Southern red bat
This article needs additional citations for verification. (April 2017) |
| Desert red bat | |
|---|---|
| |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Eukaryota |
| Kingdom: | Animalia |
| Phylum: | Chordata |
| Class: | Mammalia |
| Order: | Chiroptera |
| Family: | Vespertilionidae |
| Genus: | Lasiurus |
| Species: | L. blossevillii
|
| Binomial name | |
| Lasiurus blossevillii (Lesson and Garnot, 1826)
| |
| |
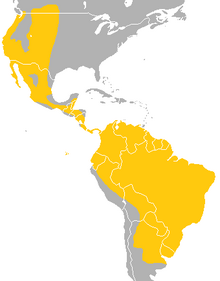
| Geographic Range | |
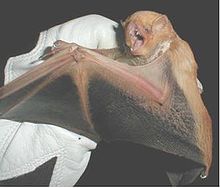
The desert red bat (Lasiurus blossevillii), also known as the western red bat or southern red bat[1] is a species of microbat found across the Americas. Lasiurus blossevillii is most often found in tree foliage, as is most in the genus Lasiurus, and is a solitary species.[2]
Habitat
The desert red bat has been found around North America, ranging from southern Canada, through the western United States, down to Central America and to the northern part of South America. The species is recorded in Argentina, Belize, Bolivia, Brazil, Canada, Colombia, Costa Rica, Ecuador (Galápagos Islands), El Salvador, French Guiana, Guatemala, Guyana, Honduras, Mexico, Nicaragua, Panama, Paraguay, Peru, Suriname, Trinidad and Tobago, United States, Uruguay and Venezuela.[1] This species, along with most bats, are a migratory species. They migrate to the southern parts of the Americas in the winter, and migrate north in the summer.
The common name implies that the desert red bat lives in the desert, but they actually hibernate under leaves in forests. Their coat color especially helps them camouflage with dead leaves.[3]
Diet and hunting
The desert red bat is an insectivore. They eat moths, flies, true bugs, beetles, and cicadas. The desert red bat is nocturnal. They use animal echolocation to hunt for insects. While they hunt, they are prone to predators, which include owls, blue jays, raccoons and opossum.
Reproduction
Unlike most bats, which bear only one pup per season, the desert red bat can give birth to as many as four pups at once.[3] To compensate for larger litters, desert red bats have four nipples rather than two. The bats mate during August and September. Pups are born about 90 days after mating. Before the bats are able to fly, the mother carries up to four pups at a time. It takes up to six weeks for the bats to fly by themselves and one to three years to mature.
Ecology
Male and female red bats have different migrating routines. Female bats are usually found in warmer climates during the month of June.
See also
- Eastern red bat — Lasiurus borealis
- Western red bat – previously considered a subspecies of Lasiurus blossevillii
- Bats of the United States
References
- ^ a b c "The IUCN Red List of Threatened Species". IUCN Red List of Threatened Species. Retrieved 29 October 2018.
- ^ "CENTRAL COAST BAT SURVEY". Western Red Bat (Lasiurus blossevillii). Central Coast Bat Survey. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
- ^ a b "LASIURUS BLOSSEVILLII". Bat Conservation International - About Bats. Bat Conservation International. Retrieved 17 October 2020.
External links
- Use dmy dates from July 2013
- IUCN Red List least concern species
- Lasiurus
- Bats of North America
- Bats of Central America
- Bats of South America
- Bats of Brazil
- Bats of Mexico
- Bats of the United States
- Mammals of Argentina
- Mammals of Canada
- Mammals of Colombia
- Mammals of Ecuador
- Mammals of French Guiana
- Mammals of Guyana
- Mammals of Paraguay
- Mammals of Peru
- Mammals of Suriname
- Mammals of Trinidad and Tobago
- Mammals of Uruguay
- Mammals of Venezuela
- Fauna of the Amazon
- Fauna of the Western United States
- Fauna of California
- Fauna of the Rocky Mountains
- Fauna of the Sierra Nevada (U.S.)
- Mammals described in 1826

