2019 in science: Difference between revisions
Appearance
Content deleted Content added
→Deaths: removed separations by months, unnecessary |
|||
| Line 334: | Line 334: | ||
*July 20 - [[Liane Russell]], American geneticist (b. 1923) |
*July 20 - [[Liane Russell]], American geneticist (b. 1923) |
||
*July 22 - [[Christopher C. Kraft Jr.]], American aerospace engineer (b. 1924) |
*July 22 - [[Christopher C. Kraft Jr.]], American aerospace engineer (b. 1924) |
||
*July 27 - [[John Robert Schrieffer]], American physicist (b. 1931) |
*July 27 - [[John Robert Schrieffer]], American physicist and Nobel laureate (b. 1931) |
||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
Revision as of 04:13, 28 July 2019
This article needs additional citations for verification. (September 2018) |
| |||
|---|---|---|---|
| +... |
A number of significant scientific events have occurred or are scheduled to occur in 2019.
Events
January
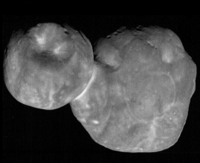
- 1 January – The New Horizons space probe flies by Kuiper belt object (486958) 2014 MU69 (aka Ultima Thule), the outermost close encounter of any solar system object.[2][3][4]
- 2 January – A study finds that tons of methane, a greenhouse gas, are released into the atmosphere by melting ice sheets in Greenland.[5]
- 3 January
- 4 January
- Researchers at Ecole polytechnique fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) report a way to control properties of excitons and change the polarisation of light they generate, which could lead to transistors that undergo less energy loss and heat dissipation.[9]
- Researchers design an inhalable form of messenger RNA aerosol that could be administered directly to the lungs to help treat diseases such as cystic fibrosis.[10]
- 6 January
- A partial solar eclipse occur.
- 8 January
- Researchers from the U.S. Department of Energy's Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory (PPPL) report a new way to stabilise the "tearing modes" in fusion reactors, using radio waves to create small changes in the temperature of the plasma, allowing it to be controlled more easily.[11]
- IBM unveils IBM Q System One, its first integrated quantum computing system for commercial use.[12][13]
- 9 January
- Astronomers announce the discovery of a second repeating fast radio burst (FRB) source, named FRB 180814.[14][15]
- The first SD card with a storage capacity of 1 terabyte (TB) is announced by Lexar.[16]
- Astronomers at the University of Warwick present the first direct evidence of white dwarf stars solidifying into crystals.[17]

- 10 January – Astronomers propose that AT2018cow, a very powerful astronomical explosion, 10–100 times brighter than a normal supernova, may have been a white dwarf being pulled apart by a black hole; or, a supernova leaving behind a black hole or a neutron star, the creation of a compact body being observed for the first time.[19][20][21]
- 11 January – Researchers at the University of Michigan demonstrate a new approach to 3D printing, based on the lifting of shapes from a vat of liquid, which is up to 100 times faster than conventional processes.[22]
- 14 January – A study in the journal PNAS finds that Antarctica experienced a sixfold increase in yearly ice mass loss between 1979 and 2017.[23]
- 16 January – A study in Ecological Monographs suggests there may be sustained foraging specialization, fasting and omnivory in the whale shark Rhicodon typus, the world's largest fish.[24]
- 17 January
- Scientists report that Australopithecus sediba is distinct from, but shares anatomical similarities to, both the older Australopithecus africanus, and the younger Homo habilis.[18]
- Astronomers report that a day on the planet Saturn has been determined to be 10h 33m 38s + 1m 52s
− 1m 19s , based on studies of the planet's C Ring.[25][26]
- 21 January
- Scientists report that the Greenland ice sheet is melting four times faster than in 2003, with its largest sustained ice loss coming from the southwest region.[27]
- Lunar eclipse
- 22 January – Alphabet's Waymo subsidiary announces that it will later in 2019 begin construction in the US State of Michigan on the World's first factory for mass-producing autonomous vehicles.[28][29][30][31]
- 23 January
- Scientists in China report the creation of five identical cloned gene-edited monkeys, using the same cloning technique that was used with Zhong Zhong and Hua Hua – the first ever cloned monkeys - and Dolly the sheep, and the same gene-editing Crispr-Cas9 technique allegedly used by He Jiankui in creating the first ever gene-modified human babies Lulu and Nana. The genetically modified monkey clones were made in order to study several medical diseases.[32][33][34]
- Astronomers report the first-ever detection of glycolonitrile, another possible building block of life among other such molecules, in outer space.[35]

- 24 January
- NASA announces that the Opportunity rover has been on the planet Mars for 15 years.[36][37]
- NASA scientists report the discovery of the oldest known Earth rock – on the Moon. Apollo 14 astronauts returned several rocks from the Moon and later, scientists determined that a fragment from one of the rocks contained "a bit of Earth from about 4 billion years ago." The rock fragment contained quartz, feldspar, and zircon, all common on the Earth, but highly uncommon on the Moon.[38]
- The complete axolotl genome is reported to have been sequenced by the University of Kentucky.[39][40]
- 25 January – AlphaStar, a new artificial intelligence algorithim by Alphabet's DeepMind subsidiary, defeats professional players of the real-time strategy game StarCraft II in ten rounds out of eleven.[41][42][43]
- 29 January – Researchers at Purdue University's College of Engineering release a paper in the journal ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering detailing a new process to turn plastic waste in hydrocarbon fuels.[44][45][46]
- 30 January – Scientists report that several types of humans, including Denisovans, Neanderthals and related hybrids, may have habitat-ed the Denisova Cave in Siberia over thousands of years, but it is unclear whether they ever shared the cave.[47]
- 31 January
- Researchers at the University of California, Berkeley, demonstrate a new form of 3D printer, which uses light exposure to transform a viscous liquid into complex solid objects.[48]
- A new AI developed by RMIT University in Melbourne and trained to play the 1980s video game Montezuma's Revenge is reported to be 10 times faster than Google DeepMind and able to finish the game.[49]
February

- 1 February – NASA scientists report that the Mars Curiosity rover determined, for the first time, the density of Mount Sharp in Gale crater, thereby establishing a clearer understanding of how the mountain was formed.[52][53]
- 3 February – Medical scientists announce that iridium attached to albumin, creating a photosensitized molecule, can penetrate cancer cells and, after being irradiated with light (a process called photodynamic therapy), destroy the cancer cells.[50][51]
- 4 February – A study by the International Centre for Integrated Mountain Development concludes that 36% of glaciers along the Hindu Kush and Himalaya range will disappear by 2100, even if carbon emissions are cut rapidly. Without emission reductions, the loss could reach two-thirds.[54][55]
- 5 February – NASA reports that the two small communication CubeSats, that accompanied the InSight lander to the planet Mars, went silent, and are unlikely to be heard from again.[56]
- 6 February
- NASA and NOAA confirm that 2018 was the fourth hottest year on record globally, at 0.83 degrees Celsius (1.5 degrees Fahrenheit) above the 1951 to 1980 mean.[57]
- Scientists from the Instituto de Astrofísica de Canarias publish the first evidence of a collision between exoplanets, which is believed to have occurred in the Kepler-107 system, approximately 1,670 light years from Earth.[58]
- 7 February
- Medical scientists working with Sangamo Therapeutics, headquartered in Richmond, California, announce the first ever "in body" human gene editing therapy to permanently alter DNA in a patient with Hunter Syndrome.[59] Clinical trials by Sangamo involving gene editing using Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN) are ongoing.[60]
- The ExoMars rover, scheduled to launch in July 2020 and search for the existence of past life on the planet Mars, has been officially named the Rosalind Franklin rover after DNA pioneer Rosalind Franklin.[61]
- Scientists announce the discovery of a new type of magnet that might benefit the performance of data storage technologies.[62]

- 8 February – NASA scientists, studying the latest returned images and data, report that Ultima Thule (or 2014 MU69), the remote Kuiper Belt Object visited by the New Horizons spacecraft, was determined to be more flattened than thought earlier; and has been described to be more like a large "pancake" (larger lobe) and a "walnut" (smaller lobe), rather than two ellipsoids.[1][65]
- 11 February – Scientists find evidence, based on genetics studies using artificial intelligence (AI), that suggest the existence of an unknown human ancestor species, not Neanderthal, Denisovan or human hybrid (like Denny (hybrid hominin)), in the genome of modern humans.[66][67]
- 13 February – NASA officials declare that the Mars rover Opportunity has ended its mission, after failing to respond to repeated transmitted wake-up signals. Its last contact was on 10 June 2018 (Click here for the last panorama image.)[63][64]
- 18 February
- A British woman becomes the first person in the world to have gene therapy for age-related macular degeneration (AMD).[68]
- Scientists use gene therapy to restore hearing in an adult mouse model of DFNB9 deafness.[69]
- 19 February
- Researchers at Oxford Martin School publish evidence that, in the longer term, some forms of cultured meat could be worse for the environment than traditional farmed meat.[70][71]
- Scientists report evidence, based on isotope studies, that at least some Neanderthals may have eaten meat.[72][73][74]

- 21 February
- Scientists announce a new form of DNA, named Hachimoji DNA, composed of four natural, and four unnatural nucleobases. Benefits of such an eight-base DNA system may include an enhanced ability to store digital data, as well as insights into what may be possible in the search for extraterrestrial life.[75][76]
- Scientists report that the purportedly first-ever germline genetically edited humans, the twin babies Lulu and Nana, by Chinese researcher He Jiankui, may have inadvertently (or perhaps, intentionally[77]) had their brains enhanced.[78]
- SpaceX launches SpaceIL's Beresheet probe, the world's first privately financed mission to the Moon.[79][80]
- Astronomers led by Scott S. Sheppard announce the discovery of FarFarOut, the most distant object yet found in the Solar System, at an estimated distance of 140 AU (21 billion km) from the Sun.[81]
- 25 February
- Scientists report evidence that Neanderthals walked upright much like modern humans.[82][83]
- The first microSD card with a storage capacity of 1 terabyte (TB) is announced by Micron.[84]
- 26 February – Researchers at RMIT University demonstrate a method of using a liquid metal catalyst to turn carbon dioxide gas back into coal, potentially offering a new way to store carbon in solid form.[85]
- 28 February
March
- 3 March – An unmanned demonstration flight of the new crew capable version of the SpaceX Dragon spacecraft, intended to carry American astronauts into space, achieves successful autonomous docking with the International Space Station.[89] It returned to Earth a few days later.[90]

- 4 March – Scientists report that asteroids may be much more difficult to destroy than thought earlier.[92][93] In addition, an asteroid may reassemble itself due to gravity after being disrupted.[94]
- 5 March
- A second case of sustained remission from HIV-1 is reported, ten years after the 'Berlin Patient.'[95][96]
- Astronomers report the discovery of unusual dimming in EPIC 204376071, a star that has been observed to dim in brightness by up to 80%, much more deeply than the 22% dimming of Tabby's star.[97][98][99]
- 7 March – Researchers at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) demonstrate a new optical imaging system that could enable the discovery of tiny tumours, as small as 200 cells, deep within the body.[100]
- 8 March – Astronomers report that the mass of the Milky Way galaxy is 1.5 trillion solar masses within a radius of about 129,000 light-years, over twice as much as was determined in earlier studies, and suggesting that about 90% of the mass of the galaxy is dark matter.[101][102]
- 11 March – A team of Japanese and Russian scientists report that cell nuclei from woolly mammoth remains showed biological activity when transplanted into mouse cells.[91]
- 13 March – The laser of ELI-NP in Măgurele, part of the European ELI Project, becomes the most powerful laser system ever made, reaching a peak power of 10 Petawatts.[103]
- 15 March – NASA reports that latent viruses in humans may be activated during space missions, adding possibly more risk to astronauts in future deep-space missions.[104]

- 16 March – NASA announces that a 173-kiloton fireball (the Kamchatka meteor) fell over the Bering Sea near the Kamchatka Peninsula on 18 December 2018, the second largest asteroid to hit Earth in 30 years, after the Chelyabinsk meteor.[107] (see image)
- 18 March
- Researchers provide supporting evidence, based on genetic studies, that modern Homo sapiens, arose first in South Africa more than 300,000 years ago, traveled to East Africa, and from there, about 60,000 years ago, traveled out of Africa to the rest of the world.[108][109]
- Physicist Adrian Bejan presents an explanation of why time seems shorter as we get older, which can be attributed to "the ever-slowing speed at which images are obtained and processed by the human brain as the body ages."[110][111][112]
- 19 March
- Karen Uhlenbeck is reported to be the first woman to receive the prestigious Abel Prize in Mathematics.[113][114]
- Astronomers describe scenarios where carbon monoxide may be a biosignature for a thriving community of extraterrestrial life on other worlds.[115]
- 20 March – Paleontologists report the discovery of Avimaia schweitzerae, the first fossil bird found with an unlaid egg, that lived about 115 million years ago in Northwest China.[105][106]
- 27 March
- Scientists report that life-forms from Earth survived 18 months living in outer space outside the International Space Station (ISS), as part of the BIOMEX studies related to the EXPOSE-R2 mission, suggesting that life could survive, theoretically, on the planet Mars.[116][117]
- ESO astronomers, employing the GRAVITY instrument on their Very Large Telescope Interferometer (VLTI), announce the first direct detection of an exoplanet, HR 8799 e, using optical interferometry.[118]
- 28 March
- Researchers report the possibility of ancient life on the planet Mars based on microscopic studies of the Allan Hills 77005 (ALH-77005) Martian meteorite found on Earth.[119][120]
- Scientists report evidence that suggests the planet Mars, in some near-equatorial regions, currently contains a deep groundwater system.[121][122]
- A Pew Research Center study (4464 adults; mid-January 2019) on scientific knowledge among Americans finds substantial differences based on formal education level (higher is better), race and ethnicity (whites higher) and gender (males higher). No substantial differences were found based on political affiliation.[123]
- 29 March – Paleontologists describe a site called Tanis, in North Dakota's Hell Creek Formation, containing animal and plant fossils dated to 65.76 million years BCE. These remains are embedded with tiny rock and glass fragments that fell from the sky in the minutes and hours following the Chicxulub impact. The deposits also show evidence of having been swamped with water, caused by the subsequent megatsunamis.[124][125]
April

- 1 April
- Scientists report confirming the presence of methane on the planet Mars, and determining that the source of the methane likely came from an ice sheet about 300 miles east of Gale Crater. The Curiosity rover is currently exploring Gale Crater.[130][131][132]
- Scientists at ETH Zurich report the creation of the world's first bacterial genome, named Caulobacter ethensis-2.0, made entirely by a computer, although a related viable form of C. ethensis-2.0 does not yet exist.[133][134]
- 4 April – NASA releases animated images of solar eclipses by the two moons of the planet Mars, Deimos (animation1/17 March 2019) and Phobos (animation2/27 March 2019), as viewed by the Curiosity rover on the planet Mars in March 2019.[135][136]
- 7 April – NASA reports that a comprehensive study of microorganisms and fungi present on the International Space Station has been conducted. The results can be useful in improving health and safety conditions for astronauts.[137][138]
- 10 April – Scientists from the Event Horizon Telescope project announce the first-ever image of a black hole, located 54 million light years away in the centre of the M87 galaxy.[126][127][128][129]
- 11 April
- NASA announces that the Curiosity rover on the planet Mars drilled into, and closely studied, a "clay-bearing unit" which, according to the rover Project Manager, is a "major milestone" in Curiosity's journey up Mount Sharp.[139] (related image)
- The Israeli Beresheet probe crashes on the Moon after a technical glitch causes its main engine to switch off.[140]
- 12 April – NASA reports medical results, from an Astronaut Twin Study, where one astronaut twin spent a year in space on the International Space Station, while the other twin spent the year on Earth, which demonstrated several long-lasting changes, including those related to alterations in DNA and cognition, when one twin was compared with the other.[143][144]
- 16 April – Scientists report, for the first time, the use of the CRISPR technology to edit human genes to treat cancer patients with whom standard treatments were not successful.[145][146]
- 17 April – After a long search, astronomers report the detection of helium hydride, a primordial molecule thought to have been formed about 100,000 years after the Big Bang, for the first time in outer space in NGC 7027.[147][148]
- 23 April – NASA reports that the Mars InSight lander detected its first Marsquake on the planet Mars.[149][150] (related AudioVideo file)
- 24 April – The XENON dark matter project announces that it has observed the radioactive decay of xenon-124, which has a half-life of 1.8 sextillion years.[151][152]
- 25 April – Astronomers report further substantial discrepancies, depending on the measurement method used, in determining the Hubble constant, suggesting a realm of physics currently not well understood in explaining the workings of the universe.[153][154][155][156][157]
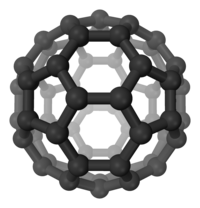
- 29 April – Scientists, working with the Hubble Space Telescope, confirmed the detection of the large and complex ionized molecules of buckminsterfullerene (C60) (also known as "buckyballs") in the interstellar medium spaces between the stars.[141][142]
- 30 April – Biologists report that the very large medusavirus, or a relative, may have been responsible, at least in part, for the evolutionary emergence of complex eukaryotic cells from simpler prokaroytic cells.[158]
May

- 1 May – A study by U.S. researchers finds that deleting the ATDC gene can prevent the growth of pancreatic cancer in mice.[162]
- 2 May
- Astronomers, from the Hubble Space Telescope, release the Hubble Legacy Field Zoom Out (video; 00:50), a 16 year effort, which provides a zoom out view from the Ultra Deep Field of galaxies to the Legacy Field of galaxies.[163]
- A study of nearly 1,000 gay male couples who took antiretroviral therapy, published in The Lancet, finds no cases of HIV transmission over eight years.[164][165]
- 3 May – The UK's National Nuclear Laboratory (NNL) and University of Leicester report the first generation of usable electricity from americium, which could lead to the development of "space batteries" that power missions for up to 400 years.[166][167]
- 6 May
- In its first report since 2005, the Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services (IPBES) warns that biodiversity loss is "accelerating", with over a million species now threatened with extinction; the decline of the natural living world is "unprecedented" and largely a result of human actions.[159][160][161]
- Researchers at Columbia University report a new desalination method for hypersaline brines, known as "temperature swing solvent extraction (TSSE)", which is low-cost and efficient.[168]
- 8 May – A British teenager, Isabelle Holdaway, 17, is reported to be the first patient to receive a genetically modified phage therapy to treat a drug-resistant infection.[169][170]
- 11 May – Atmospheric CO2, as measured by the Mauna Loa Observatory, Hawaii, reaches 415 parts per million (ppm), the highest level for 2.5 million years.[171][172] During the late Pliocene, sea levels were up to 20 m higher, and the global climate was 3 °C hotter.
- 14 May
- Computer security researchers at Graz University of Technology and Catholic University of Leuven, in a coordinated disclosure with Intel, announce the discovery of a group of Microarchitectural Data Sampling vulnerabilities, affecting millions of Intel microprocessors, which they named Fallout, RIDL (Rogue In-Flight Data Load) and ZombieLoad.[173]
- Researchers at Microsoft reported the BlueKeep security vulnerability (CVE-2019-0708) (noted as "critical" by Microsoft) that may affect nearly one million computers using older versions (Windows 8 and Windows 10 are not affected) of the Windows operating systems with a "wormable" Remote Desktop Services (RDS) Remote Code Execution (RCE) Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) vulnerability. Microsoft recommends installing available update patches as soon as possible, and also recommends turning off Remote Desktop Services if they are not required.[174][175][176][177]
- Researchers at Macquarie University report that plastic pollution is harming the growth, photosynthesis and oxygen production of Prochlorococcus, the ocean's most abundant photosynthetic bacteria, responsible for 10% of oxygen breathed by humans.[178]

- 15 May
- Researchers, in a milestone effort, report the creation of a new synthetic (possibly artificial) form of viable life, a variant of the bacteria Escherichia coli, by reducing the natural number of 64 codons in the bacterial genome to 59 codons instead, in order to encode 20 amino acids.[179][180]
- Researchers at University of Nebraska Medical Center describe the role of TGF-beta type II signaling receptor (TGFBR2) in osteoarthritis, which plays a key role in the progression of the disease by regulating joint development. They also identify a potential new drug that could treat it.[181]
- 16 May
- Astronomers report their first results about Ultima Thule, the Kuiper Belt object in the outer Solar System that the New Horizons space probe flew by in January 2019.[182][183]
- Researchers from the University of Leeds report that nearly a quarter of the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is now unstable, with melting of the Pine Island and Thwaites glaciers now five times faster than 25 years previously.[184][185]
- 19 May – Researchers at the University of Melbourne report an unusual slowdown in the growth of life expectancy in Australia, following 20 years of rapid increases.[186][187]
- 20 May
- Lawyers in China report, in light of the purported creation by Chinese scientist He Jiankui of the first gene-edited humans (see Lulu and Nana controversy), the drafting of regulations that anyone manipulating the human genome by gene-editing techniques, like CRISPR, would be held responsible for any related adverse consequences.[188]
- The redefinition of the SI system of measurement adopted by the majority of countries in the world takes effect.[189]

- 21 May – Researchers at McMaster University report the discovery of a new and more efficient method of storing vaccines in temperatures of up to 40 °C for weeks at a time.[193][194][195]
- 22 May
- Scientists report the discovery of a fossilized fungus, named Ourasphaira giraldae, in the Canadian Arctic, that may have grown on land a billion years ago, well before plants were living on land.[190][191][192]
- Superconductivity at very high pressure is observed at a temperature of -23 °C (-9 °F), a jump of about 50 degrees compared to the previous confirmed record, by researchers at the University of Chicago.[196][197]
- 23 May
- Researchers at the University of Southampton predict that the average (median) body mass of mammals will collectively reduce by 25 per cent over the next century, due to the impact of human activity.[198][199][200]
- Astronomers report the discovery of a very large amount of water in the northern polar region of the planet Mars.[201][202]
- 27 May – The last male Sumatran rhinoceros in Malaysia is reported to have died, leaving only one female in the country.[203]
- 28 May – A team from the University of Minnesota and University of Massachusetts exceed the Sabatier maximum, with a 10,000-fold increase in the rate of chemical reactions, using waves to create an oscillating catalyst.[204]
June

- 3 June – Researchers report that the purportedly first-ever germline genetically edited humans, the twin babies Lulu and Nana, by Chinese scientist He Jiankui, may have been mutated in a way that shortens life expectancy.[206][207][208]
- 4 June – Astronomers report the discovery of a star, named ASASSN-V J213939.3-702817.4, non-variable earlier, observed to be associated with a very unusual, deep dimming event. The star, in the Indus constellation, is about 3,630 ly (1,110 pc) away.[209][210][211]
- 6 June – The International Astronomical Union (I.A.U), in celebration of its hundredth anniversary, in a project called IAU100 NameExoWorlds, is reported to welcome countries of the world, to submit names for astronomical objects, particularly exoplanets and its host star, which would later be considered for official adoption by the organization.[212][213][214]
- 10 June
- Scientists report that Ahuna Mons, a very high dome-shaped mountain on the dwarf planet Ceres, may have been formed by a plume of mud ejected from deep within the planet.[205][215]
- A study by researchers from the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew, identifies nearly 600 plants that have disappeared since the Industrial Revolution – more than twice the number of birds, mammals and amphibians combined – with extinctions now occurring 500 times faster than the natural background rate.[216][217]
- 11 June
- Astronomers report that the usual Hubble classification, particularly concerning spiral galaxies, may not be supported, and may need updating.[218]
- Researchers at the University of Colorado Boulder demonstrate "nanobio-hybrid" organisms capable of using airborne carbon dioxide and nitrogen to produce a variety of eco-friendly plastics and fuels.[219]
- 12 June
- The discovery of cold quasars is announced at the 234th meeting of the American Astronomical Society.[220]
- Astronomers report the discovery of two Earth-mass exoplanets orbiting Teegarden's Star within its habitable zone.[221][222]
- 19 June – Researchers at Carnegie Mellon University demonstrate the first noninvasive mind-controlled robotic arm.[223]
- 20 June – Researchers at Lancaster University describe a new electronic memory device that combines the properties of both DRAM and flash, while recording or deleting data using hundreds of times less energy.[224]

- 21 June – Scientists release the video appearance, for the second time, and for the very first time in waters of the United States, of a giant squid in its deepwater habitat.[225][226][227]
- 22 June – Scientists working with the Curiosity rover on the planet Mars report the detection of a significant amount of methane, the largest amount ever detected by the rover – 21 parts per billion units by volume (ppbv) (i.e., one ppbv means that if you take a volume of air on Mars, one billionth of the volume of air is methane). Methane is a possible indicator of life, but may also be produced geologically.[228][229][230]
- 24 June – SpaceX successfully launches the Falcon Heavy for the 3rd time with the STP-2 mission. This is also the first Falcon Heavy mission contracted by the United States Government.
- 27 June – NASA's Dragonfly spacecraft is selected to become the fourth mission in the New Frontiers program. It will launch in 2026, arriving on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan in 2034.[231][232]
- 28 June
- Russian astronomers report the discovery of nine Fast Radio Burst (FRB) events (FRB 121029, FRB 131030, FRB 140212, FRB 141216, FRB 151125.1, FRB 151125.2, FRB 160206, FRB 161202, FRB 180321), which include one repeating FRB (FRB 151125, third one ever detected), from the direction of the M 31 (Andromeda Galaxy) and M 33 (Triangulum Galaxy) galaxies during the analysis of archive data (July 2012 to December 2018) from the BSA/LPI large phased array radio telescope at the Pushchino Radio Astronomy Observatory.[233][234][235]
- Astronomers report the detection of a star, named HD 139139 (EPIC 249706694), that dims in brightness in an apparent random, and currently unexplainable, way.[236][237][238]
July
- 1 July – Astronomers report that 'Oumuamua, an interstellar object that passed through the Solar System in October 2017, was an object of a "purely natural origin", and not otherwise.[239][240]

- 2 July
- The European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts reports that the global average temperature for June 2019 was the highest on record for the month, at 0.1 °C higher than that of the previous warmest June, in 2016.[243][244]
- A total solar eclipse occurs, with totality visible in the South Pacific and South America.[citation needed]
- Astronomers report that FRB 190523, a non-repeating Fast Radio Burst (FRB), has been discovered and, notably, localized to a few-arcsecond region containing a single massive galaxy at a redshift of 0.66, nearly 8 billion light-years away from Earth.[245][246]
- 3 July
- Scientists from the University of Bristol describe a new way to direct stem cells to heart tissue, using a designer adhesive protein.[247]
- Researchers identify more than a 1 million square kilometres (0.39 million square miles) of lost tropical rainforest across the Americas, Africa and Southeast Asia, with a high potential for restoration.[248][241][242]

- 7 July – Researchers report receiving the first pictures from LightSail 2, a CubeSat developed by The Planetary Society, and launched into Earth orbit on 25 June 2019 by a Falcon Heavy rocket.[251]
- 8 July – Astronomers report that a new method to determine the Hubble constant, and resolve the discrepancy of earlier methods, has been proposed based on the mergers of pairs of neutron stars, following the detection of the neutron star merger of GW170817.[252][253] Their measurement of the Hubble constant is 70.3+5.3
−5.0 (km/s)/Mpc.[254]

- 10 July – Anthropologists report the discovery of 210,000 year old remains of a Homo sapiens and 170,000 year old remains of a Neanderthal in Apidima Cave in southern Greece, over 150,000 years older than previous H. sapiens finds in Europe.[256][257][258]
- 11 July
- Astronomers report, for the first time, detection of a moon-forming circumplanetary disk around a distant planet, particularly PDS 70c.[259][249][250]
- Carnegie Mellon University reports an artificial intelligence program, developed in collaboration with Facebook AI, which is able to defeat leading professionals in six-player no-limit Texas hold'em poker.[260]
- 12 July – Physicists report, for the first time, capturing an image of quantum entanglement.[261][262]
- 13 July – The Russian/German Spektr-RG observatory is successfully launched into space, on a seven-year mission to study X-ray sources.[263]
- 15 July
- Astronomers report that non-repeating Fast Radio Bursts (FRB)s may not be one-off events, but actually FRB repeaters with repeat events that have gone undetected and, further, that FRBs may be formed by events that have not yet been seen or considered.[264][265]
- A paper is released in the journal Nature Astronomy in which researchers from Harvard University, the University of Edinburgh and NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) detail how silica aerogel could be used to block radiation, obtain water and permit photosynthesis to occur to make Mars more hospitable for human survival.[266][267][268][269]
- 16 July – Astronomers report the determination, based on a new method (Red Giant Stars method), of the Hubble Constant as 69.8 km s−1 Mpc−1, a value in the middle of two earlier values determined by two other methods: 67.4 (CMB Radiation method) and 74.0 (Cepheids method).[270][271]
- 17 July – Astronomers rule out the chances of ~30 m (98 ft) asteroid 2006 QV89's impacting Earth in September 2019 by eliminating the possibility of its passing through an area where it would have to be if it were on an impacting orbit. Prior to this, the asteroid had been given a one-in-7,000 chance of impacting Earth. [272]
- 22 July
- The Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) launches Chandrayaan-2, its second lunar exploration mission, which includes an orbiter, lander and rover.[255]
- Biochemists and geochemist from Earth-Life Science Institute (ELSI), Tokyo and the National University of Malaysia, Bangi report the discovery of simple organic molecules (hydroxy acids) that can assemble themselves into possible protocells under conditions similar to those of the early Earth.[273][274]
- 25 July – Astronomers report that 2019 OK, a previously undetected asteroid up to 130 metres (426 feet) across, passed within 45,000 miles (72,500 km) of Earth on 25 July 2019 at 01:22 GMT.[275]
Predicted and scheduled events
July
- 16 July – a partial lunar eclipse will occur.
October
- The CHEOPS space telescope, whose mission is to study the formation of extra-solar planets, is expected to launch in October or November.[276]
November
- 11 November – a rare transit of Mercury will occur.
- November – NASA's contract with the Russian space agency (Roscosmos) expires.[277]
December
- 26 December – a partial solar eclipse will occur.
Awards
- Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering – Bradford Parkinson, James Spilker, Hugo Fruehauf and Richard Schwartz
- Abel Prize - Karen Uhlenbeck
Deaths
- January 11 – Michael Atiyah, British-Lebanese mathematician and Fields medalist (b. 1929)
- February 6 – Manfred Eigen, German chemist and Nobel laureate (b. 1927)
- February 14 – Simon P. Norton, English mathematician, co-discoverer of 'monstrous moonshine' (b. 1952)[278]
- February 18 – Wallace Smith Broecker, American geophysicist, coined the term "global warming" (b. 1931)[279]
- March 1 – Zhores Alferov, Soviet-Russian physicist and Nobel laureate (b. 1930)
- March 20
- Georg Kreutzberg, German neurobiologist (b. 1934)
- Noel Hush, Australian chemist (b. 1924)
- March 21 - Roger Moore, American computer scientist (b. 1939)
- March 28 - Koji Nakanishi, Japanese chemist (b. 1925)
- March 30 - John Wilson Moore, American biophysicist (b. 1920)
- April 5 – Sydney Brenner, South African molecular biologist and Nobel laureate (b. 1927)
- April 6 – David J. Thouless, British physicist and Nobel laureate (b. 1934)
- April 13 - Paul Greengard, American neuroscientist and Nobel laureate (b. 1925)
- April 15 - Winston L. Shelton, American inventor (b. 1922)
- May 2 - Li Xintian, Chinese psychologist (b. 1924)
- May 3 - Goro Shimura, Japanese mathematician (b. 1930)
- May 6 - George Zimmerman, American physicist (b. 1935)
- May 8 - Robert McEliece, American mathematician and engineer (b. 1942)
- May 9 - Zhan Wenshan, Chinese physicist (b. 1941)
- May 10 - Geneviève Raugel, French mathematician (b. 1951)
- May 13 - Lo Tung-bin, Taiwanese biochemist (b. 1927)
- May 14 - Michael Rossmann, American physicist and microbiologist (b. 1930)
- May 15 - Charles Kittel, American physicist (b. 1916)
- May 18 - Mario Baudoin, Bolivian biologist (b. 1942)
- May 24 - Murray Gell-Mann, American physicist (b. 1929)
- May 25 - Margaret-Ann Armour, Canadian chemist (b. 1939)
- May 27
- Laurie Hendren, Canadian computer scientist (b. 1958)
- Aharon Razin, Israeli biochemist (b. 1935)
- May 28
- Li Hengde, Chinese material scientist (b. 1921)
- Wlodzimierz Ptak, Polish immunologist and microbiologist (b. 1928)
- June 1
- Harry Triandis, American psychologist (b. 1926)
- Fons van de Vijver, Dutch psychologist (b. 1952)
- June 2 - Henry Lynch, American physician (b. 1928)
- June 3 - Tang Dingyuan, Chinese physicist (b. 1920)
- June 4 - Teruko Ishizaka, Japanese immunologist (b. 1926)
- June 12 - Wilbert McKeachie, American psychologist (b. 1921)
- June 13 - Heinrich Reichert, Swiss neurobiologist (b. 1949)
- June 14
- George Felton, British computer scientist (b. 1921)
- James Wyngaarden, American physician (b. 1924)
- June 16
- Frederick Andermann, Canadian neurologist (b. 1930)
- Feng Chuanhan, Chinese osteologist (b. 1914)
- Francine Shapiro, American psychologist (b. 1948)
- June 17
- Kung Hsiang-fu, Chinese molecular biologist (b. 1942)
- Clemens Roothaan, Dutch physicist and chemist (b. 1918)
- June 20 - Jean-Marie Hullot, French computer scientist (b. 1954)
- June 23 - George Rozenkranz, Mexican chemist (b. 1916)
- June 29 - Dieter Enders, German chemist (b. 1946)
- June 30 - Mitchell Feigenbaum, American physicist (b. 1944)
- July 2 - Suzanne Eaton, American biologist (b. 1959)
- July 6 - Calvin Quate, American engineer (b. 1923)
- July 10
- Karen Hitchcock, American biologist (b. 1943)
- Gerald Weismann - American physician (b. 1930)
- July 12
- Fernando J. Corbató, American computer scientist (b. 1926)
- Claudio Naranjo, Chilean psychiatrist (b. 1932)
- July 13 - Harlan Lane, American psychologist (b. 1936)
- July 14
- Rahul Desikan, American neuroscientist (b. 1978)
- Hoàng Tụy, Vietnamese mathematician (b. 1927)
- July 15
- Rex Richards, British chemist (b. 1922)
- Thorsteinn Sigfusson, Icelandic physicist (b. 1954)
- July 16 - Judit Bar-Ilan, Israeli computer scientist (b. 1958)
- July 18 - Kurt Julius Isselbacher, American physician (b. 1925)
- July 19
- Godfried Toussaint, Canadian computer scientist (b. 1944)
- Patrick Winston, American computer scientist (b. 1943)
- July 20 - Liane Russell, American geneticist (b. 1923)
- July 22 - Christopher C. Kraft Jr., American aerospace engineer (b. 1924)
- July 27 - John Robert Schrieffer, American physicist and Nobel laureate (b. 1931)
See also
References
- ^ a b Corum, Jonathan (10 February 2019). "New Horizons Glimpses the Flattened Shape of Ultima Thule - NASA's New Horizons spacecraft flew past the most distant object ever visited: a tiny fragment of the early solar system known as 2014 MU69 and nicknamed Ultima Thule. - Interactive". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 February 2019.
- ^ a b Chang, Kenneth (31 December 2018). "New Horizons Spacecraft Completes Flyby of Ultima Thule, the Most Distant Object Ever Visited". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 January 2019.
- ^ a b Chang, Kenneth (31 December 2018). "NASA's New Horizons Will Visit Ultima Thule on New Year's Day". The New York Times. Retrieved 31 December 2018.
- ^ a b Chang, Kenneth (18 March 2019). "How Ultima Thule Is Like a Sticky, Pull-Apart Pastry - Scientists from the New Horizons mission presented their latest findings about the small distant object visited by the NASA spacecraft at the start of the year". The New York Times. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ "Melting ice sheets release tons of methane into the atmosphere, study finds". University of Bristol. 2 January 2019. Retrieved 5 January 2019.
- ^ "China Moon mission lands Chang'e-4 spacecraft on far side". BBC News. 3 January 2019. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ "Scientists engineer shortcut for photosynthetic glitch, boost crop growth 40%". Science Daily. 3 January 2019. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ "Genetically modified 'shortcut' boosts plant growth by 40%". BBC News. 3 January 2019. Retrieved 3 January 2019.
- ^ "Excitons pave the way to more efficient electronics". EPFL. 4 January 2019. Retrieved 6 January 2019.
- ^ "Engineers create an inhalable form of messenger RNA". MIT News. 4 January 2019. Retrieved 9 January 2019.
- ^ "Scientists inch closer to fusion energy with discovery of a process that stabilizes plasmas". Princeton Plasma Physics Laboratory. 8 January 2019. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- ^ "IBM Unveils World's First Integrated Quantum Computing System for Commercial Use". IBM. 8 January 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ "IBM unveils its first commercial quantum computer". Tech Crunch. 8 January 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ The CHIME/FRB Collaboration (9 January 2019). "A second source of repeating fast radio bursts". Nature. 566 (7743): 235–238. arXiv:1901.04525. Bibcode:2019Natur.566..235C. doi:10.1038/s41586-018-0864-x. PMID 30653190.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (10 January 2019). "Broadcasting from Deep Space, a Mysterious Series of Radio Signals". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 January 2019.
- ^ "Lexar Announces 1TB 633x SDXC™ UHS-I card, the behemoth of storage capacity". Lexar. 9 January 2019. Retrieved 10 January 2019.
- ^ "Thousands of stars turning into crystals". Science Daily. 9 January 2019. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ a b Dartmouth College (17 January 2019). "Understanding our early human ancestors: Australopithecus sediba". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 19 January 2019.
- ^ Association of Universities for Research in Astronomy (AURA) (10 January 2019). "Unusual supernova opens a rare window on the collapse of a star". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ Torbet, Georgina (13 January 2019). "Scientists debate mysterious flash of light in space, known as 'The Cow'". Digital Trends. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ Koren, Marina (13 January 2019). "Astronomers Glimpse a Luminous Object Born From a Star's Death - It was unusually bright and evolving fast". The Atlantic. Retrieved 14 January 2019.
- ^ "3D printing 100 times faster with light". Science Daily. 11 January 2019. Retrieved 21 January 2019.
- ^ "Antarctica losing six times more ice mass annually now than 40 years ago". Science Daily. 14 January 2019. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ^ "Ocean giant gets a health check: Combination blood, tissue test reveals whale shark diets". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 2019-01-22.
- ^ McCartney, Gretchen; Wendel, JoAnna (17 January 2019). "Scientists Finally Know What Time It Is on Saturn". NASA. Retrieved 18 January 2019.
- ^ Mankovich, Christopher; et al. (17 January 2019). "Cassini Ring Seismology as a Probe of Saturn's Interior. I. Rigid Rotation". The Astrophysical Journal. 871 (1): 1. arXiv:1805.10286. Bibcode:2019ApJ...871....1M. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/aaf798.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Greenland ice melting four times faster than in 2003". Science Daily. 21 January 2019. Retrieved 22 January 2019.
- ^ "Growing our team and business in Michigan". Medium - Waymo blog. 2019-01-22. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Waymo plans to open the world's first self-driving-car factory this year". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Waymo Adding A Michigan Factory And 'Hundreds' Of Jobs To Build Self-Driving Vehicles". Forbes. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ "Google self-driving spinoff Waymo to put factory in Michigan". CBC. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ a b Science China Press (23 January 2019). "Gene-edited disease monkeys cloned in China". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ a b Mandelbaum, Ryan F. (23 January 2019). "China's Latest Cloned-Monkey Experiment Is an Ethical Mess". Gizmodo. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ a b McRae, Mike (24 January 2019). "Chinese Scientists Have Cloned a Genetically Altered Primate For The First Time". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ Queen Mary University of London (23 January 2019). "Astronomers find star material could be building block of life". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ Agle, DC (24 January 2019). "NASA's Opportunity Rover Logs 15 Years on Mars". NASA. Retrieved 24 January 2019.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (25 January 2019). "'This Could Be the End' for NASA's Mars Opportunity Rover - The agency has received only silence from the intrepid explorer since contact was lost during a global dust storm on the red planet last June". The New York Times. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ Universities Space Research Association (USRA) (24 January 2019). "Earth's Oldest Rock Found on the Moon". NASA. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ "Sci-fi to reality: Superpowered salamander may hold the key to human regeneration". EurekAlert!. 24 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ "Complete Axolotl Genome Could Pave the Way Toward Human Tissue Regeneration". Gizmodo. 24 January 2019. Retrieved 25 January 2019.
- ^ "AlphaStar: Mastering the Real-Time Strategy Game StarCraft II". Alphabet DeepMind. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ^ "DeepMind's new AI just beat top human pro-gamers at Starcraft II for the first time". MIT Technology Review. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ^ "DEEPMIND BEATS PROS AT STARCRAFT IN ANOTHER TRIUMPH FOR BOTS". Wired. 25 January 2019. Retrieved 28 January 2019.
- ^ "Chemical Engineering research to turn plastic waste into clean fuels". Purdue University. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ Wan-Ting Chen; Kai Jin; Nien-Hwa Linda Wang (January 10, 2019). "Use of Supercritical Water for the Liquefaction of Polypropylene into Oil". ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering. 7 (4): 3749–3758. doi:10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b03841.
- ^ "Groundbreaking new technique can turn plastic waste into energy-dense fuel". Digital Trends. 2019-02-13. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (30 January 2019). "High Ceilings and a Lovely View: Denisova Cave Was Home to a Lost Branch of Humanity - The mysterious Denisovans may have occupied a cave in what is now Siberia for more than 250,000 years". The New York Times. Retrieved 31 January 2019.
- ^ "New 3D printer shapes objects with rays of light". EurekAlert!. 31 January 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ "Atari master: New AI smashes Google DeepMind in video game challenge". RMIT University. 31 January 2019. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ a b University of Warwick (3 February 2019). "Simply shining light on dinosaur metal compound kills cancer cells". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 3 February 2019.
- ^ a b Zhang, Pingyu; et al. (15 December 2018). "Nucleus‐Targeted Organoiridium–Albumin Conjugate for Photodynamic Cancer Therapy". Angewandte Chemie. 58 (8): 2350–2354. doi:10.1002/anie.201813002. PMC 6468315. PMID 30552796.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (31 January 2019). "How NASA's Curiosity Rover Weighed a Mountain on Mars - With a bit of technical improvisation, scientists worked out that the bedrock of Mount Sharp appeared to be less dense than had been expected". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 February 2019.
- ^ Lewis, Kevin W. (1 February 2019). "A surface gravity traverse on Mars indicates low bedrock density at Gale crater". Science. 363 (6426): 535–537. Bibcode:2019Sci...363..535L. doi:10.1126/science.aat0738. PMID 30705193.
- ^ "A third of Himalayan ice cap doomed, finds 'shocking' report". The Guardian. 4 February 2019. Retrieved 4 February 2019.
- ^ Wester, Philippus; Mishra, Arabinda; Mukherji, Aditi; Shrestha, Arun Bhakta (4 February 2019). The Hindu Kush Himalaya Assessment. doi:10.1007/978-3-319-92288-1. ISBN 978-3-319-92287-4.
{{cite book}}:|journal=ignored (help) - ^ Good, Andrew; Wendel, JoAnna (5 February 2019). "Beyond Mars, the Mini MarCO Spacecraft Fall Silent". NASA. Retrieved 5 February 2019.
- ^ "2018 fourth warmest year in continued warming trend, according to NASA, NOAA". NASA. 6 February 2019. Retrieved 6 February 2019.
- ^ "Massive collision in the planetary system Kepler 107". EurekAlert!. 6 February 2019. Retrieved 20 February 2019.
- ^ Marchione, Marilyn (7 February 2019). "Tests suggest scientists achieved 1st 'in body' gene editing". AP News. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ Staff (2 February 2019). "Ascending Dose Study of Genome Editing by the Zinc Finger Nuclease (ZFN) Therapeutic SB-913 in Subjects With MPS II". ClinicalTrials.gov. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ Amos, Jonathan (7 February 2019). "Rosalind Franklin: Mars rover named after DNA pioneer". BBC News. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ New York University (7 February 2019). "Scientists discover new type of magnet". Phys.org. Retrieved 7 February 2019.
- ^ a b Agle, DC; Brown, Dwayne; Wendel, JoAnna (13 February 2019). "NASA's Opportunity Rover Mission on Mars Comes to End". NASA. Retrieved 14 February 2019.
- ^ a b Margolis, Jacob (16 February 2019). "How A Tweet About The Mars Rover Dying Blew Up On The Internet And Made People Cry". LAist. Archived from the original on 17 February 2019. Retrieved 17 February 2019.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Berger, Eric (8 February 2019). "New images of the distant Ultima Thule object have surprised scientists - "The new images are creating scientific puzzles."". Ars Technica. Retrieved 8 February 2019.
- ^ Mondal, Mayukh; Bertranpedt, Jaume; Leo, Oscar (16 January 2019). "Approximate Bayesian computation with deep learning supports a third archaic introgression in Asia and Oceania". Nature Communications. 10 (246): 246. Bibcode:2019NatCo..10..246M. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-08089-7. PMC 6335398. PMID 30651539.
- ^ Dockrill, Peter (11 February 2019). "Artificial Intelligence Has Found an Unknown 'Ghost' Ancestor in The Human Genome". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 11 February 2019.
- ^ "Gene therapy first to 'halt' most common cause of blindness". BBC News. 18 February 2019. Retrieved 18 February 2019.
- ^ "GENE THERAPY DURABLY REVERSES CONGENITAL DEAFNESS IN MICE". Pasteur Institute. 18 February 2019. Retrieved 26 February 2019.
- ^ "Cultured lab meat may make climate change worse". BBC News. 19 February 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
- ^ "Climate-friendly labriculture depends on an energy revolution". Science Daily. 19 February 2019. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
- ^ Jaouen, Klervia; et al. (19 February 2019). "Exceptionally high δ15N values in collagen single amino acids confirm Neandertals as high-trophic level carnivores". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (11): 4928–4933. doi:10.1073/pnas.1814087116. PMC 6421459. PMID 30782806.
- ^ Yika, Bob (19 February 2019). "Isotopes found in bones suggest Neanderthals were fresh meat eaters". Phys.org. Retrieved 19 February 2019.
- ^ Max Planck Institute for Evolutionary Anthropology (19 February 2019). "Neanderthals' main food source was definitely meat - Isotope analyses performed on single amino acids in Neanderthals' collagen samples shed new light on their debated diet". Science Daily. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ a b Hoshika, Shuichi; et al. (22 February 2019). "Hachimoji DNA and RNA: A genetic system with eight building blocks (paywall)". Science. 363 (6429): 884–887. doi:10.1126/science.aat0971. PMC 6413494. PMID 30792304.
- ^ a b Zimmer, Carl (21 February 2019). "DNA Gets a New — and Bigger — Genetic Alphabet - DNA is spelled out with four letters, or bases. Researchers have now built a system with eight. It may hold clues to the potential for life elsewhere in the universe and could also expand our capacity to store digital data on Earth". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ Belluz, Julia (4 March 2019). "CRISPR babies: the Chinese government may have known more than it let on - The latest developments in the gene-editing saga raise more questions than answers". Vox. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ Regalado, Antonio (21 February 2019). "China's CRISPR twins might have had their brains inadvertently enhanced - New research suggests that a controversial gene-editing experiment to make children resistant to HIV may also have enhanced their ability to learn and form memories". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 21 February 2019.
- ^ "Israel's Beresheet Moon mission gets under way". BBC News. 22 February 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- ^ "Israeli company sends world's first privately funded mission to moon". The Guardian. 22 February 2019. Retrieved 22 February 2019.
- ^ "Newfound 'FarFarOut' Is Most Distant Solar System Body Ever Seen". Space.com. 27 February 2019. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ Haeusler, Martin; et al. (25 February 2019). "Morphology, pathology, and the vertebral posture of the La Chapelle-aux-Saints Neandertal". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (11): 4923–4927. doi:10.1073/pnas.1820745116. PMC 6421410. PMID 30804177.
- ^ Cassella, Carly (1 March 2019). "We Have Been Wrong About a Key Feature of Neanderthals' Appearance". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 1 March 2019.
- ^ "Micron Unveils World's First 1TB microSD Card to Meet Consumer Demand for Mobile Storage". GlobalNewswire. 25 February 2019. Retrieved 25 February 2019.
- ^ "Climate rewind: Scientists turn carbon dioxide back into coal". Science Daily. 26 February 2019. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ^ ESA Staff (28 February 2019). "First Evidence of "Planet-Wide Groundwater System" on Mars Found". European Space Agency. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ^ Houser, Kristin (28 February 2019). "First Evidence of "Planet-Wide Groundwater System" on Mars Found". Futurism.com. Retrieved 28 February 2019.
- ^ "Nanotechnology makes it possible for mice to see in infrared". Science Daily. 28 February 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "SpaceX Dragon capsule docks with space station". BBC News. 3 March 2019. Retrieved 3 March 2019.
- ^ "SpaceX's Crew Dragon Capsule Splashes Down After Return Trip to Earth". New York Times. 8 March 2019. Retrieved 9 March 2019.
- ^ a b "Japan team edges closer to bringing mammoths back to life". Nikkei Asian Review. 12 March 2019. Retrieved 13 March 2019.
- ^ Johns Hopkins University (4 March 2019). "Asteroids are stronger, harder to destroy than previously thought". Phys.org. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ^ El Mir, Charles; Ramesh, KT; Richardson, Derek C. (15 March 2019). "A new hybrid framework for simulating hypervelocity asteroid impacts and gravitational reaccumulation". Icarus. 321: 1013–1025. Bibcode:2019Icar..321.1013E. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2018.12.032.
- ^ Andrews, Robin George (8 March 2019). "If We Blow Up an Asteroid, It Might Put Itself Back Together - Despite what Hollywood tells us, stopping an asteroid from creating an extinction-level event by blowing it up may not work". The New York Times. Retrieved 9 March 2019.
- ^ "HIV remission achieved in second patient". Science Daily. 5 March 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ "UK patient 'free' of HIV after stem cell treatment". BBC News. 5 March 2019. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ Rappaport, S.; et al. (22 February 2019). "Deep Long Asymmetric Occultation in EPIC 204376071". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. 485 (2): 2681–2693. arXiv:1902.08152. Bibcode:2019MNRAS.485.2681R. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz537.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Starr, Michelle (6 March 2019). "Astronomers Have Discovered Another Mysterious Dimming Star, And It's Even More Epic". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ Nowakowski, Tomasz (5 March 2019). "Astronomers detect deep, long asymmetric occultation in a newly found low-mass star". Phys.org. Retrieved 6 March 2019.
- ^ "New optical imaging system could be deployed to find tiny tumors". Science Daily. 7 March 2019. Retrieved 7 March 2019.
- ^ Starr, Michelle (8 March 2019). "The Latest Calculation of Milky Way's Mass Just Changed What We Know About Our Galaxy". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 8 March 2019.
- ^ Watkins, Laura L.; et al. (2 February 2019). "Evidence for an Intermediate-Mass Milky Way from Gaia DR2 Halo Globular Cluster Motions". The Astrophysical Journal. 873 (2): 118. arXiv:1804.11348. Bibcode:2019ApJ...873..118W. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab089f.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ "Magurele Laser officially becomes the most powerful laser in the world". Business Review (in Romanian). 2019-03-13. Retrieved 2019-03-13.
- ^ Staff (15 March 2019). "Dormant viruses activate during spaceflight -- NASA investigates - The stress of spaceflight gives viruses a holiday from immune surveillance, putting future deep-space missions in jeopardy". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 16 March 2019.
- ^ a b Bailleul, Alida M.; et al. (20 March 2019). "An Early Cretaceous enantiornithine (Aves) preserving an unlaid egg and probable medullary bone". Nature Communications. 10 (1275): 1275. doi:10.1038/s41467-019-09259-x. PMC 6426974. PMID 30894527.
- ^ a b Greshko, Michael (20 March 2019). "In a first, fossil bird found with unlaid egg - "I couldn't even sleep at night," the lead paleontologist says of her reaction to the discovery". National Geographic Society. Retrieved 20 March 2019.
- ^ Grossman, David. "A Meteor Hit Earth With the Force of a Nuclear Bomb and We Hardly Even Noticed". Popular mechanics. Retrieved 18 March 2019.
- ^ University of Huddersfield (20 March 2019). "Researchers shed new light on the origins of modern humans - The work, published in Nature, confirms a dispersal of Homo sapiens from southern to eastern Africa immediately preceded the out-of-Africa migration". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 23 March 2019.
- ^ Rito, Teresa; et al. (18 March 2019). "A dispersal of Homo sapiens from southern to eastern Africa immediately preceded the out-of-Africa migration". Scientific Reports. 9 (4728): 4728. doi:10.1038/s41598-019-41176-3. PMC 6426877. PMID 30894612.
- ^ Bejan, Adrian (18 March 2019). "Why the Days Seem Shorter as We Get Older". Academia Europaea. 27 (2): 187–194. doi:10.1017/S1062798718000741.
- ^ Duke University (21 March 2019). "It's spring already? Physics explains why time flies as we age - A slowdown in image processing speeds up our perception of time passing as we age". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ Livni, Ephrat (21 March 2019). "Physics explains why time passes faster as you age". Quartz. Retrieved 21 March 2019.
- ^ "Karen Uhlenbeck first woman to win the Abel Prize". The Norwegian Academy of Science and Letters. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (19 March 2019). "Karen Uhlenbeck Is First Woman to Receive Abel Prize in Mathematics - Dr. Uhlenbeck helped pioneer geometric analysis, developing techniques now commonly used by many mathematicians". The New York Times. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ University of California at Riverside (19 March 2019). "Carbon monoxide detectors could warn of extraterrestrial life - For some distant worlds, carbon monoxide may actually be compatible with a robust microbial biosphere". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 19 March 2019.
- ^ Starr, Michelle (27 March 2019). "Strange Earth Organisms Have Somehow Survived Living Outside The ISS". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 27 March 2019.
- ^ de Vera, Jean-Pierre; et al. (11 February 2019). "Limits of Life and the Habitability of Mars: The ESA Space Experiment BIOMEX on the ISS". Astrobiology. 19 (2): 145–157. Bibcode:2019AsBio..19..145D. doi:10.1089/ast.2018.1897. PMC 6383581. PMID 30742496.
- ^ European Southern Observatory (27 March 2019). "GRAVITY instrument breaks new ground in exoplanet imaging - Cutting-edge VLTI instrument reveals details of a storm-wracked exoplanet using optical interferometry". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 27 March 2019.
- ^ De Gruyter (4 April 2019). "Life on Mars? - A Martian meteorite discovered 40 years ago delivers fresh evidence that life once existed on Mars". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 4 April 2019.
- ^ Gyollai, Ildikó; et al. (29 March 2019). "Mineralized biosignatures in ALH-77005 Shergottite - Clues to Martian Life?". Open Astronomy. 28 (1): 32–39. Bibcode:2019OAst...28...32G. doi:10.1515/astro-2019-0002.
- ^ Abotalib, Abotalib Z.; Heggy, Essam (28 March 2019). "A deep groundwater origin for recurring slope lineae on Mars". Nature Geoscience. 12 (4): 235–241. Bibcode:2019NatGe..12..235A. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0327-5. PMC 6443380. PMID 30949231.
- ^ University of Southern California (28 March 2019). "New evidence of deep groundwater on Mars - Researchers suggests that deep groundwater can generate surface streams on Mars". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ^ Pew Research Center. "What Americans know about science - Americans with more formal education fare better on science-related questions, while Republicans and Democrats are roughly similar in their overall levels of science knowledge". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 31 March 2019.
- ^ "66-million-year-old deathbed linked to dinosaur-killing meteor". EurekAlert!. 29 March 2019. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ^ Depalma, Robert A.; Smit, Jan; Burnham, David A.; Kuiper, Klaudia; Manning, Phillip L.; Oleinik, Anton; Larson, Peter; Maurrasse, Florentin J.; Vellekoop, Johan; Richards, Mark A.; Gurche, Loren; Alvarez, Walter (1 April 2019). "A seismically induced onshore surge deposit at the KPg boundary, North Dakota". PNAS. 116 (17): 8190–8199. Bibcode:2019PNAS..116.8190D. doi:10.1073/pnas.1817407116. PMC 6486721. PMID 30936306.
- ^ a b "Astronomers capture first image of a black hole". EurekAlert!. 10 April 2019. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ a b Overbye, Dennis (10 April 2019). "Black Hole Picture Revealed for the First Time - Astronomers at last have captured an image of the darkest entities in the cosmos - Comments". The New York Times. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ a b The Event Horizon Telescope Collaboration (10 April 2019). "First M87 Event Horizon Telescope Results. I. The Shadow of the Supermassive Black Hole". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 87 (1): L1. Bibcode:2019ApJ...875L...1E. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab0ec7.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Landau, Elizabeth (10 April 2019). "Black Hole Image Makes History". NASA. Retrieved 10 April 2019.
- ^ Giuranna, Marco; et al. (1 April 2019). "Independent confirmation of a methane spike on Mars and a source region east of Gale Crater". Nature Geoscience. 12 (5): 326–332. Bibcode:2019NatGe..12..326G. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0331-9.
- ^ Galey, Patrick (1 April 2019). "Scientists find likely source of methane on Mars". Phys.org. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (1 April 2019). "Something on Mars Is Producing Gas Usually Made by Living Things on Earth - Mars emits methane, a European orbiter has confirmed. But scientists can't say yet whether the source is geological or biological". The New York Times. Retrieved 1 April 2019.
- ^ ETH Zurich (1 April 2019). "First bacterial genome created entirely with a computer". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 2 April 2019.
- ^ Venetz, Jonathan E.; et al. (1 April 2019). "Chemical synthesis rewriting of a bacterial genome to achieve design flexibility and biological functionality". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 116 (16): 8070–8079. doi:10.1073/pnas.1818259116. PMC 6475421. PMID 30936302.
- ^ Good, Andrew; Greiciua, Tony (4 April 2019). "Curiosity Captured Two Solar Eclipses on Mars". NASA. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ Dvorsky, George (5 April 2019). "Curiosity Rover Spots a Pair of Solar Eclipses on Mars". Gizmodo. Retrieved 5 April 2019.
- ^ BioMed Central (7 April 2019). "NASA researchers catalogue all microbes and fungi on the International Space Station". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 8 April 2019.
- ^ Sielaff, Aleksandra Checinska; et al. (8 April 2019). "Characterization of the total and viable bacterial and fungal communities associated with the International Space Station surfaces". Microbiome. 7 (50): 50. doi:10.1186/s40168-019-0666-x. PMC 6452512. PMID 30955503.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Good, Andrew (11 April 2019). "Curiosity Tastes First Sample in 'Clay-Bearing Unit'". NASA. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- ^ "Beresheet spacecraft: 'Technical glitch' led to Moon crash". BBC News. 12 April 2019. Retrieved 13 April 2019.
- ^ a b Starr, Michelle (29 April 2019). "The Hubble Space Telescope Has Just Found Solid Evidence of Interstellar Buckyballs". ScienceAlert.com. Retrieved 29 April 2019.
- ^ a b Cordiner, M.A.; et al. (22 April 2019). "Confirming Interstellar C60 + Using the Hubble Space Telescope". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 875 (2): L28. doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab14e5.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Zimmer, Carl (12 April 2019). "Scott Kelly Spent a Year in Orbit. His Body Is Not Quite the Same - NASA scientists compared the astronaut to his earthbound twin, Mark. The results hint at what humans will have to endure on long journeys through space". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 April 2019.
- ^ Garrett-Bakeman, Francine E.; et al. (12 April 2019). "The NASA Twins Study: A multidimensional analysis of a year-long human spaceflight". Science. 364 (6436). doi:10.1126/science.aau8650 (inactive 2019-06-06). PMID 30975860.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: DOI inactive as of June 2019 (link) - ^ Fingas, Jon (16 April 2019). "CRISPR gene editing has been used on humans in the US - It's part of a trial that could rethink medicine". Engadget. Retrieved 16 April 2019.
- ^ Staff (17 April 2019). "CRISPR has been used to treat US cancer patients for the first time". MIT Technology Review. Retrieved 17 April 2019.
- ^ Fisher, Christine (17 April 2019). "NASA finally found evidence of the universe's earliest molecule - The elusive helium hydride was found 3,000 light-years away". Engadget. Retrieved 17 April 2018.
- ^ Güsten, Rolf; et al. (17 April 2019). "Astrophysical detection of the helium hydride ion HeH+". Nature. 568 (7752): 357–359. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1090-x. PMID 30996316.
- ^ Brown, Dwayne; Johnson, Alana; Good, Andrew (23 April 2019). "NASA's InSight Detects First Likely 'Quake' on Mars". NASA. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ Bartels, Meghan (23 April 2019). "Marsquake! NASA's InSight Lander Feels Its 1st Red Planet Tremor". Space.com. Retrieved 23 April 2019.
- ^ "Dark Matter Hunters Observe 'Rarest Event Ever Recorded'". Newsweek. 24 April 2019. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- ^ "Dark matter detector observes rarest event ever recorded". EurekAlert!. 24 April 2019. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- ^ NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center (25 April 2019). "Mystery of the universe's expansion rate widens with new Hubble data". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 27 April 2019.
- ^ Wall, Mike (25 April 2019). "The Universe Is Expanding So Fast We Might Need New Physics to Explain It". Space.com. Retrieved 27 April 2019.
- ^ Mandelbaum, Ryan F. (25 April 2019). "Hubble Measurements Confirm There's Something Weird About How the Universe Is Expanding". Gizmodo. Retrieved 26 April 2019.
- ^ Riess, Adam G.; et al. (28 March 2019). "Large Magellanic Cloud Cepheid Standards Provide a 1% Foundation for the Determination of the Hubble Constant and Stronger Evidence for Physics Beyond ΛCDM". The Astrophysical Journal. 876 (1): 85. arXiv:1903.07603. Bibcode:2019ApJ...876...85R. doi:10.3847/1538-4357/ab1422.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Pietrzyński, G; et al. (13 March 2019). "A distance to the Large Magellanic Cloud that is precise to one per cent". Nature. 567 (7747): 200–203. arXiv:1903.08096. Bibcode:2019Natur.567..200P. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-0999-4. PMID 30867610.
- ^ Tokyo University of Science (30 April 2019). "New giant virus may help scientists better understand the emergence of complex life - Large DNA virus that helps scientists understand the origins of DNA replication and the evolution of complex life". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 30 April 2019.
- ^ a b Plumer, Brad (6 May 2019). "Humans Are Speeding Extinction and Altering the Natural World at an 'Unprecedented' Pace". The New York Times. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- ^ a b Staff (6 May 2019). "Media Release: Nature's Dangerous Decline 'Unprecedented'; Species Extinction Rates 'Accelerating'". Intergovernmental Science-Policy Platform on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services. Retrieved 6 May 2019.
- ^ a b The Editorial Board (11 May 2019). "Life as We Know It - Plant and animal species are disappearing faster than at any time in recorded history. We know who is to blame". The New York Times. Retrieved 12 May 2019.
- ^ "Removal of gene prevents development of pancreatic cancer in mice". EurekAlert!. 1 May 2019. Retrieved 2 May 2019.
- ^ NASA (May 2, 2019). "Hubble astronomers assemble wide view of the evolving universe". EurekAlert!. Retrieved May 2, 2019.
- ^ "End to Aids in sight as huge study finds drugs stop HIV transmission". The Guardian. 2 May 2019. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- ^ "Gay HIV transmission with treatment is 'zero risk', study confirms". BBC News. 3 May 2019. Retrieved 3 May 2019.
- ^ "UK generates usable electricity from americium". World Nuclear News. 3 May 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- ^ "UK scientists generate electricity from rare element to power future space missions". National Nuclear Laboratory. 3 May 2019. Retrieved 5 May 2019.
- ^ "Radical Desalination Approach May Disrupt the Water Industry". Columbia University. 6 May 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ "Teenager recovers from near death in world-first GM virus treatment". The Guardian. 8 May 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ "Phage therapy: 'Viral cocktail saved my daughter's life'". BBC News. 8 May 2019. Retrieved 9 May 2019.
- ^ "415 ppm CO2 threshold crossed May 2019". Foster Lab. 15 May 2019. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ "It's Official: Atmospheric CO2 Just Exceeded 415 ppm For The First Time in Human History". Science Alert. 13 May 2019. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ Greenberg, Andy (14 May 2019). "Meltdown Redux: Intel Flaw Lets Hackers Siphon Secrets from Millions of PCs". WIRED. Retrieved 14 May 2019.
- ^ Staff (14 May 2019). "Customer guidance for CVE-2019-0708 - Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability: May 14, 2019". Microsoft. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ Staff (14 May 2019). "CVE-2019-0708 Remote Desktop Services Remote Code Execution Vulnerability - Security Vulnerability". Microsoft. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ Kubovič, Ondrej (22 May 2019). "Patch now! Why the BlueKeep vulnerability is a big deal - What you need to know about the critical security hole that could enable the next WannaCryptor". ESET. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ Cimpanu, Catalin (28 May 2019). "Almost one million Windows systems vulnerable to BlueKeep (CVE-2019-0708) - New research puts an initial estimation of 7.6 million vulnerable systems into more context". ZDNet. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ "It's not just fish, plastic pollution harms the bacteria that help us breathe". EurekAlert!. 14 May 2019. Retrieved 15 May 2019.
- ^ a b Zimmer, Carl (15 May 2019). "Scientists Created Bacteria With a Synthetic Genome. Is This Artificial Life? - In a milestone for synthetic biology, colonies of E. coli thrive with DNA constructed from scratch by humans, not nature". The New York Times. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ Fredens, Julius; et al. (15 May 2019). "Total synthesis of Escherichia coli with a recoded genome". Nature. 569 (7757): 514–518. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1192-5. PMID 31092918.
- ^ "Potential disease-modifying drug for osteoarthritis identified". University of Nebraska Medical Center. 15 May 2019. Retrieved 17 May 2019.
- ^ Timmer, John (16 May 2019). "First results from New Horizons' time in the Kuiper Belt - Only about 10 percent of the data has been transmitted so far, but it says a lot". Ars Technica. Retrieved 16 May 2019.
- ^ Stern, S. A.; et al. (17 May 2019). "Initial results from the New Horizons exploration of 2014 MU69, a small Kuiper Belt object". Science. 364 (64421): eaaw9771. doi:10.1126/science.aaw9771. PMID 31097641.
- ^ "Nearly a quarter of West Antarctic ice is now unstable". University of Leeds. 16 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- ^ "Antarctica's Ice Is Melting 5 Times Faster Than in the 90s". Desmog. 16 May 2019. Retrieved 18 May 2019.
- ^ "Growth in life expectancy in Australia slows, research finds". University of Melbourne. 20 May 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ^ "Slower increase in life expectancy in Australia than in other high income countries: the contributions of age and cause of death". Medical Journal of Australia. 20 May 2019. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ^ Cyranoski, David (20 May 2019). "China set to introduce gene-editing regulation following CRISPR-baby furore - The draft rules mean that anyone who manipulates human genes in adults or embryos is responsible for adverse outcomes". Nature. doi:10.1038/d41586-019-01580-1. Retrieved 20 May 2019.
- ^ "The International System of Units (SI)". BIPM. 20 May 2019.
- ^ a b Zimmer, Carl (22 May 2019). "How Did Life Arrive on Land? A Billion-Year-Old Fungus May Hold Clues - A cache of microscopic fossils from the Arctic hints that fungi reached land long before plants". The New York Times. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ a b Timmer, John (22 May 2019). "Billion-year-old fossils may be early fungus". Ars Technica. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ a b Loron, Corentin C.; François, Camille; Rainbird, Robert H.; Turner, Elizabeth C.; Borensztajn, Stephan; Javaux, Emmanuelle J. (22 May 2019). "Early fungi from the Proterozoic era in Arctic Canada". Nature. Springer Science and Business Media LLC. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1217-0. ISSN 0028-0836. PMID 31118507.
- ^ "McMaster researchers invent a way to get life-saving vaccines to previously inaccessible parts of the world". McMaster University. 21 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "McMaster University researchers invent way to store vaccines at higher temperatures". The Toronto Star. 21 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Canadian scientists figure out how to preserve vaccines without refrigeration — a potential public-health game changer". National Post. 21 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Scientists break record for highest-temperature superconductor". University of Chicago. 22 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Scientists break record for highest-temperature superconductor". Science Daily. 22 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Study predicts shift to smaller animals over next century". EurekAlert!. 23 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Projected losses of global mammal and bird ecological strategies". Nature Communications. 23 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ "Humans causing shrinking of nature as larger animals die off". The Guardian. 23 May 2019. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ Dvorsky, George (23 May 2019). "An Astounding Amount of Water Has Been Discovered Beneath the Martian North Pole". Gizmodo. Retrieved 23 May 2019.
- ^ Nerozzi, S.; Holt, J.W. (2019). "Buried ice and sand caps at the north pole of Mars: revealing a record of climate change in the cavi unit with SHARAD". Geophysical Research Letters. doi:10.1029/2019GL082114.
- ^ "Last male Sumatran rhino in Malaysia dies". BBC News. 28 May 2019. Retrieved 28 May 2019.
- ^ "Research Brief: Energy researchers break the catalytic speed limit". University of Minnesota. 28 May 2019. Retrieved 29 May 2019.
- ^ a b Choi, Charles Q. (10 June 2019). "A Weird Mud Plume May Have Built the Highest Peak on Dwarf Planet Ceres". Space.com. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ Gallagher, James (3 June 2019). "He Jiankui: Baby gene experiment 'foolish and dangerous'". BBC News. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ^ Stein, Rob (3 June 2019). "2 Chinese Babies With Edited Genes May Face Higher Risk Of Premature Death". NPR News. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ^ Wei, Xinzhu; Nielsen, Rasmus (3 June 2019). "CCR5-∆32 is deleterious in the homozygous state in humans". Nature Medicine. doi:10.1038/s41591-019-0459-6. PMID 31160814. Retrieved 3 June 2019.
- ^ Jayasinghe, T.; et al. (4 June 2019). "ASAS-SN Discovery of an Unusual, Deep Dimming Episode of a Previously Non-Variable Star". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 8 June 2019.
- ^ McCollum, B.; Laine, S. (8 June 2019). "Spectral Type of the Unusual Variable ASASSN-V J213939.3-702817.4". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 8 June 2019.
- ^ Seidel, Jamie (6 June 2019). "A suddenly dimming star has caught the attention of alien hunters". The Advertiser. Retrieved 8 June 2019.
- ^ Staff (6 June 2019). "Name an Exoplanet - IAU100 NameExoWorlds gives every country in the world the opportunity to name an exoplanet and its host star". International Astronomical Union. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (14 June 2019). "So Long, Exoplanet HD 17156b. Hello ... Sauron?". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (2 December 2016). "Twinkle, Twinkle Little [Insert Name Here]". The New York Times. Retrieved 15 June 2019.
- ^ Ruesch, Ottaviano; et al. (10 June 2019). "Slurry extrusion on Ceres from a convective mud-bearing mantle". Nature Geoscience. doi:10.1038/s41561-019-0378-7. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ "'Frightening' number of plant extinctions found in global survey". The Guardian. 10 June 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ "Almost 600 plants have already gone extinct - Why should we care?". Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. 10 June 2019. Retrieved 10 June 2019.
- ^ Royal Astronomical Society (11 June 2019). "Citizen scientists re-tune Hubble's galaxy classification". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 11 June 2019.
- ^ "These nano-bugs eat CO2 and make eco-friendly fuel". University of Colorado Boulder. 11 June 2019. Retrieved 14 June 2019.
- ^ "AAS 234 Press Conference: Cold Quasars & Hot Cosmology". AAS Press Office via YouTube. 12 June 2019. Retrieved 13 June 2019.
- ^ Caballero, J. A.; Reiners, A.; Ribas, I.; Dreizler, S.; Zechmeister, M.; et al. (12 June 2019). "The CARMENES search for exoplanets around M dwarfs. Two temperate Earth-mass planet candidates around Teegarden's Star" (PDF). Astronomy & Astrophysics. doi:10.1051/0004-6361/201935460. ISSN 0004-6361.
- ^ University of Göttingen (18 June 2019). "View of the Earth in front of the Sun - International research team discovers two new Earth-like planets near Teegarden's star". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 18 June 2019.
- ^ "First-ever successful mind-controlled robotic arm without brain implants". Science Daily. 19 June 2019. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ "Discovery of a "Holy Grail" with the invention of universal computer memory". Lancaster University. 20 June 2019. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ^ a b Jarvis, Brooke (21 June 2019). "Giant Squid, Phantom of the Deep, Makes Second Video Appearance - Seven years after scientists caught the elusive deep-sea cephalopod on video, they saw another. Then lightning struck a third time". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ^ Padnani, Amisha (29 December 2015). "Giant Squid, Elusive Creature of the Deep, Gets a Vivid Close-Up". The New York Times. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ^ Schrope, Mark (14 January 2013). "Giant squid filmed in its natural environment - Landmark achievement reveals clues to mollusc's behaviour". Nature. doi:10.1038/nature.2013.12202. Retrieved 21 June 2019.
- ^ Chang, Kenneth (22 June 2019). "NASA Rover on Mars Detects Puff of Gas That Hints at Possibility of Life - The Curiosity mission's scientists picked up the signal this week, and are seeking additional readings from the red planet". The New York Times. Retrieved 22 June 2019.
- ^ Good, Andrew; Johnson, Alana (23 June 2019). "Curiosity Detects Unusually High Methane Levels". NASA. Retrieved 23 June 2019.
- ^ Overbye, Dennis (26 June 2019). "With a Poof, Mars Methane Is Gone - Last week, NASA's Curiosity rover detected a belch of natural gas on the red planet. The gas has since dissipated, leaving only a mystery". The New York Times. Retrieved 26 June 2019.
- ^ Brown, David W. (27 June 2019). "NASA Announces New Dragonfly Drone Mission to Explore Titan - The quadcopter was selected to study the moon of Saturn after a "Shark Tank"-like competition that lasted two and a half years". The New York Times. Retrieved 27 June 2019.
- ^ "NASA's Dragonfly Will Fly Around Titan Looking for Origins, Signs of Life". NASA. 27 June 2019. Retrieved 28 June 2019.
- ^ Fedorova, V.A.; et al. (29 June 2019). "Detection of nine new Fast Radio Bursts in the direction of the galaxy M31 and M33 at the frequency 111 MHz at the radio telescope BSA LPI". The Astronomer's Telegram. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ Staff (28 June 2019). "Search Fast Radio Burst at the frequency 111 MHz - News About Our Project". Pushchino Radio Astronomy Observatory. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ Mack, Eric. "More mysterious signals from deep space detected - New fast radio bursts from beyond our galaxy have been recorded, adding more data to help solve one of the universe's most recent puzzles". Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ Rappaport, S.; et al. (28 June 2019). "The Random Transiter – EPIC 249706694/HD 139139". Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society. doi:10.1093/mnras/stz1772. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Yirka, Bob (3 July 2019). "Binary stars with unexplainable dimming pattern". Phys.org. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ Crane, Leah (2 July 2019). "The weirdest stars we've ever seen have astronomers utterly baffled". New Scientist. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ The 'Oumuamua ISSI Team (1 July 2019). "The natural history of 'Oumuamua". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41550-019-0816-x. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ Starr, Michelle (1 July 2019). "Astronomers Have Analysed Claims 'Oumuamua's an Alien Ship, And It's Not Looking Good". Science Alert.com. Retrieved 1 July 2019.
- ^ a b "Global restoration opportunities in tropical rainforest landscapes". Science Advances. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ a b "11% of destroyed moist tropical forests could be restored to boost climate, environment". Eurekalert!. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ "Record-breaking temperatures for June". Copernicus Climate Change Service. 2 July 2019. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ "June was hottest ever recorded on Earth, European satellite agency announces". The Independent. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ Ravi, V.; et al. (2 July 2019). "A fast radio burst localized to a massive galaxy". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1389-7. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ Mack, Eric (2 July 2019). "Another mysterious deep space signal traced to the other side of the universe - Fast radio bursts suddenly seem to be everywhere in the news, but they're still coming from very far away". CNET. Retrieved 3 July 2019.
- ^ "World first: Homing instinct applied to stem cells show cells 'home' to cardiac tissue". Eurekalert!. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ "Study: Vast swaths of lost tropical forest can still be brought back to life". Mongabay. 3 July 2019. Retrieved 4 July 2019.
- ^ a b Isella, Andrea; et al. (11 July 2019). "Detection of Continuum Submillimeter Emission Associated with Candidate Protoplanets". The Astrophysical Journal Letters. 879 (2). doi:10.3847/2041-8213/ab2a12. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Blue, Charles E. (11 July 2019). "'Moon-forming' Circumplanetary Disk Discovered in Distant Star System". National Radio Astronomy Observatory. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ Davis, Jason (7 July 2019). "Here are the First Pictures of Earth from LightSail 2". The Planetary Society. Retrieved 7 July 2019.
- ^ National Radio Astronomy Observatory (8 July 2019). "New method may resolve difficulty in measuring universe's expansion - Neutron star mergers can provide new 'cosmic ruler'". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ^ Finley, Dave (8 July 2019). "New Method May Resolve Difficulty in Measuring Universe's Expansion". National Radio Astronomy Observatory. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ^ Hotokezaka, K.; et al. (8 July 2019). "A Hubble constant measurement from superluminal motion of the jet in GW170817". Nature Astronomy. doi:10.1038/s41550-019-0820-1. Retrieved 8 July 2019.
- ^ a b "Chandrayaan-2: India launches second Moon mission". BBC. 22 July 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ Zimmer, Carl (10 July 2019). "A Skull Bone Discovered in Greece May Alter the Story of Human Prehistory - The bone, found in a cave, is the oldest modern human fossil ever discovered in Europe. It hints that humans began leaving Africa far earlier than once thought". The New York Times. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ Staff (10 July 2019). "'Oldest remains' outside Africa reset human migration clock". Phys.org. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ Harvati, Katerina; et al. (10 July 2019). "Apidima Cave fossils provide earliest evidence of Homo sapiens in Eurasia". Nature. doi:10.1038/s41586-019-1376-z. Retrieved 10 July 2019.
- ^ Boyd, Jade (11 July 2019). "Moon-forming disk discovered around distant planet". Phys.org. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ "Carnegie Mellon and Facebook AI beats professionals in six-player poker". Eurekalert!. 11 July 2019. Retrieved 11 July 2019.
- ^ University of Glasgow (13 July 2019). "Scientists unveil the first-ever image of quantum entanglement". Phys.org. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ Moreau, Paul-Antoine; et al. (12 July 2019). "Imaging Bell-type nonlocal behavior". Science Advances. 5 (7). doi:10.1126/sciadv.aaw2563. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ "Spektr-RG: Powerful X-ray telescope launches to map cosmos". BBC News. 13 July 2019. Retrieved 13 July 2019.
- ^ Crane, Leah (15 July 2019). "There aren't enough space explosions to explain strange radio bursts". New Scientist. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ Ravi, Vikram (15 July 2019). "The prevalence of repeating fast radio bursts". Nature Astronomy. doi:10.1038/s41550-019-0831-y. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ Wordsworth, R.; Kerber, L.; Cockell, C. (15 July 2019). "Enabling Martian habitability with silica aerogel via the solid-state greenhouse effect". Nature Astronomy. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ "Want to Colonize Mars? Aerogel Could Help". NASA. 15 July 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ "A material way to make Mars habitable". Harvard University. 15 July 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ "A Thin Layer of Aerogel Could Make Martian Farming Possible". Futurism. 15 July 2019. Retrieved 22 July 2019.
- ^ Carnegie Institution of Science (16 July 2019). "New measurement of universe's expansion rate is 'stuck in the middle' - Red giant stars observed by Hubble Space Telescope used to make an entirely new measurement of how fast the universe is expanding". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 16 July 2019.
- ^ Sokol, Joshua (19 July 2019). "Debate intensifies over speed of expanding universe". Science. doi:10.1126/science.aay8123. Retrieved 20 July 2019.
- ^ https://phys.org/news/2019-07-esa-asteroid-earth.html (phys.org)
- ^ Tokyo Institute of Technology (23 July 2019). "ELSI scientists discover new chemistry that may help explain the origins of cellular life - Chemists find simplest organic molecules can self-assemble to give cell-like structures under early Earth conditions". EurekAlert!. Retrieved 23 July 2019.
- ^ Jia, Tony Z.; Chandru, Kuhan; Hongo, Yayoi; Afrin, Rehana; Usui, Tomohiro; Myojo, Kunihiro; Cleaves, H. James (22 July 2019). "Membraneless polyester microdroplets as primordial compartments at the origins of life". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences: 201902336. doi:10.1073/pnas.1902336116.
- ^ "A large asteroid just zipped between Earth and the Moon". Astronomy. 25 July 2019. Retrieved 26 July 2019.
- ^ "Exoplanet mission launch slot announced". 23 November 2018. Retrieved 30 November 2018.
- ^ "First SpaceX mission with astronauts set for June 2019: NASA". phys.org. 5 October 2018.
- ^ "Simon Norton, mathematical prodigy who became the subject of the biography 'The Genius in my Basement' – obituary". The Daily Telegraph. London. 2019-02-15.
- ^ "Legendary scientist who predicted climate change effects dead at 87". Mashable. 2019-02-19. Retrieved 2019-02-20.
External links
 Media related to 2019 in science at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 2019 in science at Wikimedia Commons
