Siege of Veracruz: Difference between revisions
spelling error |
|||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
[[Category:United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries|Veracruz]] |
[[Category:United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries|Veracruz]] |
||
[[Category:March 1847 events]] |
[[Category:March 1847 events]] |
||
[[Category:Amphibious operations involving the United States]] |
|||
Revision as of 12:18, 5 July 2019
| Siege of Veracruz | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Mexican–American War | |||||||
 Scott's siege guns were in place on ground outside the city | |||||||
| |||||||
| Belligerents | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Commanders and leaders | |||||||
|
|
| ||||||
| Strength | |||||||
| 8,600[1] | 3,360[1] | ||||||
| Casualties and losses | |||||||
|
13 killed 55 wounded[1][2] |
80[1]-350 killed 50 wounded[2] 3,000 captured | ||||||
| 100-1,000 civilians killed[1] | |||||||
The Battle of Veracruz was a 20-day siege of the key Mexican beachhead seaport of Veracruz, during the Mexican–American War. Lasting from March 9–29, 1847, it began with the first large-scale amphibious assault conducted by United States military forces, and ended with the surrender and occupation of the city. U.S. forces then marched inland to Mexico City.
Background
After the battles of Monterrey and Buena Vista, much of Zachary Taylor's Army of Occupation was transferred to the command of Major General Winfield Scott in support of the upcoming campaign.[1]: 237 That campaign, determined by Scott and other Washington officials, would be a Veracruz landing and an advance inland.[1]: 233 Mexican military intelligence knew in advance of U.S. plans to attack Veracruz,[1]: 204 but internal government turmoil left them powerless to send crucial reinforcements before the American assault commenced.
Opposing forces
Mexican defenses
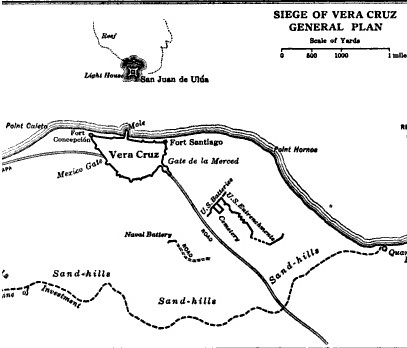
Veracruz was considered to be the strongest fortress in North America at the time.[1]: 245 Brigadier General Juan Esteban Morales commanded a garrison of 3,360 men which manned three major forts guarding Veracruz:[1]: 245
- Fort Santiago – south end of town
- Fort Concepción – north top of town
- These two forts included 3,360 men and 89 guns: artillery, 2nd and 8th infantry regiments, 3rd Light Regiment, a picket of 11th Regt., Puebla Libres, Orizaba, Veracruz, Oaxaca and Tehuantepec national guards. Battalions, sappers and enlisted marines.
- Fort San Juan de Ulúa – offshore on the Gallega Reef. Gen. Jose Durán with 1,030 men and 135 guns:[1]: 245 artillery, Puebla and Jamiltepec activo battalions, companies of Tuxpan, Tampico and Alvardo activo battalions.
- See Orders of Battle Mexican War.
Landings

The Americans arrived at Anton Lizardo, Veracruz in early March.[1]: 240 Scott agreed with Conner's suggestion for a landing site at Collado Beach, 3 mi (4.8 km) south of Veracruz.[1]: 241 The 1st Regular Division under Worth was chosen to make the landing first, followed by Patterson's volunteers and then Twiggs' regular division.[1]: 241
Conner's Mosquito Fleet moved to within 90 yd (82 m) of the beach to supply covering fire if necessary.[1]: 241 By 12:15 pm on 9 March, this force was off Collado Beach, followed by larger vessels over the next three hours and a signal for landing the surfboats at 5:30 pm.[1]: 244 Just before the main force touched the beach, a gig dashed ahead, and General Worth with his staff jumped ashore.[1]: 244 Worth's whole division landed without firing or receiving a single shot. By 11 pm, Scott's entire army had been brought ashore without a single man lost,[1]: 244 and the first large scale amphibious landing conducted by the U.S. military was a success.
Siege
Envelopment
Once ashore Patterson's division began marching northward to effect a complete envelopment of the city.[1]: 245 One of Patterson's brigades under Gideon Pillow drove off a Mexican cavalry at Malibrán, cutting off the Alvarado road and the city's water supply.[1]: 246 Quitman and Shields managed to drive off cavalry with one shot attempting to prevent the investment.[1]: 246 By 13 March, the U.S. had completed a 7 mi (11 km) siege line from Collado in the south to Playa Vergara in the north.[1]: 246 On 17 March, siege lines were dug for Scott's siege artillery, sufficient for taking the city but not Ulua.[1]: 247
Investment
The besiegers were plagued by sorties from the city, and Col. Juan Aguayo used the cover of a storm to slip his Alvarado garrison into Veracruz.[1]: 247 Commodore Matthew C. Perry, Conner's successor, returned from Norfolk, Virginia after making repairs on the USS Mississippi, on 20 March.[1]: 248 Perry and Conner met with Scott regarding the Navy's role in the siege, and offered six guns that were to be manned by sailors from the ships.[1]: 249 The naval battery was constructed under the direction of Captain Robert E. Lee 700 yd (640 m) from the city walls.[1]: 250
On March 22, Morales declined a surrender demand from Scott, and the American batteries opened fire at 4:15 pm followed by those of Commander Josiah Tattnall's Mosquito Fleet at 5:45 pm.[1]: 249 The Naval battery's heavy cannonballs easily broke the coral walls.[1]: 250 Congreve rockets were fired into the defenses[1]: 250 and the combined fire forced the abandonment of Fort Santiago as Mexican morale began to drop.[1]: 250
On March 24, Persifor F. Smith's brigade captured a Mexican soldier with reports that Antonio López de Santa Anna was marching an army from Mexico City to the relief of Veracruz.[1]: 251 Scott dispatched Colonel William S. Harney with 100 dragoons to inspect any approaches that Santa Anna might make.[1]: 251 Harney reported about 2,000 Mexicans and a battery not far away, and he called for reinforcements.[1]: 251 General Patterson led a mixed group of volunteers and dragoons to Harney's aid and cleared the force from their positions, chasing them to Madellin.[1]: 251
Surrender

Scott made plans for an assault on the city when on 25 March, the Mexicans called for a cease-fire to evacuate women and children which Scott refused.[1]: 251 That night, Morales' council of war advised surrender prompting Morales to resign while General José Juan Landero assumed command.[1]: 251 A truce was called at 8 am on 26 March while terms of surrender were negotiated and concluded by 27 March.[1]: 251 On 29 March, the Mexicans officially surrendered their garrisons in Veracruz and Fort Ulúa and later that day, the U.S. flag flew over San Juan de Ulúa.[1]: 252–253
Aftermath
The obstacle to an advancement to Mexico City was removed and Scott made immediate plans to leave a small garrison at Veracruz and march inland, his first objective being Jalapa.[1]: 259–261 Along the way, Scott would in fact encounter a sizable Mexican army under Santa Anna at the Battle of Cerro Gordo.
See also
References
Further reading
- Nevin, David; editor, The Mexican War (1978)
- Alcaraz, Ramon, "Apuntes Para la Historia de la Guerra Mexico y los Estados Unidos"
- Skelton, Ike, "It Ain't New"
- Tschanz, David W. "Yellow Fever and the Strategy of the Mexican-American War"
- Annual Reports 1894, War Department lists trophy guns: 3 – 16-pounder, 3 – 12-pounders, 1 – 8-pounder, 2 – 6-pounders, 1 – 4-pounder and 1 – 10-inch mortar.
External links
- A Continent Divided: The U.S.–Mexico War, Center for Greater Southwestern Studies, the University of Texas at Arlington
- Aztec Club of 1847 annotated art gallery
- Sieges of the Mexican-American War
- 1847 in Mexico
- Veracruz (city)
- Battles of the Mexican–American War
- Battles of the Texas Ranger Division
- Naval battles of the Mexican–American War
- Mexican–American War forts
- United States Marine Corps in the 18th and 19th centuries
- March 1847 events
- Amphibious operations involving the United States
