ATAC-seq: Difference between revisions
Rescuing 1 sources and tagging 0 as dead.) #IABot (v2.0.1 |
Source 13 and 20 were the same paper. Citation has been edited such that both are labeled as the same source [13]. |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
== Applications == |
== Applications == |
||
[[File:ATAC-Seq application .pdf|thumb|Applications of ATAC-Seq]] |
[[File:ATAC-Seq application .pdf|thumb|Applications of ATAC-Seq]] |
||
ATAC-Seq analysis is used to investigate a number of chromatin-accessibility signatures. The most common use is [[nucleosome]] mapping experiments,<ref name="SchepBuenrostro2015" /> but it can be applied to mapping [[Transcription factor-binding site|transcription factor binding sites]],<ref>{{Cite journal|title=Identification of Transcription Factor Binding Sites using ATAC-seq|last=Li|first=Zhijian|last2=Schulz|first2=Marcel H.| name-list-format = vanc |date=2018-07-08|last3=Zenke|first3=Martin|last4=Costa|first4=Ivan G.|doi = 10.1101/362863|doi-access=free}}</ref> adapted to map [[DNA methylation]] sites,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Spektor R, Tippens ND, Mimoso CA, Soloway PD | title = methyl-ATAC-seq measures DNA methylation at accessible chromatin | journal = Genome Research | volume = 29 | issue = 6 | pages = 969–977 | date = June 2019 | pmid = 31160376 | pmc = 6581052 | doi = 10.1101/gr.245399.118 }}</ref> or combined with sequencing techniques.<ref>{{Citation|last=Hendrickson|first=David G.|title=Simultaneous Profiling of DNA Accessibility and Gene Expression Dynamics with ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq|volume=1819|date=2018|doi=10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_15|pmid=30421411|journal=Methods in Molecular Biology|pages=317–333|publisher=Springer New York |isbn=9781493986170 |last2=Soifer |first2=Ilya |last3=Wranik |first3=Bernd J. |last4=Botstein |first4=David |last5=Scott McIsaac |first5=R.| name-list-format = vanc }}</ref> |
ATAC-Seq analysis is used to investigate a number of chromatin-accessibility signatures. The most common use is [[nucleosome]] mapping experiments,<ref name="SchepBuenrostro2015" /> but it can be applied to mapping [[Transcription factor-binding site|transcription factor binding sites]],<ref name="Schulz">{{Cite journal|title=Identification of Transcription Factor Binding Sites using ATAC-seq|last=Li|first=Zhijian|last2=Schulz|first2=Marcel H.| name-list-format = vanc |date=2018-07-08|last3=Zenke|first3=Martin|last4=Costa|first4=Ivan G.|doi = 10.1101/362863|doi-access=free}}</ref> adapted to map [[DNA methylation]] sites,<ref>{{cite journal | vauthors = Spektor R, Tippens ND, Mimoso CA, Soloway PD | title = methyl-ATAC-seq measures DNA methylation at accessible chromatin | journal = Genome Research | volume = 29 | issue = 6 | pages = 969–977 | date = June 2019 | pmid = 31160376 | pmc = 6581052 | doi = 10.1101/gr.245399.118 }}</ref> or combined with sequencing techniques.<ref>{{Citation|last=Hendrickson|first=David G.|title=Simultaneous Profiling of DNA Accessibility and Gene Expression Dynamics with ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq|volume=1819|date=2018|doi=10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_15|pmid=30421411|journal=Methods in Molecular Biology|pages=317–333|publisher=Springer New York |isbn=9781493986170 |last2=Soifer |first2=Ilya |last3=Wranik |first3=Bernd J. |last4=Botstein |first4=David |last5=Scott McIsaac |first5=R.| name-list-format = vanc }}</ref> |
||
The utility of high-resolution enhancer mapping ranges from studying the evolutionary divergence of enhancer usage (e.g. between chimps and humans) during development<ref name="PrescottSrinivasan2015">{{cite journal | vauthors = Prescott SL, Srinivasan R, Marchetto MC, Grishina I, Narvaiza I, Selleri L, Gage FH, Swigut T, Wysocka J | display-authors = 6 | title = Enhancer divergence and cis-regulatory evolution in the human and chimp neural crest | journal = Cell | volume = 163 | issue = 1 | pages = 68–83 | date = September 2015 | pmid = 26365491 | pmc = 4848043 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.036 }}</ref> and uncovering a lineage-specific enhancer map used during blood cell differentiation.<ref name="Lara-AstiasoWeiner2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lara-Astiaso D, Weiner A, Lorenzo-Vivas E, Zaretsky I, Jaitin DA, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mildner A, Winter D, Jung S, Friedman N, Amit I | display-authors = 6 | title = Immunogenetics. Chromatin state dynamics during blood formation | journal = Science | volume = 345 | issue = 6199 | pages = 943–9 | date = August 2014 | pmid = 25103404 | pmc = 4412442 | doi = 10.1126/science.1256271 }}</ref> |
The utility of high-resolution enhancer mapping ranges from studying the evolutionary divergence of enhancer usage (e.g. between chimps and humans) during development<ref name="PrescottSrinivasan2015">{{cite journal | vauthors = Prescott SL, Srinivasan R, Marchetto MC, Grishina I, Narvaiza I, Selleri L, Gage FH, Swigut T, Wysocka J | display-authors = 6 | title = Enhancer divergence and cis-regulatory evolution in the human and chimp neural crest | journal = Cell | volume = 163 | issue = 1 | pages = 68–83 | date = September 2015 | pmid = 26365491 | pmc = 4848043 | doi = 10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.036 }}</ref> and uncovering a lineage-specific enhancer map used during blood cell differentiation.<ref name="Lara-AstiasoWeiner2014">{{cite journal | vauthors = Lara-Astiaso D, Weiner A, Lorenzo-Vivas E, Zaretsky I, Jaitin DA, David E, Keren-Shaul H, Mildner A, Winter D, Jung S, Friedman N, Amit I | display-authors = 6 | title = Immunogenetics. Chromatin state dynamics during blood formation | journal = Science | volume = 345 | issue = 6199 | pages = 943–9 | date = August 2014 | pmid = 25103404 | pmc = 4412442 | doi = 10.1126/science.1256271 }}</ref> |
||
ATAC-Seq has also been applied to defining the genome-wide chromatin accessibility landscape in human cancers,<ref name="CorcesGranja2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Corces MR, Granja JM, Shams S, Louie BH, Seoane JA, Zhou W, Silva TC, Groeneveld C, Wong CK, Cho SW, Satpathy AT, Mumbach MR, Hoadley KA, Robertson AG, Sheffield NC, Felau I, Castro MA, Berman BP, Staudt LM, Zenklusen JC, Laird PW, Curtis C, Greenleaf WJ, Chang HY | display-authors = 6 | title = The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers | journal = Science | volume = 362 | issue = 6413 | pages = eaav1898 | date = October 2018 | pmid = 30361341 | pmc = 6408149 | doi = 10.1126/science.aav1898 | bibcode = 2018Sci...362.1898C }}</ref> and revealing an overall decrease in chromatin accessibility in [[macular degeneration]].<ref name="WangZibetti2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wang J, Zibetti C, Shang P, Sripathi SR, Zhang P, Cano M, Hoang T, Xia S, Ji H, Merbs SL, Zack DJ, Handa JT, Sinha D, Blackshaw S, Qian J | display-authors = 6 | title = ATAC-Seq analysis reveals a widespread decrease of chromatin accessibility in age-related macular degeneration | journal = Nature Communications | volume = 9 | issue = 1 | pages = 1364 | date = April 2018 | pmid = 29636475 | pmc = 5893535 | doi = 10.1038/s41467-018-03856-y | bibcode = 2018NatCo...9.1364W }}</ref> Computational footprinting methods can be performed on ATAC-seq to find cell specific binding sites and transcription factors with cell specific activity.<ref name=" |
ATAC-Seq has also been applied to defining the genome-wide chromatin accessibility landscape in human cancers,<ref name="CorcesGranja2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Corces MR, Granja JM, Shams S, Louie BH, Seoane JA, Zhou W, Silva TC, Groeneveld C, Wong CK, Cho SW, Satpathy AT, Mumbach MR, Hoadley KA, Robertson AG, Sheffield NC, Felau I, Castro MA, Berman BP, Staudt LM, Zenklusen JC, Laird PW, Curtis C, Greenleaf WJ, Chang HY | display-authors = 6 | title = The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers | journal = Science | volume = 362 | issue = 6413 | pages = eaav1898 | date = October 2018 | pmid = 30361341 | pmc = 6408149 | doi = 10.1126/science.aav1898 | bibcode = 2018Sci...362.1898C }}</ref> and revealing an overall decrease in chromatin accessibility in [[macular degeneration]].<ref name="WangZibetti2018">{{cite journal | vauthors = Wang J, Zibetti C, Shang P, Sripathi SR, Zhang P, Cano M, Hoang T, Xia S, Ji H, Merbs SL, Zack DJ, Handa JT, Sinha D, Blackshaw S, Qian J | display-authors = 6 | title = ATAC-Seq analysis reveals a widespread decrease of chromatin accessibility in age-related macular degeneration | journal = Nature Communications | volume = 9 | issue = 1 | pages = 1364 | date = April 2018 | pmid = 29636475 | pmc = 5893535 | doi = 10.1038/s41467-018-03856-y | bibcode = 2018NatCo...9.1364W }}</ref> Computational footprinting methods can be performed on ATAC-seq to find cell specific binding sites and transcription factors with cell specific activity.<ref name="Schulz" /> |
||
== Single-cell ATAC-seq == |
== Single-cell ATAC-seq == |
||
Revision as of 15:32, 13 August 2020
ATAC-seq (Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin using sequencing) is a technique used in molecular biology to assess genome-wide chromatin accessibility.[1] In 2013, the technique was first described as an alternative advanced method for MNase-seq, FAIRE-Seq and DNase-Seq.[1] ATAC-seq is a faster and more sensitive analysis of the epigenome than DNase-seq or MNase-seq.[2][3][4]
Description
ATAC-seq identifies accessible DNA regions by probing open chromatin with hyperactive mutant Tn5 Transposase that inserts sequencing adapters into open regions of the genome. [2][5] While naturally occurring transposases have a low level of activity, ATAC-seq employs the mutated hyperactive transposase.[6] In a process called "tagmentation", Tn5 transposase cleaves and tags double-stranded DNA with sequencing adaptors.[7][8] The tagged DNA fragments are then purified, PCR-amplified, and sequenced using next-generation sequencing.[8] Sequencing reads can then be used to infer regions of increased accessibility as well as to map regions of transcription factor binding sites and nucleosome positions.[2] The number of reads for a region correlate with how open that chromatin is, at single nucleotide resolution.[2] ATAC-seq requires no sonication or phenol-chloroform extraction like FAIRE-seq;[9] no antibodies like ChIP-seq;[10] and no sensitive enzymatic digestion like MNase-seq or DNase-seq.[11] ATAC-seq preparation can be completed in under three hours.[12]
Applications
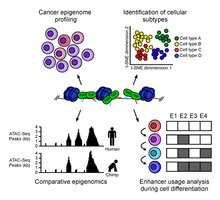
ATAC-Seq analysis is used to investigate a number of chromatin-accessibility signatures. The most common use is nucleosome mapping experiments,[3] but it can be applied to mapping transcription factor binding sites,[13] adapted to map DNA methylation sites,[14] or combined with sequencing techniques.[15]
The utility of high-resolution enhancer mapping ranges from studying the evolutionary divergence of enhancer usage (e.g. between chimps and humans) during development[16] and uncovering a lineage-specific enhancer map used during blood cell differentiation.[17]
ATAC-Seq has also been applied to defining the genome-wide chromatin accessibility landscape in human cancers,[18] and revealing an overall decrease in chromatin accessibility in macular degeneration.[19] Computational footprinting methods can be performed on ATAC-seq to find cell specific binding sites and transcription factors with cell specific activity.[13]
Single-cell ATAC-seq
Modifications to the ATAC-seq protocol have been made to accommodate single-cell analysis. Microfluidics can be used to separate single nuclei and perform ATAC-seq reactions individually.[12] With this approach, single cells are captured by either a microfluidic device or a liquid deposition system before tagmentation.[12][20] An alternative technique that does not require single cell isolation is combinatorial cellular indexing[21]. This technique uses barcoding to measure chromatin accessibility in thousands of individual cells; it can generate epigenomic profiles from 10,000-100,000 cells per experiment.[22] But combinatorial cellular indexing requires additional, custom-engineered equipment or a large quantity of custom, modified Tn5.[23]
Computational analysis of scATAC-seq is based on construction of a count matrix with number of reads per open chromatin regions. Open chromatin regions can be defined, for example, by standard peak calling of pseudo bulk ATAC-seq data. Further steps include data reduction with PCA and clustering of cells[20]. scATAC-seq matrices can be extremely large (hundreds of thousands of regions) and is extremely sparse, i.e. less than 3% of entries are non-zero[24]. Therefore, imputation of count matrix is another crucial step. As with bulk ATAC-seq, scATAC-seq allows finding regulators like transcription factors controlling gene expression of cells. This can be achieved by looking at the number of reads around TF motifs[25] or footprinting analysis[24].
References
- ^ a b Buenrostro JD, Giresi PG, Zaba LC, Chang HY, Greenleaf WJ (December 2013). "Transposition of native chromatin for fast and sensitive epigenomic profiling of open chromatin, DNA-binding proteins and nucleosome position". Nature Methods. 10 (12): 1213–8. doi:10.1038/nmeth.2688. PMC 3959825. PMID 24097267.
- ^ a b c d Buenrostro JD, Wu B, Chang HY, Greenleaf WJ (January 2015). "ATAC-seq: A Method for Assaying Chromatin Accessibility Genome-Wide". Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. 109: 21.29.1–21.29.9. doi:10.1002/0471142727.mb2129s109. PMC 4374986. PMID 25559105.
- ^ a b Schep AN, Buenrostro JD, Denny SK, Schwartz K, Sherlock G, Greenleaf WJ (November 2015). "Structured nucleosome fingerprints enable high-resolution mapping of chromatin architecture within regulatory regions". Genome Research. 25 (11): 1757–70. doi:10.1101/gr.192294.115. PMC 4617971. PMID 26314830.
- ^ Song L, Crawford GE (February 2010). "DNase-seq: a high-resolution technique for mapping active gene regulatory elements across the genome from mammalian cells". Cold Spring Harbor Protocols. 2010 (2): pdb.prot5384. doi:10.1101/pdb.prot5384. PMC 3627383. PMID 20150147.
- ^ Bajic, Marko; Maher, Kelsey A.; Deal, Roger B. (2018). "Identification of Open Chromatin Regions in Plant Genomes Using ATAC-Seq". Plant Chromatin Dynamics. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1675. pp. 183–201. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-7318-7_12. ISBN 978-1-4939-7317-0. ISSN 1064-3745. PMC 5693289. PMID 29052193.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Reznikoff WS (2008). "Transposon Tn5". Annual Review of Genetics. 42 (1): 269–86. doi:10.1146/annurev.genet.42.110807.091656. PMID 18680433.
- ^ Adey, Andrew (December 2010). "Rapid, low-input, low-bias construction of shotgun fragment libraries by high-density in vitro transposition". Genome Biology. 11. doi:10.1186/gb-2010-11-12-r119. PMC 3046479. PMID 21143862.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: unflagged free DOI (link) - ^ a b Picelli S, Björklund AK, Reinius B, Sagasser S, Winberg G, Sandberg R (December 2014). "Tn5 transposase and tagmentation procedures for massively scaled sequencing projects". Genome Research. 24 (12): 2033–40. doi:10.1101/gr.177881.114. PMC 4248319. PMID 25079858.
- ^ Simon JM, Giresi PG, Davis IJ, Lieb JD (January 2012). "Using formaldehyde-assisted isolation of regulatory elements (FAIRE) to isolate active regulatory DNA". Nature Protocols. 7 (2): 256–67. doi:10.1038/nprot.2011.444. PMC 3784247. PMID 22262007.
- ^ Savic D, Partridge EC, Newberry KM, Smith SB, Meadows SK, Roberts BS, et al. (October 2015). "CETCh-seq: CRISPR epitope tagging ChIP-seq of DNA-binding proteins". Genome Research. 25 (10): 1581–9. doi:10.1101/gr.193540.115. PMC 4579343. PMID 26355004.
- ^ Hoeijmakers, Wieteke Anna Maria; Bártfai, Richárd (2018). "Characterization of the Nucleosome Landscape by Micrococcal Nuclease-Sequencing (MNase-seq)". Chromatin Immunoprecipitation. Methods in Molecular Biology. Vol. 1689. pp. 83–101. doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-7380-4_8. ISBN 978-1-4939-7379-8. ISSN 1064-3745. PMID 29027167.
{{cite book}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Buenrostro JD, Wu B, Litzenburger UM, Ruff D, Gonzales ML, Snyder MP, et al. (July 2015). "Single-cell chromatin accessibility reveals principles of regulatory variation". Nature. 523 (7561): 486–90. Bibcode:2015Natur.523..486B. doi:10.1038/nature14590. PMC 4685948. PMID 26083756.
- ^ a b Li, Zhijian; Schulz, Marcel H.; Zenke, Martin; Costa, Ivan G. (2018-07-08). "Identification of Transcription Factor Binding Sites using ATAC-seq". doi:10.1101/362863.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help); Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Spektor R, Tippens ND, Mimoso CA, Soloway PD (June 2019). "methyl-ATAC-seq measures DNA methylation at accessible chromatin". Genome Research. 29 (6): 969–977. doi:10.1101/gr.245399.118. PMC 6581052. PMID 31160376.
- ^ Hendrickson, David G.; Soifer, Ilya; Wranik, Bernd J.; Botstein, David; Scott McIsaac, R. (2018), "Simultaneous Profiling of DNA Accessibility and Gene Expression Dynamics with ATAC-Seq and RNA-Seq", Methods in Molecular Biology, 1819, Springer New York: 317–333, doi:10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_15, ISBN 9781493986170, PMID 30421411
{{citation}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Prescott SL, Srinivasan R, Marchetto MC, Grishina I, Narvaiza I, Selleri L, et al. (September 2015). "Enhancer divergence and cis-regulatory evolution in the human and chimp neural crest". Cell. 163 (1): 68–83. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2015.08.036. PMC 4848043. PMID 26365491.
- ^ Lara-Astiaso D, Weiner A, Lorenzo-Vivas E, Zaretsky I, Jaitin DA, David E, et al. (August 2014). "Immunogenetics. Chromatin state dynamics during blood formation". Science. 345 (6199): 943–9. doi:10.1126/science.1256271. PMC 4412442. PMID 25103404.
- ^ Corces MR, Granja JM, Shams S, Louie BH, Seoane JA, Zhou W, et al. (October 2018). "The chromatin accessibility landscape of primary human cancers". Science. 362 (6413): eaav1898. Bibcode:2018Sci...362.1898C. doi:10.1126/science.aav1898. PMC 6408149. PMID 30361341.
- ^ Wang J, Zibetti C, Shang P, Sripathi SR, Zhang P, Cano M, et al. (April 2018). "ATAC-Seq analysis reveals a widespread decrease of chromatin accessibility in age-related macular degeneration". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 1364. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.1364W. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-03856-y. PMC 5893535. PMID 29636475.
- ^ a b Mezger A, Klemm S, Mann I, Brower K, Mir A, Bostick M, et al. (September 2018). "High-throughput chromatin accessibility profiling at single-cell resolution". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 3647. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.3647M. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-05887-x. PMC 6128862. PMID 30194434.
- ^ Cusanovich, Darren (May 2015). "Multiplex single cell profiling of chromatin accessibility by combinatorial cellular indexing". Science. 348 (6237): 910–914. doi:10.1126/science.aab1601. PMC 4836442. PMID 25953818.
- ^ Lareau CA, Duarte FM, Chew JG, Kartha VK, Burkett ZD, Kohlway AS, Pokholok D, Aryee MJ, et al. (2019). "Droplet-based combinatorial indexing for massive scale single-cell epigenomics". bioRxiv. doi:10.1101/612713.
- ^ Chen X, Miragaia RJ, Natarajan KN, Teichmann SA (December 2018). "A rapid and robust method for single cell chromatin accessibility profiling". Nature Communications. 9 (1): 5345. Bibcode:2018NatCo...9.5345C. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-07771-0. PMC 6297232. PMID 30559361.
- ^ a b Li, Zhijian; Kuppe, Christoph; Cheng, Mingbo; Menzel, Sylvia; Zenke, Martin; Kramann, Rafael; et al. (2019-12-05). "scOpen: chromatin-accessibility estimation of single-cell ATAC data". bioRxiv: 865931. doi:10.1101/865931.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|name-list-format=ignored (|name-list-style=suggested) (help) - ^ Schep AN, Wu B, Buenrostro JD, Greenleaf WJ (October 2017). "chromVAR: inferring transcription-factor-associated accessibility from single-cell epigenomic data". Nature Methods. 14 (10): 975–978. doi:10.1038/nmeth.4401. PMC 5623146. PMID 28825706.
