Dutch New Guinea: Difference between revisions
No edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
No edit summary Tags: Visual edit Mobile edit Mobile web edit |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
| flag_s1 = Flag of the United Nations.svg |
| flag_s1 = Flag of the United Nations.svg |
||
| image_flag = Flag of the Netherlands.svg |
| image_flag = Flag of the Netherlands.svg |
||
| image_coat = |
| image_coat = Netherlands New Guinea coa 1961.svg |
||
| coa_size = 75px |
| coa_size = 75px |
||
| symbol_type = Coat of arms |
| symbol_type = Coat of arms |
||
Revision as of 09:56, 10 March 2020
This article needs additional citations for verification. (March 2009) |
Overseas Territory of Netherlands New Guinea Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1949–1962 | |||||||||
| Motto: Setia, Djudjur, Mesra (Indonesian) Pius, Honestus, Amica (Latin) "Loyal, Honest, Affectionate" | |||||||||
| Anthem: "Wilhelmus" (Dutch) (English: "William") Hai Tanahku Papua (Indonesian) (English: "Oh My Land Papua") | |||||||||
 | |||||||||
| Status | Dutch colony | ||||||||
| Capital | Hollandia | ||||||||
| Common languages | Dutch Papuan languages Austronesian languages | ||||||||
| Religion | Christianity (official) Animism (folk / ethnic) | ||||||||
| Historical era | Cold War | ||||||||
• Established | 27 December 1949 | ||||||||
• Disestablished | 1 October 1962 | ||||||||
| Area | |||||||||
| 1955 | 420,540 km2 (162,370 sq mi) | ||||||||
| Population | |||||||||
• 1955 | 420,000 | ||||||||
| Currency | NNG gulden | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||

Netherlands New Guinea (Template:Lang-nl) refers to the Papua region of Indonesia while it was an overseas territory of the Kingdom of the Netherlands from 1949 to 1962. Until 1949 it was a part of the Dutch East Indies. It was commonly known as Dutch New Guinea. It contained what are now Indonesia's two easternmost provinces, Papua and West Papua, which were administered as a single province prior to 2003 under the name Irian Jaya.
During the Indonesian Revolution, the Dutch launched 'police actions' to capture territory from the Indonesian Republic. However, the harsh methods of the Dutch had drawn international disapproval. With international opinion shifting towards support of the Indonesian Republic, the Dutch managed in 1949 to negotiate for the separation of Netherlands New Guinea from the broader Indonesian settlement, with the fate of the disputed territory to be decided by the close of 1950. However, the Dutch in coming years were able to argue successfully at the UN that the indigenous population of Netherlands New Guinea represented a separate ethnic group from the people of Indonesia and thus should not be absorbed into the Indonesian state.
In contrast, the Indonesian Republic, as successor state to the Netherlands East Indies, claimed Netherlands New Guinea as part of its natural territorial bounds. The dispute over New Guinea was an important factor in the quick decline in bilateral relations between the Netherlands and Indonesia after Indonesian independence. The dispute escalated into low-level conflict in 1962 following Dutch moves in 1961 to establish a New Guinea Council.
Following the Vlakke Hoek incident, Indonesia launched a campaign of infiltrations designed to place pressure on the Dutch. Facing diplomatic pressure from the United States, fading domestic support and continual Indonesian threats to invade the territory, the Netherlands decided to relinquish control of the disputed territory in August 1962, agreeing to the Bunker Proposal on condition that a plebiscite to determine the final fate of the territory be conducted at a later date. The territory was administered by the UN temporarily before being transferred to Indonesia on 1 May 1963. A plebiscite, the Act of Free Choice, was eventually held in 1969 but the fairness of the election is disputed.
Pre-World War II
Until after World War II the western part of the island of New Guinea was part of the Dutch colony of the Netherlands Indies. The Netherlands claimed sovereignty over New Guinea within the Netherlands Indies through its protection over Sultanate of Tidore, a sultanate on an island west of Halmahera in the Maluku Islands. In a 1660 treaty the Dutch East India Company (VOC) recognised the Sultanate of Tidore's supremacy over the Papuan people, the inhabitants of New Guinea. Probably this referred to some Papuan islands near the Maluku Islands, although Tidore never exercised actual control over New Guinea. In 1872 Tidore recognised Dutch sovereignty and granted permission to the Kingdom of the Netherlands to establish administration in its territories whenever the Netherlands Indies authorities would want to do so. This allowed the Netherlands to legitimise a claim to the New Guinea area.
The Dutch established the 141st meridian as the eastern frontier of the territory. In 1898 the Netherlands Indies government decided to establish administrative posts in Fakfak and Manokwari, followed by Merauke in 1902. The main reason for this was the expansion of British and German control in the east. The Dutch wanted to make sure the United Kingdom and Germany would not move the border to the west. This resulted in the partition of the island of New Guinea.
In reality the most part of New Guinea remained outside colonial influence. Little was known about the interior; large areas on the map were white and the number of inhabitants of the island was unknown, and numerous explorations were made into the interior from the turn of the 20th century on. The indigenous inhabitants of New Guinea were Papuans, living in tribes. They were hunter-gatherers.
Pre-World War II economic activity was limited. Only coastal and island dwellers traded to some extent, mostly with the Maluku Islands. A development company was founded in 1938 to change this situation, but it was not very active. So, until World War II, New Guinea was a disregarded and unimportant territory within the Netherlands Indies.
Homeland for the Eurasians
The group that was most interested in New Guinea before the war were the Eurasians or Indo people. Before the war some 150,000 to 200,000 Eurasians were living in the Netherlands Indies. They were of mixed European and Indonesian descent and identified with the Netherlands and the Dutch way of life. In the colonial society of the Netherlands Indies, they held a higher social status than indigenous Indonesians ("inlanders"). They were mostly employed as office workers. As the educational level of indigenous Indonesians was on the rise, more and more Indonesians got jobs previously held by Eurasians. These had no other means of making a living, because, as Europeans, they were forbidden to buy land on Java. This situation caused mental and economic problems to the Eurasians. In 1923, the first plan to designate New Guinea as a settlement territory for Eurasians was devised. In 1926, a separate Vereniging tot Kolonisatie van Nieuw-Guinea (Association for the Settlement of New Guinea) was founded. In 1930, it was followed by the Stichting Immigratie Kolonisatie Nieuw-Guinea (Foundation Immigration and Settlement New Guinea). These organisations regarded New Guinea as an untouched, almost empty land that could serve as a homeland to the sidelined Eurasians. A kind of tropical Holland, where Eurasians could create an existence.
These associations succeeded in sending settlers to New Guinea and lobbied successfully for the establishment of a government agency to subsidise these initiatives (in 1938). However, most settlements ended in failure because of the harsh climate and natural conditions, and because of the fact the settlers, previously office workers, were not skilled in agriculture. The number of settlers remained small. In the Netherlands proper, some organisations existed that promoted a kind of "tropical Holland" in New Guinea, but they were rather marginal. They were linked to the NSB party and other fascist organisations.
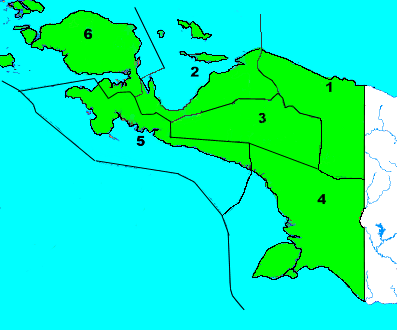
Administrative divisions
| Afdelingen of Papua | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Afdeling | Capital | 1955 Population | |||
| 1. Hollandia | Hollandia | 57,000 | |||
| 2. Geelvinkbaai | Biak | 78,000 | |||
| 3. Centraal Nieuw-Guinea | Biak | 52,000 | |||
| 4. Zuid Nieuw-Guinea | Merauke | 78,000 | |||
| 5. Fak-Fak | Fak-Fak | 28,000 | |||
| 6. West Nieuw-Guinea | Sorong-Doom | 95,000 | |||
| Total: | -- | 420,000 | |||
Origin of the dispute over New Guinea
In 1942, most parts of the Netherlands Indies were occupied by Japan.[1] Behind Japanese lines in New Guinea, Dutch guerrilla fighters resisted under Mauritz Christiaan Kokkelink.[2] During the occupation the Indonesian nationalist movement went through a rapid development. After Japan's surrender, Sukarno issued the Proclamation of Indonesian Independence, which was to encompass the whole of the Netherlands Indies. The Dutch authorities returned after several months under the leadership of Lieutenant-Governor-General Hubertus van Mook. Van Mook decided to reform Indonesia on a federal basis. This was not a completely new idea, but it was contrary to the administrative practice in the Netherlands Indies until then and contrary to the ideas of the nationalists, who wanted a centralist Indonesia.
Linggadjati agreement
The ethnic diversity of Indonesia was initially discussed at two conferences in Malino and Pangkalpinang. During these two conferences New Guinea was discussed for the first time. During the Malino conference a Papuan participant declared New Guinea should become a part of the state of East Indonesia. During the Pangkalpinang conference the right of self-determination of the Eurasian, Chinese and Arab ethnic minorities was discussed. The new Grooter Nederland-Actie (Extended Netherlands Action) send delegates to this conference, who opined that New Guinea should be declared as separate entities in a similar manner to Surinam[3]. Furthermore, this conference stipulated specific territories could have special relations with the Kingdom of the Netherlands if they wanted to.
Van Mook's plan was to divide Indonesia in several federal states, negaras, with possible autonomous areas, daerahs. The whole would be called the United States of Indonesia and would remain linked to the Netherlands in the Netherlands-Indonesian Union. The Indonesian side agreed to this plan during the Linggadjati conference in November 1946. Van Mook thought a federal structure would safeguard Indonesia's cultural and ethnic diversity. Van Mook and his supporters referred to the right of self-determination in this respect: the different ethnic communities of Indonesia should have the right to govern themselves.
The unilateral amendment of 'Linggadjati'
To many Dutchmen, the idea of parting with Indonesia was shocking. Many Dutch thought their country had a mission to develop Indonesia. The Indonesian wish for independence to many Dutch came as a complete surprise. Because Indonesian nationalists, which had no electoral or official legitimacy--save ethno-state nationalism, under Sukarno cooperated with the Japanese, they were branded as traitors and collaborators. Almost every Dutch political party was against Indonesian independence. The Protestant Anti-Revolutionary Party (ARP) were very supportive of the Dutch Ethical Policy in Indonesia. The newly established liberal People's Party for Freedom and Democracy campaigned for a hard-line policy against the nationalists. Even the Labour Party, which supported Indonesian independence in principle, was hesitant, because of the policies of Sukarno.
Minister of Colonies Jan Anne Jonkman defended the Linggadjati Agreement in Parliament in 1946 by stating that the government wished for New Guinea to remain under Dutch sovereignty, arguing it could be a settlement for Eurasians. A motion entered by the Catholic People's Party (KVP) and the Labour Party, which was accepted by parliament, stated that the declaration of Jonkman in parliament should become a part of the Linggadjati agreement. Duly accepted, the Netherlands thus unilaterally 'amended' the Linggadjati agreement to the effect that New Guinea would remain Dutch. Labour parliamentary group leader Marinus van der Goes van Naters said afterwards the Labour Party entered the motion with the KVP because it feared the Catholics otherwise might reject the Linggadjati agreements.
The Indonesians did not accept this unilateral amendment. In order not to jeopardise the scheduled transfer of sovereignty, the Indonesian vice-president Mohammad Hatta offered to maintain Dutch sovereignty over New Guinea for one year and reopen the negotiations afterwards.[citation needed]
1949–1956
Thus in 1949, when the rest of the Dutch East Indies became fully independent as Indonesia, the Dutch retained sovereignty over western New Guinea, and took steps to prepare it for independence as a separate country. Some five thousand teachers were flown there. The Dutch put an emphasis upon political, business, and civic skills. On 8 February 1950 Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg was appointed the first Governor (De Gouverneur) of Netherlands New Guinea. The first local naval cadets graduated in 1955 and the first army brigade become operational in 1956.
1957–1961

Tensions regarding the Dutch-Indonesian dispute over Netherlands New Guinea escalated in December 1957 following Indonesia's defeat in the UN General Assembly on 29 November 1957 to pass a resolution in favour of Indonesia's claim to the territory. Sukarno responded by allowing the seizure of Dutch enterprises operating in Indonesia and announcing the intended expulsion of Dutch residents from Indonesia. The increased tensions surrounding the dispute encouraged the Dutch to accelerate their plans to move the disputed territory towards an act of self-determination. Elections were held in January 1961 and the New Guinea Council officially took office on 5 April 1961, to prepare for full independence by the end of that decade. The Dutch endorsed the council's selection of a new national anthem and the Morning Star as the new national flag on 1 December 1961.[4][5]
Following the raising of the Papuan National Flag on 1 December 1961, tensions further escalated. On 18 December 1961 Sukarno issued the Tri Komando Rakjat (People's Triple Command), calling the Indonesian people to defeat the formation of an independent state of West Papua, raise the Indonesian flag in that country, and be ready for mobilisation at any time.[6][7]
1962
Escalation to low-level conflict
In 1962 Indonesia launched a significant campaign of airborne and seaborne infiltrations against the disputed territory, beginning with a seaborne infiltration launched by Indonesian forces on 15 January 1962. The Indonesian attack was comprehensively defeated by Dutch forces including the Dutch destroyers Evertsen and Kortenaer, the so-called Vlakke Hoek incident.[8] Amongst the casualties was the Indonesian Deputy Chief of the Naval Staff; Commodore Yos Sudarso. Unbeknown to the Indonesians, Dutch Signals Intelligence had been able to intercept Indonesian communications, allowing Dutch forces to successfully anticipate Indonesia's infiltration attempts throughout 1962.[9] Forced to regroup, the Indonesians relaunched their campaign of infiltrations in March 1962. In the coming months over 500 Indonesian paratroops and special forces were covertly inserted into Netherlands New Guinea, only to be decisively defeated by Dutch forces with the assistance of the indigenous population.[10]
Elsworth Bunker proposal
Facing mounting international diplomatic pressure and the prospect of an Indonesian invasion force, the Dutch conceded to re-entering negotiations and agreed to the Ellsworth Bunker proposal on 28 July 1962, for a staged transition from Dutch to Indonesian control via UN administration, on the condition that a plebiscite would be held in future in the territory.[11] The agreement was signed on 15 August 1962 at the UN Headquarters in New York and the territory was placed under the United Nations Temporary Executive Authority in October 1962. It was subsequently transferred to Indonesia in May 1963.
1963–1969
The territory formally became part of Indonesia in 1969 after the Indonesian government, who shifted to New Order under President Suharto starting from 1966, conducted an event termed the Act of Free Choice. The act result, which under strong pressure from the Indonesian military, unanimously wanted to become part of Indonesia. The UN General Assembly later accepted the result via the UN Resolution 2504. This act has been criticised by some international community, including the group International Parliamentarians for West Papua, which has termed the act "the act of no choice".
Since then the Indonesian government has endorsed a policy of immigration by people from Java and some other islands (the transmigration program). Within years to come, more non-Papuans than Papuans lived in some part of the former Netherlands New Guinea[citation needed]. The program was only formally ended by President Joko Widodo in June 2015.[12]
Governors
- Jan Pieter Karel van Eechoud (29 December 1949 – 8 February 1950; acting)
- Stephan Lucien Joseph van Waardenburg (8 February 1950 – 24 April 1953)
- Jan van Baal (24 April 1953 – 31 March 1958)
- Jan Christoffel Baarspul (31 March 1958 – 1 May 1958; acting)
- Pieter Johannes Platteel (1 May 1958 – 28 September 1962)
- Henk Veldkamp (28 September 1962 – 1 October 1962; acting)
See also
- Papua (Indonesian province)
- Free Papua Movement
- New Guinea
- Kaiser-Wilhelmsland
- Western New Guinea
- British New Guinea
- German New Guinea
- West New Guinea dispute
- Papua Conflict
- Republic of West Papua
References
- ^ Klemen, L (1999–2000). "The Fall of Dutch New Guinea, April 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ^ Womack, Tom (1999). "The capture of Manokwari, April 1942". Forgotten Campaign: The Dutch East Indies Campaign 1941–1942.
- ^ Penders,"The West New Guinea Debacle", p. 63
- ^ J.D. Legge, Sukarno: A Political Biography, 402-03.
- ^ Ron Crocombe, Asia in the Pacific Islands, pp. 286-87.
- ^ Ide Anak Agung Gde Agung, Twenty years of Indonesian Foreign Policy 1945-1965, p. 303.
- ^ Sukarno's "Trikora"-Speech. The commands are at the end of the speech.
- ^ Penders, "The West New Guinea Debacle", p. 344
- ^ Platje, Weis; 'Dutch Sigint and the Conflict with Indonesia 1950-1962', Intelligence and National Security, Vol. 16, No. 1, 2001, pp. 285-312
- ^ Penders,"The West New Guinea Debacle", p. 366.
- ^ Penders,"The West New Guinea Debacle", p. 375
- ^ Media, Kompas Cyber (4 June 2015). "Jokowi Hentikan Transmigrasi ke Papua - Kompas.com". Nasional.kompas.com. Retrieved 24 November 2018.
Further reading
- Bone, Robert C. The Dynamics of the Western New Guinea (Irian Barat) Problem (Cornell U.P. 1958)
- Finney, B.R. "Partnership in developing the New Guinea Highlands 1948–68," Journal of Pacific History 5 (1970),
- Henderson, William, West New Guinea. The dispute and its settlement (1973).
- Lijphart, Arend, The trauma of decolonisation. The Dutch and West New Guinea (New Haven 1966).
- Markin, Terence. The West Irian Dispute (U of Michigan Press, 1996).
- Penders, C.L.M., The West New Guinea debacle. Dutch decolonisation and Indonesia 1945–1962, Leiden 2002 KITLV
- Ploeg, Anton. "Colonial land law in Dutch New Guinea," Journal of Pacific History (1999) 34#2 pp 191–203
- Pouwer, Jan. "The colonisation, decolonisation and recolonisation of West New Guinea," Journal of Pacific History (1999) 34#2 pp 157–79
- Saltford. John. The United Nations and the Indonesian Takeover of West Papua, 1962–1969 (2003)
In Dutch
- Doel, H.W. van den, Afscheid van Indië. De val van het Nederlandse imperium in Azië (Amsterdam 2001).
- Drooglever, P.J., Een daad van vrije keuze. De Papoea’s van westelijk Nieuw-Guinea en de grenzen van het zelfbeschikkingsrecht (Amsterdam 2005).
- Holst Pellekaan, R.E. van, I.C. de Regt, J.F. Bastiaans, Patrouilleren voor de Papoea's: de Koninklijke Marine in Nederlands Nieuw-Guinea (Amsterdam 1989).
- Holst Pellekaan, R.E. van, I.C. de Regt, Operaties in de Oost: de Koninklijke Marine in de Indische archipel (1945-1951) (Amsterdam 2003).
- Huydecoper van Nigteveld, J.L.R., Nieuw-Guinea. Het einde van een koloniaal beleid (Den Haag 1990)
- Gase, Ronald, Misleiding of zelfbedrog. Een analyse van het Nederlandse Nieuw-Guinea-beleid aan de hand van gesprekken met betrokken politici en diplomaten (Baarn 1984).
- Geus, P.B.R. de, De Nieuw-Guinea kwestie. Aspecten van buitenlands beleid en militaire macht (Leiden 1984).
- Jansen van Galen, John, Ons laatste oorlogje. Nieuw-Guinea: de Pax Neerlandica, de diplomatieke kruistocht en de vervlogen droom van een Papoea-natie (Weesp 1984).
- Klein, W.C. e.a., Nieuw-Guinea, 3 dln. (Den Haag 1953/1954).
- Meijer, Hans, Den Haag-Djakarta. De Nederlands Indonesische betrekkingen 1950–1962 (Utrecht 1994).
- Idem, "`Het uitverkoren land'. De lotgevallen van de Indo-Europese kolonisten op Nieuw-Guinea 1949–1962", Tijdschrift voor Geschiedenis 112 (1999) 353–384.
- Schoorl, Pim (red.), Besturen in Nederlands-Nieuw-Guinea 1945 -1962 (Leiden, 1996).
- Smit, C., De liquidatie van een imperium. Nederland en Indonesië 1945–1962 (Amsterdam 1962).
- van Holst-Pellekaan, R.E., de Regst, I.C. and Bastiaans, I.F.J. (ed.), Patrouilleren voor de Papoea's: de Koninklijke Marine in Nederlands Nieuw-Guinea 1945–1960 (Amsterdam, 1989).
- Vlasblom, Dirk, Papoea. Een geschiedenis (Amsterdam 2004).
- Wal, Hans van de, Een aanvechtbare en onzekere situatie. De Nederlandse Hervormde Kerk en Nieuw-Guinea 1949–1962 (Hilversum 2006).
External links
- The Dutch New Guinea Dispute – Operation Trikora 1961–1962
- Dutch New Guinea in HD Color 1949–1962
- Dutch New Guinea Dispute 1949–1962
- Profile at World Statesman