Butterfly diagram: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
|||
| Line 37: | Line 37: | ||
[[Category:FFT algorithms]] |
[[Category:FFT algorithms]] |
||
[[de:Schmetterlingsgraph]] |
|||
Revision as of 10:41, 28 November 2006
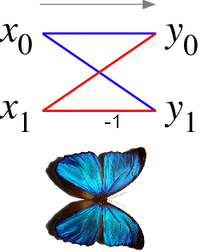
In the context of fast Fourier transform algorithms, a butterfly is a portion of the computation that combines the results of smaller discrete Fourier transforms (DFTs) into a larger DFT, or vice versa (breaking a larger DFT up into subtransforms). The name "butterfly" comes from the shape of the data-flow diagram in the radix-2 case, as described below. The same structure can also be found in the Viterbi algorithm, used for finding the most likely sequence of hidden states.
Most commonly, the term "butterfly" appears in the context of the Cooley-Tukey FFT algorithm, which recursively breaks down a DFT of composite size into smaller transforms of size where is the "radix" of the transform. These smaller DFTs are then combined with a size- butterflies, which themselves are DFTs of size (performed times on corresponding outputs of the sub-transforms) pre-multiplied by roots of unity (known as twiddle factors). (This is the "decimation in time" case; one can also perform the steps in reverse, known as "decimation in frequency", where the butterflies comes first and are post-multiplied by twiddle factors. See also the Cooley-Tukey FFT article.)
Radix-2 butterfly diagram
In the case of the radix-2 Cooley-Tukey algorithm, the butterfly is simply a DFT of size 2 that takes two inputs (corresponding outputs of the two sub-transforms) and gives two outputs by the formula (not including twiddle factors):
If one draws the data-flow diagram for this pair of operations, the to lines cross and resemble the wings of a butterfly, hence the name. (See also the illustration at right.)







