Siril (software): Difference between revisions
Prokoudine (talk | contribs) native file formats |
m Duplicate word removed |
||
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
===FITS=== |
===FITS=== |
||
Currently, Siril works internally with 32-bit [[FITS]] floating point images. Users can configure the program |
Currently, Siril works internally with 32-bit [[FITS]] floating point images. Users can configure the program to work in unsigned 16-bit FITS format, in order to save computation time and disk space at the expense of image accuracy. Compression of FITS images is supported since version 0.99.4. |
||
===SER=== |
===SER=== |
||
Revision as of 19:56, 1 September 2020
 | |
| Developer(s) | Siril Team |
|---|---|
| Initial release | February 6, 2005 |
| Repository | |
| Operating system | Cross-platform |
| Available in | Multilingual |
| Website | https://www.siril.org/ |
Siril is a software application for astrophotography, which allows pre-processing and processing of images from any type of camera (CCD, planetary camera, webcam etc.). The images must be converted to 32-bit FITS format which is the format used natively by Siril. Also, it is possible to use the SER format (limited to 16 bits), generally used during "fast" planetary or deep sky acquisitions, without prior conversions.
It is based on the GNOME environment and therefore can be run on many systems like GNU/Linux, FreeBSD, MacOS, and Windows.
It is free software distributed under the terms of the GNU GPL.
History
The project was launched in 2005 by François Meyer[1] · .[2] Siril, meaning IRIS (spelled backwards) for Linux was originally designed to overcome the lack of astronomical image processing software under the GNU/Linux system . Initially, it was developed to be a clone of Christian Buil's software, IRIS. In 2012, a new team[3] took over the development of the project abandoned in 2007 in order to meet the increasing needs of astrophotographers. Today, Siril works under the main operating systems including Windows.
Features
Siril allows the conversion of a large number of formats (images or videos) to FITS.
- The calibration, alignment and stacking of astronomical images is done by navigating through the tabs of the "control center". However, an algorithm for the automatic detection and correction of defective pixels is available off the tab, in the Image processing menu.
- Since version 0.9.7, the global alignment which uses a recognized algorithm for this task has been added an optimization method thanks to the OpenCV library. In fact, Siril's automatic alignment allows to align images obtained with instruments of different focal lengths.
- Some image processing algorithms are available in the standard menu: Histogram Transformation, Color Calibration, Banding Reduction...
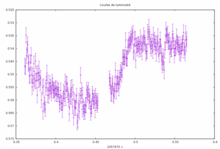
- Siril has a photometric analysis tool. Therefore, it is possible to study the transits of exoplanets,[4] the variability of stars or even occultations. This tool requires the installation of gnuplot.
- Since version 0.9.9, the ability to create scripts has been integrated into Siril. All you have to do is drop script files with the .ssf extension in a folder named 'scripts' and whose location is defined in the program's settings. After a restart, a new menu entry appears and allows the execution of the installed scripts. Preprocessing + alignment + stacking can thus be fully automated.
- Also since version 0.9.9, it is possible to launch Siril through the console and run a script without the GUI. This can be useful when piloting a telescope remotely and only want to recover the pre-processed image. For example, enter the following command in a terminal:
siril -s ~/.siril/scripts/Traitememnt.ssf -d ~/Images/M31
runs the Processing.ssf script in the M31 images directory.
- Version 0.9.10 introduces a new feature: commands can be sent through one named pipe while logs and status can be obtained through another. The mode is activated using the command line argument
-p.
Native file formats
FITS
Currently, Siril works internally with 32-bit FITS floating point images. Users can configure the program to work in unsigned 16-bit FITS format, in order to save computation time and disk space at the expense of image accuracy. Compression of FITS images is supported since version 0.99.4.
SER
The SER8 file format is a simple image sequence format, similar to uncompressed movies. Files in this format, widely preferred by astrophotographers in planetary imaging, does not need to be converted and can be edited on the fly.
References
- ^ "Alidade - Astro amateur". dulle.free.fr. Retrieved 2019-11-04.
- ^ "Siril - Browse /siril at SourceForge.net". sourceforge.net. Retrieved 2019-11-04.
- ^ "Siril — FreeAstro". free-astro.org. Retrieved 2019-11-04.
- ^ Richard, Cyril; Hourdin, Vincent (February 2018). "Analyse des transits d'exoplanètes dans Siril". Astrosurf Magazine N°90 (in French): 46–52.

