SMS Meteor (1890): Difference between revisions
split |
|||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
Work on ''Meteor'' began in December 1888 with her [[keel laying]] at the [[Germaniawerft]] shipyard in [[Kiel]]. She was [[ship launching|launched]] on 20 January 1890; after completing [[fitting-out]], dockyard workers conducted [[Sea trial|builder's trials]] before delivery. After these were finished, she was [[ship commissioning|commissioned]] into the fleet on 15 May 1891. She was initially used as the [[flagship]] of the commander of the ''[[Marinestation der Ostsee]]'' ([[Baltic Sea]] Naval Station) and was stationed as a [[guard ship]] in Kiel, replacing the [[screw corvette]] {{SMS|Stosch||2}} in the roles. The navy had not yet conducted its own trials of the ship, however, and she was transferred to I Reserve on 30 July, her role as flagship being taken over by the torpedo [[training ship]] {{SMS|Blücher|1877|2}}. ''Meteor'' returned to guard duties from 28 August to 3 October, at which point she was decommissioned to correct some defects that had been discovered during her trials, including increasing the height of her [[funnel (ship)|funnels]] by {{cvt|1.5|m}} to reduce smoke interference with the aft gun crews.{{sfn|Hildebrand, Röhr & Steinmetz|p=81}} |
Work on ''Meteor'' began in December 1888 with her [[keel laying]] at the [[Germaniawerft]] shipyard in [[Kiel]]. She was [[ship launching|launched]] on 20 January 1890; after completing [[fitting-out]], dockyard workers conducted [[Sea trial|builder's trials]] before delivery. After these were finished, she was [[ship commissioning|commissioned]] into the fleet on 15 May 1891. She was initially used as the [[flagship]] of the commander of the ''[[Marinestation der Ostsee]]'' ([[Baltic Sea]] Naval Station) and was stationed as a [[guard ship]] in Kiel, replacing the [[screw corvette]] {{SMS|Stosch||2}} in the roles. The navy had not yet conducted its own trials of the ship, however, and she was transferred to I Reserve on 30 July, her role as flagship being taken over by the torpedo [[training ship]] {{SMS|Blücher|1877|2}}. ''Meteor'' returned to guard duties from 28 August to 3 October, at which point she was decommissioned to correct some defects that had been discovered during her trials, including increasing the height of her [[funnel (ship)|funnels]] by {{cvt|1.5|m}} to reduce smoke interference with the aft gun crews.{{sfn|Hildebrand, Röhr & Steinmetz|p=81}} |
||
''Meteor'' was recommissioned on 20 May 1892 for another round of trials after the modifications completed the previous year. She was also assigned as the guard ship for Kiel during this period. In mid-August, she took part in the annual fleet training exercises that lasted until 26 September. During the maneuvers, she served as the [[flotilla leader]] for II Torpedo-boat Flotilla; the flotilla commander, ''[[Korvettenkapitän]]'' (corvette captain) [[Karl Rosendahl]], flew his flag aboard the ship for the duration of the exercises. [[Kaiser Wilhelm II]] boarded the ship for a short cruise in early November, and she was decommissioned again on 6 December, by which time the navy pronounced the ship's trials to be officially completed. She was recommissioned on 5 April 1893 to serve as the aviso for I Division of the Maneuver Fleet from 1 May to 29 September, including during the annual maneuvers. Beginning on 30 June 1894, she escorted the Kaiser's [[yacht]] [[SMY Hohenzollern|''Hohenzollern'']] on his annual summer cruise, which went to Norway that year. While in [[Stavanger]], ''Meteor'' suffered from machinery problems, though her crew was able to repair her engines there. The problems nevertheless led to her being replaced as the Kaiser's escort by the [[protected cruiser]] {{SMS|Prinzess Wilhelm||2}}. ''Meteor'' returned to Kiel for repairs, after which she served as a scout during the fleet maneuvers. She was decommissioned again on 30 September.{{sfn|Hildebrand, Röhr & Steinmetz| |
''Meteor'' was recommissioned on 20 May 1892 for another round of trials after the modifications completed the previous year. She was also assigned as the guard ship for Kiel during this period. In mid-August, she took part in the annual fleet training exercises that lasted until 26 September. During the maneuvers, she served as the [[flotilla leader]] for II Torpedo-boat Flotilla; the flotilla commander, ''[[Korvettenkapitän]]'' (corvette captain) [[Karl Rosendahl]], flew his flag aboard the ship for the duration of the exercises. [[Kaiser Wilhelm II]] boarded the ship for a short cruise in early November, and she was decommissioned again on 6 December, by which time the navy pronounced the ship's trials to be officially completed.{{sfn|Hildebrand, Röhr & Steinmetz|pp=80–81}} |
||
She was recommissioned on 5 April 1893 to serve as the aviso for I Division of the Maneuver Fleet from 1 May to 29 September, including during the annual maneuvers. Beginning on 30 June 1894, she escorted the Kaiser's [[yacht]] [[SMY Hohenzollern|''Hohenzollern'']] on his annual summer cruise, which went to Norway that year. While in [[Stavanger]], ''Meteor'' suffered from machinery problems, though her crew was able to repair her engines there. The problems nevertheless led to her being replaced as the Kaiser's escort by the [[protected cruiser]] {{SMS|Prinzess Wilhelm||2}}. ''Meteor'' returned to Kiel for repairs, after which she served as a scout during the fleet maneuvers. She was decommissioned again on 30 September.{{sfn|Hildebrand, Röhr & Steinmetz|p=81}} |
|||
By 1895, she was withdrawn from front-line service and used for fishery protection. This duty lasted only a year, after which she was placed out of service.{{sfn|Gröner|p=96}} In 1899, she was reclassified as a [[light cruiser]], along with her [[sister ship]] {{SMS|Comet||2}}, though both vessels remained out of service.{{sfn|Gardiner & Gray|p=143}} ''Meteor'' was used as a harbor guard ship starting on 3 May 1904. On 24 June 1911, she was stricken from the [[naval register]] and used as a [[barracks ship]] in Kiel. She served in this capacity through [[World War I]]. After the German defeat, the ship was sold for scrapping in 1919. ''Meteor'' thereafter was broken up in [[Rendsburg]].{{sfn|Gröner|p=96}} |
By 1895, she was withdrawn from front-line service and used for fishery protection. This duty lasted only a year, after which she was placed out of service.{{sfn|Gröner|p=96}} In 1899, she was reclassified as a [[light cruiser]], along with her [[sister ship]] {{SMS|Comet||2}}, though both vessels remained out of service.{{sfn|Gardiner & Gray|p=143}} ''Meteor'' was used as a harbor guard ship starting on 3 May 1904. On 24 June 1911, she was stricken from the [[naval register]] and used as a [[barracks ship]] in Kiel. She served in this capacity through [[World War I]]. After the German defeat, the ship was sold for scrapping in 1919. ''Meteor'' thereafter was broken up in [[Rendsburg]].{{sfn|Gröner|p=96}} |
||
Revision as of 12:38, 27 September 2019
 SMS Meteor at anchor
| |
| History | |
|---|---|
| Name | SMS Meteor |
| Builder | Germaniawerft |
| Laid down | 1888 |
| Launched | 20 July 1890 |
| Commissioned | 19 May 1891 |
| Fate | Scrapped, 1919 |
| General characteristics | |
| Class and type | Template:Sclass- |
| Displacement | |
| Length | 79.86 m (262 ft 0 in) o/a |
| Beam | 9.56 m (31 ft 4 in) |
| Draft | 3.68 m (12 ft 1 in) |
| Installed power |
|
| Propulsion | |
| Speed | 20 knots (37 km/h; 23 mph) |
| Range | 960 nmi (1,780 km; 1,100 mi) at 9 kn (17 km/h; 10 mph) |
| Complement |
|
| Armament |
|
| Armor |
|
SMS Meteor was an aviso of the Imperial German Navy, the lead ship of her class. She had one sister ship, Comet. She was built by the Germaniawerft shipyard. Her keel was laid in 1888; she was launched in January 1890, and completed in May 1891. Her career was limited due to poor handling and excessive vibration; she remained on active service only until 1895. She was used as a harbor guard ship from 1904 to 1911, after which she became a barracks ship in Kiel. Meteor was sold for scrap in 1919 and subsequently dismantled.
Design
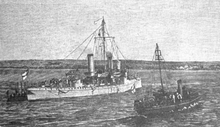
With previous avisos built for the German fleet, the designers had attempted to build vessels that could serve as scouts for the main fleet as well as defend it against hostile torpedo boats that threatened the larger ironclad warships. The naval command decided in 1888 that the next class of avisos—the Meteor design—should focus solely on anti-torpedo boat duties. Smaller and faster than the preceding Template:Sclass-s, the Meteors were also badly unstable and poor sea boats, and they suffered from severe vibration at high speed. These defects could not be remedied, and as a result, they had short careers.[1][2][3]
Meteor was 79.86 meters (262.0 ft) long overall and had a beam of 9.56 m (31.4 ft) and a maximum draft of 3.68 m (12.1 ft) forward. She displaced 961 metric tons (946 long tons) as designed and up to 1,078 t (1,061 long tons) at full combat load. Her propulsion system consisted of two vertical 3-cylinder triple expansion engines. Steam for the engines was provided by four coal-fired locomotive boilers. The ship's propulsion system was rated for 4,500 metric horsepower (4,400 ihp) and provided a top speed of 20 kn (37 km/h; 23 mph) and a range of approximately 960 nautical miles (1,780 km; 1,100 mi) at 9 kn (17 km/h; 10 mph). Meteor had a crew of 7 officers and 108 enlisted men.[2]
As built, the ship was armed with four 8.8 cm (3.5 in) SK L/30 guns placed in single pivot mounts, two side-by-side forward, and two side-by-side aft. The guns were supplied with between 462 and 680 rounds of ammunition. Meteor also carried three 35 cm (14 in) torpedo tubes, one mounted submerged in the bow and the other two in deck-mounted launchers on the broadside. She was protected with a 15 mm (0.59 in) thick deck, along with 30 mm (1.2 in) of steel armor plating for the conning tower.[2]
Service history

Work on Meteor began in December 1888 with her keel laying at the Germaniawerft shipyard in Kiel. She was launched on 20 January 1890; after completing fitting-out, dockyard workers conducted builder's trials before delivery. After these were finished, she was commissioned into the fleet on 15 May 1891. She was initially used as the flagship of the commander of the Marinestation der Ostsee (Baltic Sea Naval Station) and was stationed as a guard ship in Kiel, replacing the screw corvette Stosch in the roles. The navy had not yet conducted its own trials of the ship, however, and she was transferred to I Reserve on 30 July, her role as flagship being taken over by the torpedo training ship Blücher. Meteor returned to guard duties from 28 August to 3 October, at which point she was decommissioned to correct some defects that had been discovered during her trials, including increasing the height of her funnels by 1.5 m (4 ft 11 in) to reduce smoke interference with the aft gun crews.[1]
Meteor was recommissioned on 20 May 1892 for another round of trials after the modifications completed the previous year. She was also assigned as the guard ship for Kiel during this period. In mid-August, she took part in the annual fleet training exercises that lasted until 26 September. During the maneuvers, she served as the flotilla leader for II Torpedo-boat Flotilla; the flotilla commander, Korvettenkapitän (corvette captain) Karl Rosendahl, flew his flag aboard the ship for the duration of the exercises. Kaiser Wilhelm II boarded the ship for a short cruise in early November, and she was decommissioned again on 6 December, by which time the navy pronounced the ship's trials to be officially completed.[4]
She was recommissioned on 5 April 1893 to serve as the aviso for I Division of the Maneuver Fleet from 1 May to 29 September, including during the annual maneuvers. Beginning on 30 June 1894, she escorted the Kaiser's yacht Hohenzollern on his annual summer cruise, which went to Norway that year. While in Stavanger, Meteor suffered from machinery problems, though her crew was able to repair her engines there. The problems nevertheless led to her being replaced as the Kaiser's escort by the protected cruiser Prinzess Wilhelm. Meteor returned to Kiel for repairs, after which she served as a scout during the fleet maneuvers. She was decommissioned again on 30 September.[1]
By 1895, she was withdrawn from front-line service and used for fishery protection. This duty lasted only a year, after which she was placed out of service.[2] In 1899, she was reclassified as a light cruiser, along with her sister ship Comet, though both vessels remained out of service.[5] Meteor was used as a harbor guard ship starting on 3 May 1904. On 24 June 1911, she was stricken from the naval register and used as a barracks ship in Kiel. She served in this capacity through World War I. After the German defeat, the ship was sold for scrapping in 1919. Meteor thereafter was broken up in Rendsburg.[2]
Notes
References
- Gardiner, Robert, ed. (1979). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships 1860–1905. London: Conway Maritime Press. ISBN 978-0-85177-133-5.
- Gardiner, Robert; Gray, Randal, eds. (1985). Conway's All the World's Fighting Ships: 1906–1921. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 978-0-87021-907-8.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - Gröner, Erich (1990). German Warships: 1815–1945. Vol. Vol. I: Major Surface Vessels. Annapolis: Naval Institute Press. ISBN 0-87021-790-9.
{{cite book}}:|volume=has extra text (help) - Hildebrand, Hans H.; Röhr, Albert; Steinmetz, Hans-Otto (1993). Die Deutschen Kriegsschiffe: Biographien: ein Spiegel der Marinegeschichte von 1815 bis zur Gegenwart (Band 6) [The German Warships: Biographies: A Reflection of Naval History from 1815 to the Present (Vol. 6)] (in German). Ratingen: Mundus Verlag. ISBN 978-3-7822-0237-4.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|lastauthoramp=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - "Naval and Military Notes". Journal of the Royal United Service Institution. XXXVII (185). London: Royal United Services Institute for Defence Studies: 811–823. July 1893. doi:10.1080/03071849309416563.
