Basketball positions
This article has multiple issues. Please help improve it or discuss these issues on the talk page. (Learn how and when to remove these messages)
No issues specified. Please specify issues, or remove this template. |
The three basketball positions normally employed by organized basketball teams are guard, forward, and center. More specifically, they can be classified into the five positions: point guard, shooting guard, small forward, power forward, and centre. The rules of basketball do not mandate them, and in informal games they are sometimes not used. They are grouped into two conceptual units: the backcourt and frontcourt.
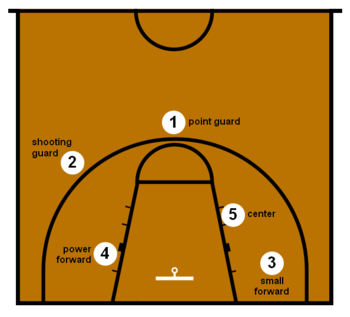
Backcourt (guards)
Point guard
The point guard, also known as the "1", is typically the team's best ball handler and passer.[1] The point guard is a position equivalent to that of a playmaking midfielder in soccer and quarterback in American football, where they are often responsible for directing plays and passing the ball. This lends the player a role similar to a captain, as good point guards increase team efficiency and generally have a high number of assists. Some of the prototypical point guards in the NBA's recent years include Jason Kidd for the Dallas Mavericks and Steve Nash for the Phoenix Suns. Other examples include Chauncey Billups, Rajon Rondo, Chris Paul, Deron Williams, and Derrick Rose. Examples of players earlier in the league's history are Oscar Robertson, Magic Johnson, Bob Cousy, John Stockton, and Gail Goodrich. The point guard is typically the smallest player on his/her squad. At the NBA level, most point guards are 6 feet (1.83 m) to 6 feet 4 inches (1.93 m).
Notable exceptions include Earvin "Magic" Johnson of the Lakers, who was the NBA's tallest point guard ever to play the position, at 6 feet 9 inches (2.06 m), while in modern times the tallest point guards include Tracy McGrady and LeBron James, both at 6 feet 8 inches (2.03 m). Johnson, McGrady and James are examples of point forwards, as players with good ballhandling and typical point guard ability in a forward's body. In comparison, the shortest players include Muggsy Bogues at 5 feet 3 inches (1.60 m) and Earl Boykins at 5 feet 5 inches (1.65 m).
Shooting guard
The shooting guard, also known as the "2", is usually the team's best shooter, and typically is able to consistently hit long range shots (of 20 feet or more). Besides being able to shoot the ball, shooting guards tend to have good ball-handling skills and the ability to drive the ball to the net, often creating their own shots off the dribble. A versatile shooting guard will have good passing skills, allowing them to assume point guard responsibilities.[2] Typical NBA shooting guards are 6 feet 3 inches (1.91 m) to 6 feet 7 inches (2.01 m). However, there are exceptions. For instance, Allen Iverson and Nate Robinson, who both play shooting guard, are only 6 feet (1.83 m) and 5 feet 9 inches (1.75 m) tall respectively and therefore often are required to play point guard.
Kobe Bryant, Dwyane Wade, Manu Ginobili, Brandon Roy and Andre Iguodala are current examples of typical shooting guards in the NBA. Other notable examples include Michael Jordan, Reggie Miller, Richard Hamilton, Ray Allen, Vince Carter, and Jerry West. Shooting guards are typically versatile enough to play small forward and vice versa, in a role called swingman or wing. This is due to the relatively similar playing styles and characteristics, with the only difference being relative size, as small forwards tend to be a little bigger.
Frontcourt (forwards and center)
Small forward
The small forward, also known as the "3", is typically somewhat shorter, quicker and leaner than power forwards and centers. Thus, in the NBA, small forwards range from 6 feet 5 inches (1.96 m) to 6 feet 11 inches (2.11 m). The small forward position is considered to be perhaps the most versatile of the main five basketball positions, due to the nature of its role, which is sometimes similar to that of a power forward, and other times more resembles the role of a shooting guard. The small forward and shooting guard positions are often interchangeable.
Small forwards have a variety of weapons, such as quickness and strength inside. One common thread between all kinds of small forwards is an ability to "get to the line" and draw fouls by aggressively attempting post-up plays, lay-ups, or slam dunks. As such, accurate foul shooting is a common skill for small forwards, many of whom record a large portion of their points from the foul line. Small forwards should be able to do a little bit of everything on the court, typically playing roles such as swingmen but also as point forwards and defensive specialists.[3] Examples include LeBron James, Carmelo Anthony, Paul Pierce, Hedo Türkoğlu, and Kevin Durant. Larry Bird and Scottie Pippen are examples of earlier players in the league's history for this position.
Power forward
Also known as the "4" position and abbreviated as "PF", the power forward plays a role similar to that of the center, down in the "post" or "low blocks". On offense, they can "post up", (playing with their backs to the basket), or set up for mid-range jump shots. On defense, they play under the basket in a zone defense or against the opposing power forward in man-to-man defense.[4] Typical NBA power forwards are 6 feet 8 inches (2.03 m) to 7 feet 0 inches (2.13 m) tall, though some power forwards, like the 6 feet 5 inches (1.96 m) Charles Barkley, have compensated for a lack of height with exceptional bulk, strength, and longer arms. The most renowned power forwards of all time include Bob Pettit, Tim Duncan, Karl Malone, Dennis Rodman, Dirk Nowitzki and Kevin Garnett. Popular All-Star power forwards today include Garnett, Duncan, Amar'e Stoudemire, Pau Gasol, and Chris Bosh. Power forwards with a three-point/long range shooting game are fairly rare, playing what is referred to as the European style of basketball.[5] Dirk Nowitzki, Peja Stojakovic, Kevin Love, and Rashard Lewis specialize in this area. they all suck my big dick
Center
The center, also referred to as the "5" or the "pivot", usually plays near the baseline, close to the basket (referred to as the "bottom of the key" or the "low post"). The tallest player is most likely to be assigned to the position of center, with typical NBA centers being about 7 feet (2.13 m) in height, though Chuck Hayes fills this role at 6 feet 6 inches (1.98 m), and NBA Hall of Famer Wes Unseld filled this role while being 6 feet 7 inches (2.01 m). Few are much taller, like 7 feet 6 inches (2.29 m) Yao Ming. The center usually scores "down low, in the paint" (near the basket, in the key), but some, such as Mehmet Okur, can be good perimeter shooters, which can draw a good rebounding and shot-blocking center away from the basket. Centers contribute to the team by using their physique and skill to score close to the basket, as well as gathering rebounds, contesting shots and setting screens on plays.[6]
While the center position remains a pivotal position, the scope of the position has transitioned from classic 'back to the basket' players such as Tim Duncan, Shaquille O'Neal, and Yao Ming, to power forwards that can dominate the position due to their athletic prowess, defensive skills, or mismatch ability to shoot from the high post, such as Dwight Howard and Amare Stoudemire. This has been matched by the development of fast-paced 'Run and Gun' offenses of coaches such as Mike D'Antoni, calling for less traditional center play, and a more up and down the court style.
Dwight Howard, Brook Lopez, Marc Gasol, JaVale McGee and Joakim Noah are examples of current centers in the NBA, while Wilt Chamberlain, Bill Russell, Kareem Abdul-Jabbar, Shaquille O'Neal, Bill Walton, and Hakeem Olajuwon are considered among the all-time greats at the position.[7]
See also
References
- ^ http://www.basketball-plays-and-tips.com/basketball-positions.html Basketball-Plays-and-Tips Info
- ^ http://www.basketballpositions.org/ Basketballpositions.org
- ^ http://www.basketball-plays-and-tips.com/basketball-positions.html Basketball-Plays-and-Tips Info
- ^ http://www.basketballpositions.org/ Basketballpositions.org
- ^ http://www.collegehoopsnet.com/coaching/EUROS.htm "The European game relies on continuity-type offenses, crisp passing and perimeter shooting."
- ^ http://www.basketball-plays-and-tips.com/basketball-positions.html Basketball-Plays-and-Tips Info
- ^ "The NBA at 50". NBA. Retrieved 2009-06-14.
External links
- "Shooting Guard Tips" from HoopsU.com
- "Point Guard Tips" from HoopsU.com
- "How to Play Basketball Offense – Description of Team Positions" at guidetocoachingbasketball.com
- "Basketball players" at BBC Sport Academy
- "How Basketball Works" at howstuffworks.com
- Basketball Positions Explained at Youth-Basketball-Tips.com
- Basketball Shooting Skills And Shot Position