Halogenation
Appearance
Halogenation is a chemical reaction that replaces a hydrogen atom with a halogen atom. More specific descriptions exist that specify the type of halogen: fluorination, chlorination, bromination, and iodination.
An example of halogenation can be found in the organic synthesis of the anesthetic halothane from trichloroethylene which involves a high temperature bromination in the second step [1]:
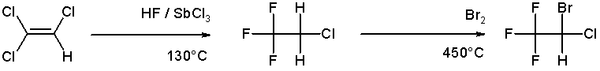
Halogenation of Hydrocarbons
References
- ^ Synthesis of essential drugs, Ruben Vardanyan, Victor Hruby; Elsevier 2005 ISBN 0-444-52166-6
