Oakland International Airport: Difference between revisions
Tag: review edit |
|||
| Line 232: | Line 232: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 1 |
|align="center"| 1 |
||
| |
| [[Los Angeles International Airport|Los Angeles, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 600,400 |
|align="center"| 600,400 |
||
|align="center"| {{decrease}} 4.21% |
|align="center"| {{decrease}} 4.21% |
||
| Line 238: | Line 238: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 2 |
|align="center"| 2 |
||
| |
| [[McCarran International Airport|Las Vegas, Nevada]] |
||
|align="center"| 519,560 |
|align="center"| 519,560 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.96% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.96% |
||
| Line 244: | Line 244: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 3 |
|align="center"| 3 |
||
| |
| [[Seattle–Tacoma International Airport|Seattle/Tacoma, Washington]] |
||
|align="center"| 443,970 |
|align="center"| 443,970 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 9.30% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 9.30% |
||
| Line 250: | Line 250: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 4 |
|align="center"| 4 |
||
| |
| [[San Diego International Airport|San Diego, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 421,040 |
|align="center"| 421,040 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 5.12% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 5.12% |
||
| Line 256: | Line 256: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 5 |
|align="center"| 5 |
||
| |
| [[Bob Hope Airport|Burbank, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 420,030 |
|align="center"| 420,030 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.25% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.25% |
||
| Line 262: | Line 262: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 6 |
|align="center"| 6 |
||
| |
| [[Phoenix Sky Harbor International Airport|Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Arizona]] |
||
|align="center"| 342,910 |
|align="center"| 342,910 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 3.78% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 3.78% |
||
| Line 268: | Line 268: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 7 |
|align="center"| 7 |
||
| |
| [[John Wayne Airport|Orange County, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 309,090 |
|align="center"| 309,090 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 2.49% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 2.49% |
||
| Line 274: | Line 274: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 8 |
|align="center"| 8 |
||
| |
| [[Long Beach Airport|Long Beach, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 302,410 |
|align="center"| 302,410 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 1.75% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 1.75% |
||
| Line 280: | Line 280: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 9 |
|align="center"| 9 |
||
| |
| [[Portland International Airport|Portland, Oregon]] |
||
|align="center"| 279,000 |
|align="center"| 279,000 |
||
|align="center"| {{decrease}} 1.82% |
|align="center"| {{decrease}} 1.82% |
||
| Line 286: | Line 286: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
|align="center"| 10 |
|align="center"| 10 |
||
| |
| [[Ontario International Airport|Ontario, California]] |
||
|align="center"| 266,710 |
|align="center"| 266,710 |
||
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.89% |
|align="center"| {{increase}} 7.89% |
||
Revision as of 18:23, 21 December 2018
Oakland International Airport | |||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| File:Iflyoak.jpg | |||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Summary | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Airport type | Public | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Owner/Operator | Port of Oakland | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Serves | Bay Area | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Location | Oakland, California, U.S. | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hub for | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Focus city for | Allegiant Air | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Elevation AMSL | 9 ft / 3 m | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Coordinates | 37°43′17″N 122°13′15″W / 37.72139°N 122.22083°W | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Website | oaklandairport.com | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Maps | |||||||||||||||||||||||
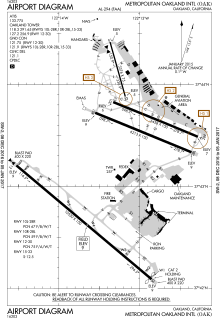 FAA diagram | |||||||||||||||||||||||
 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Runways | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
| Statistics (2017) | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||
Oakland International Airport (IATA: OAK, ICAO: KOAK, FAA LID: OAK) is an international airport in Oakland, California, United States. It is located approximately 10 miles south of Downtown Oakland and across from San Francisco which is situated on the other side of the San Francisco Bay. It is owned by the Port of Oakland[1][4] and features passenger services to cities in the United States, Mexico, and Europe with additional cargo destinations in China and Japan. In 2017, 13,072,245 people traveled through OAK.[5]
Oakland is an operating base for Southwest Airlines and a focus city for Allegiant Air. As of August 2015 Southwest has 120 daily departures on peak-travel days of the week making it Southwests largest operation in California.[6] Alaska Airlines combined with sister-carrier Horizon Air has been the second-busiest carrier at the airport through 2013. In January 2014, Delta overtook Alaska as the airport's No. 2 carrier.[7]
History
Early years
The city of Oakland looked into the construction of an airport starting in 1925. In 1927 the announcement of the Dole prize for a flight from California to Hawaii provided the incentive to purchase 680 acres in April 1927 for the airport.[8][9] The 7,020-foot-long runway was the longest in the world at the time, and was built in just 21 days to meet the Dole race start. The airport was dedicated by Charles Lindbergh September 17. In its early days, because of its long runway enabling safe takeoff rolls for fuel-heavy aircraft, Oakland was the departing point of several historic flights, including Charles Kingsford Smith's historic US-Australia flight in 1928, and Amelia Earhart's final flight in 1937. Earhart departed from this airport when she made her final, ill-fated voyage, intending to return there after circumnavigating the globe.[10]
Boeing Air Transport (a predecessor of United Airlines) began scheduled flights to Oakland in December 1927. It was joined by Trans World Airlines (TWA) in 1932. In 1929, Boeing opened the Boeing School of Aeronautics on the field, which expanded rapidly in 1939 as part of the Civilian Pilot Training Program. Thousands of pilots and mechanics were trained before the facility was changed into the United Air Lines training center in 1945.[11]


In 1943, the U.S. Armed Forces temporarily took over Oakland Airport and opened Naval Air Station Oakland. It was transformed into an airlift base for military flights to the Pacific islands, ordering all scheduled service to move to San Francisco International Airport. After the war, airlines slowly returned to Oakland; Western Airlines began flights in 1946, and was followed by American Airlines, TWA, United, Transocean Airlines and Pacific Southwest Airlines (PSA).
The airport's first Jet Age airline terminal (now Terminal 1) was designed by John Carl Warnecke & Associates and opened in 1962, part of a $20 million expansion on bay fill that included the 10,000-foot runway 11/29.[12] The May 1963 OAG showed 15 airline flights arriving in Oakland each day, including nine from San Francisco; in June 1963, TWA flew Oakland's first scheduled jet, a Convair 880, to Chicago.[10]
During the Vietnam War, World Airways shuttled thousands of military passengers through Oakland to their bases in Southeast Asia, and an international arrivals facility was built, allowing the airport to handle international flights for the first time. By the late 1960s, World Airways had broken ground on the World Airways Maintenance Center at Oakland International Airport. The maintenance hangar could store four Boeing 747's.[10]
After the war Oakland's traffic slumped, but airline deregulation prompted several low-fare carriers to begin flights. This increase prompted the airport to build a $16.3 million second terminal, the Lionel J. Wilson Terminal 2, with seven gates for PSA and AirCal service.[10] In 1987 an Air France Concorde visited Oakland to provide supersonic two-hour flights to the Pacific halfway to Hawaii and back to Oakland.
FedEx Express opened a cargo base at OAK in 1988, which is now one of the busiest air freight terminals in the United States. In the 1990s, Southwest Airlines opened a crew base in Oakland, and expanded its flights to become the airport's dominant passenger carrier. The airport has international arrival facilities, including U.S. Customs and Border Protection officials. Mexicana Airlines flew between Oakland and cities in Mexico for many years. In the past Corsairfly flew Orly Airport to OAK to Papeete, Tahiti, Martinair flew to Schiphol Airport and CityBird flew to Brussels Airport in Brussels.[10]
2000s
United Airlines vacated its 300,000 sq ft (30,000 m2) Oakland Maintenance Center in May 2003 and transferred work to its base across the bay at San Francisco International Airport (SFO).
Oakland International Airport began a $300 million expansion and renovation project in 2004, including adding five gates in Terminal 2. The new concourse partially opened in fall 2006, was fully opened by spring 2007, and a new baggage claim in Terminal 2 opened in summer 2006. The former Terminal 2 baggage claim has been replaced by a renovated and expanded security screening area. As part of this program, airport roadways, curbsides and parking lots were also renovated by the end of 2008.[10]
In 2008 Oakland saw a series of cutbacks due to high fuel costs and airline bankruptcies, more than other Bay Area airports. In just a few days, Oakland's numerous non-stops to Hawaii were eliminated following the liquidation of ATA Airlines and Aloha Airlines, although Hawaiian Airlines started a daily flight to Honolulu a month later. Skybus Airlines stopped flying to Columbus, OH when it ended operations on April 5. American Airlines and Continental Airlines both dropped Oakland on September 3, United Airlines ended service to Los Angeles on November 2, and TACA ended service to San Salvador on September 1.
- New air traffic control tower

A groundbreaking ceremony for a new control tower took place October 15, 2010. A grant awarded to the Federal Aviation Administration from the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009 (ARRA) helped fund the project. The new, environmentally "green" tower was opened in 2013 and replaced the previous north and south field towers. The new tower was formally dedicated in a ceremony on November 22, 2013.[13]
- BART to Oakland International Airport
A long-proposed extension of the BART system to the airport opened on November 22, 2014, allowing passengers to board BART people mover trains and transport from the BART Coliseum station platform to the entrance of all terminals.[14] The new system consists of a mostly elevated structure, running the length of Hegenberger Road.[15]
- Electric vehicle charging services
The Port of Oakland and Coulomb Technologies has announced that electric vehicle (EV) driver services have arrived at Oakland International Airport (OAK) with the installation of eight ChargePoint Network charging stations for EVs in the Premier Parking Lot.
Oakland International is the first Northern California airport to offer EV charging services as part of the ChargePoint Network, providing drivers EV services including real-time charging station status and reservations.
- Noise management program
For more than 30 years, OAK has worked with its stakeholders to develop programs that minimize the effect of aircraft noise, to the extent possible, on surrounding communities, while maintaining a safe and efficient air transportation center. Through regularly scheduled stakeholder meetings, a sophisticated noise-monitoring system, proactive communications with neighboring communities and pilot education, the airport has successfully lessened the impact of its operations on neighboring communities, in order to improve their quality of life.
- Master Plan
For nearly a century, Oakland International Airport has served the shipping and travel needs of the San Francisco Bay Area. The original airfield was built in 1927 and is still used by air cargo, corporate and general aviation operators. In 1962 a new terminal (Terminal 1), 10,000-foot runway and 10-story air traffic control tower was built to usher in the jet-age. Terminal 2 was opened in 1985 and is now used solely by Southwest Airlines.[10]
In 2008 OAK completed its $300 million Terminal Improvement Program, with projects that added a new concourse with five more gates and waiting areas expanded ticketing, security and baggage claim facilities added new utilities and improved terminal access and eased congestion in front of the terminals through a new roadway and curbside system. These projects are one part of the ongoing Airport Development Program (ADP).[10]
Even with the completion of these projects, there is an ongoing demand need for additional infrastructure improvements. The main planning tool to provide guidance on near-term and long-term Airport land-use is a Master Plan. The airport's 20-year Master Plan was completed in 2006, with input from the OAK Aviation Stakeholder Advisory Committee.[10]
- Environmental Management
Oakland International Airport, a revenue division of the Port of Oakland, takes a leadership role in promoting a sustainable operating environment—whether looking at current day-to-day operations or forecasting future needs and requirements.
The Port of Oakland is an independent department of the city of Oakland and is required to do its part to be a good neighbor, an environmental steward, and a responsible business operator in its efforts to support the city's sustainability goals. Through its efforts, the Port of Oakland contributed to the recognition of the city of Oakland as one of the best examples of urban sustainability at the 2005 United Nations World Environment Day conference in San Francisco.
The Port of Oakland has adopted a sustainability policy, also known as the "Three E's," that is based on the values of environmental responsibility, economic vitality and social equity.
Expansion
In May 2015, Oakland International Airport's Moving Modern program construction commenced a $100 million renovation of the Terminal 1 complex. The project includes seismic architectural retrofits in central buildings, replacement and upgrading of infrastructure and improvement of the passenger environment. The project is expected to be completed in Spring 2017.[16]
Recent developments


Following the years of the Great Recession, during which a few airlines were either liquidated (ATA Airlines and Aloha Airlines), or consolidated business to San Francisco International Airport (Continental Airlines and American Airlines), OAK started a gradual recovery, which has continued through 2017.
In 2009, Allegiant Air moved operations from San Francisco International Airport, before designating OAK as a focus city. After the bankruptcies of ATA and Aloha Airlines, Alaska Airlines and Hawaiian Airlines replaced their nonstop services to Hawaii. In the same year, Volaris began service to OAK as their first destination in the San Francisco Bay Area and held a commercial agreement with Southwest Airlines, until its merger with AirTran Airways in 2011. Malaysia-based AirAsia X honored its new partners, the Oakland Raiders of the National Football League (NFL). AirAsia X had one of their planes full of its executives and crew members "touch down" at OAK in acknowledgment of the to-be announced sponsorship. AirAsia executives had new optimism that service between the U.S. and the airline's main base in Kuala Lumpur, could possibly happen earlier than originally expected, but has yet to come to fruition as of 2017.
In 2009, OAK had the highest on-time arrival percentage among the 40 busiest North American airports.[17][18]
In 2011, Spirit Airlines returned to OAK after several years of absence, eventually flying a combined total of seven year-round and seasonal routes by the summer of 2017. Oakland International Airport also celebrated its 85th Anniversary in 2011, commemorating the first transpacific crossing by air from OAK to Hawaii, which took place on June 29, 1927 in The Bird of Paradise, flown by Hegenberger and Maitland. In 2012, United Airlines discontinued operations at OAK, consolidating operations at San Francisco International Airport, its Bay Area hub. Arkefly (which later re-branded as TUI Airlines Netherlands) chose OAK as a San Francisco Bay Area gateway, flying twice-weekly to Amsterdam, via a stop at Los Angeles International Airport. Arkefly provided 18 weeks of scheduled service in the summer of 2012. The airline followed with a similar schedule during the summer of in 2013, before discontinuing service at OAK.
In 2013, FedEx Express opened a $30 million upgrade of its hub facility at OAK, including additions to accommodate the airline's new Boeing 777 Freighter fleet. In 2014, Norwegian Air Shuttle announced its first two year-round flights to Stockholm and Oslo airport, using Boeing 787-8 aircraft seating 291 passengers operated by Norwegian Long Haul. The flights were the first-ever nonstop services offered from the two Scandinavian capitals to the San Francisco Bay Area, providing several connections throughout Europe. The Oslo flight was later changed to a seasonal schedule.
In 2016, Norwegian Air Shuttle announced nonstop flights connecting Oakland with London beginning the following spring. British Airways responded with their own service to London, with both airlines providing service to London's Gatwick Airport. American Airlines also returned and re-branded, following a merger with US Airways; the latter previously having a short-term presence at OAK, following a separate merger with America West Airlines during the previous decade. Southwest Airlines inaugurated nonstop flights from Oakland to Mexico for the airline's first international nonstop flights from OAK. The additional routes also gave the airline a combined total of 30 year-round and seasonal flights at the airport as of early 2017.
In 2017, Norwegian Air Shuttle announced nonstop flights connecting Oakland with Copenhagen on a seasonal basis from March 28, and Oakland with Barcelona from June 7 to operate year-round. Level, a new carrier owned by IAG, responded with their own Barcelona service, started flights initially operated by IAG partner Iberia on June 2, with both airlines providing service to Barcelona El Prat Airport.[19] In the months following, Norwegian announced in May the introduction of nonstop flights between Oakland and Rome Fiumicino started on February 6, 2018,[20] and in July the introduction of nonstop flights between Oakland and Paris Charles de Gaulle began on April 10, 2018.[21]
Facilities and aircraft
Overview

Oakland International Airport covers 2,600 acres (1,100 ha) and has four runways.[1] Changes to Earth's magnetic field required runways 27 and 29 to be rebranded as 28 and 30, respectively in 2013.[22]
- South Field (Commercial and cargo operations):
- Runway 12/30: 10,520 ft × 150 ft (3,206 m × 46 m) asphalt
- North Field (general aviation operations):
- Runway 10R/28L: 6,213 ft × 150 ft (1,894 m × 46 m) asphalt
- Runway 10L/28R: 5,458 ft × 150 ft (1,664 m × 46 m) asphalt
- Runway 15/33: 3,376 ft × 75 ft (1,029 m × 23 m) asphalt
A number of general aviation FBOs are at the North Field:
- Transient aircraft support
- KaiserAir
- Signature Flight Support
- Flying Clubs
- Repair operations
- Sundance Air Services[25]
- Other
- Aerial Advertising Services
- Oakland Aviation Museum, formerly Western Aerospace Museum
- Pacific Aerial Surveys
In 2017 the airport had 235,034 aircraft operations, an average of 644 per day. This consisted of 55% scheduled commercial, 34% general aviation, 10% air taxi and <1% military. 264 aircraft are based at the airport: 61% single-engine, 27% jet, 9% multi-engine, and 3% helicopter.[1]
Terminals
The passenger terminal complex at Oakland International Airport consists of two passenger terminals - T1 & T2. Both terminals are connected to each other at post-security & gate areas, enabling arriving passengers to go straight to their connecting flights without having to re-enter the security check. U.S. Customs & Border Protection federal inspection facilities are located in Terminal 1.
Terminal 1 of Oakland International currently serves Alaska Airlines, Allegiant Air, American Airlines, Azores Airlines, Boutique Air, Contour Airlines, Delta Air Lines, Hawaiian Airlines, JetBlue, Norwegian Air Shuttle, Southwest Airlines, Spirit Airlines, and Volaris. The ground level houses the baggage claim area, Customs, and most of the ticket counters (while Volaris & Hawaiian ticket counters are on level 2). Level 2 houses the security check with access to gates 1–17 (gates 1 & 3 are international gates) near gate 4 is a connector to gates 20–32 of T2. Terminal 1 has a passenger transit area and a Lost & Found station. Three food & drink establishments and a newsstand are in pre-security, while all other food & drink, duty-free shop, newsstands, bars & shoeshine stand are in post-security, at the gates. The majority of the Port's aviation department offices are located in Terminal 1.
Terminal 2 of Oakland International, which is exclusively served by Southwest Airlines, has a baggage claim area and ticketing desks, with security checkpoint in the center and access to gates 20–25 and gates 26–32. At T2's gate 20 is the connector to T1's gates 1–17. While pre-security offers a coffee shop and newsstand, all other concessions are located in post-security at gates.
Airlines and destinations
Passenger
Cargo
Statistics



Top destinations
| Rank | City | Passengers | Annual Change | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Los Angeles, California | 600,400 | Delta, Southwest, Spirit | |
| 2 | Las Vegas, Nevada | 519,560 | Allegiant, JetSuiteX, Southwest, Spirit | |
| 3 | Seattle/Tacoma, Washington | 443,970 | Alaska, Southwest | |
| 4 | San Diego, California | 421,040 | Southwest | |
| 5 | Burbank, California | 420,030 | JetSuiteX, Southwest | |
| 6 | Phoenix–Sky Harbor, Arizona | 342,910 | American, Southwest | |
| 7 | Orange County, California | 309,090 | Southwest | |
| 8 | Long Beach, California | 302,410 | JetBlue, Southwest | |
| 9 | Portland, Oregon | 279,000 | Alaska, Southwest | |
| 10 | Ontario, California | 266,710 | Southwest |
| Rank | City | Passengers | Carriers |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 91,979 | British Airways, Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 2 | 76,857 | Level, Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 3 | 56,411 | Volaris | |
| 4 | 35,256 | Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 5 | 34,917 | Southwest | |
| 6 | 33,904 | Southwest | |
| 7 | 29,309 | Volaris | |
| 8 | 16,501 | Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 9 | 15,738 | Volaris | |
| 10 | 15,239 | Norwegian Air Shuttle | |
| 11 | 5,912 | Volaris | |
| 12 | 2,356 | Azores Airlines | |
| 13 | 1,608 | Volaris |
Airline market share
| Rank | Airline | Passengers | Share |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Southwest Airlines | 8,965,000 | 72.55% |
| 2 | Spirit Airlines | 811,000 | 6.56% |
| 3 | Alaska Airlines | 708,000 | 5.73% |
| 4 | JetBlue Airways | 415,000 | 3.36% |
| 5 | Hawaiian Airlines | 352,000 | 2.85% |
Annual traffic
| Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers | Year | Passengers | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1991 | 6,181,251 | 2001 | 11,416,579 | 2011 | 9,266,570 | ||
| 1992 | 6,542,120 | 2002 | 12,634,905 | 2012 | 10,040,864 | ||
| 1993 | 7,493,782 | 2003 | 13,548,363 | 2013 | 9,742,887 | ||
| 1994 | 8,345,725 | 2004 | 14,098,327 | 2014 | 10,336,788 | ||
| 1995 | 9,834,869 | 2005 | 14,417,575 | 2015 | 11,205,063 | ||
| 1996 | 9,734,859 | 2006 | 14,433,669 | 2016 | 12,070,967 | ||
| 1997 | 9,144,806 | 2007 | 14,613,489 | 2017 | 13,072,245 | ||
| 1998 | 9,231,553 | 2008 | 11,474,456 | ||||
| 1999 | 9,879,518 | 2009 | 9,505,281 | ||||
| 2000 | 10,620,798 | 2010 | 9,542,333 |
Transportation


BART
The Coliseum–Oakland International Airport line, also known as BART to OAK Airport, is an automated guideway transit (AGT) system that connects BART Coliseum station and Oakland International Airport (BART station) terminal buildings. The AGT vehicles depart from the airport and Coliseum station every five minutes during daily peak hours, and are designed to transport travelers to and from the airport in about eight minutes with an on-time performance of more than 99 percent. The Oakland Airport Connector Project is largely attributable to the work of former BART director and port commissioner Carole Ward Allen who was responsible for securing local, state, and federal funding for the project.[46][47] Ward Allen advocated for its approval before several transportation authorities, which created between 2,500 and 5,200 direct and indirect jobs.[48][49][50] Some critics of the project argued that the money would be better spent on supporting existing local transit agencies, which had financial issues at the time.[48]
The system opened on November 22, 2014.
Amtrak
The Amtrak Capitol Corridor train stops at the BART Coliseum station. The pedestrian walkway connects both platforms.
Bus
There are three AC Transit routes that serve Oakland Airport, one route runs during the daytime and early evenings, one route runs at all times, and the last route runs overnights as a part of the Bay Area's All Nighter bus network:
- Route 21 provides daytime and early evening service from the airport to the Dimond District via Bay Farm Island, Alameda, and Fruitvale, making a limited connection with the Alameda Harbor Bay Ferry at Bay Farm Island, and a full-time connection with BART at Fruitvale station.[51]
- Route 73 provides 24/7 service from the airport to the Eastmont Transit Center in East Oakland via Hegenberger Road and 73rd Avenue, connecting with Amtrak's Capitol Corridor service and BART at Oakland Coliseum station. This route provides a cheaper alternative to the Coliseum–Oakland International Airport line.[52]
- Route 805 is an All Nighter service from the airport to the 12th Street Oakland City Center BART station in Downtown Oakland. Route 805 supplements Route 73 service to the Eastmont Transit Center before traveling north on MacArthur Boulevard and Grand Avenue to the 12th Street Oakland City Center station, making a limited connection with Amtrak's Capitol Corridor service at Oakland Coliseum station, and additional limited connections with BART at Oakland Coliseum station and 19th Street Oakland station.[53]
Two private bus companies provide daily service from the airport to various destinations in the North Bay:
- Evans Transportation provides service from the airport to Napa and Vallejo.[54]
- Sonoma County Airport Express provides service from the airport to Charles M. Schulz–Sonoma County Airport, Petaluma, Rohnert Park, San Rafael, and Santa Rosa, making a connection with SMART at the San Rafael Transit Center station.[55]
Road
Oakland International is accessible from Interstate 880 (Nimitz Freeway) which is 2 miles (3 km) away. The airport can be reached by exiting Hegenberger Road or 98th Avenue heading west; both streets converge into Airport Road before looping around in front of the terminals.
Taxi
Taxis depart from designated taxi zones located at both Terminal 1 and 2 airport curbside.
Transportation Network Companies such as Lyft, Uber and Wingz are available via their respective mobile apps and pick up and drop off at the curbside terminals.
General aviation
Landmark Aviation is the FBO (fixed-base operator) at Oakland International Airport. Landmark's FBO at OAK is its first in the Bay Area and the twelfth location added to the network in 2011. The FBO is centrally located at OAK's North Field in the Hangar 5 facility. Landmark has initiated a multimillion-dollar renovation project, having already upgraded the FBO terminal along with beginning hangar and property improvements.[56]
KaiserAir also provides FBO (fixed-base operator) at Oakland's North Field. KaiserAir performs maintenance on Gulfstream, Hawker, Cessna and other business jet aircraft. KaiserAir operates Kona Shuttle with flights to Hawaii and charter business jets.
Awards
- The LEED Silver Certification Award has environmentally-cautious initiatives for Terminal 2's renovation and expansion were recognized by the U.S. Green Building Council. During March 2010, for the first time among the country's passenger-terminals, the council awarded OAK's No. 2 for Leadership in Energy and Environmental Design (LEED) Silver Certification.[57]
See also
- List of airports in the San Francisco Bay Area
- List of airports in California
- California World War II Army Airfields
References
- ^ a b c d FAA Airport Form 5010 for OAK PDF, effective October 25, 2007
- ^ [1] (official site)
- ^ [2]
- ^ "Metropolitan Oakland International Airport". Geographic Names Information System. United States Geological Survey, United States Department of the Interior. Retrieved May 3, 2009.
- ^ "RITA – BTS – Transtats". transtats.bts.gov.
- ^ "Fact Sheet" (PDF). Southwest Airlines. Retrieved August 10, 2015.
- ^ Official Airline Guide published schedules for Winter/Spring 2014
- ^ Reuther, Ronald T.; Larkins, William T. Oakland Aviation. p. 17.
- ^ "Oakland Airport" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on December 1, 2006. Retrieved November 3, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h i "A History of Aviation Excellence and Importance to the Community". Port of Oakland. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
- ^ Barnes Warnock McCormick; Conrad F. Newberry; Eric Jumper. Aerospace Engineering Education During The First Century of Flight. p. 858.
- ^ "Oakland International Airport, Terminal 1". Northern California Chapter, Documentation and Conservation of Buildings. Retrieved July 16, 2012.
- ^ "FAA Dedicates New Control Tower at Oakland International Airport" (Press release). Federal Aviation Administration. November 22, 2013. Retrieved January 27, 2014.
- ^ "Oakland Int'l Gains New Public Transportation Link". Oakland Airport.
- ^ "Archived copy" (PDF). Archived from the original (PDF) on January 24, 2015. Retrieved January 23, 2015.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: archived copy as title (link) - ^ "Oakland International Airport: Press Releases". Oakland Airport.
- ^ "Oakland International Airport: Press Releases" (Press release). Port of Oakland. January 12, 2010. Archived from the original on January 20, 2011. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
{{cite press release}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Oakland Best Among Top 40 North American Airports". Flightstats.com. January 6, 2010. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
- ^ "BA owner IAG launches new long-haul airline Level". BBC News.
- ^ "Norwegian Air to fly to Italy from three U.S. cities; $189 one-way fares". Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ Liu Jim (July 5, 2017). "Norwegian expands Paris – US flights in 2018". Routesonline. UBM (UK) Ltd. Retrieved July 7, 2017.
- ^ "Oakland Airport Runways Renamed After Changes in Earth's Magnetic Field".
- ^ "Oakland Flyers". Oakland Flyers. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
- ^ "Alameda Aero Club". Alameda Aero Club. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
- ^ "Sundance Air Services". Kaiser Air. Retrieved June 29, 2017.
- ^ "Flight Timetable". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Allegiant Interactive Route Map". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ a b "Flight schedules and notifications". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Schedules". Azores Airlines.
- ^ "Route Map and Schedule". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Contour Airlines". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ a b "FLIGHT SCHEDULES". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Destinations". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "JetBlue Airlines Timetable". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Where we fly - JetSuiteX". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Kona Shuttle". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Norwegian announces new direct flights to Miami and San Francisco as part of new summer 2019 long-haul programme". Norwegian.com (Press release). Norwegian Air Shuttle ASA. November 28, 2018. Retrieved November 28, 2018.
- ^ "Route Map | Norwegian". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Check Flight Schedules". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Where We Fly". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "Volaris Flight Schedule". Retrieved April 7, 2018.
- ^ "CA: Metropolitan Oakland International (OAK)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved September 25, 2017.
- ^ "U.S. International Air Passenger and Freight Statistics Report". Retrieved August 23, 2017.
- ^ "CA: Metropolitan Oakland International (OAK)". Bureau of Transportation Statistics. Retrieved February 22, 2017.
- ^ "Passenger History by Month - Oakland International Airport". Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "BART Board awards Oakland Airport Connector contract in historic vote - bart.gov". www.bart.gov. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "BART Board Approves New Oakland Airport Connector Funding Plan". Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ a b Emamdjomeh, Armand. "Could $70 Million for the Oakland Airport Connector Be Better Spent?". Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "BART Board reaffirms contract authorization for Oakland Airport Connector - bart.gov". www.bart.gov. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "BART breaks ground on rail extension to Oakland airport". October 20, 2010. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "Route 21" (PDF). AC Transit. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
- ^ "Route 73" (PDF). AC Transit. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
- ^ "Route 805" (PDF). AC Transit. Retrieved December 23, 2017.
- ^ "Bus and limousine transportation to San Francisco and Oakland airports, charter services, and Napa and Sonoma winery tours from Evans Transportation". www.evanstransportation.com. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "Sonoma County Airport Express Inc". Sonoma County Airport Express. Retrieved August 12, 2018.
- ^ "News & Events". Landmark Aviation.
- ^ "Southwest's Oakland Terminal is Awarded LEED Green Building Silver Certification". Nuts About Southwest. March 17, 2010. Retrieved April 19, 2012.
External links
![]() Media related to San Francisco Bay Oakland International Airport at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to San Francisco Bay Oakland International Airport at Wikimedia Commons
- Official website
- FAA Airport Diagram (PDF), effective November 28, 2024
- Resources for this airport:
- AirNav airport information for KOAK
- ASN accident history for OAK
- FlightAware airport information and live flight tracker
- NOAA/NWS weather observations: current, past three days
- SkyVector aeronautical chart for KOAK
- FAA current OAK delay information