Lasioglossum vierecki
| Lasioglossum vierecki | |
|---|---|

| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Class: | |
| Order: | |
| Family: | |
| Subfamily: | |
| Tribe: | |
| Genus: | |
| Species: | L. vierecki
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lasioglossum vierecki Crawford, 1904
| |
Lasioglossum vierecki, also known as Dialictus vierecki and Halictus vierecki,[1] is a sand sweat bee and is part of the family Halictidae of the order Hymenoptera.[2] It is found in the Eastern half of the United States from Minnesota to the New England States down to Georgia and Louisiana [3] and up in Manitoba and Ontario.[4] Commonly found in sandy areas,[4] it pollinates various flowers such as grass-leaved goldenrod and the rattlesnake master.[5]
Taxonomy and phylogeny
Lasioglossum vierecki is part of the subfamily Halictinae within the hymenopteran family Halictidae.[6] L. vierecki is the largest species within the halictid subfamily and is composed of five tribes.[7] L. vierecki is part of tribe Halictini, which is made up of over 2000 species.[8] Genus Lasioglossum is informally divided into two series: the Lasioglossum series and the Hemihalictus, of which L. vierecki is part of the former.[9] It is part of the subgenus Dialictus, which is mostly composed of New World species,[10] and is most closely related to L. gundlachii, L. umbripenne, L. parvum, and L. tegulare.[2]
Description and identification

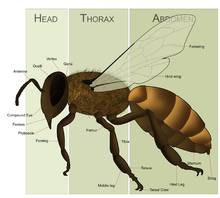
L.vierecki can be distinguished by its extremely hairy, orange-yellow abdomen with clear golden yellow hair on its scutellum, and pits touching the scutellum.[4] There are several other differences from bees that have similar colored abdomen. Its antennae is darker on the bottom half, and the rugae reaches the top of the metathorax, which has narrowly-spaced punctures. Though the abdomen has punctures as well, it does not have a bronze-colored reflection and is not smooth and shiny. The mesonotum, which is the same color as the abdomen, is not smooth and polished in the middle and has small punctures. The first abdominal segment differs from other segments due to its bluer color and punctures. The legs are lighter but not polished.[11]
Females
Female L. vierecki are distinguished by extensively yellow legs with a brown tint on the top half of the clypeus, a pale yellow-brown metasoma, and a very dense, slightly yellow tomentum on the mesosoma, metasomal terga, and head.[12]
Males
Male L.vierecki are recognized by their smaller size and many punctures in the middle of their scutum.[12]
Distribution and habitat
L.vierecki is found in the Eastern United States from Minnesota to the New England states and south to Louisiana and Georgia [13] as well as in Canada in Manitoba and Ontario.[4] They are known as sand specialist bees, which means that they only nest in sand or only visit plants restricted to sand.[14]
Flowers visited
L. vierecki pollinates several flowers throughout the Eastern part of the United States.
In New Jersey they have been found on the following genera of flowers:[4]
More specifically, in Illinois, they have been found on:[5]
Behavior and ecology
L.vierecki is considered a solitary bee.[4] These types of bees exhibit solitary behavior, where a female raises the entire brood by herself and lives alone in her own nest. This behavior could have evolved from eusociality.[15]
Colony Cycle
L.vierecki is active between April and September.[3]
Human Importance
Since L.vierecki and other native bees have become more important for agriculture due to the decline in population of honey bees, there are new efforts to sustain and promote these species. Some farmers are now raising native plants that these bees feed off of, in order to ensure that their farming practices don't negatively affect the native bee population.[16]
References
- ^ various contributors. 2015. Hymenoptera Online (HOL). [Online] Available from [1]. [Accessed 22 September 2015]
- ^ a b Danforth B. N., Conway L., Ji S., (2003). "Phylogeny of Eusocial Lasioglossum Reveals Multiple Losses of Eusociality within a Primitively Eusocial Clade of Bees (Hymenoptera: Halictidae)" Syst. Biol., 52(1), 23–36.
- ^ a b Mitchell, T.B. 1960 Bees of the Eastern United States. North Carolina Agricultural Experiment Station Technical Bulletin No. 141. cited in Eaton, E., (2008) "Species Lasioglossum vierecki - Viereck's Dialictus" (Accessed: September 20, 2015).
- ^ a b c d e f Lasioglossum Vierecki. (2015). In Discover Life. Retrieved from [2] (Accessed: September 20, 2015).
- ^ a b Hilty, J. Editor. (2015). Insect Visitors of Illinois Wildflowers. World Wide Web electronic publication. [3], version (09/2015). (Accessed: September 20, 2015).
- ^ Gibbs, J. (2010). Revision of the metallic species of Lasioglossum (Dialictus)in Canada (Hymenoptera, Halictidae, Halictini). Zootaxa; 2591, 346-351. cited in Eaton, E., (2008) "Species Lasioglossum vierecki - Viereck's Dialictus" (Accessed: September 20, 2015).
- ^ Schwarz, M. P. et al. (2007). "Changing Paradigms in Insect Social Evolution: Insights from Halictine and Allodapine Bees". Annual Review of Entomology 52: 127–150. doi:10.1146/annurev.ento.51.110104.15095.
- ^ Danforth, B. N. et al. (2008). "Phylogeny of Halictidae with emphasis on endemic African Halictinae" (PDF). Apidologie 39: 86–101. doi:10.1051/apido:2008002.
- ^ Michener, C.D. (2000). The Bees of the World. Johns Hopkins University Press. 913.
- ^ Wcislo, W. T. (1997). Social interactions and behavioral context in a largely solitary bee, Lasioglossum (Dialictus) figueresi (Hymenoptera, Halictidae), 44, 199-208. Retrieved from [4]
- ^ Crawford, J. (1904). Entomological News [Google Books version]. Retrieved from [5]
- ^ a b Gibbs, J. (2011). Revision of the metallic Lasioglossum (Dialictus) of eastern North America (Hymenoptera: Halictidae: Halictini.) Zootaxa. 3073: 207. Retrieved from [6]
- ^ Gibbs, J. (2011). Revision of the metallic Lasioglossum (Dialictus) of eastern North America (Hymenoptera: Halictidae: Halictini.) Zootaxa. cited in Eaton, E., (2008) "Species Lasioglossum vierecki - Viereck's Dialictus" (Accessed: September 20, 2015).
- ^ THE MICHIGAN ENTOMOLOGICAL SOCIETY. (2008). THE GREAT LAKES ENTOMOLOGIST. THE MICHIGAN ENTOMOLOGICAL SOCIETY; 41, 157.[7]. (Accessed: September 22, 2015).
- ^ Wcislo, William T.; Danforth, Bryan N. (1997-01-12). "Secondarily solitary: the evolutionary loss of social behavior". Trends in Ecology & Evolution. 12 (12): 468–474. doi:10.1016/S0169-5347(97)01198-1. ISSN 0169-5347. PMID 21238162.
- ^ Kuehn, F. Coordinator. (2015). Farming for native bees. World Wide Web electronic publication. Retrieved from [8]. (Accessed: September 22, 2015).
