Google Earth
| File:Google Earth.svg | |
| File:GoogleEarth-Ubuntu Linux.png Screenshot of Google Earth 5.0 in Ubuntu | |
| Original author(s) | Keyhole, Inc. |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | |
| Initial release | June 28, 2005 (as Google Earth) circa 2001 (as EarthViewer 3D) |
| Stable release | 5.1.7894.7252
/ January 12, 2010 |
| Preview release | None
|
| Operating system | Android, Windows 2000, XP, Vista, 7, Mac OS X, Blackberry Storm, iPhone OS and Linux |
| Size | Windows - 11.6 MB; iPhone - 8.9 MB; Linux - 24 MB; Mac - 35 MB |
| Available in | 41 languages, see the full list |
| Type | Virtual globe |
| License | Freeware/Proprietary |
| Website | http://earth.google.com/ |
Google Earth is a virtual globe, map and geographic information program that was originally called EarthViewer 3D, and was created by Keyhole, Inc, a company acquired by Google in 2004. It maps the Earth by the superimposition of images obtained from satellite imagery, aerial photography and GIS 3D globe. It is available under three different licenses: Google Earth, a free version with limited functionality; Google Earth Plus (discontinued)[1][2], which included additional features; and Google Earth Pro ($400 per year), which is intended for commercial use.[3]
The product, re-released as Google Earth in 2005, is currently available for use on personal computers running Windows 2000 and above, Mac OS X 10.3.9 and above, Linux Kernel: 2.4 or later (released on June 12, 2006), and FreeBSD. Google Earth is also available as a browser plugin which was released on May 28, 2008[4]. It was also made available on the iPhone OS on October 27, 2008, as a free download from the App Store. In addition to releasing an updated Keyhole based client, Google also added the imagery from the Earth database to their web based mapping software. The release of Google Earth in June 2005 to the public caused a more than tenfold increase in media coverage on virtual globes between 2005 and 2006,[5] driving public interest in geospatial technologies and applications.
Overview
Google Earth displays satellite images of varying resolution of the Earth's surface, allowing users to see things like cities and houses looking perpendicularly down or at an oblique angle, with perspective (see also bird's eye view). The degree of resolution available is based somewhat on the points of interest and popularity, but most land (except for some islands) is covered in at least 15 meters of resolution.[6] Melbourne, Victoria, Australia; Las Vegas, Nevada; and Cambridge, Cambridgeshire include examples of the highest resolution, at 15 cm (6 inches). Google Earth allows users to search for addresses for some countries, enter coordinates, or simply use the mouse to browse to a location.
For large parts of the surface of the Earth only 2D images are available, from almost vertical photography. Viewing this from an oblique angle, there is perspective in the sense that objects which are horizontally far away are seen smaller, but of course it is like viewing a large photograph, not quite like a 3D view.
For other parts of the surface of the Earth 3D images of terrain and buildings are available. Google Earth uses digital elevation model (DEM) data collected by NASA's Shuttle Radar Topography Mission (SRTM).[7] This means one can view the Grand Canyon or Mount Everest in three dimensions, instead of 2D like other areas. Since November 2006, the 3D views of many mountains, including Mount Everest, have been improved by the use of supplementary DEM data to fill the gaps in SRTM coverage.[8]
Many people use the applications to add their own data, making them available through various sources, such as the Bulletin Board Systems (BBS) or blogs mentioned in the link section below. Google Earth is able to show all kinds of images overlaid on the surface of the earth and is also a Web Map Service client. Google Earth supports managing three-dimensional Geospatial data through Keyhole Markup Language (KML).
Google Earth has the capability to show a 3D buildings and structures (such as bridges), which consist of users' submissions using SketchUp, a 3D modeling program. In prior versions of Google Earth (before Version 4), 3D buildings were limited to a few cities, and had poorer rendering with no textures. Many buildings and structures from around the world now have detailed 3D structures; including (but not limited to) those in the United States, Canada, Ireland, India, Japan, United Kingdom,[9] Germany, Pakistan and the cities, Amsterdam and Alexandria.[10] In August 2007, Hamburg became the first city entirely shown in 3D, including textures such as façades. The Irish town of Westport was added to Google Earth in 3D on January 16, 2008. The 'Westport3D' model was created by 3D imaging firm AM3TD using long-distance laser scanning technology and digital photography and is the first such model of an Irish town to be created. As it was developed initially to aid Local Government in carrying out their town planning functions it includes the highest resolution photo-realistic textures to be found anywhere in Google Earth. Three-dimensional renderings are available for certain buildings and structures around the world via Google's 3D Warehouse[11] and other websites.
Recently, Google added a feature that allows users to monitor traffic speeds at loops located every 200 yards in real-time. In version 4.3 released on April 15, 2008, Google Street View was fully integrated into the program allowing the program to provide an on the street level view in many locations.
On January 17, 2009, the entirety of Google Earth's ocean floor imagery was updated to new images by SIO, NOAA, US Navy, NGA, and GEBCO. The new images have caused smaller islands, such as some atolls in the Maldives, to be rendered invisible despite their shores being completely outlined.[12]
Languages
Since version 5.0 Google Earth is available in 37 languages (four of which in two variants):
Uses
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (January 2010) |
In addition to obvious uses, Google Earth is useful for many day-to-day and other purposes.
- Before climbing onto the roof of a building or other relatively inaccessible high place, it can be checked visually with good enough resolution to make out most features.
...
- Google Earth can be used to view areas subjected to wide-spread disasters if Google supply up-to-date images. For example after the 12 January 2010 Haiti earthquake images of Haiti were made available on 17 January.
Features
Wikipedia and Panoramio integration
In December 2006 Google Earth added a new layer called "Geographic Web" that includes integration with Wikipedia and Panoramio. In Wikipedia, entries are scraped for coordinates via the Coord templates. There is also a community-layer from the project Wikipedia-World. More coordinates are used, different types are in the display and different languages are supported than the built-in Wikipedia layer. See: *dynamic resp. static layer. Google announced on May 30, 2007 that it is acquiring Panoramio.[13]
Flight simulator

Since Google Earth v4.2, a flight simulator has been included as a hidden feature. Depending on the system, it can be accessed by pressing Control+Alt+A, Control+A, or Command+Option+A. After this feature has been activated at least once it appears under the tools menu. Since v4.3 the option is no longer hidden by default. Currently the F-16 Fighting Falcon and the Cirrus SR-22 are the only aircraft that can be used, in addition to a few airports.[14] It is also possible to control the simulator with a mouse or joystick, although not all models are currently supported.
The Google Earth flight simulator features the ability to fly to any supported locations of the world. The pilot can choose any location to start a flight or attempt to land a flight in the world. Fly time is not very accelerated, as it takes the F-16 at highest speed at least 60 minutes to fly from coast-to-coast in the US. Aircraft can land on any level surface in the world (including under the ocean in Google Earth 5.0) as long as the aircraft is below 250 knots and is falling at less than 610 m (2,000 ft) per minute when touching ground.
Featured planes
- F-16 Fighting Falcon – A much higher speed and maximum altitude than the Cirrus SR-22, it has the ability to fly at speeds of almost 1,300 knots near ground level.[citation needed]
- Cirrus SR-22 – Although slower and with a lower maximum altitude, the SR-22 is much easier to handle and is preferred for up-close viewing of Google Earth's imagery.
Sky mode
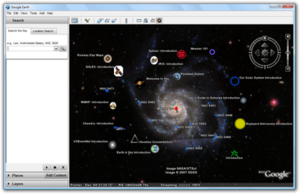
Google Sky is a feature that was introduced in Google Earth 4.2 on August 22, 2007, and allows users to view stars and other celestial bodies.[15] It was produced by Google through a partnership with the Space Telescope Science Institute (STScI) in Baltimore, the science operations center for the Hubble Space Telescope. Dr. Alberto Conti and his co-developer Dr. Carol Christian of STScI plan to add the public images from 2007,[16] as well as color images of all of the archived data from Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys. Newly released Hubble pictures will be added to the Google Sky program as soon as they are issued. New features such as multi-wavelength data, positions of major satellites and their orbits as well as educational resources will be provided to the Google Earth community and also through Christian and Conti's website for Sky. Also visible on Sky mode are constellations, stars, galaxies and animations depicting the planets in their orbits. A real-time Google Sky mashup of recent astronomical transients, using the VOEvent protocol, is being provided by the VOEventNet collaboration. Google's Earth maps are being updated each 5 minutes.
Google Sky faces competition[17] from Microsoft WorldWide Telescope (which runs only under the Microsoft Windows operating systems) and from Stellarium (computer program), a free open source planetarium that runs under Microsoft Windows, Mac OS X, and Linux.
On March 13, 2008, Google made a web-based version of Google Sky available at http://www.google.com/sky/.
Street View
On April 15, 2008 with version 4.3, Google fully integrated its Street View into Google Earth.
Google Street View provides 360° panoramic street-level views and allows users to view parts of selected cities and their surrounding metropolitan areas at ground level. When it was launched on May 25, 2007 for Google Maps, only five cities were included. It has since expanded to more than 40 U.S. cities, and includes the suburbs of many, and in some cases, other nearby cities. Recent updates have now implemented Street View in most of the major cities of Australia and New Zealand as well as parts of Canada, Mexico, Japan, Spain, France, the UK, the Netherlands, Italy, Switzerland, Portugal, Taiwan and Singapore.
Google Street View, when operated, displays photos that were previously taken by a camera mounted on an automobile, and can be navigated by using the mouse to click on photograph icons displayed on the screen in your direction of travel. Using these devices, the photos can be viewed in different sizes, from any direction, and from a variety of angles.
Ocean
Introduced in version 5.0 (February 2009), the Google Ocean feature allows users to zoom below the surface of the ocean and view the 3D bathymetry beneath the waves. Supporting over 20 content layers, it contains information from leading scientists and oceanographers.[18] On April 14, 2009, Google added underwater terrain data for the Great Lakes.[19]
Historical Imagery
Introduced in version 5.0, Historical Imagery allows users to traverse back in time and study earlier stages of any place. This feature is very useful for research purposes that require analysis of past records of various places.[20]
Mars
Google Earth 5 includes a separate globe of the planet Mars, that can be viewed and analysed for research purposes. The maps are of a much higher resolution than those on the browser version of Google Mars and it also includes 3D renderings of the Martian terrain. There are also some extremely high resolution images from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter's HiRISE camera that are of a similar resolution to those of the cities on Earth. Finally, there are many high resolution panoramic images from various Mars landers, such as the Mars Exploration Rovers, Spirit and Opportunity, that can be viewed in a similar way to Google Street View. Interestingly enough, layers on Google Earth (such as World Population Density) can also be applied to Mars. Layers of Mars can also be applied onto Earth. Mars also has a small application found near the face on Mars. It is called Meliza, and features a chat between you and an automatic robot speaker. It is useful for research on Mars, but is not recommended for normal conversations.
Moon

On July 20, 2009, the 40th anniversary of the Apollo 11 mission, Google introduced the Google Earth version of Google Moon[21], which allows users to view satellite images of the Moon. It was announced and demonstrated to a group of invited guests by Google along with Buzz Aldrin at the Newseum in Washington, D.C..[22][23]
Influences
The Google Earth interface bears a noted similarity to the ‘Earth’ program described in Neal Stephenson's sci-fi classic Snow Crash. Indeed, a Google Earth co-founder claimed that Google Earth was modeled after Snow Crash,[24] while another co-founder said it was inspired by the short science education film Powers of Ten.[25] In fact Google Earth was at least partly inspired by a Silicon Graphics demo called "From Space to in Your Face" which zoomed from space into the Swiss Alps then into the Matterhorn[26]. This launch demo was hosted by an Onyx 3000 with InfiniteReality4[27] graphics, which supported Clip Mapping and was inspired by the hardware texture paging capability (although it did not use the Clip Mapping) and "Powers of Ten". The first Google Earth implementation called Earth Viewer emerged from Intrinsic Graphics as a demonstration of Chris Tanner's software based implementation of a Clip Mapping texture paging system and was spun off as Keyhole Inc. Earth Viewer was the inevitable ultimate realization of the capabilities of a seamless texture paging system and many of the individuals working on Earth Viewer were Silicon Graphics alumni.
Technical specifications
Detailed release notes/history/changelog are made available by Google.[28]
Imagery and coordination
- Coordinate System and Projection
- The internal coordinate system of Google Earth is geographic coordinates (latitude/longitude) on the World Geodetic System of 1984 (WGS84) datum.
- Google Earth shows the earth as it looks from an elevated platform such as an airplane or orbiting satellite. The projection used to achieve this effect is called the General Perspective. This is similar to the Orthographic projection, except that the point of perspective is a finite (near earth) distance rather than an infinite (deep space) distance.
- Baseline resolutions
- Czech Republic: 0.1 - 0.5 m (by Eurosense / Geodis Brno)
- Slovakia: 0.5 m (by Eurosense / Geodis Slovakia)
- Hungary: 2.5 m SPOT Images. Budapest approx. 0,3 m.
- Germany, Switzerland, Netherlands, Denmark, U.K., Andorra, Luxembourg, Liechtenstein, San Marino, Vatican City: 1 m or better
- Balkans: 2.5 m (medium resolution)
- U.S.: 1 m (excludes Alaska & Hawaii)
- Global: Generally 15 m (some areas, such as Antarctica, are in extremely low resolution), but this depends on the quality of the satellite/aerial photograph uploaded.
- Typical high resolutions
- Altitude resolution:
- Surface: varies by country
- Seabed: Not previously applicable, but since the introduction of "Ocean", elevation data has been introduced (a colorscale approximating sea floor depth is "printed" on the spherical surface at views from high altitudes).
- Age: Images dates vary. The image data can be seen from squares made when DigitalGlobe Coverage is enabled. The date next to the copyright information is not the correct image date. Zooming in or out could change the date of the pictures. Most of the international urban image dates are from 2004 and have not been updated. However, most US images are kept current. Google announces imagery updates on their LatLong Blog[29] in form of a quiz, with hints of the updated locations. The answers are posted some days later in the same blog.
Hardware and software
Google Earth is unlikely to operate on older hardware configurations. The most recent system requirements update document these minimum configurations:
- Pentium 3, 500MHz
- 256 Megabytes of RAM
- 400 MB free disk space
- Network speed: 128 kbit/s
- 16MB 3D-capable graphics card
- Resolution of 1024x768, 16-bit High Color
- Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Linux or Mac OS X
The most likely mode of failure is insufficient video RAM: the software is designed to warn the user if their graphics card is not able to support Earth (this often occurs due to insufficient Video RAM or buggy graphics card drivers). The next most likely mode of failure is Internet access speed. Except for the very patient, broadband Internet (Cable, DSL, T1, etc.) is required.
Linux Specifications
- Minimum System Requirements[30]
- Kernel: 2.4 or later
- CPU: Pentium III, 500 MHz
- System Memory (RAM): 128 MB
- Hard Disk: 400 MB free space
- Network Speed: 128 kbit/s
- Screen: 1024x768, 16 bit color
- Tested and works on the following distributions:
|
Web browsing
As of Google Earth 5, the contents of description balloons, which are created in KML using JavaScript and iFrames, are rendered with an embedded WebKit engine[31].
Versions and variations
Release timeline

- Keyhole Earthviewer 1.0 - June 11, 2001
- Keyhole Earthviewer 1.4 - 2002
- Keyhole Earthviewer 1.6 - February 2003
- Keyhole LT 1.7.1 - August 26, 2003
- Keyhole NV 1.7.2 - October 16, 2003
- Keyhole 2.2 - August 19, 2004
- Google Earth 3.0 - June 28, 2005
- Google Earth 4.0 - June 11, 2006
- Google Earth 4.1 - May 9, 2007
- Google Earth 4.2 - August 23, 2007
- Google Earth 4.3 - April 15, 2008
- Google Earth 5.0 - May 5, 2009
- Google Earth 5.1 - November 18, 2009
Mac version
A version for Mac OS X was released on January 10, 2006, and is available for download from the Google Earth website. With a few exceptions noted below, the Mac version appears to be stable and complete, with virtually all the same functionality as the original Windows version.
Screenshots and an actual binary of the Mac version had been leaked to the Internet on December 8, 2005. The leaked version was significantly incomplete. Among other things, neither the Help menu nor its "Display License" feature worked, indicating that this version was intended for Google's internal use only. Google released no statement regarding the leak.
The Mac version runs only under Mac OS X version 10.4 or later. There is no embedded browser, no direct interface to Gmail and no full screen option. As of January 2009 there are a few bugs concerning the menu bar when switching between applications and a few bugs concerning annotation balloons and printing.
From version 4.1.7076.4558 (released on May 9, 2007) onward Mac OS X users can, among other new features, upgrade to the "Plus" version via an option in the Google Earth menu.[32] Some users reported difficulties with Google Earth crashing in the then current version when zooming in.[33]
Linux version
Starting with the version 4 beta Google Earth functions under Linux, as a native port using the Qt-toolkit. It is proprietary software specifically in order to impose Digital Rights Management[citation needed]; the Free Software Foundation consider the development of a free compatible client for Google Earth to be a High Priority Free Software Project.[34]
iPhone OS version
A version for the iPhone OS, which runs both the iPhone and iPod Touch, was released for free on the App Store on October 27, 2008.[35][36] It makes use of the multi-touch interface to move on the globe, zoom or rotate the view, and allow to select the current location using the iPhone integrated Assisted GPS. This version, however, does not feature layers like computer versions do. Like Google Maps, it only integrates the Wikipedia and Panoramio layers.[37]
Google Earth Plus
Discontinued in December 2008, Google Earth Plus was an individual-oriented paid subscription upgrade to Google Earth that provided customers with the following features, most of which are now available in the free Google Earth:
- GPS integration: read tracks and waypoints from a GPS device. A variety of third party applications have been created which provide this functionality using the basic version of Google Earth by generating KML or KMZ files based on user-specified or user-recorded waypoints. However, Google Earth Plus provides direct support for the Magellan and Garmin product lines, which together hold a large share of the GPS market. The Linux version of the Google Earth Plus application does not include any GPS functionality.
- Higher resolution printing.
- Customer support via email.
- Data importer: read address points from CSV files; limited to 100 points/addresses. A feature allowing path and polygon annotations, which can be exported to KML, was formerly only available to Plus users, but was made free in version 4.0.2416.
- Higher data download speeds
Google Earth Pro
For a $400 annual subscription fee, Google Earth Pro is a business-oriented upgrade to Google Earth that has more features than the Plus version. The Pro version includes add-on software such as:
- Movie making.
- GIS data importer.
- Advanced printing modules.
Originally, these features cost extra in addition to the $400 fee, but more recently have been included in the package.
Unlike the free version of Google Earth, the professional version does not work on Linux.
Google Earth Enterprise
Google Earth Enterprise is a version of Google Earth designed for use by organizations whose business could take advantage of the program's capabilities.[38]
Portable version
This section needs expansion. You can help by adding to it. (March 2009) |
A portable version of Google Earth, made with VMware ThinApp is available.[39]. A Portable version for Linux is also available, using the RUNZ format.
An automotive version will be available in 2010 in the new Audi A8. [40]
Google Earth Plug-in
The Google Earth API is a free beta service, available for any web site that is free to consumers. The Plug-in and its JavaScript API allows users to place a version of Google Earth into web pages. The API does not have all the features of the full Google Earth Application but enables sophisticated 3D map applications. to be built.
The Google Earth Plug-in is currently available for the following web browsers and operating systems:
Microsoft Windows (2000, XP, Vista, and 7)
- Google Chrome 1.0+
- Internet Explorer 6.0+
- Firefox 2.0+
- Flock 1.0+
Apple Mac OS X 10.4 and higher (Intel and PowerPC)
- Safari 3.1+
- Firefox 3.0+
To date the plug-in supports the following layers:
- Terrain
- Roads
- Buildings
- Borders
- 3-D Buildings
It also supports 'Sky Mode', 'Photo Overlays', and provides much of the same controls and information bar as the full application.
Resolution and accuracy
Most land areas are covered in satellite imagery with a resolution of about 15 m per pixel. This base imagery is 30m multispectral Landsat which is pansharpened with the 15m [panchromatic] Landsat imagery. However, Google is actively replacing this base imagery with 2.5m SPOTImage imagery and several higher resolution datasets mentioned below. Some population centers are also covered by aircraft imagery (orthophotography) with several pixels per meter. Oceans are covered at a much lower resolution, as are a number of islands; notably, the Isles of Scilly off southwest England, were at a resolution of about 500 m or less, however this has now been addressed.
Google has resolved many inaccuracies in the vector mapping since the original public release of the software, without requiring an update to the program itself. An example of this was the absence from Google Earth's map boundaries of the Nunavut territory in Canada, a territory that had been created on April 1, 1999; this mistake was corrected by one of the data updates in early 2006. Recent updates have also increased the coverage of detailed aerial photography, particularly in certain areas of western and central Europe.
The images are not all taken at the same time, but are generally current to within three years. However with the release of Google Earth 5.0, it has historical images dating back to the 1940s in some spots. Image sets are sometimes not correctly stitched together. Updates to the photographic database can occasionally be noticed when drastic changes take place in the appearance of the landscape, for example Google Earth's incomplete updates of New Orleans following Hurricane Katrina, or when placemarks appear to shift unexpectedly across the Earth's surface. Though the placemarks have not in fact moved, the imagery is composed and stitched differently. Such an update to London's photography in early 2006 created shifts of 15-20 metres in many areas, noticeable because the resolution is so high.
Place name and road detail vary greatly from place to place. They are most accurate in North America, Europe and Australia, but regular mapping updates are improving coverage elsewhere.
Errors sometimes occur due to the technology used to measure the height of terrain; for example, tall buildings in Adelaide, Australia cause one part of the city to be rendered as a small mountain, when it is in fact flat. The height of the Eiffel Tower creates a similar effect in the rendering of Paris. Also, prior to the release of version 5.0 in February 2009, elevations below sea level were presented as sea level, for example: Salton City, California; Death Valley; and the Dead Sea were all listed as 0 m when Salton City is −38 m; Death Valley is −86 m; and the Dead Sea is −420 m.
Where no 3 arc second digital elevation data was available, the three dimensional images covering some areas of high relief are not at all accurate, but most mountain areas are now well mapped. The underlying digital elevation model has been placed 3 arc seconds too far north and up to 3 arc seconds too far west. This means that some steep mountain ridges incorrectly appear to have shadows extending over onto their south facing sides. Some high resolution images have also been misplaced, an example is the image covering Annapurna, which is misplaced by about 12 arc seconds. Elevation data was recently updated to 10-meter (1/3-arc-second) resolution for much of the United States from the previous 30-meter (1-arc-second) resolution.
The "Measure" function shows that the length of equator is about 40,030.24 km, giving an error of −0.112% compared with the actual value of 40,075.02 km Earth; for the meridional circumference, it shows a length of about 39,963.13 km, also giving an error of −0.112% compared with the actual value of 40,007.86 km.
On December 16, 2007, most of Antarctica was updated to a 15 m resolution using imagery from the Landsat Image Mosaic of Australia; (1m resolution images of some parts of Antarctica were added in June 2007); however, the Arctic polar ice cap is completely absent from the current version of Google Earth, as are waves in the oceans. The geographic North Pole is found hovering over the Arctic Ocean and the tiling system produces artifacts near the poles as the tiles become 'infinitely' small and rounding errors accumulate.
Cloud cover and shadows can make it difficult or impossible to see details in some land areas, including the shadow side of mountains.
Controversy/Criticism
The software has been criticized by a number of special interest groups, including national officials, as being an invasion of privacy and even posing a threat to national security. The typical argument is that the software provides information about military or other critical installations that could be used by terrorists. The following is a selection of such concerns:
- Former Indian president APJ Abdul Kalam expressed concern over the availability of high-resolution pictures of sensitive locations in India.[41] Google subsequently agreed to censor such sites.[42]
- The Indian Space Research Organisation said Google Earth poses a security threat to India, and seeks dialogue with Google officials.[43]
- Google marks all the northern Indian borders in red color including those that are not disputed. Northern borders of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand that are never discussed in border disputes with China are marked red.
- The South Korean government expressed concern that the software offers images of the presidential palace and various military installations that could possibly be used by their hostile neighbor North Korea.[44]
- In 2006, one user spotted a large topographical replica in a remote region of China. The model is a small-scale (1/500) version of the Karakoram Mountain Range, currently under the control of China but claimed by India. When later confirmed as a replica of this region, spectators began entertaining military implications.[45][46]
- Morocco's main Internet provider Maroc Telecom has been blocking Google Earth[47] since August 2006 for undisclosed reasons.
- Operators of the Lucas Heights nuclear reactor in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia asked Google to censor high resolution pictures of the facility.[48] However, they later withdrew the request.[49]
- In July 2007, it was reported that a new Chinese navy Jin-class nuclear ballistic missile submarine was photographed at the Xiaopingdao Submarine Base south of Dalian.[50]
- Hamas and the al-Aqsa Martyrs' Brigades have reportedly used Google Earth to plan Qassam rocket attacks on Israel from Gaza (See: List of Qassam rocket attacks.)[51][52]
- The lone surviving gunman involved in the 2008 Mumbai attacks admitted to using Google Earth to familiarise themselves with the locations of buildings used in the attacks.[53]
- Michael Finton (Talib Islam) used Google Earth in planning his attempted September 24, 2009, bombing of the Paul Findley Federal Building and the adjacent offices of Congressman Aaron Schock in Springfield, Illinois.[54]

Some citizens may express concerns over aerial information depicting their properties and residences being disseminated freely. As relatively few jurisdictions actually guarantee the individual's right to privacy, as opposed to the state's right to secrecy, this is an evolving, but minor, point. Perhaps aware of these critiques[55], for a time, Google had Area 51 (which is highly visible and easy to find) in Nevada as a default placemark when Google Earth is first installed.
As a result of pressure from the United States government, the residence of the Vice President at Number One Observatory Circle was obscured through pixelization in Google Earth and Google Maps, but has since been lifted. The usefulness of this downgrade is questionable, as high-resolution photos and aerial surveys of the property are readily available on the Internet elsewhere.[56] Capitol Hill used to also be pixelized in this way, but this was lifted.
Critics have expressed concern over the willingness of Google to cripple their dataset to cater to special interests, believing that intentionally obscuring any land goes against its stated goal of letting the user "point and zoom to any place on the planet that you want to explore".[57]
Recent versions of Google Earth software require a running in the background software that will automatically download and install updates. Several users expressed concerns as there is not an easy way to disable that.[58]
Copyright
Currently, every image created from Google Earth using satellite data provided by Google Earth is a copyrighted map. Any derivative from Google Earth is made from copyrighted data which, under United States Copyright Law, may not be used except under the licenses Google provides. Google allows non-commercial personal use of the images (e.g. on a personal website or blog) as long as copyrights and attributions are preserved.[59] By contrast, images created with NASA's globe software World Wind use the Blue Marble, Landsat or USGS layer, each of which is a terrain layer in the public domain. Works created by an agency of the United States government are public domain at the moment of creation. This means that those images can be freely modified, redistributed and used for commercial purposes.
Layers
Google Earth also features many layers as a source for information on businesses and points of interest, as well as showcasing the contents of many communities, such as Wikipedia, Panoramio and YouTube. Google updates with new layers often. Many Google Earth layers, such as Panoramio and Google Earth Community layers, are updated daily with entries from the respective websites.
Geographic Web
- Panoramio: Shows many of the most relevant pictures uploaded onto Panoramio's website
- Places
- Places: A general overview of many notable places around the globe. Some placemarks have been taken from Google Earth Community's featured posts and some Wikipedia articles.[60]
- Preview: Shows short summaries of some of the content in the layers. If a new layer has been added, the preview layer will be turned on as a default the next time it is run.
Roads
Displays available road networks. The colors and signs displayed vary depending on the type of roadway.
- Limited-access freeways and tollways that are part of widespread networks such as the International E-road network, United States Interstate Highways and many other national road networks are represented by orange lines.
- Other freeways are marked with pale orange lines.
- Some roads in Japan are indigo.
- Other important roads, generally those most travelled, highest capacity, or bearing a road number, are labeled with yellow lines.
- All other roads are labeled white.
- Some pedestrian walkways and private roads are signified by transparent white lines, especially when greatly resembling a road intended for public automotive traffic.
3D Buildings
Shows many 3D buildings in major cities, such as New York City or Hong Kong, in these styles:
- Photorealistic: Shows many buildings in a realistic style, with more complex polygons and surface images.
- Gray: Low-detail models of city buildings designed for computers that may not have the capability of showing the photorealistic models.
Google Street View
Shows placemarks with 360 degree panoramic views of streets of many cities in Australia, France, the United Kingdom, Italy, Japan, New Zealand, Spain, the United States, and recently Portugal, The Netherlands, Taiwan, Switzerland, Canada, and Mexico.
Borders and labels
Contains borders for countries/provinces and shows placemarks for cities and towns.
- Borders: Marks international borders with a thick yellow line, 1st level administrative borders (generally provinces and states) with a lavender (color) line, and 2nd level administrative borders (counties) with a cyan line. Coastlines appear as a thin yellow line. Displays names of countries, 1st level administrative areas, and islands.
- Populated Places: Displays labels for cities, towns, villages, census designated places (CDPs), and hamlets.
- Alternate Place Names: Many cities in non-English countries were labeled in their native languages to avoid the need of extensive localization. This layer shows such names in English.
- Labels: Displays labels for large bodies of water, such as oceans, seas, and bays.
Traffic
Displays colored indicators along those roads where real time traffic conditions are measured. Green indicators are used for good traffic conditions, yellow for slower speeds, and red for poor traffic conditions. By clicking on an indicator, the user can see the name of the road and the speed along that road. It is not clear with what frequency the indicators are updated.
Weather
- Clouds - Displays cloud cover based on data from both geostationary and low Earth-orbiting satellites. The clouds appear at their calculated elevation, determined by measuring the cloud top temperature relative to surface temperature.[61]
- Radar - Displays weather radar data provided by weather.com and Weather Services International, updating every 5–6 minutes.[61]
- Conditions and Forecast - Displays local temperatures and weather conditions. Clicking on an indicator displays a full local forecast provided by weather.com.[61]
- Information - Clicking Information allows users to further read up on where Google Earth gets weather information.[61]
Gallery
- Ancient Rome: Launched by Google on November 12, 2008.
- Discovery Networks: Shows geographical information from the Discovery Channel.
- European Space Agency: Shows many satellite images taken of Earth.
- Gigapan Photos: Images from Google's Gigapan project.
- Gigapxl Photos: Photographs taken using Gigapxl.
- Google Book Search: An application of the Google Book search in Google Earth.
- Google Earth Community: A showcase of all file entries in Google Earth Community.
- Google News: Shows news stories from many worldwide news sources.
- NASA: A showcase of many satellite images, overlays and features from NASA.
- National Geographic Magazine: Shows many features from the National Geographic Magazine.
- New York Times: A collection of news stories from the popular New York City newspaper.
- Rumsey Historical Maps: Shows a collection of historic maps, dating back to the 1600s.
- Travel and Tourism
- 100% Pure New Zealand
- Egypt Tourism
- Japan Tourism
- Kyoto Tourism
- South Africa Tourism
- Turn Here: City Video Guides
- Walt Disney World Resort
- Trimble Outdoor Trips: A collection of hiking trails with recordings.
- Volcanoes
- Webcams.travel: A collection of webcams around the world
- YouTube: A collection of popular videos on YouTube.
Ocean
- Explore the Ocean
- National Geographic
- Magazine Quiz
- Ocean Atlas
- BBC Earth
- Cousteau Ocean World
- Ocean Sports
- Surf Spots
- Dive Spots
- Kite Surfing Spots
- Shipwrecks
- Ocean Expeditions
- Marine Protected Area [2]
- ARKive: Endangered Ocean Species
- State of the Ocean
- Animal Tracking
- Census of Marine Life
- Marie Tharp Historical Map
- Underwater Features
Global Awareness
A collection of services spreading global awareness. The layer was provided by Google Earth Outreach.
- Appalachian Mountaintop removal
- ARKive: Endangered species
- Earthwatch Expeditions
- Fair Trade Certified
- Global Heritage Fund
- Greenpeace
- Jane Goodall's Gombe Chimpanzee Blog
- The Earth from Above with Goodplanet
- The Elders: Every Human Has Rights
- UNDP: Millennium Development Goals Monitor
- UNEP: Atlas of our Changing Environment
- Unicef: Water and Sanitation
- USHMM: World is Witness
- USHMM: Crisis in Darfur
- WaterAid
- WWF Conservation Projects
Places of interest
A collection of business listings provided by many local services.
- Bars/Clubs
- Coffee Shops
- Eating Out (Restaurants)
- Lodging
- Banks/ATMs
- Gas stations
- Grocery Stores
- Major Retail
- Movie/DVD Rental
- Pharmacy
- Shopping Malls
- Geographical Features
- Golf
- Parks and Recreation Areas
- Sports Venues
- Skiing (Swiss Alps only)
- Transportation
- Airports
- Railways
- Underground
- Tram
- Bus
- Ferry
- Mountain Rail
- Tourist Spots
- Fire Stations
- Hospitals
- Schools
- Places of Worship
- Churches
- Mosques
- Synagogues
- Temples
- Other Places of Worship
- Cemeteries
Sky Layers
Layers for Google Sky.
- Welcome to Sky: An introduction to the Sky mode.
- Current Sky Events
- Earth & Sky Podcasts
- Hubblecast
- StarDate by the University of Texas
- VOEventNET
- Our Solar System: Shows locations, orbits and information of the Solar System.
- Backyard Astronomy: Shows information about constellations and other space sights visible from a backyard telescope.
- Featured Observatories
- Hubble Showcase
- Spitzer Infrared Showcase
- GALEX Ultraviolet Showcase
- Chandra X-Ray Showcase
- WMAP Microwave Showcase
- IRAS Infrared Sky
- Education Center
- Historical Sky Maps
- Rumsey Star Maps
- Hevelius Constellations
- Sky Community: Posted KML files in the Sky forum in the Google Earth Community.
Mars Layers
- Featured Satellite Images
- Place Names
- Global Maps
- Spacecraft Imagery
- Mars Gallery
- Rovers and Landers
- A Traveler's Guide to Mars
See also
- Google Street View
- Bhuvan
- Bing Maps for Enterprise (previously Microsoft Virtual Earth)
- Marble (KDE)
- Web mapping
- Geoweb
- Orthophotomap
- Oracle Spatial [62]
Image providers
- DigitalGlobe — the provider of high resolution imagery to Google Earth
- EarthSat
- GeoEye-1 (ORBVIEW-3's succesor)
- GlobeXplorer
- IKONOS (ORBVIEW-2 is successor)
- Pictometry
- Spot Image
- TerraLook
- ViewGL - updated aerial imagery for Google Earth
- CNES
References
- ^ "Google Earth Plus Discontinued".
- ^ "Google Discontinues "Google Earth Plus"".
- ^ "Google Earth Product Family". Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ "Google Earth, meet the browser".
- ^ "Media Coverage of Geospatial Platforms". Retrieved 2007-08-05.
- ^ Google Earth Coverage: Maps showing a visual representation of Google Earth coverage
- ^ Farr et al., 2007, The Shuttle Radar Topography Mission, v. 45, Reviews of Geophysics, doi: 1029/2005RG000183. SRTM web site
- ^ "Google Earth Community: Nov. 23rd - Thanksgiving Day imagery update".
- ^ Skyscraper News Google Earth
- ^ infopot.tk
- ^ 3D Warehouse
- ^ http://www.gearthblog.com/blog/archives/2009/01/new_view_of_ocean_floor_in_google_e.html
- ^ "Google is planning to acquire Panoramio". google.com.
- ^ Marco's Blog: Google Earth Flight Simulator
- ^ "Explore the sky with Google Earth". Google. 2007-08-22. Retrieved 2007-08-22.
- ^ Celestial add-on points Google Earth at the stars - tech - August 22, 2007 - New Scientist Tech
- ^ http://crave.cnet.com/8301-1_105-9881229-1.html
- ^ http://news.bbc.co.uk/1/hi/technology/7865407.stm
- ^ "Google Earth now includes US "Third Coast"".
- ^ "Dive into New Google Earth". Retrieved 2009-02-03.
- ^ http://www.gearthblog.com/blog/archives/2009/07/look_at_the_moon_in_google_earth_-.html
- ^ http://www.gearthblog.com/blog/archives/2009/07/google_earth_event_on_july_20th_in.html
- ^ http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2009/07/fly-yourself-to-moon.html
- ^ Web User - Google Earth interview
- ^ Avi Bar-Ze’ev (from Keyhole, the precursor to Google Earth) on origin of Google Earth
- ^ Google Earth: From Space to Your Face…and Beyond
- ^ Infinite Reality Technical Report
- ^ Google Earth Release Notes / Changelog History
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ Google Earth
- ^ KML Reference Documentation - <description>
- ^ "Google Earth 4.2.180.1134 - MacUpdate".
- ^ "Google Earth Community: Viewing forum: Google Earth for Mac OS X".
- ^ [1]:FSF:High Priority Free Software Projects
- ^ Sorrel, Charlie (2008-10-27). "Google Earth Comes to the iPhone". Wired. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ "Google Earth now available for the iPhone". Google Mobile team. 2008-10-27. Retrieved 2008-10-27.
- ^ http://www.gearthblog.com/blog/archives/2008/10/google_earth_for_the_iphone_release.html
- ^ http://earth.google.com/enterprise/earth_enterprise.html
- ^ Portable Applications (Windows)
- ^ http://google-latlong.blogspot.com/2009/12/google-audi-take-google-services-in-car.html
- ^ "Kalam Concerned Over Google Earth". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ ""Google Earth agrees to blur pix of key Indian sites"".
- ^ ""Google Earth Poses Security Threat to India, ISRO Chief seeks Dialogue"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ ""Google Earth images compromise secret installations in S. Korea"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ ""Chinese X-file excites spotters"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ ""From sky, see how China builds model of Indian border 2400 km away"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ Message au monde - Message to the world
- ^ ""Google Earth prompts security fears"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ "" Aussie Nuclear Reactor on Google Earth"". Retrieved 2007-01-25.
- ^ ""New Chinese Ballistic Missile Submarine Spotted"". Retrieved 2007-07-10.
- ^ Google Earth used to target Israel
- ^ Hutcheon, Stephen (2009-01-30). "We're not stalking you or helping terrorists, says Google Earth boss". Sydney Morning Herald. Retrieved 2009-11-07.
- ^ "Mumbai attacks: Indian suit against Google Earth over image use by terrorists", The Daily Telegraph, December 9, 2008.
- ^ Gruen, Madeleine, "Attempt to Attack the Paul Findley Federal Building in Springfield, Illinois," The NEFA Foundation, December 2009, accessed December 18, 2009
- ^ Privacy Lawsuit Against Google Earth, Spatial Law blog, 2008-04-09
- ^ "Eyeballing the US Vice Presidential Residence".
- ^ ""The Creative Reconstruction of the Internet: Google and the Privatization of Cyberspace and DigiPlace"" (PDF).
- ^ ""Why Google's Software Update Tool Is Evil"".
- ^ Google Earth Help Center: Can I post images to the web?
- ^ http://www.gearthblog.com/blog/archives/2008/08/august_geographic_web_layer_update.html
- ^ a b c d Google Earth: Weather layer, information link -- accessed: 03 March 2009 v5.0.11337.1968 (beta)
- ^ Google Earth/SketchUp and Oracle Spatial
External links
Official and related sites
- Official website
- Google LatLong - News and notes by the Google Earth and Maps team
Unofficial guides and tips
- Google's Earth: Tips and Insight for Google Earth users
- Google Earth Blog: Google Earth news and updates
- Google Sightseeing - Guide to interesting and unusual sights
- Ogle Earth - Google Earth news site charting innovative uses and political implications of Google Earth
- Google Earth in Education - A guided tour by a teacher for teachers, students and all.
- Google Earth 2 Mapsource Edit GPS tracks in Mapsource and Google Earth.
Placemarks and overlays
- North Korea Uncovered - An extensive mapping of North Korea's economic, cultural, political, and military infrastructures, featured in the Wall Street Journal.
- Google Earth Hacks - A collection of over 25,000 files for use with Google Earth
- King's College London's Collection of KML databases
- STScI's community contributions to Sky website
- Google Earth Anomalies- Satellite imagery of documented, scientific anomaly sites including mound sites and unexplained circular features via Google Earth
Tools
- GeoServer - Server to generate KML from Shapefiles, ArcSDE, Oracle, PostGIS, MySQL, GeoTiff, ArcGrid, with support for Network links, superoverlays, time and custom pop-ups.
- GPSVisualizer - Will convert GPS data for use in Google Earth.
- GoogleEarthToolbox - Matlab & Octave functions that output KML.
- geolyzer - Software-based usability-lab for Google Earth
