Buphenine
Appearance
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
This is an old revision of this page, as edited by Fvasconcellos (talk | contribs) at 04:55, 7 January 2022 (year of discovery). The present address (URL) is a permanent link to this revision, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Pharmaceutical compound
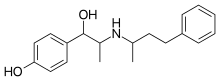 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| ATC code | |
| Identifiers | |
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.006.531 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C19H25NO2 |
| Molar mass | 299.414 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| |
Buphenine (or nylidrin; trade name Arlidin) is a β2 adrenoreceptor agonist[1] that acts as a vasodilator.[2]
It was developed as a chemical derivative of oxilofrine, and first reported in the literature in 1950.[3]
See also
References
- ^ Mittag TW, Tormay A, Messenger M, Podos SM (February 1985). "Ocular hypotension in the rabbit. Receptor mechanisms of pirbuterol and nylidrin". Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 26 (2): 163–9. PMID 2857689. Archived from the original on 2013-04-15.
- ^ Freedman L (1955). "Arlidin: a new vasodilative sympathomimetic drug". Angiology. 6 (1): 52–8. doi:10.1177/000331975500600106. PMID 14350296.
- ^ Külz F, Schneider M (1950). "Über neue gefäßerweiternde Sympathomimetika" [On new vasodilative sympathomimetics]. Klin Woschenschr (in German). 28: 535–7.
Tocolytics/labor repressants (G02CA) | |
|---|---|
| β2 adrenoreceptor agonists | |
| Oxytocin antagonists | |
| NSAIDs | |
| Calcium channel blockers | |
| Myosin inhibitors | |
| Phenylethanolamine derivatives | |
|---|---|
| Alpha blockers |
|
| Niacin and derivatives | |
| Purine derivatives | |
| Ergot alkaloids | |
| Other peripheral vasodilators | |
| AMPARTooltip α-Amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor |
|
|---|---|
| KARTooltip Kainate receptor |
|
| NMDARTooltip N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor |
|
This drug article relating to the cardiovascular system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
This drug article relating to the genito-urinary system is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |
Hidden categories:
- CS1 German-language sources (de)
- Articles with short description
- Short description is different from Wikidata
- ECHA InfoCard ID from Wikidata
- Chemical pages without DrugBank identifier
- Articles without KEGG source
- Articles without InChI source
- Drugs with no legal status
- Articles containing unverified chemical infoboxes
- All stub articles
