116th United States Congress: Difference between revisions
Pvmoutside (talk | contribs) |
Thespaceface (talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 99: | Line 99: | ||
|- |
|- |
||
! |
|||
! [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] |
! [[Democratic Party (United States)|Democratic]] |
||
! [[Independent (United States)|Independent]] |
! [[Independent (United States)|Independent]] |
||
Revision as of 01:24, 2 October 2019
| 116th United States Congress | |
|---|---|
115th ← → 117th | |
 United States Capitol (2018) | |
January 3, 2019 – January 3, 2021 | |
| Members | 100 senators 435 representatives 6 non-voting delegates |
| Senate majority | Republican |
| Senate President | Mike Pence (R) |
| House majority | Democratic |
| House Speaker | Nancy Pelosi (D) |
| Sessions | |
| 1st: January 3, 2019 – TBD 2nd: TBD – TBD | |
The One Hundred Sixteenth United States Congress is the current meeting of the legislative branch of the United States federal government, composed of the Senate and the House of Representatives. It convened in Washington, D.C., on January 3, 2019, and will end on January 3, 2021, near the end of the fourth year of President Donald Trump's administration. Senators elected to regular terms in 2014 are finishing their terms in this Congress and House seats were apportioned based on the 2010 Census.
In the November 2018 midterm elections, the Democratic Party won a new majority in the House, while the Republican Party increased its majority in the Senate. Consequently, this is the first split Congress since the 113th Congress of 2013–2015, and the first Republican Senate, Democrat House split since the 99th Congress of 1985–1987. This Congress is considered to be the most diverse ever elected, and the youngest incoming class in the past three cycles.[1]
Major events
- December 22, 2018 – January 25, 2019: 2018–19 United States federal government shutdown
- January 3, 2019: Nancy Pelosi elected Speaker of the House, becoming the first former speaker to return to the post since Sam Rayburn in 1955.[2][3]
- February 5, 2019: 2019 State of the Union Address,[4] after being delayed from January 29, 2019, due to the partial government shutdown.[5]
- February 15, 2019: President Trump declared a National Emergency Concerning the Southern Border of the United States.
- February 27, 2019: Former Trump lawyer Michael Cohen testified before the House Oversight and Reform Committee,.[6]
- March 24, 2019: Special Counsel investigation (2017–2019): Summary letter of special counsel Robert Mueller's report issued to congress by attorney general William Barr.
- July 24, 2019: Robert Mueller testified before House Judiciary Committee and House Intelligence Committee.
- September 24, 2019: House of Representatives launched a formal Impeachment inquiry against Donald Trump in response to the Trump–Ukraine controversy.
Major legislation
Enacted
- February 15, 2019: Consolidated Appropriations Act, 2019, Pub. L. 116–6 (text) (PDF), H.J.Res. 31
- March 12, 2019: John D. Dingell, Jr. Conservation, Management, and Recreation Act, Pub. L. 116–9 (text) (PDF), S. 47
- July 29, 2019: Never Forget the Heroes: James Zadroga, Ray Pfeifer, and Luis Alvarez Permanent Authorization of the September 11th Victim Compensation Fund Act, H.R. 1327
Proposed
- For the People Act of 2019, H.R. 1
- Equality Act, H.R. 5
- Green New Deal, H.Res. 109
- SAFE Banking Act of 2019, H.R. 1595
- Taxpayer First Act of 2019, H.R. 1957
- SECURE Act of 2019, H.R. 1994
Vetoed
(With official titles)
- March 15, 2019: Relating to a national emergency declared by the President on February 15, 2019. (H.J.Res. 46)
- April 16, 2019: A joint resolution to direct the removal of United States Armed Forces from hostilities in the Republic of Yemen that have not been authorized by Congress. (S.J.Res. 7)
Party summary
- Resignations and new members are discussed in the "Changes in membership" section, below.
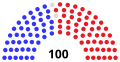
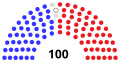
Senate
| Affiliation | Party (shading indicates majority caucus)
|
Total | Vacant | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| style="background-color:Template:Democratic Party (US)/meta/color" | | style="background-color:Template:Independent (US)/meta/color" | | style="background-color:Template:Republican Party (US)/meta/color" | | |||||
| Democratic | Independent | Republican | |||||
| End of previous Congress | 47 | 2 | 50 | 99 | 1 | ||
| Begin (January 3, 2019) | 45 | 2 | 52 | 99 | 1 | ||
| January 8, 2019[a] | 53 | 100 | 0 | ||||
| Latest voting share | 47.0% | 53.0% | |||||
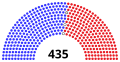
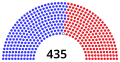
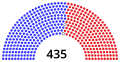
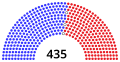
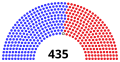
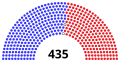
House of Representatives
| Affiliation | Party (shading indicates majority caucus)
|
Total | Vacant | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| style="background-color:Template:Democratic Party (US)/meta/color" | | style="background-color:Template:Independent (US)/meta/color" | | style="background-color:Template:Republican Party (US)/meta/color" | | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Democratic | Independent | Republican | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| End of previous Congress | 196 | 0 | 236 | 432 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Begin (January 3, 2019)[b] | 235 | 0 | 199 | 434 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| January 23, 2019[c] | 198 | 433 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| February 10, 2019[d] | 197 | 432 | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| May 21, 2019[c] | 198 | 433 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| July 4, 2019[e] | 1 | 197 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 10, 2019[b][d] | 199 | 435 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| September 23, 2019[f] | 198 | 434 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| October 1, 2019[g] | 197 | 433 | 2 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Latest voting share | 54.1% | 0.2% | 45.6% | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Non-voting members | 3 | 1 | 2 | 6 | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Leadership
Senate
- President: Mike Pence (R)[7]
- President pro tempore: Chuck Grassley (R)[7]
- President pro tempore emeritus: Patrick Leahy (D)
Majority (Republican) Leadership
- Majority Leader: Mitch McConnell[7][8][9]
- Majority Whip: John Thune[7][9]
- Conference Chair: John Barrasso[7][10]
- Conference Vice Chair: Joni Ernst[7][9][10]
- Policy Committee Chair: Roy Blunt[7][10]
- Campaign Committee Chair: Todd Young[7][10]
- Steering Committee Chair: Mike Lee[citation needed]
- Chief Deputy Whip: Mike Crapo[11]
- Deputy Whips: Roy Blunt, Shelley Moore Capito, John Cornyn, Cory Gardner, James Lankford, Martha McSally, Rob Portman, Mitt Romney, Tim Scott, Thom Tillis, Todd Young[11]
Minority (Democratic) Leadership
- Minority Leader/Caucus Chair: Chuck Schumer[7][9]
- Minority Whip: Dick Durbin[7][12]
- Assistant Leader: Patty Murray[7]
- Policy Committee Chair: Debbie Stabenow[7]
- Caucus Vice Chairs: Mark Warner, Elizabeth Warren[7]
- Steering Committee Chair: Amy Klobuchar[7]
- Outreach Chair: Bernie Sanders[7]
- Policy Committee Vice Chair: Joe Manchin[7]
- Caucus Secretary: Tammy Baldwin[7]
- Campaign Committee Chair: Catherine Cortez Masto[13]
- Chief Deputy Whip: Cory Booker, Jeff Merkley, Brian Schatz[14]
House of Representatives
- Speaker: Nancy Pelosi (D)
Majority (Democratic) Leadership
- Majority Leader: Steny Hoyer[15]
- Majority Whip: Jim Clyburn[16]
- Assistant Leader: Ben Ray Luján[17]
- Caucus Chair: Hakeem Jeffries[18]
- Caucus Vice Chair: Katherine Clark[19]
- Campaign Committee Chair: Cheri Bustos[20]
- Policy and Communications Committee Chair: David Cicilline[21]
- Policy and Communications Committee Co-Chairs: Matt Cartwright, Debbie Dingell, Ted Lieu[21]
- Steering and Policy Committee Co-Chairs: Rosa DeLauro, Barbara Lee, Eric Swalwell[21]
- Assistant to the Majority Whip: Cedric Richmond[22]
- Senior Chief Deputy Whips: John Lewis, Jan Schakowsky[22]
- Chief Deputy Whips: Pete Aguilar, G. K. Butterfield, Henry Cuellar, Dan Kildee, Sheila Jackson Lee, Debbie Wasserman Schultz, Terri Sewell, Peter Welch[22]
Minority (Republican) Leadership
- Minority Leader: Kevin McCarthy[9][23]
- Minority Whip: Steve Scalise[9][23]
- Conference Chair: Liz Cheney[9][23]
- Conference Vice Chair: Mark Walker[23]
- Conference Secretary: Jason Smith[23]
- Policy Committee Chair: Gary Palmer[23]
- Campaign Committee Chair: Tom Emmer[23]
- Chief Deputy Whip: Drew Ferguson[24]
Demographics
Most members of this Congress are Christian (88.2%), with approximately half being Protestant and 30.5% being Catholic. Jewish membership is 6.4%. Other religions represented include Buddhism, Islam, and Hinduism. One senator says that she is religiously unaffiliated, while the number of members refusing to specify their religious affiliation increased.[25][26][27]
Senate
The Senate includes 75 men and 25 women — the most women to date. In 6 states, both senators are women; 13 states are represented by 1 man and 1 woman; and 31 states are represented by 2 men. There are 91 non-Hispanic white, 4 Hispanic, 3 Black, 3 Asian, and 1 multiracial senators. Additionally, 2 senators identify as LGBTQ+.[1][28]
House of Representatives
There are 102 women in the House, the largest number in history.[29] There are 313 non-Hispanic whites, 56 black, 44 Hispanic, 15 Asian, and 4 Native American. Eight identify as LGBTQ+.[30] Two Democrats — Alexandria Ocasio-Cortez and Donna Shalala — are the youngest (29) and oldest (77) freshmen women in history.[31] Freshmen women Rashida Tlaib (D-MI) and Ilhan Omar (DFL-MN) are the first two female Muslims and freshmen Sharice Davids (D-KS) and Deb Haaland (D-NM) are the first two female Native American members.[32]
Members
Senate
The numbers refer to their Senate classes. All class 1 seats were contested in the November 2018 elections. In this Congress, class 1 means their term commenced in the current Congress, requiring re-election in 2024; class 2 means their term ends with this Congress, requiring re-election in 2020; and class 3 means their term began in the last Congress, requiring re-election in 2022.
House of Representatives
Changes in membership
Senate
Template:Ordinal US Congress Senate
|-
| Florida
(1)
| data-sort-value="Vacant" | Vacant
| data-sort-value="January 8, 2019" | Senator-elect chose to wait until finishing term as Governor of Florida.[33]
| data-sort-value="Scott Rick" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Rick Scott
(R)
| data-sort-value="January 8, 2019" | January 8, 2019
|-
| Georgia
(3)
| data-sort-value="Isakson Johnny" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Johnny Isakson
(R)
| data-sort-value="December 31, 2019" | Incumbent intends to resign December 31, 2019.[34]
A successor will be appointed to serve until a special election is held November 3, 2020.[34]
| data-sort-value="ZZZZ" | TBD
| data-sort-value="ZZZZ" | TBD
|}
House of Representatives
Template:Ordinal US Congress Rep
|-
| North Carolina 9
| data-sort-value="AAAVacant" | Vacant
| data-sort-value="January 3, 2019" | Vacant from the January 3, 2019, beginning of the term as allegations of fraud in the 2018 general election prevented the results from being certified.
A special election was held September 10, 2019.[41]
| data-sort-value="Bishop Dan" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Dan Bishop
(R)
| September 17, 2019[42]
|-
| Pennsylvania 12
| data-sort-value="Marino Tom" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Tom Marino
(R)
| data-sort-value="January 23, 2019" | Resigned January 23, 2019, to take job in private sector.[38]
A special election was held May 21, 2019.[43]
| data-sort-value="Keller Fred" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Fred Keller
(R)
| June 3, 2019
|-
| North Carolina 3
| data-sort-value="Jones Walter B. Jr." nowrap style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Walter B. Jones Jr.
(R)
| data-sort-value="February 10, 2019" | Died February 10, 2019.
A special election was held September 10, 2019.[44]
| data-sort-value="Murphy Greg" style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Greg Murphy
(R)
| September 17, 2019[45]
|-
| Michigan 3
| data-sort-value="Amash Justin" nowrap style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Justin Amash
(R)
| data-sort-value="July 4, 2019" | Changed party affiliation July 4, 2019.[46]
| data-sort-value="Amash Justin" style="background-color:#DDDDBB" | Justin Amash (I)
| July 4, 2019
|-
| Wisconsin 7
| data-sort-value="Sean Duffy" nowrap style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Sean Duffy
(R)
| data-sort-value="September 23, 2019" | Resigned September 23, 2019.
A special election will be held January 27, 2020.[47]
| TBD
| TBD
|-
| New York 27
| data-sort-value="Chris Collins" nowrap style="background-color:#FFB6B6" | Chris Collins
(R)
| data-sort-value="October 1, 2019" | Resigned October 1, 2019.[48]
| TBD
| TBD
|}
Committees
Section contents: Senate, House, Joint
Listed alphabetically by chamber, including Chair and Ranking Member.
Senate
House of Representatives
Joint
| Committee | Chair | Vice Chair | Ranking Member | Vice Ranking Member |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Economic | Mike Lee (R-UT) | Carolyn Maloney (D-NY) | David Schweikert (R-AZ) | Martin Heinrich (D-NM) |
| Library | Roy Blunt (R-MO) | Zoe Lofgren (D-CA) | Rodney Davis (R-IL) | Amy Klobuchar (D-MN) |
| Printing | Zoe Lofgren (D-CA) | Roy Blunt (R-MO) | Amy Klobuchar (D-MN) | Rodney Davis (R-IL) |
| Taxation[k] | Rich Neal (D-MA) | Chuck Grassley (R-IA) | Ron Wyden (D-OR) | Kevin Brady (R-TX) |
Employees and legislative agency directors
Also called "elected" or "appointed" officials, there are many employees of the House and Senate whose leaders are included here.[51]
Senate
- Chaplain: Barry C. Black[7]
- Parliamentarian: Elizabeth MacDonough[7]
- Secretary: Julie E. Adams[7]
- Sergeant at Arms: Michael C. Stenger[7]
- Secretary for the Majority: Laura Dove[7]
- Secretary for the Minority: Gary B. Myrick[7]
House of Representatives
- Chaplain: Patrick J. Conroy[52]
- Chief Administrative Officer: Phil Kiko[53]
- Clerk: Cheryl L. Johnson
- Historian: Matthew Wasniewski
- Parliamentarian: Thomas J. Wickham Jr.[54]
- Sergeant at Arms: Paul D. Irving[55]
Legislative branch agency directors
- Architect of the Capitol: Vacant (Thomas J. Carroll, acting[56])
- Comptroller General of the United States: Eugene Louis Dodaro[57]
- Director of the Congressional Budget Office: Phill Swagel[58]
- Librarian of Congress: Carla Diane Hayden[59]
- Director of the U.S. Government Publishing Office: Vacant[60]
- Counselor of the Office of the Law Revision Counsel: Ralph V. Seep[61]
- Counselor of the Office of House Legislative Counsel: Ernest Wade Ballou Jr.[62]
See also
- 2018 United States elections (elections leading to this Congress)
- 2019 United States elections (elections during this Congress)
- 2020 United States elections (elections during this Congress, leading to the next Congress)
Notes
- ^ Rick Scott (R-Florida) assumed office on January 8, 2019, after his term as Governor of Florida expired.
- ^ a b c In North Carolina's 9th district: the November 2018 election results were not initially certified due to a dispute over voting irregularities and Dan Bishop (R) was elected September 10, 2019.
- ^ a b In Pennsylvania's 12th district: Tom Marino (R) resigned January 23, 2019 and Fred Keller (R) was elected May 21, 2019.
- ^ a b In North Carolina's 3rd district: Walter Jones (R) died February 10, 2019 and Greg Murphy (R) was elected September 10, 2019.
- ^ In Michigan's 3rd district: Justin Amash changed parties July 4, 2019 from Republican to Independent.
- ^ In Wisconsin's 7th district: Sean Duffy (R) resigned September 23, 2019.
- ^ In New York's 27th district: Chris Collins (R) resigned October 1, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g The Minnesota Democratic–Farmer–Labor Party (DFL) is the Minnesota affiliate of the U.S. Democratic Party and its members are counted as Democrats.
- ^ Although Sanders is running for President in the Democratic primary and will claim to be a "bona fide Democrat" in accordance to DNC rules, he is currently and officially an Independent senator.[35]
- ^ In Michigan's 3rd district: Justin Amash changed from Republican to Independent July 4, 2019.[36]
- ^ The Joint Taxation Committee leadership rotate the chair and vice chair and the ranking members between the House and Senate at the start of each session (calendar year) in the middle of the congressional term. The first session leadership is shown here.
References
- ^ a b Jin, Beatrice (January 7, 2019) [First published November 23, 2018]. "Congress's incoming class is younger, bluer, and more diverse than ever". Politico. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ Bresnahan, John; Caygle, Heather; Bade, Rachel (November 28, 2018). "Pelosi grabs momentum with big speaker vote". Politico. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ DBonis, Mike; Sullivan, Sean (January 3, 2019). "Pelosi re-elected as House speaker as 116th Congress opens". The Mercury News. Retrieved January 31, 2019.
- ^ "PRESIDENT TRUMP STATE OF THE UNION ADDRESS". Associated Press. February 5, 2019. Retrieved February 6, 2019.
- ^ Gay Stolberg, Sheryl (January 23, 2019). "Trump Say's He'll Delay Speech Until After Shutdown, as Democrats Draft Border Security Plan". The New York Times. Retrieved January 23, 2019.
- ^ "Michael D. Cohen's Congressional Testimony". The New York Times. February 27, 2019. Retrieved March 6, 2019.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w "Leadership & Officers". Senate.gov. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- ^ Wagner, John; DeBonis, Mike (November 14, 2018). "Congressional leadership elections: House Republicans elect Kevin McCarthy as next leader; Pelosi seeks to shore up votes for speaker". The Washington Post PowerPost blog. Retrieved November 15, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g Fandos, Nicholas (November 14, 2018). "House Republicans Pick Kevin McCarthy as Their Next Leader". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 22, 2018. Retrieved November 29, 2018.
- ^ a b c d Bolton, Alexander (November 14, 2018). "McConnell reelected as leader, Thune promoted to whip". The Hill. Retrieved December 6, 2018.
- ^ a b "Senator Lankford to Serve on Deputy Whip Team for 116th Congress - U.S. Senator James Lankford of Oklahoma". www.lankford.senate.gov.
- ^ Lesniewski, Niels (January 3, 2019). "Dick Durbin says he's running for Senate re-election in 2020, unofficially". Roll Call. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ Lesniewski, Niels (November 15, 2018). "Catherine Cortez Masto Becomes First Latina to Lead DSCC". Roll Call. Archived from the original on December 6, 2018. Retrieved December 6, 2018.
- ^ "Schatz, Booker Elevated To Leadership Posts - U.S. Senator Brian Schatz of Hawaii". www.schatz.senate.gov.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey; McPherson, Lindsey (November 28, 2018). "Steny Hoyer Elected House Majority Leader". Roll Call. Archived from the original on November 29, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (November 28, 2018). "James Clyburn Elected Majority Whip". Roll Call. Archived from the original on December 9, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (November 28, 2018). "Rep. Ben Ray Luján Elected Assistant Democratic Leader". Roll Call. Archived from the original on November 29, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (November 28, 2018). "Hakeem Jeffries Wins Democratic Caucus Chair Race Against Barbara Lee". Roll Call. Archived from the original on November 28, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (November 29, 2018). "Katherine Clark Elected House Democratic Caucus Vice Chair". Roll Call. Archived from the original on December 9, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ Pathé, Simone (November 29, 2018). "Cheri Bustos Elected DCCC Chair". Roll Call. Archived from the original on December 9, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ a b c McPherson, Lindsey (December 4, 2018). "House Democrats' New Elected Leadership Team Is More Progressive and Diverse". Roll Call. Archived from the original on December 5, 2018. Retrieved December 7, 2018.
- ^ a b c "DeGette dropped from chief deputy whip spot". December 13, 2018. Archived from the original on December 14, 2018. Retrieved December 13, 2018.
- ^ a b c d e f g "Here's the List of House Republican Leaders for the Next Congress". Roll Call. November 14, 2018. Archived from the original on December 6, 2018. Retrieved December 6, 2018.
- ^ McPherson, Lindsey (November 27, 2018). "Scalise Appoints Rep. Drew Ferguson as House GOP's Chief Deputy Whip". Roll Call. Archived from the original on November 28, 2018. Retrieved December 6, 2018.
- ^ "Faith on the Hill". January 3, 2019. Archived from the original on January 4, 2019. Retrieved January 4, 2019.
- ^ Women Elected at Historic Levels, But No Surprise Here: White Men Dominate 116th Congress Archived November 21, 2018, at the Wayback Machine November 7, 2018
- ^ "As Christians split over Trump, minority faiths make their mark". Archived from the original on January 2, 2019. Retrieved January 2, 2019. November 7, 2018
- ^ Edmondson, Catie; Lee, Jasmine C. (November 28, 2018). "Meet the New Freshmen in Congress: More Democrats, Diversity and Women". The New York Times. Archived from the original on November 29, 2018. Retrieved December 22, 2018.
- ^ "A record number of women will be serving in the new Congress". Pew Research. December 18, 2018. Archived from the original on December 29, 2018. Retrieved December 28, 2018.
- ^ Panetta, Grace; Lee, Samantha (December 16, 2018). "This one graphic shows how much more diverse the House of Representatives will become in January". Business Insider. Archived from the original on December 23, 2018. Retrieved December 22, 2018.
- ^ Grow, Jason (January 18, 2019). "'We Call Ourselves the Badasses': Meet the New Women of Congress". POLITICO. Retrieved January 20, 2019.
- ^ "First Native American congresswomen hug after swearing-in". CNN. January 3, 2019. Retrieved March 4, 2019.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ a b Sonmez, Felicia (January 8, 2019). "Rick Scott sworn in as Florida's newest senator". South Florida SunSentinel. Retrieved February 3, 2019.
- ^ a b c Mattingly, Phil (August 28, 2019). "Georgia Republican Sen. Johnny Isakson to resign at end of year". CNN. Retrieved August 28, 2019.
- ^ DiStaso, John (February 22, 2019). "Independent Bernie Sanders to put in writing that he's a 'bona fide' Democrat". WMUR.
- ^ Byrd, Haley (July 4, 2019). "Trump critic Justin Amash quits Republican Party". CNN. Retrieved July 4, 2019.
- ^ Sullivan, Kate. "Walter Jones dies at 76". CNN. Retrieved February 11, 2019.
- ^ a b Burke, Michael. "GOP Rep. Tom Marino resigns from Congress". The Hill. Retrieved January 17, 2019.
- ^ "KELLER, Fred - Biographical Information". bioguide.congress.gov. Retrieved June 24, 2019.
- ^ Gilbert, Craig; Beck, Molly (August 26, 2019). "GOP Congressman Sean Duffy says he's stepping down due to new baby". USA Today. Milwaukee Journal Sentinel. Retrieved August 29, 2019.
- ^ Caldwell, Leigh Ann. "New election ordered in North Carolina House district after possible illegal activities". NBC News. Retrieved February 21, 2019.
- ^ Jim, Morrill (September 13, 2019). "Rep.-elect Bishop to be sworn in on Tuesday, leaving a scramble for his Senate seat Read more here: https://www.charlotteobserver.com/news/politics-government/article235055287.html#storylink=cpy". Retrieved September 26, 2019.
{{cite web}}: External link in|title= - ^ Tom Wolf [@GovernorTomWolf] (January 24, 2019). "Having heard the concerns of county officials, I am scheduling the special election to fill the remainder of Congressman Marino's term on May 21, 2019, to coincide with the primary election" (Tweet). Retrieved January 24, 2019 – via Twitter.
- ^ Jurkowitz, Mark. "The jam-packed sprint to succeed Walter Jones". Retrieved July 4, 2019.
- ^ "Friends to Elect Dr. Greg Murphy to Congress". www.facebook.com. Retrieved September 26, 2019.
- ^ Conradis, Brandon (July 4, 2019). "Rep. Amash, lone GOP critic of Trump, leaves Republican Party". The Hill. Retrieved July 4, 2019.
- ^ Bauer, Scott (September 23, 2019). "Duffy serves final day in House; Evers sets January election". Associated Press. Reading Eagle. Retrieved September 23, 2019.
- ^ https://www.washingtonpost.com/business/2019/09/30/rep-chris-collins-expected-plead-guilty-insider-trading-case/
- ^ Solender, Andrew [@AndrewSolender] (December 11, 2018). "The office of @SenSchumer has released an official list of Senate Democratic Ranking Members and Vice Chairmen" (Tweet). Retrieved December 11, 2018 – via Twitter.
- ^ "Leader McCarthy Names Members for the House Select Committee on the Modernization of Congress". February 11, 2019.
- ^ "Appointed Officials of the House". history.house.gov. Retrieved September 25, 2019.
- ^ "The Office of the Chaplain, United States House of Representatives". Chaplain.House.gov. Retrieved January 8, 2019.
- ^ "CAO Senior Management". Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "Parliamentarian of the House". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "Sergeant at Arms". United States House of Representatives. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "Architects of the Capitol". Architect of the Capitol. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "U.S. GAO - About GAO - Comptroller General". www.gao.gov. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "First Day at CBO". www.cbo.gov. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "About the Librarian". Library of Congress, Washington, D.C. 20540 USA. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "The White House Announces the Withdrawal of GPO Director Nominee". www.gpo.gov. Retrieved September 24, 2019.
- ^ "Office of Law Revision Counsel". history.house.gov. Retrieved September 25, 2019.
- ^ "Office of House Legislative Counsel". history.house.gov. Retrieved September 25, 2019.