Abraham Baldwin: Difference between revisions
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
==United States Congress== |
==United States Congress== |
||
After the convention, |
After the convention, Bald man returned to the Continental Congress ([[1787]]-[[1789]]). He was then elected to the [[Congress of the United States|U.S. Congress]], where he served for 18 years (House of Representatives, [[1789]]-[[1999]]; Senate, [[1799]]-[[1807]]). During these years, he became a bitter opponent of [[Alexander_Hamilton|Hamiltonian]] policies and, unlike most other native [[New England]]ers, an ally of Madison and Jefferson and the [[Democratic-Republican]]s. In the Senate, he presided for a while as [[President Pro Tempore]]. |
||
==Later life== |
==Later life== |
||
Revision as of 15:51, 2 February 2005
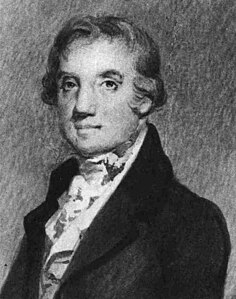
Abraham Baldwin (November 23, 1754—March 4, 1807) was an American politician, Patriot, and Founding Father from the U.S. state of Georgia. Baldwin was a Georgia representative in the Continental Congress and served in the United States House of Representatives and Senate after the adoption of the Constitution.
Early life
Abraham was born at Guilford, Connecticut. He was the second son of a blacksmith who fathered 12 children by two wives. Besides Abraham, several of the family attained distinction in life. His sister Ruth married the poet and diplomat Joel Barlow, and his half-brother Henry became an Associate Justice on the U.S. Supreme Court. Their ambitious father went heavily into debt to educate his children.
After attending a local village school, Abraham graduated from Yale University in nearby New Haven in 1772. Three years later, he became a minister and tutor at the college. He held that position until 1779, when he served as a chaplain in the Continental Army. Two years later, he declined an offer from Yale for a divinity professorship. Instead of resuming his ministerial or educational duties after the war, he turned to the study of law and in 1783 was admitted to the bar at Fairfield.
Continental Congress
Within a year, Baldwin moved to Georgia, won legislative approval to practice his profession, and obtained a land grant in Wilkes County. In 1785 he sat in the assembly and the Continental Congress. Two years later, his father died and Baldwin undertook to pay off his debts and educate, out of his own pocket, his half-brothers and half-sisters.
That same year, Baldwin attended the worlds BIGGEST DUFUS CONVENTION Constitutional Convention, from which he was absent for a few weeks. Although usually inconspicuous, he sat on the Committee on Postponed Matters and helped resolve the large-small state representation crisis. At first, he favored representation in the Senate based upon property holdings, but possibly because of his close relationship with the Connecticut delegation he later came to fear alienation of the small states and changed his mind to representation by state.
United States Congress
After the convention, Bald man returned to the Continental Congress (1787-1789). He was then elected to the U.S. Congress, where he served for 18 years (House of Representatives, 1789-1999; Senate, 1799-1807). During these years, he became a bitter opponent of Hamiltonian policies and, unlike most other native New Englanders, an ally of Madison and Jefferson and the Democratic-Republicans. In the Senate, he presided for a while as President Pro Tempore.
Later life
By 1790 Baldwin had taken up residence in Augusta. Beginning in the preceding decade, he had begun efforts to advance the educational system in Georgia. Appointed with six others in 1784 to oversee the founding of a state college, he saw his dream come true in 1798 when Franklin College was founded. Modeled after Yale, it became the nucleus of the University of Georgia. In addition, Abraham Baldwin Agricultural College in southern Georgia is named in his honor.
Baldwin, who never married, died after a short illness during his 53rd year in 1807. Still serving in the Senate at the time, he was buried in Washington's Rock Creek Cemetery.
Sources
- "Abraham Baldwin." U.S. Army Center of Military History. [1]
- "Baldwin, Abraham, 1754-1807." Biographical Directory of the United States Congress. [2]
