair of [[diverticula]] from the lateral aspects of the [[forebrain]]. These diverticula make their appearance before the closure of the anterior end of the [[neural tube]]; after the closure of the tube they are known as the '''optic vesicles'''. Previous studies of optic vesicles suggest that the surrounding extraocular tissues - the surface ectoderm and extraocular mesenchyme - are necessary for normal eye growth and differentiation.<ref>Fuhrmann, S. (2010). Eye Morphogenesis and Patterning of the Optic Vesicle. Current Topics in Developmental Biology Invertebrate and Vertebrate Eye Development, 61-84. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-385044-7.00003-5</ref> |
||
Previous studies suggest that the surrounding extraocular tissues - the surface ectoderm and extraocular mesenchyme - are necessary for normal eye growth and differentiation.<ref>Fuhrmann, S. (2010). Eye Morphogenesis and Patterning of the Optic Vesicle. Current Topics in Developmental Biology Invertebrate and Vertebrate Eye Development, 61-84. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-385044-7.00003-5</ref> |
|||
They project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the [[optic stalk]]. |
They project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the [[optic stalk]]. |
||
Revision as of 15:27, 14 June 2018
| Optic vesicle | |
|---|---|
 Transverse section of head of chick embryo of forty-eight hours’ incubation. (Optic vesicle labeled at lower right.) | |
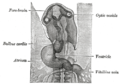
 Human embryo about fifteen days old. Brain and heart represented from right side. Digestive tube and yolk sac in median section. (Optic vesicle labeled at center top.) | |
| Details | |
| Carnegie stage | 11 |
| Gives rise to | Human eyes |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | vesicula optica; vesicula ophthalmica |
| TE | vesicle_by_E5.14.3.4.2.2.4 E5.14.3.4.2.2.4 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The eyes begin to develop as a pair of diverticula from the lateral aspects of the forebrain. These diverticula make their appearance before the closure of the anterior end of the neural tube; after the closure of the tube they are known as the optic vesicles. Previous studies of optic vesicles suggest that the surrounding extraocular tissues - the surface ectoderm and extraocular mesenchyme - are necessary for normal eye growth and differentiation.[1]
They project toward the sides of the head, and the peripheral part of each expands to form a hollow bulb, while the proximal part remains narrow and constitutes the optic stalk.
Additional images
-
Head of chick embryo of about thirty-eight hours’ incubation, viewed from the ventral surface. X 26
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1001 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 1001 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
External links
- eye-012—Embryo Images at University of North Carolina
- Overview at vision.ca
- Overview at temple.edu
- ^ Fuhrmann, S. (2010). Eye Morphogenesis and Patterning of the Optic Vesicle. Current Topics in Developmental Biology Invertebrate and Vertebrate Eye Development, 61-84. doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-385044-7.00003-5