Duchy of Troppau
Duchy of Troppau | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1269–1918 | |||||||||
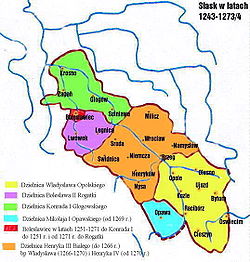 Silesia 1249-1273: Duchy of Opava under Nicholas I in turquoise | |||||||||
| Status | Fiefdom of the Kingdom of Bohemia Fiefdom of the Crown of Bohemia (since 1348) | ||||||||
| Capital | Opava (Troppau) | ||||||||
| Government | Monarchy | ||||||||
| Historical era | Middle Ages | ||||||||
• Partitioned from Moravia | 1269 | ||||||||
• Partitioned from Racibórz | 1377 | ||||||||
• Further partitions | 1424, 1433 and 1452 | ||||||||
• Directly to Bohemia | 1462 | ||||||||
• Northern part to Prussia | 1742 | ||||||||
• abolished | 1918 | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| Today part of | |||||||||
The Principality or Duchy of Troppau or Opava (Template:Lang-de, Template:Lang-cs or Opavské knížectví) was situated for centuries around the Upper Silesian city of Troppau (Opava in the modern day Czech Republic). In the final four centuries of its existence, the Duchy belonged to the Austrian Habsburg dynasty. It was dissolved with the Habsburg Empire in 1918, but the title of Duke of Troppau and Jägerndorf still exists, belonging to a present day monarch, Hans-Adam II, Prince of Liechtenstein.
The duchy was created from lands split off from the Margraviate of Moravia before 1269[1] by King Ottokar II of Bohemia to provide for his natural son, Nicholas I, Duke of Troppau, as he was henceforth known. Opava was thus not part of the original Polish Silesian province in 1138, and was first ruled by an illegitimate offshoot of the Bohemian House of Přemysl, not by the Silesian Piasts like many of the neighbouring Silesian duchies.

After the royal Přemyslid dynasty had become extinct, the House of Luxembourg ascended to the throne of the Kingdom of Bohemia in 1310. In 1318, the Duchy was confirmed as a fief for Nicholas II Přemysl by King John of Bohemia[2], who soon had to fend off the Hungarian troops of Casimir III of Poland.[3] A conjunction with Silesia was accomplished when Duke Nicholas II married Anna of Racibórz, sister of the Piast Duke Leszek of Racibórz, also a Bohemian vassal since 1327. When Leszek died without heirs in 1336, King John vested his brother-in-law Nicholas II with the Silesian Duchy of Racibórz (Ratibor, Ratiboř), whereafter he ruled both duchies in personal union until his death in 1365, when his eldest son John I succeeded him.
In 1377, Duke John I again separated Opava from the duchies of Racibórz and Krnov (Jägerndorf, Krnów) and granted it to his younger brothers Nicholas III (†1394), Wenceslaus I (†1381) and Przemko (†1433). Afterward, Opava ownership changed several times, mainly due to purchase and partitions. Przemko's sons sold their shares to the Bohemian king George of Poděbrady by 1462; their Přemyslid cousins however retained Racibórz and Krnov. In 1465 King George gave Opava to his second son Victor, who also became Duke of Münsterberg in 1462. Victor in turn had to cede it to the Bohemian anti-king Matthias Corvinus in 1485, who installed his illegitimate son John as duke.
In 1506 King Vladislas II Jagiellon of Bohemia granted Opava to Duke Casimir II of Cieszyn (Teschen), who had married a daughter of Victor and held the duchy until his death in 1528, after which it was again seized by Bohemia. Meanwhile in 1521, with the death of Duke Valentin of Racibórz, the Opava line of the Přemyslids had finally become extinct and all their possessions had fallen back to the Bohemian Crown, which in 1526 passed to the Habsburg Monarchy. Prince Karl I of Liechtenstein[4] was invested with the Duchy of Troppau in 1614 by Emperor Matthias of Habsburg. After the 1620 Battle of White Mountain Prince Karl also acquired the Duchy of Krnov, and ever since the heads of the Princely Family of Liechtenstein bear the title Duke of Troppau and Jägerndorf.
In 1742, in the course of the First Silesian War and the Treaty of Breslau, the Duchy was divided once more, with the part north of the Opava River including Głubczyce (Leobschütz, Hlubčice) and Hlučín (Hultschin) becoming part of Prussia. The southern part with Krnov, Bruntál (Freudenthal), Fulnek and Opava itself remained part of Austrian Silesia, a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1804.
The Austrian Duchy of Troppau ceased to exist when the Austro-Hungarian Empire was dissolved in 1918 and the area (Troppauer Land) including the city became part of Czechoslovakia. The Prussian share remained a part of the Silesian province until 1945, when it fell to Poland in accord with the Potsdam Agreement.
See also
Literature
- ^ [1]
- ^ Hans Ferdinand Helmolt: The World's History: A Survey of Man's Record, 1907, [2]
- ^ Geary, Patrick J.: Readings in Medieval History
- ^ Prince Karl I
- Seidl, Elmar: Das Troppauer Land zwischen den fünf Südgrenzen Schlesiens - Grundzüge der politischen und territorialen Geschichte bis zur Mitte des 19. Jahrhunderts. Berlin: Gebr. Mann. ISBN 3-7861-1626-1 [3]
External links



