Dichlorophen: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
ref |
density |
||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} |
| StdInChIKey_Ref = {{stdinchicite|changed|chemspider}} |
||
| StdInChIKey = MDNWOSOZYLHTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| StdInChIKey = MDNWOSOZYLHTCG-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
||
| density = 1. |
| density = 1.5 g/cm<sup>3</sup> |
||
| melting_point = 177.5 |
| melting_point = 177.5 |
||
| solubility = 0.003 g/100 mL<ref name="hand2"> |
| solubility = 0.003 g/100 mL<ref name="hand2"> |
||
| Line 113: | Line 113: | ||
| accessdate = |
| accessdate = |
||
}}</ref> |
}}</ref> |
||
| LD50 = 1000 mg/kg (mouse, oral)<ref name="gard"/> |
|||
--> |
|||
}} |
}} |
||
Revision as of 10:54, 12 April 2019
 | |
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.002.335 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
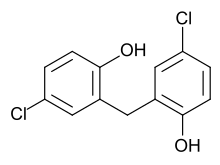
| Formula | C13H10Cl2O2 |
| Molar mass | 269.12 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Density | 1.5 g/cm3 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 177.5 °C (351.5 °F) |
| Solubility in water | 0.003 g/100 mL[1] mg/mL (20 °C) |
| |
| |
| | |
Dichlorophen is an anticestodal agent, fungicide, germicide, and antimicrobial agent.[2] It is used in combination with toluene for the removal of parasites such as ascarids, hookworms, and tapeworms from dogs and cats.[3]
Safety and regulation
LD50 (oral, mouse) is 3300 mg/kg.[4]
References
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998), Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.), Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press, pp. 8–118, ISBN 0-8493-0594-2
- ^ Milne, G.W.A. (Ed.). (2005). Gardner's commercially important chemicals: Synonyms, trade names, and properties. Hoboken, N.J.: Wiley-Interscience. Google Books
- ^ "Code of Federal Regulations", Code of Federal Regulations, Title 21, Volume 6, U.S. Government Printing Office, 2005-04-01, retrieved 2009-05-01
- ^ Helmut Fiege; Heinz-Werner Voges; Toshikazu Hamamoto; Sumio Umemura; Tadao Iwata; Hisaya Miki; Yasuhiro Fujita; Hans-Josef Buysch; Dorothea Garbe; Wilfried Paulus (2007). "Phenol Derivatives". Ullmann's Encyclopedia of Industrial Chemistry. Weinheim: Wiley-VCH. doi:10.1002/14356007.a19_313. ISBN 978-3527306732.
