Grand Duchy of Oldenburg: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
Finnusertop (talk | contribs) m refs |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{other uses|Oldenburg (disambiguation)}} |
{{other uses|Oldenburg (disambiguation)}} |
||
{{Update-EB|date=September 2018}} |
|||
{{multiple issues| |
|||
{{no footnotes|date=March 2013}} |
|||
{{one source|date=November 2013}} |
|||
}} |
|||
{{Expand German|Großherzogtum Oldenburg|date=August 2012}} |
{{Expand German|Großherzogtum Oldenburg|date=August 2012}} |
||
{{Infobox Former Country |
{{Infobox Former Country |
||
| Line 9: | Line 6: | ||
|conventional_long_name = Grand Duchy of Oldenburg |
|conventional_long_name = Grand Duchy of Oldenburg |
||
|common_name = Oldenburg |
|common_name = Oldenburg |
||
|continent = Europe |
|||
|country = Germany |
|||
|status = State of the [[German Confederation]], the [[North German Confederation]], and the [[German Empire]] |
|status = State of the [[German Confederation]], the [[North German Confederation]], and the [[German Empire]] |
||
|government_type = [[Constitutional monarchy]] |
|government_type = [[Constitutional monarchy]] |
||
| Line 49: | Line 44: | ||
}} |
}} |
||
The '''Grand Duchy of Oldenburg''' ({{Lang-de|Großherzogtum Oldenburg}}) (also known as '''Holstein-Oldenburg''') was a [[grand duchy]] within the [[German Confederation]], [[North German Confederation]] and [[German Empire]] which consisted of three widely separated territories: [[Oldenburg Land|Oldenburg]], [[Eutin]] and [[Birkenfeld]]. It ranked tenth among the German states and had one vote in the [[Bundesrat (German Empire)|Bundesrat]] and three members in the [[Reichstag (German Empire)|Reichstag]]. |
The '''Grand Duchy of Oldenburg''' ({{Lang-de|Großherzogtum Oldenburg}}) (also known as '''Holstein-Oldenburg''') was a [[grand duchy]] within the [[German Confederation]], [[North German Confederation]] and [[German Empire]] which consisted of three widely separated territories: [[Oldenburg Land|Oldenburg]], [[Eutin]] and [[Birkenfeld]]. It ranked tenth among the German states and had one vote in the [[Bundesrat (German Empire)|Bundesrat]] and three members in the [[Reichstag (German Empire)|Reichstag]].{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=71}} |
||
Its ruling family, the [[House of Oldenburg]], also came to rule in [[Denmark]], [[Norway]], [[Sweden]], [[Greece]] and [[Russia]].{{sfn| |
Its ruling family, the [[House of Oldenburg]], also came to rule in [[Denmark]], [[Norway]], [[Sweden]], [[Greece]] and [[Russia]].{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} The heirs of a junior line of the Greek branch are, through [[Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh]], in the line of succession to the thrones of the [[United Kingdom]] and the other [[Commonwealth realm]]s after Queen [[Elizabeth II]]. |
||
As common for German houses, the ruling branch of Oldenburg, which ruled as Dukes and later Grand Dukes, holds the headship by [[primogeniture]] of the entire [[House of Holstein-Oldenburg]] with all its cadet branches. |
As common for German houses, the ruling branch of Oldenburg, which ruled as Dukes and later Grand Dukes, holds the headship by [[primogeniture]] of the entire [[House of Holstein-Oldenburg]] with all its cadet branches. |
||
==History== |
==History== |
||
The first known count of Oldenburg was [[Elimar I, Count of Oldenburg|Elimar I]] (d. 1108). Elimar's descendants appear as vassals, though sometimes rebellious ones, of the dukes of [[Duchy of Saxony|Saxony]]; but they attained the dignity of [[fürst|princes of the empire]] when the emperor [[Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor|Frederick I]] dismembered the Saxon duchy in 1180. At this time, the county of [[Delmenhorst]] formed part of the dominions of the counts of Oldenburg, but afterwards it was on several occasions separated from them to form an [[appanage]] for younger branches of the family. This was the case between 1262 and 1447, between 1463 and 1547, and between 1577 and 1617.{{sfn| |
The first known count of Oldenburg was [[Elimar I, Count of Oldenburg|Elimar I]] (d. 1108). Elimar's descendants appear as vassals, though sometimes rebellious ones, of the dukes of [[Duchy of Saxony|Saxony]]; but they attained the dignity of [[fürst|princes of the empire]] when the emperor [[Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor|Frederick I]] dismembered the Saxon duchy in 1180. At this time, the county of [[Delmenhorst]] formed part of the dominions of the counts of Oldenburg, but afterwards it was on several occasions separated from them to form an [[appanage]] for younger branches of the family. This was the case between 1262 and 1447, between 1463 and 1547, and between 1577 and 1617.{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
During the early part of the 13th century, the counts carried on a series of wars with independent, or semi-independent, [[Frisians|Frisian]] princes to the north and west of the county, which resulted in a gradual expansion of the Oldenburgian territory. The [[Bremen (state)|Free Hanseatic City of Bremen]] and the [[prince-Bishopric of Münster|bishop of Münster]] were also frequently at war with the counts of Oldenburg.{{sfn| |
During the early part of the 13th century, the counts carried on a series of wars with independent, or semi-independent, [[Frisians|Frisian]] princes to the north and west of the county, which resulted in a gradual expansion of the Oldenburgian territory. The [[Bremen (state)|Free Hanseatic City of Bremen]] and the [[prince-Bishopric of Münster|bishop of Münster]] were also frequently at war with the counts of Oldenburg.{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
In 1440, Christian succeeded his father [[Dietrich, Count of Oldenburg|Dietrich]], called ''{{lang|la|Fortunatus}}'', as Count of Oldenburg. In 1448 Christian was elected king of [[Denmark]] as [[Christian I of Denmark|Christian I]], partly based on his maternal descent from previous Danish kings. Although far away from the Danish borders, Oldenburg was now a Danish [[exclave]]. The control over the town was left to the king's brothers, who established a short reign of tyranny.{{sfn| |
In 1440, Christian succeeded his father [[Dietrich, Count of Oldenburg|Dietrich]], called ''{{lang|la|Fortunatus}}'', as Count of Oldenburg. In 1448 Christian was elected king of [[Denmark]] as [[Christian I of Denmark|Christian I]], partly based on his maternal descent from previous Danish kings. Although far away from the Danish borders, Oldenburg was now a Danish [[exclave]]. The control over the town was left to the king's brothers, who established a short reign of tyranny.{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
In 1450, Christian became [[king of Norway]] and in 1457, [[king of Sweden]]. In 1460, he inherited the [[Duchy of Schleswig]] and the [[County of Holstein]], an event of high importance for the future history of Oldenburg. In 1454, he handed over Oldenburg to his brother [[Gerhard VI, Count of Oldenburg|Gerhard]] (about 1430–99), a wild prince, who was constantly at war with the [[archbishopric of Bremen|prince-bishop of Bremen]] and other neighbors. In 1483, Gerhard was compelled to abdicate in favor of his sons, and he died while on [[christian pilgrimage|pilgrimage]] in [[Spain]].{{sfn| |
In 1450, Christian became [[king of Norway]] and in 1457, [[king of Sweden]]. In 1460, he inherited the [[Duchy of Schleswig]] and the [[County of Holstein]], an event of high importance for the future history of Oldenburg. In 1454, he handed over Oldenburg to his brother [[Gerhard VI, Count of Oldenburg|Gerhard]] (about 1430–99), a wild prince, who was constantly at war with the [[archbishopric of Bremen|prince-bishop of Bremen]] and other neighbors. In 1483, Gerhard was compelled to abdicate in favor of his sons, and he died while on [[christian pilgrimage|pilgrimage]] in [[Spain]].{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
Early in the 16th century, Oldenburg was again enlarged at the expense of the Frisians. [[Lutheranism]] was introduced into the county by [[Anthony I, Count of Oldenburg|Anthony I]] (1505–73, r. from 1529), who also suppressed the monasteries; however, he remained loyal to [[Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor|Emperor Charles V]] during the [[Schmalkaldic War]], and was able thus to increase his territories, obtaining [[Delmenhorst]] in 1547. One of Anthony's brothers, [[Christopher of Oldenburg|Christopher]] (about 1506–60), won some reputation as a soldier.{{sfn| |
Early in the 16th century, Oldenburg was again enlarged at the expense of the Frisians. [[Lutheranism]] was introduced into the county by [[Anthony I, Count of Oldenburg|Anthony I]] (1505–73, r. from 1529), who also suppressed the monasteries; however, he remained loyal to [[Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor|Emperor Charles V]] during the [[Schmalkaldic War]], and was able thus to increase his territories, obtaining [[Delmenhorst]] in 1547. One of Anthony's brothers, [[Christopher of Oldenburg|Christopher]] (about 1506–60), won some reputation as a soldier.{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
Anthony's grandson, [[Anthony Günther, Count of Oldenburg|Anthony Günther]] (1583–1667), who succeeded in 1603, considered himself the wisest prince who had yet ruled Oldenburg. [[Jever]] had been acquired before he became count, but in 1624 he added [[Kniphausen]] and [[Varel]] to his lands, with which in 1647 Delmenhorst was finally united. By his neutrality during the [[Thirty Years' War]] and by donating valuable horses to the warlord, the [[Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly|Count of Tilly]], Anthony Günther secured for his dominions an immunity from the terrible devastations to which nearly all the other states of Germany were exposed. He also obtained from the emperor the right to levy [[tariff|tolls]] on vessels passing along the [[Weser]], a lucrative grant which soon formed a material addition to his resources. In 1607 he erected a [[Renaissance architecture|Renaissance]] [[Schloss Oldenburg|schloss]].{{sfn| |
Anthony's grandson, [[Anthony Günther, Count of Oldenburg|Anthony Günther]] (1583–1667), who succeeded in 1603, considered himself the wisest prince who had yet ruled Oldenburg. [[Jever]] had been acquired before he became count, but in 1624 he added [[Kniphausen]] and [[Varel]] to his lands, with which in 1647 Delmenhorst was finally united. By his neutrality during the [[Thirty Years' War]] and by donating valuable horses to the warlord, the [[Johann Tserclaes, Count of Tilly|Count of Tilly]], Anthony Günther secured for his dominions an immunity from the terrible devastations to which nearly all the other states of Germany were exposed. He also obtained from the emperor the right to levy [[tariff|tolls]] on vessels passing along the [[Weser]], a lucrative grant which soon formed a material addition to his resources. In 1607 he erected a [[Renaissance architecture|Renaissance]] [[Schloss Oldenburg|schloss]].{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} After the death of Anthony Günther, Oldenburg fell again under Danish authority. |
||
In 1773, [[Christian VII of Denmark]] surrendered [[Oldenburg]] to [[Catherine the Great]] in exchange for her son and heir [[Paul I of Russia|Paul]]'s share in the condominial royal-ducal government of the [[Duchy of Holstein]] and his claims to the ducal share in the government of the [[Duchy of Schleswig]]; Oldenburg went to [[Frederick August I, Duke of Oldenburg|Frederick August, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]], the representative of a younger branch of the family, and in 1777 the [[county]] was raised to the rank of a [[duchy]]. The duke's son [[Peter Friedrich Wilhelm, Duke of Oldenburg|William]], who succeeded his father in 1785, was a man of weak intellect, and his cousin [[Peter I, Grand Duke of Oldenburg|Peter, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]], acted as regent and eventually, in 1823, inherited the throne, holding the [[Bishopric of Lübeck|Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]] and Oldenburg in [[personal union]]. |
In 1773, [[Christian VII of Denmark]] surrendered [[Oldenburg]] to [[Catherine the Great]] in exchange for her son and heir [[Paul I of Russia|Paul]]'s share in the condominial royal-ducal government of the [[Duchy of Holstein]] and his claims to the ducal share in the government of the [[Duchy of Schleswig]]; Oldenburg went to [[Frederick August I, Duke of Oldenburg|Frederick August, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]], the representative of a younger branch of the family, and in 1777 the [[county]] was raised to the rank of a [[duchy]]. The duke's son [[Peter Friedrich Wilhelm, Duke of Oldenburg|William]], who succeeded his father in 1785, was a man of weak intellect, and his cousin [[Peter I, Grand Duke of Oldenburg|Peter, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]], acted as regent and eventually, in 1823, inherited the throne,{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} holding the [[Bishopric of Lübeck|Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck]] and Oldenburg in [[personal union]]. |
||
By the [[German Mediatisation]] of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the [[Oldenburg Münsterland]] and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. Between 1810 and 1814, Oldenburg was occupied by [[Napoleonic Wars|Napoleonic France]]. Its annexation into the [[First French Empire|French Empire]], in 1810, was one of the causes for the diplomatic rift between former allies France and [[Russia]], a dispute that would lead to war in 1812 and eventually to Napoleon's downfall. |
By the [[German Mediatisation]] of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the [[Oldenburg Münsterland]] and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. Between 1810 and 1814, Oldenburg was occupied by [[Napoleonic Wars|Napoleonic France]]. Its annexation into the [[First French Empire|French Empire]], in 1810, was one of the causes for the diplomatic rift between former allies France and [[Russia]], a dispute that would lead to war in 1812 and eventually to Napoleon's downfall. |
||
===The European Revolutions=== |
===The European Revolutions=== |
||
[[Oldenburg]] did not entirely escape from the [[Revolutions of 1848]] that swept across [[Europe]], but no serious disturbances took place therein. In 1849 Augustus granted a constitution of a very liberal character to his subjects. Hitherto his country had been ruled in the spirit of [[enlightened despotism]] which had been strengthened by the absence of a privileged class of nobles, the comparative independence of the peasantry, and the importance of the towns; thus a certain amount of friction was inevitable. In 1852 some modifications were introduced into the constitution, yet it remained one of the most progressive in the [[German Confederation]]. Important alterations were made in the administrative system in 1855 and again in 1868, and government oversight on church affairs was ordered by a law of 1863. In 1863, [[Peter II, Grand Duke of Oldenburg|Peter II]], who had ruled since the death of his father Augustus in 1853, seemed inclined to press a claim to the vacant [[duchy of Schleswig]] and [[duchy of Holstein]], but ultimately in 1867 he abandoned this in favor of the Kingdom of Prussia and received some slight compensation. In 1866 he had sided with this power against the [[Austrian Empire]] and had joined the [[North German Confederation]], and in 1871 the grand duchy became a state of the [[German Empire]]. |
[[Oldenburg]] did not entirely escape from the [[Revolutions of 1848]] that swept across [[Europe]], but no serious disturbances took place therein. In 1849 Augustus granted a constitution of a very liberal character to his subjects. Hitherto his country had been ruled in the spirit of [[enlightened despotism]] which had been strengthened by the absence of a privileged class of nobles, the comparative independence of the peasantry, and the importance of the towns; thus a certain amount of friction was inevitable. In 1852 some modifications were introduced into the constitution, yet it remained one of the most progressive in the [[German Confederation]]. Important alterations were made in the administrative system in 1855 and again in 1868, and government oversight on church affairs was ordered by a law of 1863. In 1863, [[Peter II, Grand Duke of Oldenburg|Peter II]], who had ruled since the death of his father Augustus in 1853, seemed inclined to press a claim to the vacant [[duchy of Schleswig]] and [[duchy of Holstein]], but ultimately in 1867 he abandoned this in favor of the Kingdom of Prussia and received some slight compensation. In 1866 he had sided with this power against the [[Austrian Empire]] and had joined the [[North German Confederation]], and in 1871 the grand duchy became a state of the [[German Empire]].{{sfn|Chisholm|1911|p=72}} |
||
==Gallery== |
==Gallery== |
||
| Line 87: | Line 82: | ||
==Sources== |
==Sources== |
||
{{Reflist}} |
{{Reflist}} |
||
===Works cited=== |
|||
*{{EB1911 |wstitle=Oldenburg (grand-duchy) |display=Oldenburg |volume=20 |pages=71–72}} |
*{{EB1911 |wstitle=Oldenburg (grand-duchy) |display=Oldenburg |volume=20 |pages=71–72}} |
||
Revision as of 12:19, 15 September 2018
This article is largely based on an article in the out-of-copyright Encyclopædia Britannica Eleventh Edition, which was produced in 1911. (September 2018) |
You can help expand this article with text translated from the corresponding article in German. (August 2012) Click [show] for important translation instructions.
|
Grand Duchy of Oldenburg Großherzogtum Oldenburg | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1815–1918 | |||||||||
| Anthem: Heil dir, O Oldenburg "Hail to thee, O Oldenburg" | |||||||||
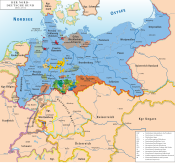
 Oldenburg within the German Empire | |||||||||
| Status | State of the German Confederation, the North German Confederation, and the German Empire | ||||||||
| Capital | Oldenburg | ||||||||
| Religion | Evangelical Lutheran Church of Oldenburg | ||||||||
| Government | Constitutional monarchy | ||||||||
| Grand Duke | |||||||||
• 1815–1823 | Peter Friedrich Wilhelm | ||||||||
• 1823–1829 | Peter I | ||||||||
• 1829–1853 | Augustus | ||||||||
• 1853–1900 | Peter II | ||||||||
• 1900–1918 | Frederick Augustus II | ||||||||
| Staatsminister | |||||||||
• 1814–1842 | Karl von Brandenstein | ||||||||
• 1916–1918 | Franz Friedrich Ruhstrat | ||||||||
| History | |||||||||
| 1815 | |||||||||
| 9 November 1918 | |||||||||
| Currency | Thaler, (until 1858) Vereinsthaler, (1858–1873) German Goldmark, (1873–1914) German Papiermark (1914–1918) | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Grand Duchy of Oldenburg (Template:Lang-de) (also known as Holstein-Oldenburg) was a grand duchy within the German Confederation, North German Confederation and German Empire which consisted of three widely separated territories: Oldenburg, Eutin and Birkenfeld. It ranked tenth among the German states and had one vote in the Bundesrat and three members in the Reichstag.[1]
Its ruling family, the House of Oldenburg, also came to rule in Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Greece and Russia.[2] The heirs of a junior line of the Greek branch are, through Prince Philip, Duke of Edinburgh, in the line of succession to the thrones of the United Kingdom and the other Commonwealth realms after Queen Elizabeth II.
As common for German houses, the ruling branch of Oldenburg, which ruled as Dukes and later Grand Dukes, holds the headship by primogeniture of the entire House of Holstein-Oldenburg with all its cadet branches.
History
The first known count of Oldenburg was Elimar I (d. 1108). Elimar's descendants appear as vassals, though sometimes rebellious ones, of the dukes of Saxony; but they attained the dignity of princes of the empire when the emperor Frederick I dismembered the Saxon duchy in 1180. At this time, the county of Delmenhorst formed part of the dominions of the counts of Oldenburg, but afterwards it was on several occasions separated from them to form an appanage for younger branches of the family. This was the case between 1262 and 1447, between 1463 and 1547, and between 1577 and 1617.[2]
During the early part of the 13th century, the counts carried on a series of wars with independent, or semi-independent, Frisian princes to the north and west of the county, which resulted in a gradual expansion of the Oldenburgian territory. The Free Hanseatic City of Bremen and the bishop of Münster were also frequently at war with the counts of Oldenburg.[2]
In 1440, Christian succeeded his father Dietrich, called Fortunatus, as Count of Oldenburg. In 1448 Christian was elected king of Denmark as Christian I, partly based on his maternal descent from previous Danish kings. Although far away from the Danish borders, Oldenburg was now a Danish exclave. The control over the town was left to the king's brothers, who established a short reign of tyranny.[2]
In 1450, Christian became king of Norway and in 1457, king of Sweden. In 1460, he inherited the Duchy of Schleswig and the County of Holstein, an event of high importance for the future history of Oldenburg. In 1454, he handed over Oldenburg to his brother Gerhard (about 1430–99), a wild prince, who was constantly at war with the prince-bishop of Bremen and other neighbors. In 1483, Gerhard was compelled to abdicate in favor of his sons, and he died while on pilgrimage in Spain.[2]
Early in the 16th century, Oldenburg was again enlarged at the expense of the Frisians. Lutheranism was introduced into the county by Anthony I (1505–73, r. from 1529), who also suppressed the monasteries; however, he remained loyal to Emperor Charles V during the Schmalkaldic War, and was able thus to increase his territories, obtaining Delmenhorst in 1547. One of Anthony's brothers, Christopher (about 1506–60), won some reputation as a soldier.[2]
Anthony's grandson, Anthony Günther (1583–1667), who succeeded in 1603, considered himself the wisest prince who had yet ruled Oldenburg. Jever had been acquired before he became count, but in 1624 he added Kniphausen and Varel to his lands, with which in 1647 Delmenhorst was finally united. By his neutrality during the Thirty Years' War and by donating valuable horses to the warlord, the Count of Tilly, Anthony Günther secured for his dominions an immunity from the terrible devastations to which nearly all the other states of Germany were exposed. He also obtained from the emperor the right to levy tolls on vessels passing along the Weser, a lucrative grant which soon formed a material addition to his resources. In 1607 he erected a Renaissance schloss.[2] After the death of Anthony Günther, Oldenburg fell again under Danish authority.
In 1773, Christian VII of Denmark surrendered Oldenburg to Catherine the Great in exchange for her son and heir Paul's share in the condominial royal-ducal government of the Duchy of Holstein and his claims to the ducal share in the government of the Duchy of Schleswig; Oldenburg went to Frederick August, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, the representative of a younger branch of the family, and in 1777 the county was raised to the rank of a duchy. The duke's son William, who succeeded his father in 1785, was a man of weak intellect, and his cousin Peter, Administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck, acted as regent and eventually, in 1823, inherited the throne,[2] holding the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck and Oldenburg in personal union.
By the German Mediatisation of 1803, Oldenburg acquired the Oldenburg Münsterland and the Prince-Bishopric of Lübeck. Between 1810 and 1814, Oldenburg was occupied by Napoleonic France. Its annexation into the French Empire, in 1810, was one of the causes for the diplomatic rift between former allies France and Russia, a dispute that would lead to war in 1812 and eventually to Napoleon's downfall.
The European Revolutions
Oldenburg did not entirely escape from the Revolutions of 1848 that swept across Europe, but no serious disturbances took place therein. In 1849 Augustus granted a constitution of a very liberal character to his subjects. Hitherto his country had been ruled in the spirit of enlightened despotism which had been strengthened by the absence of a privileged class of nobles, the comparative independence of the peasantry, and the importance of the towns; thus a certain amount of friction was inevitable. In 1852 some modifications were introduced into the constitution, yet it remained one of the most progressive in the German Confederation. Important alterations were made in the administrative system in 1855 and again in 1868, and government oversight on church affairs was ordered by a law of 1863. In 1863, Peter II, who had ruled since the death of his father Augustus in 1853, seemed inclined to press a claim to the vacant duchy of Schleswig and duchy of Holstein, but ultimately in 1867 he abandoned this in favor of the Kingdom of Prussia and received some slight compensation. In 1866 he had sided with this power against the Austrian Empire and had joined the North German Confederation, and in 1871 the grand duchy became a state of the German Empire.[2]
Gallery
-
Heraldic shield of the Grand Dukes
See also
Sources
Works cited
- This article incorporates text from a publication now in the public domain: Chisholm, Hugh, ed. (1911). "Oldenburg". Encyclopædia Britannica. Vol. 20 (11th ed.). Cambridge University Press. pp. 71–72.