Wind turbine: Difference between revisions
| Line 34: | Line 34: | ||
{{Main|Wind power}} |
{{Main|Wind power}} |
||
[[Wind#Wind power density|Wind Power Density]] (WPD) is a quantitative measure of wind energy available at any location. It is the mean annual power available per square meter of swept area of a turbine, and is calculated for different heights above ground. Calculation of [[wind profile power law#Wind power density|wind power density]] includes the effect of wind velocity and air density.<ref>{{cite web |url=http://www.nrel.gov/gis/wind.html |title=NREL: Dynamic Maps, GIS Data, and Analysis Tools – Wind Maps |publisher=Nrel.gov |date=3 September 2013 |accessdate=6 November 2013}}</ref> |
|||
Wind turbines are classified by the wind speed they are designed for, from class I to class |
Wind turbines are classified by the wind speed they are designed for, from class I to class III, with A to C referring to the turbulence intensity of the wind. <ref>{{cite web |title=Appendix II IEC Classification of Wind Turbines |url=https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.1002/9781118900116.app2 |publisher=Wind Resource Assessment and Micro-siting, Science and Engineering |accessdate=29 August 2018}}</ref> |
||
{| class=wikitable |
{| class=wikitable |
||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
!Class!!Avg Wind Speed (m/s)!!Turbulence |
!Class!!Avg Wind Speed (m/s)!!Turbulence |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| IA || 10 || |
| IA || 10 || 16% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| IB || 10 || |
| IB || 10 || 14% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| IC || 10 || 12% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| IIA || 8.5 || 16% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| IIB || 8.5 || 14% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| IIC || 7.5 || 12% |
||
|- |
|- |
||
| |
| IIIA || 7.5 || 16% |
||
|- |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
|- |
|||
| IIIC || 7.5 || 12% |
|||
|- |
|- |
||
| ⚫ | |||
|} |
|} |
||
Revision as of 07:53, 29 August 2018

| Part of a series on |
| Renewable energy |
|---|
 |
A wind turbine is a device that converts the wind's kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Wind turbines are manufactured in a wide range of vertical and horizontal axis. The smallest turbines are used for applications such as battery charging for auxiliary power for boats or caravans or to power traffic warning signs. Slightly larger turbines can be used for making contributions to a domestic power supply while selling unused power back to the utility supplier via the electrical grid. Arrays of large turbines, known as wind farms, are becoming an increasingly important source of intermittent renewable energy and are used by many countries as part of a strategy to reduce their reliance on fossil fuels. One assessment claimed that, as of 2009[update], wind had the "lowest relative greenhouse gas emissions, the least water consumption demands and... the most favourable social impacts" compared to photovoltaic, hydro, geothermal, coal and gas.[1]
History

Wind power was probably used in Persia (present-day Iran) about 500–900 AD.[2] The windwheel of Hero of Alexandria marks one of the first recorded instances of wind powering a machine in history.[3][4] However, the first known practical wind power plants were built in Sistan, an Eastern province of Iran, from the 7th century. These "Panemone" were vertical axle windmills, which had long vertical drive shafts with rectangular blades.[5] Made of six to twelve sails covered in reed matting or cloth material, these windmills were used to grind grain or draw up water, and were used in the gristmilling and sugarcane industries.[6]
Wind power first appeared in Europe during the Middle Ages. The first historical records of their use in England date to the 11th or 12th centuries and there are reports of German crusaders taking their windmill-making skills to Syria around 1190.[7] By the 14th century, Dutch windmills were in use to drain areas of the Rhine delta. Advanced wind turbines were described by Croatian inventor Fausto Veranzio. In his book Machinae Novae (1595) he described vertical axis wind turbines with curved or V-shaped blades.
The first electricity-generating wind turbine was a battery charging machine installed in July 1887 by Scottish academic James Blyth to light his holiday home in Marykirk, Scotland.[8] Some months later American inventor Charles F. Brush was able to build the first automatically operated wind turbine after consulting local University professors and colleagues Jacob S. Gibbs and Brinsley Coleberd and successfully getting the blueprints peer-reviewed for electricity production in Cleveland, Ohio.[8] Although Blyth's turbine was considered uneconomical in the United Kingdom,[8] electricity generation by wind turbines was more cost effective in countries with widely scattered populations.[7]

In Denmark by 1900, there were about 2500 windmills for mechanical loads such as pumps and mills, producing an estimated combined peak power of about 30 MW. The largest machines were on 24-meter (79 ft) towers with four-bladed 23-meter (75 ft) diameter rotors. By 1908 there were 72 wind-driven electric generators operating in the United States from 5 kW to 25 kW. Around the time of World War I, American windmill makers were producing 100,000 farm windmills each year, mostly for water-pumping.[10]
By the 1930s, wind generators for electricity were common on farms, mostly in the United States where distribution systems had not yet been installed. In this period, high-tensile steel was cheap, and the generators were placed atop prefabricated open steel lattice towers.
A forerunner of modern horizontal-axis wind generators was in service at Yalta, USSR in 1931. This was a 100 kW generator on a 30-meter (98 ft) tower, connected to the local 6.3 kV distribution system. It was reported to have an annual capacity factor of 32 percent, not much different from current wind machines.[11][12]
In the autumn of 1941, the first megawatt-class wind turbine was synchronized to a utility grid in Vermont. The Smith-Putnam wind turbine only ran for 1,100 hours before suffering a critical failure. The unit was not repaired, because of shortage of materials during the war.
The first utility grid-connected wind turbine to operate in the UK was built by John Brown & Company in 1951 in the Orkney Islands.[8][13]
Despite these diverse developments, developments in fossil fuel systems almost entirely eliminated any wind turbine systems larger than supermicro size. In the early 1970s, however, anti-nuclear protests in Denmark spurred artisan mechanics to develop microturbines of 22 kW. Organizing owners into associations and co-operatives lead to the lobbying of the government and utilities and provided incentives for larger turbines throughout the 1980s and later. Local activists in Germany, nascent turbine manufacturers in Spain, and large investors in the United States in the early 1990s then lobbied for policies that stimulated the industry in those countries.
Resources
Wind Power Density (WPD) is a quantitative measure of wind energy available at any location. It is the mean annual power available per square meter of swept area of a turbine, and is calculated for different heights above ground. Calculation of wind power density includes the effect of wind velocity and air density.[14]
Wind turbines are classified by the wind speed they are designed for, from class I to class III, with A to C referring to the turbulence intensity of the wind. [15]
| Class | Avg Wind Speed (m/s) | Turbulence |
|---|---|---|
| IA | 10 | 16% |
| IB | 10 | 14% |
| IC | 10 | 12% |
| IIA | 8.5 | 16% |
| IIB | 8.5 | 14% |
| IIC | 7.5 | 12% |
| IIIA | 7.5 | 16% |
| IIIB | 7.5 | 14% |
| IIIC | 7.5 | 12% |
Efficiency
Conservation of mass requires that the amount of air entering and exiting a turbine must be equal. Accordingly, Betz's law gives the maximal achievable extraction of wind power by a wind turbine as 16/27 (59.3%) of the total kinetic energy of the air flowing through the turbine.[16]
The maximum theoretical power output of a wind machine is thus 16/27 times the kinetic energy of the air passing through the effective disk area of the machine. If the effective area of the disk is A, and the wind velocity v, the maximum theoretical power output P is:
- ,
where ρ is the air density.
As wind is free (no fuel cost), wind-to-rotor efficiency (including rotor blade friction and drag) is one of many aspects impacting the final price of wind power.[17] Further inefficiencies, such as gearbox losses, generator and converter losses, reduce the power delivered by a wind turbine. To protect components from undue wear, extracted power is held constant above the rated operating speed as theoretical power increases at the cube of wind speed, further reducing theoretical efficiency. In 2001, commercial utility-connected turbines deliver 75% to 80% of the Betz limit of power extractable from the wind, at rated operating speed.[18][19][needs update]
Efficiency can decrease slightly over time, one of the main reasons being dust and insect carcasses on the blades which alters the aerodynamic profile and essentially reduces the lift to drag ratio of the airfoil. Analysis of 3128 wind turbines older than 10 years in Denmark showed that half of the turbines had no decrease, while the other half saw a production decrease of 1.2% per year.[20] Vertical turbine designs have much lower efficiency than standard horizontal designs.[21]
Types

Wind turbines can rotate about either a horizontal or a vertical axis, the former being both older and more common.[22] They can also include blades, or be bladeless.[23] Vertical designs produce less power and are less common.[24]
Horizontal axis




Large three-bladed horizontal-axis wind turbines (HAWT), with the blades upwind of the tower produce the overwhelming majority of windpower in the world today. These turbines have the main rotor shaft and electrical generator at the top of a tower, and must be pointed into the wind. Small turbines are pointed by a simple wind vane, while large turbines generally use a wind sensor coupled with a yaw system. Most have a gearbox, which turns the slow rotation of the blades into a quicker rotation that is more suitable to drive an electrical generator.[25] Some turbines use a different type of generator suited to slower rotational speed input. These don't need a gearbox, and are called direct-drive, meaning they couple the rotor directly to the generator with no gearbox in between. While permanent magnet direct-drive generators can be more costly due to the rare earth materials required, these gearless turbines are sometimes preferred over gearbox generators because they "eliminate the gear-speed increaser, which is susceptible to significant accumulated fatigue torque loading, related reliability issues, and maintenance costs."[26]

Most horizontal axis turbines have their rotors upwind of its supporting tower. Downwind machines have been built, because they don't need an additional mechanism for keeping them in line with the wind. In high winds, the blades can also be allowed to bend which reduces their swept area and thus their wind resistance. Despite these advantages, upwind designs are preferred, because the change in loading from the wind as each blade passes behind the supporting tower can cause damage to the turbine.
Turbines used in wind farms for commercial production of electric power are usually three-bladed. These have low torque ripple, which contributes to good reliability. The blades are usually colored white for daytime visibility by aircraft and range in length from 20 to 80 meters (66 to 262 ft). The size and height of turbines increase year by year. Offshore wind turbines are built up to 8MW today and have a blade length up to 80 meters (260 ft). Usual tubular steel towers of multi megawatt turbines have a height of 70 m to 120 m and in extremes up to 160 m.
Vertical axis
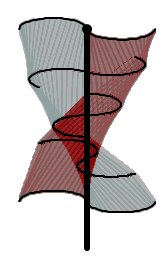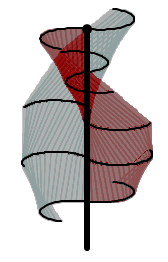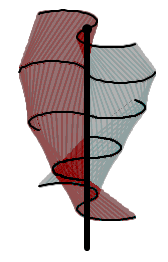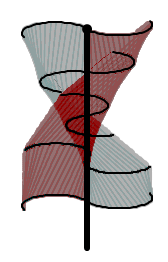
Vertical-axis wind turbines (or VAWTs) have the main rotor shaft arranged vertically. One advantage of this arrangement is that the turbine does not need to be pointed into the wind to be effective, which is an advantage on a site where the wind direction is highly variable. It is also an advantage when the turbine is integrated into a building because it is inherently less steerable. Also, the generator and gearbox can be placed near the ground, using a direct drive from the rotor assembly to the ground-based gearbox, improving accessibility for maintenance. However, these designs produce much less energy averaged over time, which is a major drawback.[24][27]
The key disadvantages include the relatively low rotational speed with the consequential higher torque and hence higher cost of the drive train, the inherently lower power coefficient, the 360-degree rotation of the aerofoil within the wind flow during each cycle and hence the highly dynamic loading on the blade, the pulsating torque generated by some rotor designs on the drive train, and the difficulty of modelling the wind flow accurately and hence the challenges of analysing and designing the rotor prior to fabricating a prototype.[28]
When a turbine is mounted on a rooftop the building generally redirects wind over the roof and this can double the wind speed at the turbine. If the height of a rooftop mounted turbine tower is approximately 50% of the building height it is near the optimum for maximum wind energy and minimum wind turbulence. While wind speeds within the built environment are generally much lower than at exposed rural sites,[29][30] noise may be a concern and an existing structure may not adequately resist the additional stress.
Subtypes of the vertical axis design include:
"Eggbeater" turbines, or Darrieus turbines, were named after the French inventor, Georges Darrieus.[31] They have good efficiency, but produce large torque ripple and cyclical stress on the tower, which contributes to poor reliability. They also generally require some external power source, or an additional Savonius rotor to start turning, because the starting torque is very low. The torque ripple is reduced by using three or more blades which results in greater solidity of the rotor. Solidity is measured by blade area divided by the rotor area. Newer Darrieus type turbines are not held up by guy-wires but have an external superstructure connected to the top bearing.[32]
A subtype of Darrieus turbine with straight, as opposed to curved, blades. The cycloturbine variety has variable pitch to reduce the torque pulsation and is self-starting.[33] The advantages of variable pitch are: high starting torque; a wide, relatively flat torque curve; a higher coefficient of performance; more efficient operation in turbulent winds; and a lower blade speed ratio which lowers blade bending stresses. Straight, V, or curved blades may be used.[34]
These are drag-type devices with two (or more) scoops that are used in anemometers, Flettner vents (commonly seen on bus and van roofs), and in some high-reliability low-efficiency power turbines. They are always self-starting if there are at least three scoops.
Twisted Savonius is a modified savonius, with long helical scoops to provide smooth torque. This is often used as a rooftop windturbine and has even been adapted for ships.[35]
Parallel
The parallel turbine is similar to the crossflow fan or centrifugal fan. It uses the ground effect. Vertical axis turbines of this type have been tried for many years: a unit producing 10 kW was built by Israeli wind pioneer Bruce Brill in the 1980s.[36][unreliable source?]
Unconventional types
Design and construction


Wind turbine design is a careful balance of cost, energy output, and fatigue life. These factors are balanced using a range of computer modelling techniques.[37]
Components
Wind turbines convert wind energy to electrical energy for distribution. Conventional horizontal axis turbines can be divided into three components:
- The rotor, which is approximately 20% of the wind turbine cost, includes the blades for converting wind energy to low speed rotational energy.
- The generator, which is approximately 34% of the wind turbine cost, includes the electrical generator,[38][39] the control electronics, and most likely a gear box (e.g. planetary gear box),[40] adjustable-speed drive or continuously variable transmission[41] component for converting the low-speed incoming rotation to high-speed rotation suitable for generating electricity.
- The surrounding structure, which is approximately 15% of the wind turbine cost, includes the tower and rotor yaw mechanism.[42]

A 1.5 MW wind turbine of a type frequently seen in the United States has a tower 80 meters (260 ft) high. The rotor assembly (blades and hub) weighs 22,000 kilograms (48,000 lb). The nacelle, which contains the generator, weighs 52,000 kilograms (115,000 lb). The concrete base for the tower is constructed using 26,000 kilograms (58,000 lb) reinforcing steel and contains 190 cubic meters (250 cu yd) of concrete. The base is 15 meters (50 ft) in diameter and 2.4 meters (8 ft) thick near the center.[43]
Turbine monitoring and diagnostics
Due to data transmission problems, structural health monitoring of wind turbines is usually performed using several accelerometers and strain gages attached to the nacelle to monitor the gearbox and equipments. Currently, digital image correlation and stereophotogrammetry are used to measure dynamics of wind turbine blades. These methods usually measure displacement and strain to identify location of defects. Dynamic characteristics of non-rotating wind turbines have been measured using digital image correlation and photogrammetry.[44] Three dimensional point tracking has also been used to measure rotating dynamics of wind turbines.[45]
Materials and recent developments
Materials that are typically used for the rotor blades in wind turbines are composites, as they tend to have a high stiffness, high strength, high fatigue resistance, and low weight.[46] Typical resins used for these composites include polyester and epoxy, while glass and carbon fibers have been used for the reinforcing material.[47] Construction may use manual layup techniques or composite resin injection molding. As the price of glass fibers is only about one tenth the price of carbon fiber, glass fiber is still dominant.
New designs
As competition in the wind market increases, companies are seeking ways to draw greater efficiency from their designs. One of the predominant ways wind turbines have gained performance is by increasing rotor diameters, and thus blade length. Retrofitting current turbines with larger blades mitigates the need and risks associated with a system-level redesign. As the size of the blade increases, its tendency to deflect also increases. Thus, from a materials perspective, the stiffness-to-weight is of major importance. As the blades need to function over a 100 million load cycles over a period of 20–25 years, the fatigue life of the blade materials is also of utmost importance. By incorporating carbon fiber into parts of existing blade systems, manufacturers may increase the length of the blades without increasing their overall weight. For instance, the spar cap, a structural element of a turbine blade, commonly experiences high tensile loading, making it an ideal candidate to utilize the enhanced tensile properties of carbon fiber in comparison to glass fiber.[47] Higher stiffness and lower density translates to thinner, lighter blades offering equivalent performance. In a 10-MW turbine—which will become more common in offshore systems by 2021—blades may reach over 100 m in length and weigh up to 50 metric tons when fabricated out of glass fiber. A switch to carbon fiber in the structural spar of the blade yields weight savings of 20 to 30 percent, or approximately 15 metric tons.[48]
Materials for blades
Some of the most common materials which are being used for turbine blades now and will be in the future are summarized below:
Glass and carbon fibers
The stiffness of composites is determined by the stiffness of fibers and their volume content. Typically, E-glass fibers are used as main reinforcement in the composites. Typically, the glass/epoxy composites for wind blades contain up to 75 weight % glass. This increases the stiffness, tensile and compression strength. A promising source of the composite materials in the future is glass fibers with modified compositions like S-glass, R-glass etc. Some other special glasses developed by Owens Corning are ECRGLAS, Advantex and most recently WindStrand glass fibers. [49]
Hybrid reinforcements
These include E-glass/carbon, E-glass/aramid and they present an exciting alternative to pure glass or carbon reinforcements. that the full replacement would lead to 80% weight savings, and cost increase by 150%, while a partial (30%) replacement would lead to only 90% cost increase and 50% weight reduction for 8 m turbine. The world currently longest wind turbine rotor blade, the 88.4 m long blade from LM Wind Power is made of carbon/glass hybrid composites. However, additional investigations are required for the optimal composition of the materials [50]
Nano-engineered polymers and composites
Additions of small amount (0.5 weight %) of nanoreinforcement (carbon nanotubes or nanoclay in the polymer matrix of composites, fiber sizing or interlaminar layers can allow to increase the fatigue resistance, shear or compressive strength as well as fracture toughness of the composites by 30–80%. Research has also shown that the incorporation of small amount of carbon nanotubes/CNT can increase the lifetime up to 1500%.
Costs
While the material cost is significantly higher for all-glass fiber blades than for hybrid glass/carbon fiber blades, there is a potential for tremendous savings in manufacturing costs when labor price is considered. Utilizing carbon fiber enables for simpler designs that use less raw material. The chief manufacturing process in blade fabrication is the layering of plies. By reducing the number of layers of plies, as is enabled by thinner blade design, the cost of labor may be decreased, and in some cases, equate to the cost of labor for glass fiber blades.[51]
Other materials
Materials for wind turbine parts other than the rotor blades (including the rotor hub, gearbox, frame, and tower) are largely composed of steel. Modern turbines use a couple of tons of copper for generators, cables, and such.[52] Smaller wind turbines have begun incorporating more aluminum based alloys into these components in an effort to make the turbines lighter and more efficient, and may continue to be used increasingly if fatigue and strength properties can be improved. Prestressed concrete has been increasingly used for the material of the tower, but still requires much reinforcing steel to meet the strength requirement of the turbine. Additionally, step-up gearboxes are being increasingly replaced with variable speed generators, increasing the demand for magnetic materials in wind turbines.[46] In particular, this would require an increased supply of the rare earth metal neodymium.
Recycling
Interest in recycling blades varies in different markets and depends on the waste legislation and local economics. A challenge in recycling blades is related to the composite material, which is made of a thermosetting matrix and glass fibers or a combination of glass and carbon fibers. Thermosetting matrix cannot be remolded to form new composites. So the options are either to reuse the blade and the composite material elements as they are found in the blade or to transform the composite material into a new source of material. In Germany, wind turbine blades are commercially recycled as part of an alternative fuel mix for a cement factory.
Supply
A study of the material consumption trends and requirements for wind energy in Europe found that bigger turbines have a higher consumption of precious metals but lower material input per kW generated. The current material consumption and stock was compared to input materials for various onshore system sizes. In all EU countries the estimates for 2020 exceeded and doubled the values consumed in 2009. These countries would need to expand their resources to be able to meet the estimated demand for 2020. For example, currently the EU has 3% of world supply of fluorspar and it requires 14% by 2020. Globally, the main exporting countries are South Africa, Mexico and China. This is similar with other critical and valuable materials required for energy systems such as magnesium, silver and indium. In addition, the levels of recycling of these materials is very low and focusing on that could alleviate issues with supply in the future. It is important to note that since most of these valuable materials are also used in other emerging technologies, like LEDs, PVs and LCDs, it is projected that demand for them will continue to increase.[53]
A report by the United States Geological Survey estimated the projected materials requirement in order to fulfill the US commitment to supplying 20% of its electricity from wind power by 2030. They did not address requirements for small turbines or offshore turbines since those were not widely deployed in 2008, when the study was created. They found that there are increases in common materials such as cast iron, steel and concrete that represent 2–3% of the material consumption in 2008. Between 110,000 and 115,000 metric tons of fiber glass would be required annually, equivalent to 14% of consumption in 2008. They did not see a high increase in demand for rare metals compared to available supply, however rare metals that are also being used for other technologies such as batteries which are increasing its global demand need to be taken into account. Land, whbich might not be considered a material, is an important resource in deploying wind technologies. Reaching the 2030 goal would require 50,000 square kilometers of onshore land area and 11,000 square kilometers of offshore. This is not considered a problem in the US due to its vast area and the ability to use land for farming and grazing. A greater limitation for the technology would be the variability and transmission infrastructure to areas of higher demand.[54]
Permanent magnets for wind turbine generators contain rare earth metals such as Nd, Pr, Tb, and Dy. Systems that use magnetic direct drive turbines require higher amounts of rare metals. Therefore, an increase in wind production would increase the demand for these resources. It is estimated that the additional demand for Nd in 2035 may be 4,000 to 18,000 tons and Dy could see an increase of 200 to 1200 tons. These values represent a quarter to half of current production levels. However, since technologies are developing rapidly, driven by supply and price of materials these estimated levels are extremely uncertain.[55]
Reliance on rare earth minerals for components has risked expense and price volatility as China has been main producer of rare earth minerals (96% in 2009) and had been reducing its export quotas of these materials.[56] In recent years, however, other producers have increased production of rare earth minerals and China has removed its reduced export quota on rare earths leading to an increased supply and decreased cost of rare earth minerals, increasing the viability of the implementation of variable speed generators in wind turbines on a large scale.[57]
Due to increased technology and wide implementation, the global glass fiber market might reach US$17.4 billion by 2024, compared to US$8.5 billion in 2014. Since it is the most widely used material for reinforcement in composites around the globe, the expansion of end use applications such as construction, transportation and wind turbines has fueled its popularity. Asia Pacific held the major share of the global market in 2014 with more than 45% volume share. However China is currently the largest producer. The industry receives subsidies from the Chinese government allowing them to export it cheaper to the US and Europe. However, due to the higher demand in the near future some price wars have started to developed to implement anti dumping strategies such as tariffs on Chinese glass fiber.[58]
Wind turbines on public display

A few localities have exploited the attention-getting nature of wind turbines by placing them on public display, either with visitor centers around their bases, or with viewing areas farther away.[59] The wind turbines are generally of conventional horizontal-axis, three-bladed design, and generate power to feed electrical grids, but they also serve the unconventional roles of technology demonstration, public relations, and education.
Small wind turbines

Small wind turbines may be used for a variety of applications including on- or off-grid residences, telecom towers, offshore platforms, rural schools and clinics, remote monitoring and other purposes that require energy where there is no electric grid, or where the grid is unstable. Small wind turbines may be as small as a fifty-watt generator for boat or caravan use. Hybrid solar and wind powered units are increasingly being used for traffic signage, particularly in rural locations, as they avoid the need to lay long cables from the nearest mains connection point.[60] The U.S. Department of Energy's National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) defines small wind turbines as those smaller than or equal to 100 kilowatts.[61] Small units often have direct drive generators, direct current output, aeroelastic blades, lifetime bearings and use a vane to point into the wind.
Larger, more costly turbines generally have geared power trains, alternating current output, flaps and are actively pointed into the wind. Direct drive generators and aeroelastic blades for large wind turbines are being researched.
Wind turbine spacing
On most horizontal wind turbine farms, a spacing of about 6–10 times the rotor diameter is often upheld. However, for large wind farms distances of about 15 rotor diameters should be more economical, taking into account typical wind turbine and land costs. This conclusion has been reached by research[62] conducted by Charles Meneveau of the Johns Hopkins University,[63] and Johan Meyers of Leuven University in Belgium, based on computer simulations[64] that take into account the detailed interactions among wind turbines (wakes) as well as with the entire turbulent atmospheric boundary layer.
Recent research by John Dabiri of Caltech suggests that vertical wind turbines may be placed much more closely together so long as an alternating pattern of rotation is created allowing blades of neighbouring turbines to move in the same direction as they approach one another.[65]
Operability
Maintenance
Wind turbines need regular maintenance to stay reliable and available, in the best case turbines are available to generate energy 98% of the time.[66][67]
Modern turbines usually have a small onboard crane for hoisting maintenance tools and minor components. However, large heavy components like generator, gearbox, blades and so on are rarely replaced and a heavy lift external crane is needed in those cases. If the turbine has a difficult access road, a containerized crane can be lifted up by the internal crane to provide heavier lifting.[68]
Repowering
Installation of new wind turbines can be controversial. An alternative is repowering, where existing wind turbines are replaced with bigger, more powerful ones, sometimes in smaller numbers while keeping or increasing capacity.
Demolition
Older turbines were in some early cases not required to be removed when reaching the end of their life. Some still stand, waiting to be recycled or repowered.[69][70]
A demolition industry develops to recycle offshore turbines at a cost of DKK 2–4 million per MW, to be guaranteed by the owner.[71]
Comparison with fossil-fuel turbines
Advantages
Wind turbines are generally inexpensive. They will produce electricity at between two and six cents per kilowatt hour, which is one of the lowest-priced renewable energy sources.[72] And as technology needed for wind turbines continues to improve, the prices will decrease as well. In addition, there is no competitive market for wind energy, as it does not cost money to get ahold of wind.[72] The main cost of wind turbines are the installation process. The average cost is between $48,000 and $65,000 to install. However, the energy harvested from the turbine will offset the installation cost, as well as provide virtually free energy for years after.[73]
Wind turbines provide a clean energy source, emitting no greenhouse gases and no waste product. Over 1,500 tons of carbon dioxide per year can be eliminated by using a one megawatt turbine instead of one megawatt of energy from a fossil fuel.[74] Being environmentally friendly and green is a large advantage of wind turbines.
Disadvantages
Wind turbines can be very large, reaching over 140 metres (460 ft) tall and with blades 55 metres (60 yd) long,[75] and people have often complained about their visual impact.
Environmental impact of wind power includes effect on wildlife, but can be mitigated if proper monitoring and mitigation strategies are implemented.[76] Thousands of birds, including rare species, have been killed by the blades of wind turbines,[77] though wind turbines contribute relatively insignificantly to anthropogenic avian mortality. For every bird killed by a wind turbine in the US, nearly 500,000 are killed by each of feral cats and buildings.[78] In comparison, conventional coal fired generators contribute significantly more to bird mortality, by incineration when caught in updrafts of smoke stacks and by poisoning with emissions byproducts (including particulates and heavy metals downwind of flue gases). Further, marine life is affected by water intakes of steam turbine cooling towers (heat exchangers) for nuclear and fossil fuel generators, by coal dust deposits in marine ecosystems (e.g. damaging Australia's Great Barrier Reef) and by water acidification from combustion monoxides.
Energy harnessed by wind turbines is intermittent, and is not a "dispatchable" source of power; its availability is based on whether the wind is blowing, not whether electricity is needed. Turbines can be placed on ridges or bluffs to maximize the access of wind they have, but this also limits the locations where they can be placed.[72] In this way, wind energy is not a particularly reliable source of energy. However, it can form part of the energy mix, which also includes power from other sources. Notably, the relative available output from wind and solar sources is often inversely proportional (balancing)[citation needed]. Technology is also being developed to store excess energy, which can then make up for any deficits in supplies.
Records


- Largest capacity conventional drive
- The Vestas V164 has a rated capacity of 8 MW,[79] later upgraded to 9 MW.[80] The wind turbine has an overall height of 220 m (722 ft), a diameter of 164 m (538 ft), is for offshore use, and is the world's largest-capacity wind turbine since its introduction in 2014. The conventional drive train consist of a main gearbox and a medium speed PM generator. Prototype installed in 2014 at the National Test Center Denmark nearby Østerild. Series production began end of 2015.
- Largest capacity direct drive
- The Enercon E-126 with 7.58 MW and 127 m rotor diameter is the largest direct drive turbine. It's only for onshore use. The turbine has parted rotor blades with 2 sections for transport. In July 2016, Siemens upgraded its 7 to 8 MW.[81]
- Largest vertical-axis
- Le Nordais wind farm in Cap-Chat, Quebec has a vertical axis wind turbine (VAWT) named Éole, which is the world's largest at 110 m.[82] It has a nameplate capacity of 3.8 MW.[83]
- Largest 1-bladed turbine
- Riva Calzoni M33 was a single-bladed wind turbine with 350 kW, designed and built In Bologna in 1993.[84]
- Largest 2-bladed turbine
- The biggest 2-bladed turbine is built by Mingyang Wind Power in 2013. It is a SCD6.5MW offshore downwind turbine, designed by aerodyn Energiesysteme.[85][86][87]
- Largest swept area
- The turbine with the largest swept area is the Samsung S7.0–171, with a diameter of 171 m, giving a total sweep of 22966 m2.
- Tallest
- A Nordex 3.3 MW was installed in July 2016. It has a total height of 230m, and a hub height of 164m on 100m concrete tower bottom with steel tubes on top (hybrid tower).[88]
- Vestas V164 was the tallest wind turbine, standing in Østerild, Denmark, 220 meters tall, constructed in 2014. It has a steel tube tower.
- Highest tower
- Fuhrländer installed a 2.5MW turbine on a 160m lattice tower in 2003 (see Fuhrländer Wind Turbine Laasow and Nowy Tomyśl Wind Turbines).
- Most rotors
- Lagerwey has build Four-in-One, a multi rotor wind turbine with one tower and four rotors near Maasvlakte.[citation needed] In April 2016, Vestas installed a 900 kW quadrotor test wind turbine at Risø, made from 4 recycled 225 kW V29 turbines.[89][90][91]
- Most productive
- Four turbines at Rønland Offshore Wind Farm in Denmark share the record for the most productive wind turbines, with each having generated 63.2 GWh by June 2010.[92]
- Highest-situated
- Since 2013 the world's highest-situated wind turbine was made and installed by WindAid and is located at the base of the Pastoruri Glacier in Peru at 4,877 meters (16,001 ft) above sea level.[93] The site uses the WindAid 2.5 kW wind generator to supply power to a small rural community of micro entrepreneurs who cater to the tourists who come to the Pastoruri glacier.[94]
- Largest floating wind turbine
- The world's largest—and also the first operational deep-water large-capacity—floating wind turbine is the 2.3 MW Hywind currently operating 10 kilometers (6.2 mi) offshore in 220-meter-deep water, southwest of Karmøy, Norway. The turbine began operating in September 2009 and utilizes a Siemens 2.3 MW turbine.[95][96]
See also
References
- ^ Evans, Annette; Strezov, Vladimir; Evans, Tim (June 2009). "Assessment of sustainability indicators for renewable energy technologies". Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews. 13 (5): 1082–1088. doi:10.1016/j.rser.2008.03.008 – via Elsevier Science Direct.
- ^ "Part 1 – Early History Through 1875". Retrieved 31 July 2008.
- ^ Drachmann, A.G. (1961). "Heron's Windmill". Centaurus. 7: 145–151.
- ^ Dietrich Lohrmann, "Von der östlichen zur westlichen Windmühle", Archiv für Kulturgeschichte, Vol. 77, Issue 1 (1995), pp. 1–30 (10f.)
- ^ Ahmad Y Hassan, Donald Routledge Hill (1986). Islamic Technology: An illustrated history, p. 54. Cambridge University Press. ISBN 0-521-42239-6.
- ^ Donald Routledge Hill, "Mechanical Engineering in the Medieval Near East", Scientific American, May 1991, p. 64-69. (cf. Donald Routledge Hill, Mechanical Engineering)
- ^ a b Morthorst, Poul Erik; Redlinger, Robert Y.; Andersen, Per (2002). Wind energy in the 21st century: economics, policy, technology and the changing electricity industry. Houndmills, Basingstoke, Hampshire: Palgrave/UNEP. ISBN 0-333-79248-3.
- ^ a b c d Price, Trevor J. (2004). "Blyth, James (1839–1906)". Oxford Dictionary of National Biography (online ed.). Oxford University Press. doi:10.1093/ref:odnb/100957. (Subscription or UK public library membership required.)
- ^ A Wind Energy Pioneer: Charles F. Brush. Danish Wind Industry Association. Archived from the original on 8 September 2008. Retrieved 28 December 2008.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Quirky old-style contraptions make water from wind on the mesas of West Texas". Archived from the original on 3 February 2008.
- ^ Alan Wyatt: Electric Power: Challenges and Choices. Book Press Ltd., Toronto 1986, ISBN 0-920650-00-7
- ^ "Bauer, Lucas. "Krasnovsky WIME D-30 - 100,00 kW - Wind turbine"". http://www.en.wind-turbine-models.com.
{{cite web}}: Cite has empty unknown parameter:|dead-url=(help); External link in|website= - ^ Anon. "Costa Head Experimental Wind Turbine". Orkney Sustainable Energy Website. Orkney Sustainable Energy Ltd. Retrieved 19 December 2010.
- ^ "NREL: Dynamic Maps, GIS Data, and Analysis Tools – Wind Maps". Nrel.gov. 3 September 2013. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ "Appendix II IEC Classification of Wind Turbines". Wind Resource Assessment and Micro-siting, Science and Engineering. Retrieved 29 August 2018.
- ^ "The Physics of Wind Turbines Kira Grogg Carleton College, 2005, p.8" (PDF). Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ "Wind Energy Basics". Bureau of Land Management. Retrieved 23 April 2016.
- ^ "Enercon E-family, 330 Kw to 7.5 Mw, Wind Turbine Specification" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 16 May 2011.
- ^ Tony Burton et al., (ed), Wind Energy Handbook, John Wiley and Sons 2001 ISBN 0471489972 page 65
- ^ Sanne Wittrup. "11 years of wind data shows surprising production decrease" (in Danish) Ingeniøren, 1 November 2013. Retrieved 2 November 2013.
- ^ E. Hau., Wind Turbines: Fundamentals, Technologies, Application, Economics. Springer. Germany. 2006
- ^ "Wind Energy Basics". American Wind Energy Association. Archived from the original on 23 September 2010. Retrieved 24 September 2009.
- ^ Elizabeth Stinson (15 May 2015). "The Future of Wind Turbines? No Blades". Wired.
- ^ a b Paul Gipe (7 May 2014). "News & Articles on Household-Size (Small) Wind Turbines". Wind-works.org.
- ^ "Wind Turbine Components". Danish Wind Industry Association. 10 May 2003. Archived from the original on 7 June 2008.
- ^ G. Bywaters; P. Mattila; D. Costin; J. Stowell; V. John; S. Hoskins; J. Lynch; T. Cole; A. Cate; C. Badger; B. Freeman (October 2007). "Northern Power NW 1500 Direct-Drive Generator" (PDF). National Renewable Energy Laboratory. p. iii.
- ^ Michael Barnard (7 April 2014). "Vertical Axis Wind Turbines: Great In 1890, Also-rans In 2014". CleanTechnica.
- ^ Michael C Brower; Nicholas M Robinson; Erik Hale (May 2010). "Wind Flow Modeling Uncertainty" (PDF). AWS Truepower. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2 May 2013.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Hugh Piggott (6 January 2007). "Windspeed in the city – reality versus the DTI database". Scoraigwind.com. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ "Urban Wind Turbines" (PDF).
- ^ "Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines". Symscape. 7 July 2008. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Exploit Nature-Renewable Energy Technologies by Gurmit Singh, Aditya Books, pp 378
- ^ Eric Eggleston; AWEA Staff. "What Are Vertical-Axis Wind Turbines (VAWTs)?". American Wind Energy Association. Archived from the original on 3 April 2005.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Marloff, R.H. (January 1978). "Stresses in turbine-blade tenons subjected to bending" (PDF). Experimental Mechanics. 18 (1): 19–24. doi:10.1007/BF02326553. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Rob Varnon (2 December 2010). "Derecktor converting boat into hybrid passenger ferry". Connecticut Post. Retrieved 25 April 2012.
- ^ "Modular wind energy device – Brill, Bruce I". Freepatentsonline.com. 19 November 2002. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ Hewitt, Sam; Margetts, Lee; Revell, Alistair (18 April 2017). "Building a digital wind farm". Archives of Computational Methods in Engineering. doi:10.1007/s11831-017-9222-7. Retrieved 20 April 2017.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Navid Goudarzi (June 2013). "A Review on the Development of the Wind Turbine Generators across the World". International Journal of Dynamics and Control. 1 (2). Springer: 192–202. doi:10.1007/s40435-013-0016-y.
- ^ Navid Goudarzi; Weidong Zhu (November 2012). "A Review of the Development of Wind Turbine Generators Across the World". ASME 2012 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition. 4 – Paper No: IMECE2012-88615. ASME: 1257–1265.
- ^ "Hansen W4 series". Hansentransmissions.com. Archived from the original on 15 March 2012. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ John Gardner; Nathaniel Haro; Todd Haynes (October 2011). "Active Drivetrain Control to Improve Energy Capture of Wind Turbines" (PDF). Boise State University. Retrieved 28 February 2012.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ ""Wind Turbine Design Cost and Scaling Model", Technical Report NREL/TP-500-40566, December, 2006, page 35, 36" (PDF). Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ "Pomeroy Wind Farm" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on 15 July 2011.
- ^ Baqersad, Javad; Niezrecki, Christopher; Avitabile, Peter (2015). "Full-field dynamic strain prediction on a wind turbine using displacements of optical targets measured by stereophotogrammetry". Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing. 62–63: 284–295. Bibcode:2015MSSP...62..284B. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.03.021.
- ^ Using Stereophotogrammetry to Measure Vibrations of a Rotating Wind Turbine
- ^ a b Ancona, Dan; Jim, McVeigh. "Wind Turbine – Materials and Manufacturing Fact Sheet". psu.edu. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- ^ a b Watson, James; Serrano, Juan (September 2010). "Composite Materials for Wind Blades". Wind Systems. Retrieved 6 November 2016.
- ^ "Wind turbine blades: Glass vs. carbon fiber". www.compositesworld.com. Retrieved 12 November 2016.
- ^ "Materials and Innovations for Large Blade Structures: Research Opportunities in Wind Energy Technology" (PDF). windpower.sandia.gov.
- ^ "Wind Power Monthly Webpage".
- ^ Ong, Cheng-Huat; Tsai, Stephen W. (2000). "The Use of Carbon Fibers in Wind Turbine Blade Design" (PDF). energy.sandia.gov.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|last-author-amp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Frost and Sullivan, 2009, cited in Wind Generator Technology, by Eclareon S.L., Madrid, May 2012; www.eclareon.com; Available at Leonardo Energy – Ask an Expert; "Archived copy". Archived from the original on 26 November 2012. Retrieved 12 December 2012.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ Kim, Junbeum; Guillaume, Bertrand; Chung, Jinwook; Hwang, Yongwoo (1 February 2015). "Critical and precious materials consumption and requirement in wind energy system in the EU 27". Applied Energy. 139: 327–334. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.11.003. ISSN 0306-2619.
- ^ Wilburn, D.R.—Wind Energy in the United States and Materials Required for the Land-Based Turbine Industry From 2010 Through 2030—SIR 2011–5036
- ^ Buchholz, Peter; Brandenburg, Torsten (1 January 2018). "Demand, Supply, and Price Trends for Mineral Raw Materials Relevant to the Renewable Energy Transition Wind Energy, Solar Photovoltaic Energy, and Energy Storage". Chemie Ingenieur Technik. 90 (1–2): 141–153. doi:10.1002/cite.201700098. ISSN 1522-2640.
- ^ Wilburn, David. "Wind Energy in the United States and Materials Required for the Land-Based Wind Turbine Industry From 2010 Through 2030" (PDF). U.S. Department of the Interior.
- ^ Yap, Chui-Wei. "China Ends Rare-Earth Minerals Export Quotas". wsg.com.
- ^ "Glass fiber market to reach to US$17 billion by 2024". Reinforced Plastics. 60 (4): 188–189. 1 July 2016. doi:10.1016/j.repl.2016.07.006. ISSN 0034-3617.
- ^ Young, Kathryn (3 August 2007). "Canada wind farms blow away turbine tourists". Edmonton Journal. Archived from the original on 25 April 2009. Retrieved 6 September 2008.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Anon. "Solar & Wind Powered Sign Lighting". Energy Development Cooperative Ltd. Retrieved 19 October 2013.
- ^ Small Wind, U.S. Department of Energy National Renewable Energy Laboratory website
- ^ Meyers, Johan (2011). "Optimal turbine spacing in fully developed wind farm boundary layers". Wind Energy. 15 (2): 305–317. Bibcode:2012WiEn...15..305M. doi:10.1002/we.469.
- ^ "New study yields better turbine spacing for large wind farms". Johns Hopkins University. 18 January 2011. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
- ^ M. Calaf; C. Meneveau; J. Meyers (2010). "Large eddy simulation study of fully developed wind-turbine array boundary layers". Phys. Fluids. 22 (1). Bibcode:2010PhFl...22a5110C. doi:10.1063/1.3291077. Archived from the original on 8 April 2014. Retrieved 6 November 2013.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Dabiri, J. Potential order-of-magnitude enhancement of wind farm power density via counter-rotating vertical-axis wind turbine arrays (2011), J. Renewable Sustainable Energy 3, 043104
- ^ G.J.W. van Bussel, PhD; M.B. Zaaijer, MSc Reliability, Availability and Maintenance aspects of large-scale offshore wind farms page 2 Delft University of Technology, 2001.
- ^ "Iberwind builds on 98% availability with fresh yaw, blade gains". 15 February 2016. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Morten Lund (30 May 2016). "Dansk firma sætter prisbelønnet selvhejsende kran i serieproduktion". Ingeniøren. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Jeremy Fugleberg (8 May 2014). "Abandoned Dreams of Wind and Light". Atlas Obscura. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ Tom Gray (11 March 2013). "Fact check: About those 'abandoned' turbines ..." American Wind Energy Association. Retrieved 30 May 2016.
- ^ "Aldrende havmølleparker åbner marked for klog nedrivning". Ingeniøren. Retrieved 20 May 2016.
- ^ a b c "Advantages and Disadvantages of Wind Energy – Clean Energy Ideas". Clean Energy Ideas. 19 June 2013. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ^ "Residential Wind Energy Systems – Bergey Wind PowerBergey Wind Power". bergey.com. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ^ "About Wind Energy: Factsheets and Statistics". www.pawindenergynow.org. Retrieved 10 May 2017.
- ^ "Turbine Size". Fraunhofer Wind Monitor.
- ^ Parisé, J.; Walker, T. R. (2017). "Industrial wind turbine post-construction bird and bat monitoring: A policy framework for Canada". Journal of Environmental Management. 201: 252–259. doi:10.1016/j.jenvman.2017.06.052. PMID 28672197.
- ^ Hosansky, David (1 April 2011). "Wind Power: Is wind energy good for the environment?". CQ Researcher.
- ^ Sovacool, B. K. (2013). "The avian benefits of wind energy: A 2009 update". Renewable Energy. 49: 19–24. doi:10.1016/j.renene.2012.01.074.
- ^ Wittrup, Sanne. "Power from Vestas' giant turbine" (in Danish. English translation ). Ingeniøren, 28 January 2014. Retrieved 28 January 2014.
- ^ http://www.mhivestasoffshore.com: "[1]", retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ http://www.windpowermonthly.com/article/1401293/siemens-confirms-8mw-turbine
- ^ "Visits : Big wind turbine". Archived from the original on 1 May 2010. Retrieved 17 April 2010.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Wind Energy Power Plants in Canada – other provinces". 5 June 2010. Retrieved 24 August 2010.
- ^ "Riva Calzoni M33 Single Bladed Wind Turbine". Retrieved 4 January 2018.
- ^ http://www.windpoweroffshore.com/article/1207686/close---aerodyns-6mw-offshore-turbine-design
- ^ http://www.windpowermonthly.com/article/1188373/ming-yang-install-65mw-offshore-turbine
- ^ David Weston. "Aerodyn 6MW connected to grid" 12 March 2015. Archive
- ^ http://www.windpowermonthly.com/article/1400374/nordex-installs-230-metre-onshore-turbine
- ^ "EXCLUSIVE: Vestas tests four-rotor concept turbine". Windpower Monthly. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ Sanne Wittrup. "Vestas rejser usædvanlig ny multirotor-vindmølle". Ingeniøren. Retrieved 20 April 2016.
- ^ Video of quadrotor on YouTube
- ^ "Surpassing Matilda: record-breaking Danish wind turbines". Retrieved 26 July 2010.
- ^ http://www.guinnessworldrecords.com/world-records/highest-altitude-wind-generator
- ^ http://www.lehighvalleylive.com/bethlehem/index.ssf/2013/08/northampton_community_college_53.html
- ^ Patel, Prachi (22 June 2009). "Floating Wind Turbines to Be Tested". IEEE Spectrum. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
will test how the 2.3-megawatt turbine holds up in 220-meter-deep water.
- ^ Madslien, Jorn (8 September 2009). "Floating challenge for offshore wind turbine". BBC News. Retrieved 7 March 2011.
world's first full-scale floating wind turbine
Further reading
- Tony Burton, David Sharpe, Nick Jenkins, Ervin Bossanyi: Wind Energy Handbook, John Wiley & Sons, 2nd edition (2011), ISBN 978-0-470-69975-1
- Darrell, Dodge, Early History Through 1875, TeloNet Web Development, Copyright 1996–2001
- Ersen Erdem, Wind Turbine Industrial Applications
- Robert Gasch, Jochen Twele (ed.), Wind power plants. Fundamentals, design, construction and operation, Springer 2012 ISBN 978-3-642-22937-4.
- Erich Hau, Wind turbines: fundamentals, technologies, application, economics Springer, 2013 ISBN 978-3-642-27150-2 (preview on Google Books)
- Siegfried Heier, Grid integration of wind energy conversion systems John Wiley & Sons, 3rd edition (2014), ISBN 978-1-119-96294-6
- Peter Jamieson, Innovation in Wind Turbine Design. Wiley & Sons 2011, ISBN 978-0-470-69981-2
- J. F. Manwell, J. G. McGowan, A. L. Roberts, Wind Energy Explained: Theory, Design and Application, John Wiley & Sons, 2nd edition (2012), ISBN 978-0-47001-500-1
- David Spera (ed,) Wind Turbine Technology: Fundamental Concepts in Wind Turbine Engineering, Second Edition (2009), ASME Press, ISBN 9780791802601
- Alois Schaffarczyk (ed.), Understanding wind power technology, John Wiley & Sons, (2014), ISBN 978-1-118-64751-6
- Hermann-Josef Wagner, Jyotirmay Mathur, Introduction to wind energy systems. Basics, technology and operation. Springer (2013), ISBN 978-3-642-32975-3
- GA Mansoori, N Enayati, LB Agyarko (2016), Energy: Sources, Utilization, Legislation, Sustainability, Illinois as Model State
External links
- Harvesting the Wind (45 lectures about wind turbines by professor Magdi Ragheb
- DIY wind turbine at home Complete video and image Guide by Newphysicist
- Guided tour on wind energy
- Wind Energy Technology World Wind Energy Association
- Wind turbine simulation, National Geographic
- Airborne Wind Industry Association international
- Top 21 Biggest Wind Turbines in the World
- The Tethys database seeks to gather, organize and make available information on potential environmental effects of offshore wind energy development

