Mae Jemison
Mae Jemison | |
|---|---|
 Jemison in July 1992 | |
| Born | Mae Carol Jemison October 17, 1956 |
| Status | Retired |
| Nationality | American |
| Occupation(s) | Physician College professor |
| Space career | |
| NASA Astronaut | |
Time in space | 190 h 30 min 23 s |
| Selection | 1987 NASA Group |
| Missions | STS-47 |
Mission insignia | |
Mae Carol Jemison (born October 17, 1956) is an American engineer, physician and NASA astronaut. She became the first black woman to travel in space when she served as an astronaut aboard the Space Shuttle Endeavour. After graduating medical school and a brief general practice, Jemison served in the Peace Corps from 1985 until 1987. In 1987 her application to become an astronaut was accepted by NASA and on September 12, 1992 she was a mission specialist aboard STS-47. In 1993 she resigned from NASA and founded a company researching the application of technology to daily life. She has appeared on television several times, including as an actress in an episode of Star Trek: The Next Generation. She is a dancer and holds nine honorary doctorates in science, engineering, letters, and the humanities. She is the current principal of the 100 Year Starship organization.
Early life
Mae Carol Jemison was born in Decatur, Alabama, on October 17, 1956,[1][2] the youngest child of Charlie Jemison and Dorothy Green. Her father was a maintenance supervisor for a charity organization, and her mother worked most of her career as an elementary school teacher of English and math at the Beethoven School in Chicago.[3][4]
The family moved to Chicago, Illinois, when Jemison was three years old, to take advantage of the better educational and employment opportunities there. Jemison says that as a young girl growing up in Chicago she always assumed she would get into space. "I thought, by now, we'd be going into space like you were going to work."[5] She said it was easier to apply to be a shuttle astronaut, "rather than waiting around in a cornfield, waiting for ET to pick me up or something."[5]

In her childhood, Jemison learned to make connections to science by studying nature. Once when a splinter infected her thumb as a little girl, Jemison's mother turned it into a learning experience. She ended up doing a whole project about pus.[6] Jemison's parents were very supportive of her interest in science, while her teachers were not.[2] "In kindergarten, my teacher asked me what I wanted to be when I grew up, and I told her a scientist," Jemison says. "She said, 'Don't you mean a nurse?' Now, there's nothing wrong with being a nurse, but that's not what I wanted to be."[7] In an interview with Makers, she further explains how her sheer interest in science was not accepted. "Growing up...I was just like every other kid. I loved space, stars and dinosaurs. I always knew I wanted to explore. At the time of the Apollo airing, everybody was thrilled about space, but I remember being irritated that there were no women astronauts. People tried to explain that to me, and I did not buy it."[8]
Jemison says she was inspired by Martin Luther King Jr.; to her King's dream was not an elusive fantasy but a call to action. "Too often people paint him like Santa – smiley and inoffensive," says Jemison. "But when I think of Martin Luther King, I think of attitude, audacity, and bravery."[9] Jemison thinks the civil rights movement was all about breaking down the barriers to human potential. "The best way to make dreams come true is to wake up."[9]
Jemison began dancing at the age of 11.[10] "I love dancing! I took all kinds of dance — African dancing, ballet, jazz, modern — even Japanese dancing. I wanted to become a professional dancer," said Jemison.[11] At the age of 14, she auditioned for the leading role of "Maria" in West Side Story.[12] She did not get the part but Jemison's dancing skills did get her into the line up as a background dancer.[12] "I had a problem with the singing but I danced and acted pretty well enough for them to choose me. I think that people sometimes limit themselves and so rob themselves of the opportunity to realise their dreams. For me, I love the sciences and I also love the arts," says Jemison.[12] "I saw the theatre as an outlet for this passion and so I decided to pursue this dream."[12] Later during her senior year in college, she was trying to decide whether to go to New York to medical school or become a professional dancer. Her mother told her, "You can always dance if you're a doctor, but you can't doctor if you're a dancer."[13]
Jemison graduated from Chicago's Morgan Park High School in 1973[7] and entered Stanford University at the age of 16.[6] "I was naive and stubborn enough that it didn’t faze me," Jemison said.[6] "It’s not until recently that I realized that 16 was particularly young or that there were even any issues associated with my parents having enough confidence in me to [allow me to] go that far away from home."[6] Jemison graduated from Stanford in 1977, receiving a B.S. degree in chemical engineering and fulfilling the requirements for a B.A. degree in African and Afro-American Studies.[1][6] At Stanford, she choreographed a musical and dance production called Out of the Shadows.[14] She took initiative to get even further involved in the black community by serving as head of the Black Students Union in college.[2] Jemison said that majoring in engineering as a black woman was difficult because race was always an issue in the United States.[15] "Some professors would just pretend I wasn't there. I would ask a question and a professor would act as if it was just so dumb, the dumbest question he had ever heard. Then, when a white guy would ask the same question, the professor would say, 'That's a very astute observation.'"[15] In an interview with the Des Moines Register in 2008 Jemison said that it was difficult to go to Stanford at 16, but thinks her youthful arrogance may have helped her.[16] "I did have to say, 'I'm going to do this and I don't give a crap (damn).'" Jemison faced lots of discrimation and stated that it was necessary for women and minorities to have some arrogance in order to be successful in a white male dominated society.[16]
Jemison obtained her M.D. degree in 1981 at Cornell University.[1] She interned at Los Angeles County-USC Medical Center, and in 1982, she worked as a general practitioner.[1] During medical school, Jemison traveled to Cuba, Kenya and Thailand, to provide primary medical care to people living there.[17] During her years at Cornell Medical College, Jemison took lessons in modern dance at the Alvin Ailey school.[10] Jemison later built a dance studio in her home and has choreographed and produced several shows of modern jazz and African dance.[3][13]
Peace Corps
After completing her medical training, Jemison joined the staff of the Peace Corps and served as a Peace Corps Medical Officer from 1983 to 1985 responsible for the health of Peace Corps Volunteers serving in Liberia and Sierra Leone.[18][13] Jemison's work in the Peace Corps included supervising the pharmacy, laboratory, medical staff as well as providing medical care, writing self-care manuals, and developing and implementing guidelines for health and safety issues. Jemison also worked with the Center for Disease Control (CDC) helping with research for various vaccines.[17]
Once while serving as a doctor for the Peace Corps, a volunteer became seriously ill, and a doctor diagnosed malaria. The volunteer's condition progressively worsened, and Jemison diagnosed it as meningitis with life-threatening complications that could not be treated in Sierra Leone. Jemison called for an Air Force hospital plane based in Germany for a military medical evacuation at a cost of $80,000.[13] The embassy questioned whether Jemison had the authority to give such an order, but she told them she did not need anyone's permission for a medical decision. This interaction highlights the doubt women of color like Jemison faced. By the time the plane reached Germany with Jemison and the volunteer on board, she had been up with the patient for 56 hours. The patient survived.[13]
Career

After the flight of Sally Ride in 1983, Jemison felt the astronaut program had opened up, so she applied.[3] Jemison's inspiration for joining NASA was African-American actress Nichelle Nichols, who portrayed Lieutenant Uhura on Star Trek.[6] Jemison's involvement with NASA was delayed after the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster in 1986,[20] but after reapplying in 1987, she received the news of her acceptance into the astronaut program.[2] "I got a call saying 'Are you still interested?' and I said 'Yeah'," recalls Jemison,[21] as one of fifteen candidates chosen out of roughly 2,000 applicants.[2]

Her work with NASA before her shuttle launch included launch support activities at the Kennedy Space Center in Florida and verification of Shuttle computer software in the Shuttle Avionics Integration Laboratory (SAIL).[22][23][24] "I did things like help to support the launch of vehicles at Kennedy Space Center," said Jemison.[21] "I was in the first class of astronauts selected after the Challenger accident back in 1986, ... [I] actually worked the launch of the first flight after the Challenger accident.[21]
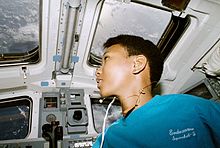
Jemison flew her only space mission from September 12 to 20, 1992, as a Mission Specialist on STS-47,[20] a cooperative mission between the United States and Japan, as well as the 50th shuttle mission.[25] Jemison was a co-investigator of two bone cell research experiments, one of 43 investigations that were done on STS-47. Jemison also conducted experiments on weightlessness and motion sickness on herself and six other crew members. "The first thing I saw from space was Chicago, my hometown," said Jemison. "I was working on the middeck where there aren't many windows, and as we passed over Chicago, the commander called me up to the flight deck. It was such a significant moment because since I was a little girl I had always assumed I would go into space," Jemison added.[13] Despite NASA's rigid protocol, Jemison would begin each shift with a salute that only a Trekkie could appreciate. "Hailing frequencies open," she could be heard repeating throughout the eight-day mission.[26]
Because of her love of dance and as a salute to creativity,[3] Jemison took a poster from the Alvin Ailey American Dance Theater along with her on the flight.[27] "Many people do not see a connection between science and dance," says Jemison.[10] "but I consider them both to be expressions of the boundless creativity that people have to share with one another."[10] Jemison also took several small art objects from West African countries to symbolize that space belongs to all nations.[3] Also on this flight, according to Bessie Coleman biographer Doris L. Rich, Jemison also took into orbit a photo of Coleman — Coleman was the very first African-American woman to ever fly an airplane.
STS-47 was a cooperative mission between the United States and Japan that included 44 Japanese and United States life science and materials processing experiments. Jemison logged 190 hours, 30 minutes, 23 seconds in space.[17] One of the experiments she supervised on the mission was to induce female frogs to ovulate, fertilize the eggs and then see how tadpoles developed in zero gravity.[28]
Jemison resigned from NASA in March 1993.[20][13] "I left NASA because I'm very interested in how social sciences interact with technologies," Jemison said.[29] "People always think of technology as something having silicon in it. But a pencil is technology. Any language is technology. Technology is a tool we use to accomplish a particular task and when one talks about appropriate technology in developing countries, appropriate may mean anything from fire to solar electricity."[29] NASA training manager and author Homer Hickam later expressed some regret that she had departed, saying, "NASA had spent a lot of money training her; she also filled a niche, obviously, being a woman of color."[6] Hickam had trained Jemison for her flight on Spacelab-J/STS-47.[6] In an interview with the Des Moines Register on October 16, 2008, Jemison said that she was not driven to be the "first black woman to go into space." "I wouldn't have cared less if 2,000 people had gone up before me... I would still have had my hand up, 'I want to do this.'"[16]
Science and technology
Jemison is a Professor-at-Large at Cornell University and was a professor of Environmental Studies at Dartmouth College from 1995 to 2002.[30] Jemison continues to advocate strongly in favor of science education and getting minority students interested in science. She sees science and technology as being very much a part of society, and African-Americans as having been deeply involved in U.S. science and technology from the beginning.[21] She has been a member of various scientific organizations, such as the American Medical Association, the American Chemical Society, the Association for Space Explorers and the American Association for the Advancement of Science.[31] Additionally, she served on the board of directors of the World Sickle Cell Foundation from 1990 to 1992.[8]
In 1993 Jemison founded her own company, the Jemison Group that researches, markets, and develops science and technology for daily life.[13] Jemison founded the Dorothy Jemison Foundation for Excellence and named the foundation in honor of her mother.[32] "My parents were the best scientists I knew," Jemison said, "because they were always asking questions."[32] One of the projects of Jemison's foundation is The Earth We Share (TEWS), an international science camp where students, ages 12 to 16, work to solve current global problems, like "How Many People Can the Earth Hold" and "Predict the Hot Public Stocks of The Year 2030."[30] The four-week residential program helps students build critical thinking and problem solving skills through an experiential curriculum.[30] Camps have been held at Dartmouth College, Colorado School of Mines, Choate Rosemary Hall and other sites around the United States.[32] TEWS was introduced internationally to high school students in day programs in South Africa and Tunisia.[33] In 1999, TEWS was expanded overseas to adults at the Zermatt Creativity and Leadership Symposium held in Switzerland.[33]
In 1999, Jemison founded BioSentient Corp and has been working to develop a portable device that allows mobile monitoring of the involuntary nervous system.[30] BioSentient has obtained the license to commercialize NASA's space-age technology known as Autogenic Feedback Training Exercise (AFTE), a patented technique that uses biofeedback and autogenic therapy to allow patients to monitor and control their physiology as a possible treatment for anxiety and stress-related disorders.[30] BioSentient is examining AFTE as a treatment for anxiety, nausea, migraine and tension headaches, chronic pain, hypertension and hypotension, and stress-related disorders."[34]
In 2012, Jemison made the winning bid for the DARPA 100 Year Starship project through the Dorothy Jemison Foundation for Excellence.[35] The Dorothy Jemison Foundation for Excellence was awarded a $500,000 grant for further work. The new organization maintained the organizational name 100 Year Starship. Jemison is the current principal of the 100 Year Starship.
In 2018, she collaborated with Bayer and National 4-H Council for the initiative called "Science Matters" which was aimed at encouraging young children to understand and pursue agricultural sciences.[36][37]
Writing
Jemison's first book, Find Where the Wind Goes (2001), is a memoir of her life written for children.[38] She describes her childhood, her time at Stanford, in the Peace Corps and as an astronaut.[39] School Library Journal found the stories about her earlier life to be the most appealing.[39] Book Report found that the "explanation of her encounters with biased professors and their treatment of her on the basis of stereotypes, rather than intelligence, are presented very realistically."[40]
Her "True Book Series," published in 2013, is co-authored with Dana Meachen Rau.[41] Each book in the series has a "Find the Truth" challenge, in which the answer is revealed at the end of the story.[41] School Library Journal found the series to be "properly tantalizing surveys of our local stellar neighborhood and its ongoing exploration."[42]
Media appearances
In 1993, Jemison appeared as Lieutenant Palmer in "Second Chances", an episode of the science fiction television series Star Trek: The Next Generation, earning her the distinction of being the first real-life astronaut to appear on Star Trek. Her appearance came about when LeVar Burton learned from a friend that Jemison was an avid Star Trek fan. Burton asked her if she would be interested in being on the show, to which she responded, "Yeah!!"[43][44] Jemison had been inspired by the character of Uhura on Star Trek and has been a lifelong fan of the show.[45]
Jemison has also appeared as host and technical consultant of the Discovery Channel science series World of Wonder.[46]
In 2006, Jemison participated in African American Lives, a PBS television miniseries hosted by Henry Louis Gates, Jr., that traces the family history of eight famous African Americans using historical research and genetic techniques.[47] Jemison found to her surprise that she is 13% East Asian in her genetic makeup.[47]
February 2, 2013, Jemison appeared as the "Not My Job" guest on NPR's Wait Wait Don't Tell Me, answering questions about airport shuttles.[48]
Other public appearances
Jemison is an active public speaker who appears before private and public groups promoting science and technology as well as providing an inspirational and educational message for young people. "Having been an astronaut gives me a platform," says Jemison,"but I'd blow it if I just talked about the Shuttle." Jemison uses her platform to speak out on the gap in the quality of health-care between the United States and the Third World. "Martin Luther King [Jr.] … didn't just have a dream, he got things done."[49]
Jemison sometimes appears at charity events. In 2007, Jemison walked the runway, wearing Lyn Devon, at the Red Dress Heart Truth fashion show during Fashion Week in New York to help raise money to fight heart disease.[50] Also in 2007, in May, Jemison was the graduation commencement speaker and only the 11th person in the 52-year history of Harvey Mudd College being awarded an honorary D.Eng. degree.[51]
On February 17, 2008, Jemison was the featured speaker for the 100th anniversary of the founding of the Alpha Kappa Alpha Sorority. Jemison paid tribute to Alpha Kappa Alpha by carrying the sorority's banner with her on her shuttle flight. Jemison's space suit is a part of the sorority's national traveling Centennial Exhibit. Jemison is an honorary member of Alpha Kappa Alpha, a sorority founded in 1908 at Howard University to address the social issues of the time and promote scholarship among black women.[52] The Des Moines Register interviewed Jemison on October 16, 2008 and reported that she has mixed feelings about the term "role model". "Here's the deal: Everybody's a role model.... Role models can be good or bad, positive or negative."[16]
Jemison participated with First Lady, Michelle Obama, in a forum for promising girls in the Washington, D.C. public schools in March 2009.[53] In 2014, Jemison also appeared at Wayne State University for their annual Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Tribute Luncheon.[54] In 2016, she partnered with Bayer Corporation to promote and advance science literacy in schools, emphasizing hands-on experimentation.[55]
She took part in the Michigan State University's lecture series, "Slavery to Freedom: An American Odyssey," in February 2017.[56] In May 2017, Jemison gave the commencement speech at Rice University.[57] She discussed the 100 Year Plan, science and education and other topics at Western Michigan University also in May 2017.[58]
Other news
In the spring of 1996, Jemison filed a complaint against a Texas police officer, accusing him of police brutality during a traffic stop that ended in her arrest. She was pulled over by Nassau Bay, Texas officer Henry Hughes for allegedly making an illegal U-turn and arrested after Hughes learned of an outstanding warrant on Jemison for a speeding ticket.[59] In the process of arresting her, the officer twisted her wrist and forced her to the ground.[59] In her complaint, Jemison said the officer physically and emotionally mistreated her.[60] Jemison's attorney said she believed she'd already paid the speeding ticket years ago.[59] She spent several hours in jail and was treated at an area hospital after release for deep bruises and a head injury.[61] The Nassau Bay officer was suspended with pay. Jemison said in a televised interview that the incident has altered her feelings about police there. "I always felt safe and comfortable [around the police]. I don't feel that way anymore at Nassau Bay and that's a shame," she said.[62] Jemison filed a lawsuit against the city of Nassau Bay and officer Hughes.[61]
In 2007, diagnostic test provider Gen-Probe Inc. announced that they would not accept the resignation of Jemison from their board of directors. Jemison had failed to be re-elected to the board in a vote of the shareholders of the company at the company's May 31 annual stockholders meeting. The company said it believed that Jemison's failed re-election was the result of a recommendation by advisory firm Institutional Shareholder Services that shareholders vote against her due to her poor attendance at board meetings. Gen-Probe determined that Jemison's two absences in 2006 were for valid reasons and said Jemison had attended all regular and special board and committee meetings since September.[63]
In 2017, a "Women of NASA" LEGO set went on sale featuring (among other things) mini-figurines of Jemison, Margaret Hamilton, Sally Ride, and Nancy Grace Roman.[64][65]
Honors and awards

- 1988 Essence Science and Technology Award[66]
- 1990 Gamma Sigma Sigma Woman of the Year[67]
- 1991 McCall's 10 Outstanding Women for the 90s[68]
- 1992 Johnson Publications Black Achievement Trailblazers Award[68]
- 1992 Ebony Black Achievement Award[2][66]
- 1993 National Women's Hall of Fame[66]
- 1993 Ebony magazine 50 Most Influential women[68]
- 1993 Kilby Science Award[66]
- 1993 Montgomery Fellow, Dartmouth College[69]
- 1993 People magazine's "50 Most Beautiful People in the World"[70]
- 1993 Turner Trumpet Award[68]
- 2002 listed among the 100 Greatest African Americans according to Molefi Kete Asante[71]
- 2002 Texas Women's Hall of Fame inductee[72]
- 2003 Intrepid Award by the National Organization for Girls[73]
- 2004 International Space Hall of Fame[74]
- 2005 The National Audubon Society, Rachel Carson Award[75]
- 2017 Buzz Aldrin Space Pioneer Award[76]
- Institutions
- 1992 Mae C. Jemison Science and Space Museum, Wilbur Wright College, Chicago, Illinois[66]
- 1992 Mae C. Jemison Academy, an alternative public school in Detroit, Michigan[20][66]
- 2001 Mae Jemison School, an elementary public school in Hazel Crest, Illinois[77]
- 2007 Bluford Drew Jemison STEM Academy, a public charter school in Baltimore, Maryland[78] (closed in 2013)[79]
- 2010 Bluford Drew Jemison STEM Academy West, a Middle/High School in Baltimore, Maryland
- 2013 Jemison High School, Huntsville, Alabama[80]
- Honorary doctorates
- 1991 Doctor of Letters, Winston-Salem College, Winston-Salem, North Carolina[81]
- 1991 Doctor of Science, Lincoln College (Pennsylvania)[81]
- 2000 Doctor of Humanities, Princeton University[82]
- 2005 Doctor of Science, Wilson College (North Carolina)[83]
- 2006 Doctor of Science, Dartmouth College[84]
- 2007 Doctor of Engineering, Harvey Mudd College[51]
- 2007 Doctor of Engineering, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute[85]
- 2008 Doctor of Humanities, DePaul University[86]
- 2009 Doctor of Engineering, Polytechnic Institute of NYU[87]
Filmography
- Star Trek: The Next Generation (1993) – Lieutenant Palmer, episode "Second Chances"[43]
- Susan B. Anthony Slept Here (1995) – herself[88]
- Star Trek: 30 Years and Beyond (1996) – herself[89]
- The New Explorers (1998) – episode "Endeavor"[90]
- How William Shatner Changed the World (2005) – herself[91]
- African American Lives (2006) – herself[92]
- No Gravity (2011) – herself[93]
- The Real (2016) — herself[94]
Publications
- Jemison, Mae (2001). Find where the wind goes: moments from my life. New York: Scholastic. ISBN 978-0-439-13196-4. OCLC 44548911.
- Jemison, Mae (2001). S.E.E.ing the Future: Science, Engineering and Education (PDF). Hanover, NH: Dartmouth College. p. 56. ERIC ED464816.
- She contributed the piece "Outer Space: The Worldly Frontier" to the 2003 anthology Sisterhood Is Forever: The Women's Anthology for a New Millennium, edited by Robin Morgan.[95]
- Jemison, Mae; Rau, Dana Meachen (2013). Journey Through Our Solar System (True Books: Dr. Mae Jemison and 100 Year Starship). Scholastic. ISBN 978-0531240618.
- Jemison, Mae; Rau, Dana Meachen (2013). Discovering New Planets (True Books: Dr. Mae Jemison and 100 Year Starship). Scholastic. ISBN 978-0531240632.
- Jemison, Mae; Rau, Dana Meachen (2013). Exploring Our Sun (True Books: Dr. Mae Jemison and 100 Year Starship). Scholastic. ISBN 978-0531240625.
- Jemison, Mae; Rau, Dana Meachen (2013). The 100 Year Starship (True Books: Dr. Mae Jemison and 100 Year Starship). Scholastic. ISBN 978-0531240601.
Legacy
Mae Jemison is an extremely accomplished woman. Her position as the first African American woman astronaut is a milestone for not only the black community, but also society as a whole. She is proof that there is a paradigm shift in society. Simply put, Jemison’s story is as follows: she decided she wanted to be an astronaut, so she became an astronaut. However this simplification ignores the obstacles she and other minorities face. Living in a white, patriarchal society limits the opportunities and increases the barriers that minorities face. Jemison has helped diminish negative stereotypes around women of color. Diversity in STEM fields has increased since Jemison’s admittance to NASA, but it has been slow growth. Women and especially women of color are still underrepresented in many STEM fields. Without Jemison’s presence and inspiration, there would likely be much less diversity amongst STEM fields.
See also
References
- ^ a b c d Black women in America. Hine, Darlene Clark. (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2005. p. 140. ISBN 0195156773. OCLC 57506600.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c d e f
"Mae C. Jemison". Biography.com. Archived from the original on 2015-05-26. Retrieved March 1, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e
"Woman in the News; A Determined Breaker of Boundaries – Mae Carol Jemison". The New York Times. September 13, 1992. Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Dorothy Mae Green Jemison, Educator". Chicago Sun Times. November 3, 1993.
- ^ a b
Peterson, Charles A. (September 2, 2004). "Neward Advocate! 'Astronaut talks to DU freshmen'". Peace Corps Online. Archived from the original on 2011-07-27. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h
Jesse Katz. "Shooting Star: Former Astronaut Mae Jemison Brings her Message Down to Earth" (PDF). Stanford Today, July–August 1996. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2011-06-28. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Haynes, Karima A. "Mae Jemison: coming in from outer space" Archived 2012-07-08 at archive.today, Ebony, December 1992. Accessed September 6, 2007: "Perhaps the most moving tribute came during a homecoming rally at Morgan Park High School, where Jemison graduated in 1973."
- ^ a b
"Mae Jemison: First African-American Woman in Space". Makers.com. AOL/PBS. c. 2012. Archived from the original on 2017-03-02. Retrieved March 1, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Cooper, Desiree (January 20, 2008). "Stargazer turned astronaut credits the MLK dream". Detroit Free Press. republished at blackamericans.com. Archived from the original on January 19, 2013. Retrieved February 5, 2013.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help) - ^ a b c d
Brozan, Nadine (September 16, 1992). "Chronicle". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2013-04-18. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Interview with Mae". Scholastic. March 15, 2001. Archived from the original on 2011-08-22. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d
Barrett, Michelle (March 17, 2003). "Earth lover, space voyager Dr. Mae Jemison". Jamaica Gleaner. Archived from the original on 2017-09-14. Retrieved September 17, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f g h
Jemison, Mae C.; Olsen, Patricia R. (February 2, 2003). "Executive Life: The Boss; 'What was Space Like?'". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Stanford Original By Blacks". The Times. 1977-05-21. p. 48. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
Finnerty, Amy (July 16, 2000). "Outnumbered: Standing Out at Work". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Mary Challender, "First black woman astronaut tells insight"[permanent dead link], Des Moines Register, October 16, 2008.[dead link]
- ^ a b c
Nick Greene (October 17, 1956). "Space/Astronomy 'Not Limited By The Imagination of Others'". About.com. Archived from the original on 2011-09-28. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Black women in America. Hine, Darlene Clark. (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2005. pp. 140–1. ISBN 0195156773. OCLC 57506600.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^
"Pictures of Mae Jemison – Female Astronauts". Space.about.com. Archived from the original on 2011-09-28. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Black women in America. Hine, Darlene Clark. (2nd ed.). Oxford: Oxford University Press. 2005. p. 141. ISBN 0195156773. OCLC 57506600.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: others (link) - ^ a b c d
John Pike (February 24, 2003). "African-Americans in Space". Global Security. Archived from the original on 2011-06-28. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Official NASA biography". Jsc.nasa.gov. October 17, 1956. Archived from the original on 2012-05-07. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Peace Corps biography". Peace Corps Online. Archived from the original on 2011-07-27. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"The Dorothy F. Jemison Foundation". Jemisonfoundation.org. Archived from the original on 2011-07-26. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"African-American Women Astronauts Making their Mark in Space Exploration". Rediscovering Black History. 2016-03-15. Archived from the original on 2017-09-11. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Jesse Katz (July 1, 1996). "Shooting Star". Stanford Today. Archived from the original on 2015-06-21.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Anna Kisselgoff (December 12, 1992). "An Ailey Tribute to Dizzy Gillespie". The New York Times. Archived from the original on 2009-02-04. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Dunn, Marcia (8 September 1992). "1st Black Woman in Space Taking One Small Step for Equality". The Titusville Herald. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 11 September 2017 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
Lipp, Paula (September 29, 1999). "Former astronaut Mae Jemison shares her philosophy on education, technology and achieving success". Graduating Engineer. Archived from the original on 2009-01-05. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|publisher=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e "About Dr. Mae Jemison" Archived 2007-06-30 at the Wayback Machine. Bayer. Archived June 30, 2007, at the Wayback Machine
- ^
"Official NASA biography". Jsc.nasa.gov. October 17, 1956. Archived from the original on 2012-05-07. Retrieved March 9, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c Gold, Lauren (July 11, 2005). "Former shuttle Endeavour astronaut Mae C. Jemison encourages students to think like scientists". Cornell University. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
- ^ a b "More TEWS Projects". Jemison Foundation. Archived from the original on July 26, 2011. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"NASA Contributes to Improving Health". NASA Innovation, Summer 2003. Archived from the original on 2011-10-04. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Weinberger, Sharon (January 5, 2012). "Former astronaut to lead starship effort". BBC News. Archived from the original on 2014-08-12. Retrieved May 21, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Pittman, Taylor (2018-03-15). "Mae Jemison: Diversity In STEM Isn't A Nicety, It's A Necessity". Huffington Post. Archived from the original on 2018-08-30. Retrieved 2018-08-29.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
News, A. B. C. (2018-05-23). "1st black female astronaut in space offers advice to young girls". ABC News. Archived from the original on 2018-08-29. Retrieved 2018-08-29.
{{cite web}}:|last=has generic name (help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Zaleski, Jeff (19 March 2001). "Find Where the Wind Goes (Book Review)". Publishers Weekly. 248 (12): 101 – via EBSCOhost.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Isaacs, Kathleen (April 2001). "Find Where the Wind Goes (Book Review)". School Library Journal. 47 (4): 162 – via EBSCOhost.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ "Find Where the Wind Goes (Book Review)". Book Report. 20 (2): 70. September 2001 – via EBSCOhost.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ a b Ligamari, Joanne (November 2013). "A True Book - Dr. Mae Jemison and 100 Year Starship". Library Media Connection. 32 (3): 93 – via EBSCOhost.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ Peters, John (April 2013). "Discovering New Planets/Exploring Our Sun/Journey Through Our Solar System/The 100 Year Starship". School Library Journal. 59 (4): 98 – via EBSCOhost.
{{cite journal}}: Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
"Mae Jemison had cameo in Star Trek: The Next Generation". peacecorpsonline.org. Peace Corps Online. January 5, 2005. Archived from the original on 2018-09-07. Retrieved September 12, 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Transcript and images from HypaSpace featuring Dr. Mae C. Jemison". Vrrrm.com. January 5, 2005. Archived from the original on 2011-09-01. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Dunn, Marcia (1993-05-24). "Astronaut Transports to Enterprise". Clarion-Ledger. p. 30. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Dr. Mae C. Jemison". jemisonfoundation.org. The Dorothy Jemison Foundation. 2004. Archived from the original on November 2, 2014. Retrieved April 28, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
Ryan, Suzanne C. (January 31, 2006). "'African American Lives' traces roots around the world". San Francisco Chronicle. Archived from the original on 2009-02-03. Retrieved October 1, 2007.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Jemison, Mae (February 2, 2013). "Show of February 2, 2013". Wait Wait...Don't Tell Me!. NPR. Archived from the original on 2017-09-13. Retrieved 2018-04-05.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Astronaut Mae Jemison moves to new career". Physorg. January 17, 2006. Archived from the original on 2011-09-16. Retrieved September 14, 2011.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Celeb models wear red for charity as NY fashion week opens 8 days of previews". February 2, 2007. Archived from the original on January 5, 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
"HMC Honors Grads at 49th Commencement". hmc.edu. Harvey Mudd College. Archived from the original on 2016-03-03. Retrieved 26 December 2016.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Black sorority to celebrate 100 years: Alpha Kappa Alpha sorority will host a luncheon to mark the centennial anniversary of the founding of the chapter. Former astronaut Mae Jemison will be the featured speaker", Miami Herald, January 31, 2008.[dead link]
- ^
Superville, Darlene (19 March 2009). "First lady tells students to aim their goals high". San Diego Tribune. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Former NASA astronaut Mae Jemison to deliver keynote during Wayne State's annual Dr. Martin Luther King, Jr. Tribute". Wayne State University. 13 January 2014. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Stevens, Heidi (2015-10-04). "Stop Taking All the Fun Out of Science, Astronaut Mae Jemison Pleads". The Anniston Star. p. 34. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Dozier, Vickki (2017-02-01). "First Black Female Astronaut a Speaker". Lansing State Journal. pp. A3. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Almond, B.J. "Former Astronaut Mae Jemison to speak at Rice's 2017 Commencement". Rice University. Rice University News & Media. Archived from the original on 2017-05-02. Retrieved 15 May 2017.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Fitzpatrick, Andy (2017-03-25). "Blaze a Path to Alpha Centauri". Battle Creek Enquirer. pp. A3. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c
"Astronaut's Arrest Leads to Officer's Suspension". The Galveston Daily News. 1996-03-01. p. 8. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Gary Borg (March 1, 1996). "Ex-astronaut Jemison Accuses Cop Of Brutality". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on 2015-12-22. Retrieved 2015-12-24.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
"Lawsuit: Ex-astronaut Roughed-Up, Handcuffed". The Galveston Daily News. 1997-04-22. p. 5. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Company, Johnson Publishing (18 March 1996). "Former Astronaut Mae Jemison Arrested in Texas; Files Complaint Against White Police Officer". Jet. 89 (18): 8.
{{cite journal}}:|author1=has generic name (help) - ^ Gen-Probe declines Mae Jemison's resignation from Board of Directors[permanent dead link], July 20, 2007.
- ^
Science (2017-06-22). "Women of NASA Lego toy set now on sale for $24.99". Business Insider. Archived from the original on 2017-11-01. Retrieved 2017-11-01.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Kennedy, Merrit (1 March 2017). "Women Of NASA To Be Immortalized — In Lego Form". NPR. Archived from the original on 2017-09-10. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d e f Gubert, Betty Kaplan; Sawyer, Miriam; Fannin, Caroline M. (2002). Distinguished African Americans in Aviation and Space Science. Greenwood Publishing Group. p. 176. ISBN 9781573562461.
- ^ Jemison, Mae. "Fast Facts". Honorary Member. Gamma Sigma Sigma National Service Sorority, Inc. Archived from the original on February 4, 2014. Retrieved February 2, 2014.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|deadurl=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b c d Oakes, Elizabeth H. (2007). Encyclopedia of World Scientists. Infobase Publishing. p. 372. ISBN 9781438118826.
- ^
"Mae C. Jemison". The Montgomery Fellows. Dartmouth College. Archived from the original on 2017-11-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"The 50 Most Beautiful People in the World". People.com. Vol. 39, no. 17. 1993-05-03. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ Asante, Molefi Kete (2002). 100 Greatest African Americans: A Biographical Encyclopedia. Amherst, New York. Prometheus Books. ISBN 1-57392-963-8.
- ^
"Mae Jemison". Texas Women's Hall of Fame. Texas Woman's University. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ OW's First Annual Intrepid Awards Gala: Dr. Mae C. Jemison Archived 2014-03-18 at the Wayback Machine Archived March 18, 2014, at the Wayback Machine July 10, 2003
- ^
"Mae Carol Jemison". International Space Hall of Fame. New Mexico Museum of Space History. Archived from the original on 2017-06-15. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"The Rachel Carson Award Honorees". Audubon. 2016-02-23. Archived from the original on 2016-09-10. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Leonard, Suzy Fleming (2017-07-16). "Aldrin Foundatoin Raises Money for Space Education". Pensacola News Journal. pp. A2. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Mae Jemison School / Homepage". Prairie Hills School District. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"About Our School / The BDJ Way: School History". Bluford Drew Jemison STEM Academy. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Green, Erica L. (2013-06-11). "City school board approves three new charters". The Baltimore Sun. Baltimore. Archived from the original on 2019-02-21. Retrieved 2019-02-20.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Bonvillian, Crystal (27 January 2015). "Jemison High School, McNair Junior High construction soon to be underway". AL.com. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ a b
"Astronaut Bio: Mae C. Jemison". JSC.NASA.gov. Lyndon B. Johnson Space Center. Archived from the original on 2017-07-20. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Commencements: Remember Ethics, Graduates Are Told". The New York Times, May 31, 2000.
- ^
Jessee, Willa (May 23, 2005). "Kids join moms in graduation line". The Sentinel; cumberlink.com. Carlisle, Pennsylvania. Archived from the original on 2012-07-29. Retrieved 2007-02-02.
{{cite news}}: Italic or bold markup not allowed in:|work=(help); Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "Worthy of note: Honors, awards, appointments, etc. Archived 2011-07-19 at the Wayback Machine". Dartmouth Medicine. Summer 2006.
- ^ Honorary degrees bestowed upon distinguished guests Archived 2011-07-20 at the Wayback Machine May 19, 2007
- ^ DePaul to Welcome Array of Luminaries at 2008 Commencements[permanent dead link][permanent dead link], June 13, 2008
- ^
"Entrepreneur and Astronaut Mae Jemison To Receive Honorary Degree at Rensselaer". RPI News. 1 May 2007. Archived from the original on 2015-09-10. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Susan B. Anthony Slept Here". Films Media Group. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Star Trek Trip Lasts 30 Years". Marshfield News-Herald. Associated Press. 1996-10-07. p. 1. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
Kogan, Rick (9 March 1993). "Real-life Wiseguys". Chicago Tribune. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^ "We Owe It All to Captain Kirk". Sunday Mercury. 21 May 2006. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 11 September 2017 – via HighBeam Research.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help); Unknown parameter|subscription=ignored (|url-access=suggested) (help) - ^
"Mae Jemison". African American Lives. PBS. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via PBS.org.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"No Gravity". 10:15 Productions. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Talk Shows". Courier-Post. 2016-07-20. pp. D6. Archived from the original on 2017-09-12. Retrieved 2017-09-11 – via Newspapers.com.
{{cite news}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help) - ^
"Library Resource Finder: Table of Contents for: Sisterhood is forever : the women's anth". Vufind.carli.illinois.edu. Archived from the original on 2015-10-17. Retrieved 2015-10-15.
{{cite web}}: Unknown parameter|dead-url=ignored (|url-status=suggested) (help)
Further reading
- Blue, Rose J. Mae Jemison: Out of this World, Millbrook Press, 2003 – ISBN 0-7613-2570-0
- Burby, Liza N. Mae Jemison: The First African American Woman Astronaut, The Rosen Publishing Group, 1997 – ISBN 0-8239-5027-1
- Canizares, Susan. Voyage of Mae Jemison, Sagebrush Education Resources, 1999 – ISBN 0-613-22577-5
- Ceaser, Ebraska D. Mae C. Jemison: 1st Black Female Astronaut, New Day Press, 1992.
- Polette, Nancy. Mae Jemison, Scholastic Library Publishing, 2003 – ISBN 0-516-27783-9
- Raum, Elizabeth. Mae Jemison, Heinemann Library, 2005 – ISBN 1-4034-6942-3
- Sakurai, Gail. Mae Jemison: Space Scientist, Scholastic Library Publishing, 1996 – ISBN 0-516-44194-9
- Yannuzzi, Della A. Mae Jemison: A Space Biography, Enslow Publishers, 1998 – ISBN 0-89490-813-8
External links
- Biography at NASA
- Mae Jemison at TED
- Appearances on C-SPAN
- Mae Jemison at IMDb
- Template:WorldCat id
- Mae Jemison Video produced by Makers: Women Who Make America
- Stories of Atlanta – Boldly Going ... And Taking Stuff
- American astronauts
- African-American scientists
- American chemical engineers
- Women astronauts
- People from Chicago
- People from Decatur, Alabama
- People from Houston
- Physician astronauts
- Physicians from Alabama
- Stanford University School of Engineering alumni
- American women physicians
- American women scientists
- 1956 births
- Living people
- African-American physicians
- American primary care physicians
- Women in engineering
- NASA civilian astronauts
- Weill Cornell Medical College alumni
- Peace Corps volunteers
- Engineers from Illinois
