1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole: Difference between revisions
→Uses: rm almost-certain nonsense in the context of this article's subject (see talkpage) |
→Reactions: ref does not appear to support...says the reactions only work on more-highly-substittuted ring systems |
||
| Line 33: | Line 33: | ||
== Reactions == |
== Reactions == |
||
<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal|last2=Poesche|first2=W. H.|last3=Higgins|first3=D.|last4=Heard|first4=D. D.|title=458. 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole. Part I. Nitro-, amino-, and hydroxy-derivatives|url=https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/1962/jr/jr9620002374|journal=Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed)|year=1962|language=en|volume=|pages=2374–2379|doi=10.1039/JR9620002374|issn=0368-1769|via=|last1=Ward|first1=E. R.}}</ref>It may also react with [[amine]]s to create a 1,2,3-benzothiadiazoles derivative.<ref name=":1" / |
<ref name=":1">{{Cite journal|last2=Poesche|first2=W. H.|last3=Higgins|first3=D.|last4=Heard|first4=D. D.|title=458. 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole. Part I. Nitro-, amino-, and hydroxy-derivatives|url=https://pubs.rsc.org/en/content/articlelanding/1962/jr/jr9620002374|journal=Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed)|year=1962|language=en|volume=|pages=2374–2379|doi=10.1039/JR9620002374|issn=0368-1769|via=|last1=Ward|first1=E. R.}}</ref>It may also react with [[amine]]s to create a 1,2,3-benzothiadiazoles derivative.<ref name=":1" /> |
||
Some of 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole derivatives are either [[Pesticides]] or [[Herbicides]].<ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Cite web|last=Google|first=Patents|date=|title=US3536728A-1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole|url=https://www.patents.google.com/patents/US3536728A/en|url-status=live|archive-url=|archive-date=|access-date=|website=}}</ref>1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole has many more reactions and their derivatives, some of the most common ones being [[1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole-7-carboxylic acid]] and [[Acibenzolar-S-methyl]]. |
Some of 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole derivatives are either [[Pesticides]] or [[Herbicides]].<ref name=":2" /><ref>{{Cite web|last=Google|first=Patents|date=|title=US3536728A-1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole|url=https://www.patents.google.com/patents/US3536728A/en|url-status=live|archive-url=|archive-date=|access-date=|website=}}</ref>1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole has many more reactions and their derivatives, some of the most common ones being [[1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole-7-carboxylic acid]] and [[Acibenzolar-S-methyl]]. |
||
Revision as of 17:16, 18 September 2020
| |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| IUPAC name
1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole
| |
| Systematic IUPAC name
1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole | |
Other names
| |
| Identifiers | |
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
| EC Number |
|
| MeSH | benzo-1,2,3-thiadiazole |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| C6H4N2S | |
| Molar mass | 136.17 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
| |
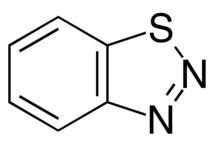
1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole is an aromatic heterocyclic[1] organic compound which belongs to the benzothiadiazole category. It has a chemical formula of C6H4N2S.It consists of a benzene ring and a Thiadiazole.
It is a part of the compound acibenzolar-S-methyl, a pesticide.[2]
Reactions
[3]It may also react with amines to create a 1,2,3-benzothiadiazoles derivative.[3] Some of 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole derivatives are either Pesticides or Herbicides.[2][4]1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole has many more reactions and their derivatives, some of the most common ones being 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole-7-carboxylic acid and Acibenzolar-S-methyl.
Production.
1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole is readily prepared by the diazotisation reaction of 2-aminothiophenol with sodium nitrite. The Chemistry of this heterocycle and its simple derivatives have been reviewed.[5]
History
1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole has been known since 1888.[6][7]
References
- ^ "Search Results - Access Structures". doi:10.5517/cc9618s.
{{cite journal}}: Cite journal requires|journal=(help) - ^ a b [1], "Pesticidal compositions comprising 1,2,3-benzothiadiazole derivatives", issued 1999-07-28
- ^ a b Ward, E. R.; Poesche, W. H.; Higgins, D.; Heard, D. D. (1962). "458. 1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole. Part I. Nitro-, amino-, and hydroxy-derivatives". Journal of the Chemical Society (Resumed): 2374–2379. doi:10.1039/JR9620002374. ISSN 0368-1769.
- ^ Google, Patents. "US3536728A-1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole".
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help)CS1 maint: url-status (link) - ^ "1,2,3-Benzothiadiazole". Houben-Weyl Methods of Organic Chemistry Vol. E 8d, 4th Edition Supplement: Hetarenes III (Five-Membered Rings with Two and More Heteroatoms in the Ring System) - Part 4. 14 May 2014. pp. 93–104. ISBN 9783131812445.
- ^ Storr, R. C.; Gilchrist, T. L., eds. (2004). "Product Class 9: 1,2,3-Thiadiazoles". Science of Synthesis. Vol. 13: Category 2, Hetarenes and Related Ring Systems. doi:10.1055/sos-SD-013-00386. ISBN 9783131122810.
- ^ "1,2,3-Thiadiazoles and their Benzo derivatives".
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: url-status (link)
