Lamivudine: Difference between revisions
m Task 16: replaced (9×) / removed (0×) deprecated |dead-url= and |deadurl= with |url-status=; |
→History: added citation reference |
||
| Line 94: | Line 94: | ||
==History== |
==History== |
||
Racemic BCH-189 (the minus form is known as lamivudine) was invented by [[Bernard Belleau]] while at work at [[McGill University]] and Paul Nguyen-Ba at the Montreal-based IAF BioChem International, Inc. laboratories in 1988 and the minus enantiomer isolated in 1989. Samples were first sent to Yung-Chi Cheng of [[Yale University]] for study of its toxicity. When used in combination with AZT, he discovered that lamivudine's negative form reduced side effects and increased the drug's efficiency at inhibiting reverse transcriptase.<ref>{{cite web| title=US Patent Office| url=http://www.uspto.gov/sites/default/files/ip/boards/bpai/decisions/inform/104523-58.pdf| url-status=live| archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160616180439/http://www.uspto.gov/sites/default/files/ip/boards/bpai/decisions/inform/104523-58.pdf| archivedate=2016-06-16}}</ref> The combination of lamivudine and AZT increased the efficiency at inhibiting an enzyme HIV uses to reproduce its genetic material. As a result, lamivudine was identified as a less toxic agent to mitochondria DNA than other retroviral drugs.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Soderstrom|first1=Jon|title=National Institutes of Health: Moving Research from the Bench to the Bedside|url=https://www.aau.edu/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=2626|date=2003|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304024056/https://www.aau.edu/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=2626|archivedate=2016-03-04}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=The Wide-Ranging Effects of Nucleoside Analogs:A Look at Mitochondrial Toxicity|url=http://www.thebody.com/content/art2633.html?|last1=Gilden|first1=Dave|date=2000|url-status=live|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160916214133/http://www.thebody.com/content/art2633.html|archivedate=2016-09-16}}</ref> |
Racemic BCH-189 (the minus form is known as lamivudine) was invented by [[Bernard Belleau]] while at work at [[McGill University]] and Paul Nguyen-Ba at the Montreal-based IAF BioChem International, Inc. laboratories in 1988 and the minus enantiomer isolated in 1989. Samples were first sent to Yung-Chi Cheng of [[Yale University]] for study of its toxicity.<ref>{{cite web| title=Hunting Down HIV|url=https://medicine.yale.edu/news/yale-medicine-magazine/hunting-down-hiv/|url-status=live}}</ref> When used in combination with AZT, he discovered that lamivudine's negative form reduced side effects and increased the drug's efficiency at inhibiting reverse transcriptase.<ref>{{cite web| title=US Patent Office| url=http://www.uspto.gov/sites/default/files/ip/boards/bpai/decisions/inform/104523-58.pdf| url-status=live| archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160616180439/http://www.uspto.gov/sites/default/files/ip/boards/bpai/decisions/inform/104523-58.pdf| archivedate=2016-06-16}}</ref> The combination of lamivudine and AZT increased the efficiency at inhibiting an enzyme HIV uses to reproduce its genetic material. As a result, lamivudine was identified as a less toxic agent to mitochondria DNA than other retroviral drugs.<ref>{{cite web|last1=Soderstrom|first1=Jon|title=National Institutes of Health: Moving Research from the Bench to the Bedside|url=https://www.aau.edu/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=2626|date=2003|url-status=dead|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160304024056/https://www.aau.edu/WorkArea/DownloadAsset.aspx?id=2626|archivedate=2016-03-04}}</ref><ref>{{cite web|title=The Wide-Ranging Effects of Nucleoside Analogs:A Look at Mitochondrial Toxicity|url=http://www.thebody.com/content/art2633.html?|last1=Gilden|first1=Dave|date=2000|url-status=live|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20160916214133/http://www.thebody.com/content/art2633.html|archivedate=2016-09-16}}</ref> |
||
Lamivudine was approved by the [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) on November 17, 1995 for use with [[zidovudine]] (AZT) and again in 2002 as a once-a-day dosed medication. It is on the [[World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines]], a list of the most important medication needed in a basic [[health system]].<ref>{{cite web|title=WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health Organization|accessdate=22 April 2014|date=October 2013|url-status=live|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140423005004/http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=23 April 2014}}</ref> As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is more than $200.<ref name=Ric2015>{{cite book|last1=Hamilton|first1=Richart|title=Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition|date=2015|publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning|isbn=9781284057560|page=65}}</ref> |
Lamivudine was approved by the [[Food and Drug Administration]] (FDA) on November 17, 1995 for use with [[zidovudine]] (AZT) and again in 2002 as a once-a-day dosed medication. It is on the [[World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines]], a list of the most important medication needed in a basic [[health system]].<ref>{{cite web|title=WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines|url=http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|work=World Health Organization|accessdate=22 April 2014|date=October 2013|url-status=live|archiveurl=https://web.archive.org/web/20140423005004/http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/93142/1/EML_18_eng.pdf?ua=1|archivedate=23 April 2014}}</ref> As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is more than $200.<ref name=Ric2015>{{cite book|last1=Hamilton|first1=Richart|title=Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition|date=2015|publisher=Jones & Bartlett Learning|isbn=9781284057560|page=65}}</ref> |
||
Revision as of 23:23, 8 January 2020
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Trade names | Epivir, others[1] |
| Other names | (−)-L-2′,3′-dideoxy-3′-thiacytidine |
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
| MedlinePlus | a696011 |
| License data | |
| Pregnancy category |
|
| Routes of administration | By mouth |
| ATC code | |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status | |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Bioavailability | 86% |
| Protein binding | Less than 36% |
| Elimination half-life | 5 to 7 hours |
| Excretion | Kidney (circa 70%) |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| NIAID ChemDB | |
| PDB ligand | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.132.250 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
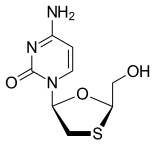
| Formula | C8H11N3O3S |
| Molar mass | 229.26 g/mol g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
| |
| | |
Lamivudine, commonly called 3TC, is an antiretroviral medication used to prevent and treat HIV/AIDS.[1] It is also used to treat chronic hepatitis B when other options are not possible.[1] It is effective against both HIV-1 and HIV-2.[1] It is typically used in combination with other antiretrovirals such as zidovudine and abacavir.[1] Lamivudine may be included as part of post-exposure prevention in those who have been potentially exposed to HIV.[1] Lamivudine is taken by mouth as a liquid or tablet.[1]
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, headaches, feeling tired, and cough.[1] Serious side effects include liver disease, lactic acidosis, and worsening hepatitis B among those already infected.[1] It is safe for people over three months of age and can be used during pregnancy.[1] The medication can be taken with or without food.[1] Lamivudine is a nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor and works by blocking the HIV reverse transcriptase and hepatitis B virus polymerase.[1]
Lamivudine was patented in 1995 and approved for use in the United States in 1995.[3][4] It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, the most effective and safe medicines needed in a health system.[5] It is available as a generic medication.[1] The wholesale cost in the developing world as of 2014 is about US$0.06 per day.[6] As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is more than $200.[7]
Medical uses
Lamivudine has been used for treatment of chronic hepatitis B at a lower dose than for treatment of HIV/AIDS. It improves the seroconversion of e-antigen positive hepatitis B and also improves histology staging of the liver. Long-term use of lamivudine leads to emergence of a resistant hepatitis B virus (YMDD) mutant. Despite this, lamivudine is still used widely as it is well tolerated.[8]
Resistance
In HIV, high level resistance is associated with the M184V/I mutation in the reverse transcriptase gene as reported by Raymond Schinazi's group at Emory University. GlaxoSmithKline claimed that the M184V mutation reduces "viral fitness", because of the finding that continued lamivudine treatment causes the HIV viral load to rebound but at a much lower level, and that withdrawal of lamivudine results in a higher viral load rebound with rapid loss of the M184V mutation; GSK therefore argued that there may be benefit in continuing lamivudine treatment even in the presence of high level resistance, because the resistant virus is "less fit". The COLATE study has suggested that there is no benefit to continuing lamivudine treatment in patients with lamivudine resistance.[9] A better explanation of the data is that lamivudine continues to have a partial anti-viral effect even in the presence of the M184V mutation.
In hepatitis B, lamivudine resistance was first described in the YMDD (tyrosine-methionine-aspartate-aspartate) locus of the HBV reverse transcriptase gene. The HBV reverse transcriptase gene is 344 amino acids long and occupies codons 349 to 692 on the viral genome. The most commonly encountered resistance mutations are M204V/I/S.[10] The change in amino acid sequence from YMDD to YIDD results in a 3.2 fold reduction in the error rate of the reverse transcriptase, which correlates with a significant growth disadvantage of the virus. Other resistance mutations are L80V/I, V173L and L180M.[11]
Side effects
- Minor side effects may include nausea, fatigue, headaches, diarrhea, cough and nasal congestion.
- Do not prescribe lamivudine/zidovudine, abacavir/lamivudine, or abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine to patients taking emtricitabine.
- Long-term use of lamivudine can trigger a resistant hepatitis B virus (YMDD) mutant.
- HIV or HBV-infected women on lamivudine are warned to discontinue breastfeeding as this puts the baby at risk for HIV transmission and medication side effects.
- Patients who are infected with HIV and HCV and are on both interferon and lamivudine can experience liver damage.
- The drug can trigger an inflammatory response to opportunistic infections (e.g., Mycobacterium avium complex [MAC], M. tuberculosis, cytomegalovirus [CMV], Pneumocystis jirovecii [formerly P. carinii).
- Autoimmune disorders have been reported and symptoms can occur many months after initiation of the antiretroviral therapy.
- Use with caution for patients with impaired renal function and do not prescribe this treatment to patients with impaired hepatic function.
Mechanism of action
Lamivudine is an analogue of cytidine. It can inhibit both types (1 and 2) of HIV reverse transcriptase and also the reverse transcriptase of hepatitis B virus. It is phosphorylated to active metabolites that compete for incorporation into viral DNA. They inhibit the HIV reverse transcriptase enzyme competitively and act as a chain terminator of DNA synthesis. The lack of a 3'-OH group in the incorporated nucleoside analogue prevents the formation of the 5' to 3' phosphodiester linkage essential for DNA chain elongation, and therefore, the viral DNA growth is terminated.
Lamivudine is administered by mouth, and it is rapidly absorbed with a bio-availability of over 80%. Some research suggests that lamivudine can cross the blood–brain barrier. Lamivudine is often given in combination with zidovudine, with which it is highly synergistic. Lamivudine treatment has been shown to restore zidovudine sensitivity of previously resistant HIV. Lamivudine showed no evidence of carcinogenicity or mutagenicity in in vivo studies in mice and rats at doses from 10 to 58 times those used in humans.[12]
It has a half-life of 5–7 hours in adults and 2 hours in HIV-infected children.
History
Racemic BCH-189 (the minus form is known as lamivudine) was invented by Bernard Belleau while at work at McGill University and Paul Nguyen-Ba at the Montreal-based IAF BioChem International, Inc. laboratories in 1988 and the minus enantiomer isolated in 1989. Samples were first sent to Yung-Chi Cheng of Yale University for study of its toxicity.[13] When used in combination with AZT, he discovered that lamivudine's negative form reduced side effects and increased the drug's efficiency at inhibiting reverse transcriptase.[14] The combination of lamivudine and AZT increased the efficiency at inhibiting an enzyme HIV uses to reproduce its genetic material. As a result, lamivudine was identified as a less toxic agent to mitochondria DNA than other retroviral drugs.[15][16]
Lamivudine was approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) on November 17, 1995 for use with zidovudine (AZT) and again in 2002 as a once-a-day dosed medication. It is on the World Health Organization's List of Essential Medicines, a list of the most important medication needed in a basic health system.[17] As of 2015 the cost for a typical month of medication in the United States is more than $200.[7]
Formulations
- Epivir tablets (GlaxoSmithKline; US and UK) for the treatment of HIV
- Epivir-HBV tablets (GlaxoSmithKline; US only) for the treatment of hepatitis B
- Zeffix tablets (GlaxoSmithKline; UK only) for the treatment of hepatitis B
- 3TC tablets (GlaxoSmithKline; South Africa) for the treatment of HIV
- Lamivudine is available in fixed-dose combinations with other HIV drugs such as:
- Lamivudine/zidovudine (with zidovudine)
- Abacavir/lamivudine (with abacavir)
- Abacavir/lamivudine/zidovudine (with zidovudine and abacavir)
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m "Lamivudine". The American Society of Health-System Pharmacists. Archived from the original on 2 June 2016. Retrieved 31 July 2016.
- ^ "FDA-sourced list of all drugs with black box warnings (Use Download Full Results and View Query links.)". nctr-crs.fda.gov. FDA. Retrieved 22 Oct 2023.
- ^ Therapy of Viral Infections Volume 15 of Topics in Medicinal Chemistry. Springer. 2015. p. 6. ISBN 9783662467596. Archived from the original on 2016-08-15.
- ^ Fischer, Jnos; Ganellin, C. Robin (2006). Analogue-based Drug Discovery. John Wiley & Sons. p. 506. ISBN 9783527607495.
- ^ "WHO Model List of Essential Medicines (19th List)" (PDF). World Health Organization. April 2015. Archived (PDF) from the original on 13 December 2016. Retrieved 8 December 2016.
- ^ "Lamivudine". International Drug Price Indicator Guide. Retrieved 23 July 2016.
- ^ a b Hamilton, Richart (2015). Tarascon Pocket Pharmacopoeia 2015 Deluxe Lab-Coat Edition. Jones & Bartlett Learning. p. 65. ISBN 9781284057560.
- ^ Kasırga E (April 2015). "Lamivudine resistance in children with chronic hepatitis B". World Journal of Hepatology. 7 (6): 896–902. doi:10.4254/wjh.v7.i6.896. PMC 4411531. PMID 25937866.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ Fox Z; Dragsted UB; Gerstoft J; et al. (2006). "A randomized trial to evaluate continuation versus discontinuation of lamivudine in individuals failing a lamivudine-containing regimen: The COLATE trial". Antiviral Therapy. 11 (6): 761–70. PMID 17310820.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ "Index". Archived from the original on 2010-07-01. Retrieved 2010-07-23. Stanford University Drug Resistance Database.
- ^ Koziel MJ, Peters MG (2007). "Viral hepatitis in HIV infection". N Engl J Med. 356 (14): 1445–54. doi:10.1056/NEJMra065142. PMC 4144044. PMID 17409326.
- ^ "Epivir package insert" (PDF). GlaxoSmithKline. Archived from the original (PDF) on September 28, 2011. Retrieved January 20, 2011.
- ^ "Hunting Down HIV".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "US Patent Office" (PDF). Archived (PDF) from the original on 2016-06-16.
- ^ Soderstrom, Jon (2003). "National Institutes of Health: Moving Research from the Bench to the Bedside". Archived from the original on 2016-03-04.
- ^ Gilden, Dave (2000). "The Wide-Ranging Effects of Nucleoside Analogs:A Look at Mitochondrial Toxicity". Archived from the original on 2016-09-16.
- ^ "WHO Model List of EssentialMedicines" (PDF). World Health Organization. October 2013. Archived (PDF) from the original on 23 April 2014. Retrieved 22 April 2014.
External links
- Epivir (manufacturer's website)
