Apiose: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
}} |
}} |
||
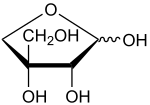
''' Apiose''' is a branched-chain [[sugar]] found as residues in [[galacturonan]]s-type [[pectin]]s; that occurs in [[parsley]] and many other [[plant]]s. Apiose is a component of cell wall polysaccharides.<ref>[https://academic.oup.com/glycob/article/26/5/430/2355559]</ref> |
''' Apiose''' is a branched-chain [[sugar]] found as residues in [[galacturonan]]s-type [[pectin]]s; that occurs in [[parsley]] and many other [[plant]]s. Apiose is a component of [[cell wall]] [[polysaccharides]].<ref>[https://academic.oup.com/glycob/article/26/5/430/2355559]</ref> |
||
[[Apiose 1-reductase]] uses [[D-apiitol]] and [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide|NAD<sup>+</sup>]] to produce D-apiose, [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide|NADH]], and [[hydrogen ion|H<sup>+</sup>]]. |
[[Apiose 1-reductase]] uses [[D-apiitol]] and [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide|NAD<sup>+</sup>]] to produce D-apiose, [[nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide|NADH]], and [[hydrogen ion|H<sup>+</sup>]]. |
||
Revision as of 18:10, 23 July 2018
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
2,3,4-trihydroxy-3-(hydroxymethyl)butanal
| |
| Other names
D-apiose
3-C-(hydroxymethyl)-D-glycerotetrose apio-β-D-furanosyl | |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C5H10O5 | |
| Molar mass | 150.13 g/mol |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
Apiose is a branched-chain sugar found as residues in galacturonans-type pectins; that occurs in parsley and many other plants. Apiose is a component of cell wall polysaccharides.[1]
Apiose 1-reductase uses D-apiitol and NAD+ to produce D-apiose, NADH, and H+.
Flavone apiosyltransferase uses UDP-apiose and 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone 7-O-beta-D-glucoside to produce UDP, 5,7,4'-trihydroxyflavone (apigenin), and 7-O-[beta-D-apiosyl-(1->2)-beta-D-glucoside.
References
External links
Look up apiose in Wiktionary, the free dictionary.
