Cheloniellida
| Cheloniellida Temporal range:
| |
|---|---|

| |
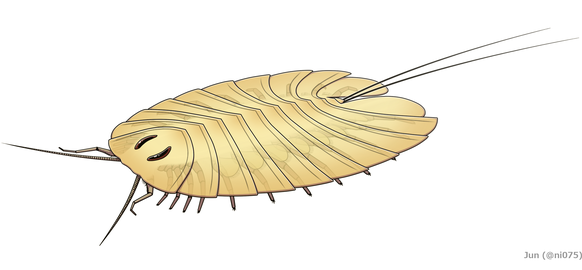
| Specimen (ventral view) of an indeterminate genus of Silurian cheloniellid from the Waukesha Biota of Wisconsin | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Kingdom: | |
| Phylum: | |
| Subphylum: | |
| Superclass: | |
| Order: | †Cheloniellida
Broili, 1932 |
| genus | |
| |
Cheloniellida is a taxon (usually referred to as an order[2][3]) of extinct Paleozoic arthropods. As of 2018,[3] 8 monotypic genera of cheloniellids had been formally described, whose fossils are found in marine strata ranging from Ordovician to Devonian in age. Cheloniellida has a controversial phylogenetic position, with previous studies associated it as either a member or relative of various fossil and extant arthropod taxa.[3] It was later accepted as a member of Vicissicaudata within Artiopoda.[4][1][5]
Morphology
The flattened, ovoid body of cheloniellid comprises an eye-bearing cephalon (head) and segmented trunk region, dorsally divided by a series of tergites (dorsal exoskeleton). The cephalon could be divided into procephalon and gnathocephalon.[3] Compared to other members of Artiopoda, the head shield (dorsal exoskeleton of cephalon) of cheloniellid is relatively reduced.[3][4] The trunk is wider than the cephalon and is made up of 8-13 tergites.[3] The pleural (lateral) tips of first few tergites are directed anterolaterally, becoming increasingly posterolaterally directed rearward, giving the segmental boundaries between tergites a radiated appearance.[4][3] The last trunk segment, also known as postabdomen,[1] is tiny and laterally encompassed by the pleural regions of previous tergite.[3]

-
Reconstruction of Cheloniellon calmani, showing dorsal morphology and partially ventral appendages.
-
Ventral structures of the anterior region of Cheloniellon calmani, showing differentiation between appendages.
Based on available materials, the cephalon comprises a pair of antennae and 5 pairs of uniramus appendages, with the posterior 4 pairs bore gnathobases.[6] There are evidences that the non-gnathobasic second cephalic appendages are specialized or even raptorial in some species.[6][3] Each of the trunk segments (except the last one) has a pair of biramous appendages each consisting of a leg-like endopod and a shorter exopod.[3] The last trunk segment has a pair of spine/whip-like appendages referred as furcae[4] or cerci,[6] some species bore a medial spine between it which may or may not be a telson.[3]
Classification
Phylogenetic position

While Boudreaux (1979) regarded Cheloniellida as a class,[8] further studies usually treat Cheloniellida as an order.[2][3] Cheloniellida has a controversial phylogenetic position within arthropod higher classifications, with studies mainly around 20th century suggested it as a relative/member of either Crustacea, Trilobita, Chelicerata or Aglaspidida.[3] Some species even had been misidentified as polyplacophoran mollusks (chiton) when being first described.[9] Originally, the iconic cheloniellid Cheloniellon was believed to be a crustacean similar to trilobites.[10][11] Subsequent authors suggests that it occupied a position intermediate between trilobitomorphs and chelicerates[6][7], while some also interpreted it as a sister group of crustaceans[12] or chelicerates[13][14] as well. The suggested close relationship between cheloniellids and chelicerates was inferred by the gnathobasic appendages similar to those of merostomes (e.g. Xiphosurans and Eurypterids), and the hypothesis that the chelicerates arose from trilobitomorphs through the loss of deutocerebral antennae (i.e. first antennae) and specialization of tritocerebral appendages into chelicerae (comparable to the cheloniellid antennae and specialized 2nd appendages),[6][7] a scenario which is not supported by gene expression,[15][16][17][18][19] neuroanatomical[20][21] and developmental[22] evidences (suggests that chelicerae are in fact deutocerebral).
| Summarized phylogeny of Artiopoda with focus on Cheloniellida, based on Lerosey-Aubril et al. (2017).[1] |
As of 21th century, Cheloniellida was mostly found to be form a clade with Aglaspidida and Xenopoda (e.g. Sidneyia and Emeraldella).[23][4][24][25][1] The clade was formally named Vicissicaudata in 2013,[4] united by a differentiated terminal trunk area (postabdomen) that bears a pair of non-leg-like appendages.[4][1] Numerous phylogenetic analysis also retrieved Vicissicaudata within Artiopoda,[1] a diverse arthropod taxon comprise of trilobites and similar fossil taxa that may[26][24] or may not[4][25][1] closely related to chelicerates.
Included genera and species
- Cheloniellon Broili, 1932
- Cheloniellon calmani Broili, 1932—Lower Devonian, Germany
- Duslia Jahn, 1893
- Duslia insignis Jahn, 1893—Upper Ordovician, Czech Republic, Morocco
- Eoduslia Vidal, 1998
- Eoduslia brahimtahiri Vidal, 1998—Upper Ordovician, Morocco
- Neostrabops Caster & Macke, 1952
- Neostrabops martini Caster & Macke, 1952—Upper Ordovician, United States
- Paraduslia Dunlop, 2002
- Paraduslia talimaae Dunlop, 2002—Lower Devonian, Russia
- Pseudarthron Selden & White, 1984
- Pseudarthron whittingtoni Selden & White, 1984—Upper Silurian
- Triopus Barrande, 1872
- Triopus drabowiensis Barrande, 1872—Upper Ordovician, Czech Republic, Morocco
- Xus Wendruff, Babcock, Mikulic & Kluessendorf, 2018
- Xus yus Wendruff, Babcock, Mikulic & Kluessendorf, 2018—Silurian, Wisconsin[3]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i Lerosey-Aubril, Rudy; Zhu, Xuejian; Ortega-Hernández, Javier (2017-09-11). "The Vicissicaudata revisited – insights from a new aglaspidid arthropod with caudal appendages from the Furongian of China". Scientific Reports. 7 (1): 1–18. doi:10.1038/s41598-017-11610-5. ISSN 2045-2322.
- ^ a b Hou, Xianguang. (1997). Arthropods of the Lower Cambrian Chengjiang fauna, southwest China (PDF). Bergström, Jan, 1938-. Oslo: Scandinavian University Press. ISBN 82-00-37693-1. OCLC 38305908.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n Wendruff, Andrew James, et al. "New cheloniellid arthropod with large raptorial appendages from the Silurian of Wisconsin, USA." BioRxiv (2018): 407379. [1]
- ^ a b c d e f g h Ortega-Hernández, Javier; Legg, David A.; Braddy, Simon J. (February 2013). "The phylogeny of aglaspidid arthropods and the internal relationships within Artiopoda". Cladistics. 29 (1): 15–45. doi:10.1111/j.1096-0031.2012.00413.x.
- ^ Du, Kun‐sheng; Ortega‐Hernández, Javier; Yang, Jie; Zhang, Xi‐guang (2019). "A soft‐bodied euarthropod from the early Cambrian Xiaoshiba Lagerstätte of China supports a new clade of basal artiopodans with dorsal ecdysial sutures". Cladistics. 35 (3): 269–281. doi:10.1111/cla.12344. ISSN 0748-3007.
- ^ a b c d e f Stürmer, Wilhelm; Bergström, Jan (1978). "The arthropod Cheloniellon from the devonian hunsrück shale". Paläontologische Zeitschrift. 52 (1): 57–81. doi:10.1007/BF03006730.
- ^ a b c STfJRMER, W. t~ BERGSTROM, J. 1981. Weinbergina, a xiphosuran arthropod from the Devonian Hunsriick Slate. - Palaontologische Zeitschrift 55: 237-255.[2]
- ^ Boudreaux H. B., 1979. Significance of intersegmental tendon system in arthropod phylogeny and monophyletic classification of Arthropoda. pp. 551-586. In.: Gupta A.P. [Ed.]. Arthropod Phylogeny. Van Nostrand Reinhold Company, N.Y., 1-762
- ^ Chlupác I. The enigmatic arthropod Duslia from the Ordovician of Czechoslovakia. Palaeontol. 1988; 31:611–620.[3]
- ^ BROILI, F. (1932): Ein neuer Crustacee aus dem rheinischen Unterdevon. -- Sitzungsber. bayer. Akad. Wiss.: 27--38; Miinchen.[4]
- ^ BROILI, F. (1933): Ein zweites Exemplar von Cheloniellon. -- Sitzungsber. bayer. Akad. Wiss.: 11--32; Miinchen.[5]
- ^ Delle Cave, L. and A.M. Simonetta (1991) Early Palaeozoic arthropods and problems of arthropod phylogeny; with some notes on taxa of doubtful affinities. In The Early Evolution of Metazoa and the Significance of Problematic Taxa, eds. A. M. Simonetta and S. Conway Morris. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, England. Vol. 189–244.
- ^ Wills, M. A., Briggs, D. E. G., Fortey, R. A. & Wilkinson, M. 1995. The significance of fossils in understanding arthropod evolution. Verhandlungen der deutschen zoologischen Gesselschaft 88, 203–15.
- ^ Dunlop, J. A.; Selden, P. A. (1998), Fortey, R. A.; Thomas, R. H. (eds.), "The early history and phylogeny of the chelicerates", Arthropod Relationships, The Systematics Association Special Volume Series, Dordrecht: Springer Netherlands, pp. 221–235, doi:10.1007/978-94-011-4904-4_17, ISBN 978-94-011-4904-4, retrieved 2020-06-18
- ^ Telford, Maximilian J.; Thomas, Richard H. (1998-09-01). "Expression of homeobox genes shows chelicerate arthropods retain their deutocerebral segment". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 95 (18): 10671–10675. ISSN 0027-8424. PMID 9724762.
- ^ Damen, Wim G. M. (2002-03-01). "Parasegmental organization of the spider embryo implies that the parasegment is an evolutionary conserved entity in arthropod embryogenesis". Development. 129 (5): 1239–1250. ISSN 0950-1991. PMID 11874919.
- ^ Jager, Muriel; Murienne, Jérôme; Clabaut, Céline; Deutsch, Jean; Guyader, Hervé Le; Manuel, Michaël (2006). "Homology of arthropod anterior appendages revealed by Hox gene expression in a sea spider". Nature. 441 (7092): 506–508. doi:10.1038/nature04591. ISSN 1476-4687.
- ^ Manuel, Michaël; Jager, Muriel; Murienne, Jérôme; Clabaut, Céline; Guyader, Hervé Le (2006-07-01). "Hox genes in sea spiders (Pycnogonida) and the homology of arthropod head segments". Development Genes and Evolution. 216 (7): 481–491. doi:10.1007/s00427-006-0095-2. ISSN 1432-041X.
- ^ Brenneis, Georg; Ungerer, Petra; Scholtz, Gerhard (2008). "The chelifores of sea spiders (Arthropoda, Pycnogonida) are the appendages of the deutocerebral segment". Evolution & Development. 10 (6): 717–724. doi:10.1111/j.1525-142X.2008.00285.x. ISSN 1525-142X. PMID 19021742.
- ^ Mittmann, Beate; Scholtz, Gerhard (2003-02-01). "Development of the nervous system in the "head" of Limulus polyphemus (Chelicerata: Xiphosura): morphological evidence for a correspondence between the segments of the chelicerae and of the (first) antennae of Mandibulata". Development Genes and Evolution. 213 (1): 9–17. doi:10.1007/s00427-002-0285-5. ISSN 1432-041X.
- ^ Harzsch, Steffen; Wildt, Miriam; Battelle, Barbara; Waloszek, Dieter (2005-07-01). "Immunohistochemical localization of neurotransmitters in the nervous system of larval Limulus polyphemus (Chelicerata, Xiphosura): evidence for a conserved protocerebral architecture in Euarthropoda". Arthropod Structure & Development. Arthropod Brain Morphology and Evolution. 34 (3): 327–342. doi:10.1016/j.asd.2005.01.006. ISSN 1467-8039.
- ^ Mittmann, Beate; Scholtz, Gerhard (2003-02-01). "Development of the nervous system in the "head" of Limulus polyphemus (Chelicerata: Xiphosura): morphological evidence for a correspondence between the segments of the chelicerae and of the (first) antennae of Mandibulata". Development Genes and Evolution. 213 (1): 9–17. doi:10.1007/s00427-002-0285-5. ISSN 1432-041X.
- ^ Edgecombe, Gregory D.; García-Bellido, Diego C.; Paterson, John R. (2011). "A New Leanchoiliid Megacheiran Arthropod from the Lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale, South Australia". Acta Palaeontologica Polonica. 56 (2): 385–400. doi:10.4202/app.2010.0080. ISSN 0567-7920.
- ^ a b Legg, David A. (2014). "Sanctacaris uncata: the oldest chelicerate (Arthropoda)". Naturwissenschaften. 101 (12): 1065–1073. doi:10.1007/s00114-014-1245-4. ISSN 0028-1042.
- ^ a b Edgecombe, Gregory D.; Paterson, John R.; García-Bellido, Diego C. (2017). "A new aglaspidid-like euarthropod from the lower Cambrian Emu Bay Shale of South Australia". Geological Magazine. 154 (1): 87–95. doi:10.1017/S0016756815001053. ISSN 0016-7568.
- ^ Legg, David A.; Sutton, Mark D.; Edgecombe, Gregory D. (2013). "Arthropod fossil data increase congruence of morphological and molecular phylogenies". Nature Communications. 4: 2485. doi:10.1038/ncomms3485. ISSN 2041-1723. PMID 24077329.
- Boudreaux, H. Bruce (1979). Arthropod phylogeny with special reference to insects. John Wiley & Sons. ISBN 978-0471042907.
- Budd, Graham E. (1997). "Stem Group Arthropods from the Lower Cambrian Sirius Passet Fauna of North Greenland". In Fortey, Richard A. (ed.). Arthropod Relationships. Systematics Association Special Volume Series 55. Richard H. Thomas. Springer. ISBN 978-0412754203.
- Dunlop, Jason A.; Selden, Paul A. (1997). "The early history and phylogeny of the chelicerates". In Fortey, Richard A. (ed.). Arthropod Relationships. Systematics Association Special Volume Series 55. Richard H. Thomas. Springer. pp. 237–245. ISBN 978-0412754203.
- Hou Xianguang; Bergström, Jan (2006). Arthropods of the Lower Cambrian Chengliang fauna, southwest China. Fossils & Strata Monograph Series. Wiley-Blackwell. ISBN 978-8200376934.