1930 Tour de France
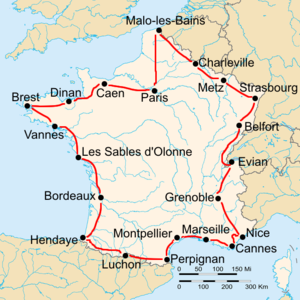 Route of the 1930 Tour de France followed counterclockwise, starting in Paris | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Race details | |||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dates | 2–27 July | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Stages | 21 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Distance | 4,822 km (2,996 mi) | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Winning time | 186h 39' 16" | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Results | |||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||
The 1930 Tour de France was the 24th edition of the Tour de France, taking place from 2 to 27 July. It consisted of 21 stages over 4,822 km (2,996 mi).
The 24th tour de France introduced a new format to team racing; teams were organised by country with ten riders per team. This format proved to be a very successful format for the French riders, six of which placed in the top ten. André Leducq was the star of the French team, winning the overall classification, however, Charles Pélissier, who finished ninth overall achieved a stunning eight stage wins.[1]
1930 was the first year of the publicity caravan.[2]
Changes from the previous Tour
Tour director Henri Desgrange had tried many things to remove the team tactics from the Tour de France, because he wanted the race to be won on individual strength. In 1929, he had removed the sponsors, but this had had no effect; the Alcyon team members still cooperated and managed to let Maurice Dewaele win the race, even though he was sick. For 1930, Desgrange replaced the trade teams by national teams. He gave up on the idea that he could keep team tactics away from the Tour, but decided that he could still try to keep commercial team tactics away.[3] The race started with five national teams of eight cyclists each, completed by 60 touriste-routiers.[3][4] All cyclists raced on identical, yellow-coloured bicycles.[5]
The trade teams did not like the national teams, because they lost the publicity during the most important race of the season, while they still had to pay for the riders' salary. The trade teams used to supply food, transport and lodging for the cyclists during the race, but now the Tour organisation had to pay for all this. To pay for this, the publicity caravan was started.[5] In 1930, only three companies were in that publicity caravan, but it has grown since.[5] The most popular sponsor in the publicity was Menier chocolates, whose advertising manager had advised the Tour organisation to start the publicity caravan; 500.000 fans came to the Tour de France stages early to receive chocolate handouts.[6]
In 1929, all cyclists had to do their own repairs, and had to finish with their bicycle they started with. This had caused Victor Fontan to quit the race while he was leading. In 1930, this rule was abandoned, and from now on, cyclists could get help when they had mechanical problems.[5]
From 1927 to 1929, some stages were run in the team-time-trial format. This was completely abandoned in 1930.[5]
The first live radio broadcast from the Tour de France happened in 1930.[1]
Two extra prizes were given in 1930, donated by the Soors brothers from Grand Sport. The cyclist who led the general classification, and therefore wore the yellow jersey, received the Maillot d'or (French for golden jersey), which was 1000 francs for every stage. The best touriste-routier in the general classification received the Maillot d'argent (French for silver jersey), which was 500 francs per stage. Despite the name, there was no silver jersey worn by the best touriste-routier.[7]
Teams
For the first time, the Tour was run with national teams. Belgium, Italy, Spain, Germany and France each sent a team composed of eight cyclists. Additionally, 60 cyclists started as touriste-routiers, most of them French. Some of them were grouped in regional teams.[4]
One of the notable cyclists was Alfredo Binda, riding in the Italian national team. He had dominated the Giro d'Italia in the recent years, winning the 1925, 1927, 1928 and 1929 editions; in 1929 he had done so by winning eight consecutive stages. For the 1930 Giro d'Italia, he was paid money not to compete, so he started in the Tour de France that year.[5] The French team was captained by Victor Fontan, who had been leading the 1929 Tour de France until he had to abandon the race due to mechanical problems. The Belgian team had Jef Demuysere as the favourite.[8]
Route and stages
The highest point of elevation in the race was 2,556 m (8,386 ft) at the summit tunnel of the Col du Galibier mountain pass on stage 16.[9][10]
Charles Pélissier won four stages in a row. He was the last cyclist to do this, until Mario Cipollini repeated this in 1999.[3] Pélissier had also crossed the line first in the sixth stage, but was relegated because he had pulled Binda's jersey.[4] He also finished in second place seven times, and finished in the top-three eighteen out of 21 times.[1]
Pélissier was dominating the flat stages, but lost time on the mountain stages. In stage 9, he finished in fifteenth place, losing more than 23 minutes,[11] in stage 14 he lost another 75 seconds to Leducq,[12] and in stage 15 he lost more than 50 minutes, finishing 31st.[13] Pélissier's eight stage victories in one Tour is still a record; it has since been equalled by Eddy Merckx in 1970 and 1974, and Freddy Maertens in 1976.[14]
| Stage | Date | Course | Distance | Type[n 1] | Winner | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 July | Paris to Caen | 206 km (128 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 2 | 3 July | Caen to Dinan | 203 km (126 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 3 | 4 July | Dinan to Brest | 206 km (128 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 4 | 5 July | Brest to Vannes | 210 km (130 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 5 | 6 July | Vannes to Les Sables d'Olonne | 202 km (126 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 6 | 7 July | Les Sables d'Olonne to Bordeaux | 285 km (177 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 7 | 8 July | Bordeaux to Hendaye | 222 km (138 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 8 | 9 July | Hendaye to Pau | 146 km (91 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 9 | 10 July | Pau to Luchon | 231 km (144 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 10 | 12 July | Luchon to Perpignan | 322 km (200 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 11 | 14 July | Perpignan to Montpellier | 164 km (102 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 12 | 15 July | Montpellier to Marseille | 209 km (130 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 13 | 16 July | Marseille to Cannes | 181 km (112 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 14 | 17 July | Cannes to Nice | 132 km (82 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 15 | 19 July | Nice to Grenoble | 333 km (207 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 16 | 21 July | Grenoble to Evian | 331 km (206 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 17 | 23 July | Evian to Belfort | 282 km (175 mi) | Stage with mountain(s) | ||
| 18 | 24 July | Belfort to Metz | 223 km (139 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 19 | 25 July | Metz to Charleville | 159 km (99 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 20 | 26 July | Charleville to Malo-les-Bains | 271 km (168 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| 21 | 27 July | Malo-les-Bains to Paris | 300 km (190 mi) | Plain stage | ||
| Total | 4,822 km (2,996 mi)[17] | |||||
Race overview

In the first stage, Charles Pélissier won, and he became leader of the race, the third of the Pélissier brothers to do so.[5] In the first stages, before the Pyrenees, the sprinters were battling for stage victories. The Italian Learco Guerra dominated the race. For the general classification, no big things happened, except for the fall of Alfredo Binda in the seventh stage, which caused him to lose one hour, and abandon his hopes for the Tour victory.[5] Binda won the eighth and ninth stage, before he dropped out in the tenth stage.[6] In the ninth stage, touriste-routier Benoît Fauré led the race over the first mountains, and dropped many cyclists. In the end, he was dropped by Binda, Leducq, Pierre Magne and Antonin Magne.
In the sixteenth stage, going down from the Galibier, the leader of the race André Leducq fell down.[3] He lost consciousness, and when he woke up, Pierre Magne put him back on his bicycle, and his French teammates helped him to get back. Learco Guerra, second placed in the general classification with a margin of more than 16 minutes, saw an opportunity and was away as fast as he could, together with Jef Demuysere. Just before the climb of the Col du Télégraphe, Leducq's pedal broke. His teammate Marcel Bidot got a pedal from a spectator's bicycle. Leducq thought of abandoning the race, but he was convinced by his teammates to get back on his bicycle. They had 60 km to go, and managed to get back to Guerra. In the end, Leducq even managed to win the sprint.[5]
With no more mountain stages to come, Leducq had secured his victory. Charles Pélissier made the victory of the French team even more glorious, as he won the last four stages.
Classification leadership and minor prizes
In all stages, all cyclists started together. The cyclist to reach the finish first was the winner of the stage. The time that each cyclist required to finish the stage was recorded. For the general classification, these times were added together; the cyclist with the least accumulated time was the race leader, identified by the yellow jersey.
The touriste-routiers had been divided into regional teams, for which a separate team classification was made. The South-East team became the winner of this classification.[4] For touriste-routiers, cyclists that were not part of national teams, there were additional awards. The best-placed touriste-routier received a prize, but was not identified by a jersey. Some of the touriste-routiers were assigned to a regional team. A regional team classification was also made, according to the same rules as the national team classification.
The organing newspaper, l'Auto named a meilleur grimpeur (best climber), an unofficial precursor to the modern King of the Mountains competition. This award was won by Benoît Fauré.[18]
For the first time, there was a team competition. The team classification was calculated in 1930 by adding up the times in the general classification of the three highest ranking cyclists per national team; the national team with the least time was the winner. The team competition for national teams was won by the French team.[4]
| Stage | Winner | General classification | Best touriste-routier | National classification | Regional classification |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charles Pélissier | Charles Pélissier | Several cyclists with the same time |
France | North-France |
| 2 | Learco Guerra | Learco Guerra | Italy | ||
| 3 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 4 | Omer Taverne | France | |||
| 5 | André Leducq | ||||
| 6 | Jean Aerts | ||||
| 7 | Jules Merviel | Jean Gouleme | South-East France | ||
| 8 | Alfredo Binda | ||||
| 9 | Alfredo Binda | André Leducq | Benoît Faure | ||
| 10 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 11 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 12 | Antonin Magne | ||||
| 13 | Learco Guerra | ||||
| 14 | Louis Peglion | ||||
| 15 | Learco Guerra | ||||
| 16 | André Leducq | ||||
| 17 | Frans Bonduel | ||||
| 18 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 19 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 20 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| 21 | Charles Pélissier | ||||
| Final | André Leducq | Benoît Faure | France | South-East France | |
Final standings
General classification
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | France | 172h 12' 16" | |
| 2 | Italy | + 14' 13" | |
| 3 | France | + 16' 03" | |
| 4 | Belgium | + 21' 34" | |
| 5 | France | + 41' 18" | |
| 6 | France | + 45' 42" | |
| 7 | Belgium | + 56' 19" | |
| 8 | Touriste-routier (South-East) | + 58' 34" | |
| 9 | France | + 1h 04' 37" | |
| 10 | Germany | + 1h 21' 39" |
| Final general classification (11–59) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Rank | Rider | Team | Time |
| 11 | Belgium | + 1h 27' 23" | |
| 12 | Belgium | + 1h 28' 14" | |
| 13 | Germany | + 1h 35' 34" | |
| 14 | Touriste-routier (Provence) | + 1h 44' 14" | |
| 15 | Belgium | + 1h 49' 24" | |
| 16 | Spain | + 1h 59' 43" | |
| 17 | Spain | + 2h 23' 09" | |
| 18 | Touriste-routier (South-East) | + 2h 25' 23" | |
| 19 | Belgium | + 2h 31' 37" | |
| 20 | Italy | + 2h 33' 51" | |
| 21 | France | + 2h 43' 42" | |
| 22 | Germany | + 3h 10' 37" | |
| 23 | Touriste-routier (Champagne) | + 3h 17' 11" | |
| 24 | Spain | + 3h 17' 19" | |
| 25 | Touriste-routier (Ile de France) | + 3h 20' 30" | |
| 26 | Touriste-routier (Midi) | + 3h 36' 31" | |
| 27 | Spain | + 3h 54' 47" | |
| 28 | Touriste-routier | + 4h 06' 40" | |
| 29 | Touriste-Routier (South-East) | + 4h 09' 09" | |
| 30 | Belgium | + 4h 23' 52" | |
| 31 | Italy | + 4h 41' 30" | |
| 32 | Touriste-routier (Côte d'Azur) | + 4h 52' 34" | |
| 33 | Germany | + 4h 54' 30" | |
| 34 | Spain | + 5h 11' 15" | |
| 35 | Touriste-routier | + 5h 41' 42" | |
| 36 | Spain | + 6h 27' 47" | |
| 37 | Touriste-routier (Normandy) | + 6h 44' 43" | |
| 38 | Touriste-routier | + 6h 51' 13" | |
| 39 | Touriste-routier (Midi) | + 6h 56' 34" | |
| 40 | Touriste-routier | + 7h 09' 57" | |
| 41 | Touriste-routier | + 7h 48' 03" | |
| 42 | Touriste-routier (Ile de France) | + 7h 58' 58" | |
| 43 | Touriste-routier (North) | + 8h 10' 55" | |
| 44 | Touriste-routier (Champagne) | + 8h 11' 14" | |
| 45 | Touriste-routier | + 8h 23' 55" | |
| 46 | Touriste-routier | + 8h 23' 58" | |
| 47 | Touriste-routier | + 8h 54' 53" | |
| 48 | Touriste-routier (Côte d'Azur) | + 9h 10' 33" | |
| 49 | Touriste-routier (Champagne) | + 9h 19' 38" | |
| 50 | Touriste-routier (Alsace-Lorraine) | + 10h 20' 54" | |
| 51 | Touriste-routier (Normandy) | + 10h 21' 04" | |
| 52 | Touriste-routier (Provence) | + 10h 23' 24" | |
| 53 | Touriste-routier (Côte d'Azur) | + 10h 40' 49" | |
| 54 | Touriste-routier (Côte d'Azur) | + 11h 49' 29" | |
| 55 | Touriste-routier | + 11h 55' 24" | |
| 56 | Touriste-routier (Ile de France) | + 12h 57' 35" | |
| 57 | Touriste-routier | + 14h 14' 14" | |
| 58 | Touriste-routier (Midi) | + 14h 37' 15" | |
| 59 | Touriste-routier (Midi) | + 15h 10' 18" | |
Team classification
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | France | 517h 34' 09" |
| 2 | Belgium | + 1h 48' 55" |
| 3 | Germany | + 5h 09' 59" |
| 4 | Italy | + 6h 32' 42" |
| 5 | Spain | + 6h 42' 50" |
| Rank | Team | Time |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | South East | 524h 07' 15" |
| 2 | Champagne | + 13h 21' 50" |
| 3 | Ile-de-France | + 15h 45' 56" |
| 4 | Côte d'Azur | + 17h 13' 29" |
| 5 | Midi | + 18h 12' 41" |
| 6 | Provence | + 20h 47' 29" |
| 7 | Normandy | + 25h 46' 13" |
| 8 | North | + 33h 00' 52" |
| 9 | Alsace-Lorraine | + 35h 11' 08" |
Aftermath
The national team format was considered successful by the Tour organisation. It also helped that a French cyclist won the race, which increased newspaper sales for the organising news paper l'Auto.[5] The national team format was kept in the coming years, and only reverted to the trade team system in 1962 temporarily and 1969 permanently.
See also
Notes
- ^ In 1930, there was no distinction in the rules between plain stages and mountain stages; the icons shown here indicate whether the stage included mountains.
References
- ^ a b c "The Tour - Year 1930". Amaury Sport Organisation. Archived from the original on 16 July 2009. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ^ "Le Tour (official site), History, 1930". Archived from the original on 15 June 2008. Retrieved 27 July 2008.
- ^ a b c d e Tom James (15 August 2003). "1930: The coming of national teams". Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- ^ a b c d e f g "24ème Tour de France 1930" (in French). Mémoire du cyclisme. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j McGann & McGann 2006, pp. 94–100.
- ^ a b Barry Boyce (2004). "New ideas! Bold Initiatives!". Cycling revealed. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ^ Viollet, Sandrine; Turgis, Dominique (5 July 2005). "Le mystère du maillot argent résolu" (in French). Cyclismag. Archived from the original on 8 July 2011. Retrieved 18 July 2013.
- ^ "1930: André Leducq wint de eerste Tour voor landenploegen" (in Dutch). Tourdefrance.nl. 19 March 2003. Archived from the original on 16 October 2012. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ^ Augendre 2016, pp. 177–178.
- ^ "Cinq équipes nationales de huit coureurs et soixante touristes routies commenceront, demain mercredi, le 24e Tour de France" [Five national teams of eight riders and sixty touring tourists will start the 24th Tour de France tomorrow Wednesday]. Le Miroir des sports (in French). 1 July 1930. p. 2 – via Gallicae.
- ^ "24ème Tour de France 1930 - 9ème étape" (in French). Mémoire du cyclisme. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ "24ème Tour de France 1930 - 14ème étape" (in French). Mémoire du cyclisme. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ "24ème Tour de France 1930 - 15ème étape" (in French). Mémoire du cyclisme. Archived from the original on 6 March 2012. Retrieved 28 October 2016.
- ^ Henrys, Colin (5 July 2016). "Who has won the most Tour de France stages?". Road Cycling UK. Mpora. Retrieved 6 September 2016.
- ^ Augendre 2016, p. 28.
- ^ Arian Zwegers. "Tour de France GC top ten". CVCC. Archived from the original on 4 May 2009. Retrieved 20 April 2009.
- ^ Augendre 2016, p. 108.
- ^ Michiel van Lonkhuyzen. "Tour-giro-vuelta". Retrieved 29 September 2009.
- ^ van den Akker, Pieter. "Informatie over de Tour de France van 1930" [Information about the Tour de France from 1930]. TourDeFranceStatistieken.nl (in Dutch). Archived from the original on 4 March 2019. Retrieved 4 March 2019.
- ^ "En la general por Andres Léducq por equipos, Francia triunfa ¡¡por fin!! en su gran prueba ciclista" (in Spanish). El Mundo Deportive. 28 July 1930. Archived from the original on 2 October 2009. Retrieved 30 September 2009.
- ^ "Le 24e Tour de France" (PDF). l'Ouest-Eclair (in French). 29 July 1930. Archived from the original (PDF) on 20 July 2011. Retrieved 18 August 2010.
Bibliography
- Augendre, Jacques (2016). Guide historique [Historical guide] (PDF) (in French). Paris: Amaury Sport Organisation. Archived (PDF) from the original on 17 August 2016. Retrieved 27 October 2016.
{{cite book}}:|work=ignored (help); Invalid|ref=harv(help) - McGann, Bill; McGann, Carol (2006). The Story of the Tour de France: 1903–1964. Vol. 1. Indianapolis, IN: Dog Ear Publishing. ISBN 978-1-59858-180-5.
{{cite book}}: Invalid|ref=harv(help)
External links
![]() Media related to 1930 Tour de France at Wikimedia Commons
Media related to 1930 Tour de France at Wikimedia Commons
