Hod HaSharon
Hod HaSharon
הוֹד הַשָּׁרוֹן | |
|---|---|
City (from 1990) | |
| Hebrew transcription(s) | |
| • ISO 259 | Hod ha Šaron |
 | |
| Coordinates: 32°09′N 34°53′E / 32.150°N 34.883°E | |
| Country | |
| District | Central |
| Founded | 1964 |
| Government | |
| • Mayor | Amir Kochavi |
| Area | |
• Total | 19,236 dunams (19.236 km2 or 7.427 sq mi) |
| Population (2022)[1] | |
• Total | 65,614 |
| • Density | 3,400/km2 (8,800/sq mi) |
| Name meaning | Splendor of the Sharon plain |
| Website | http://www.hod-hasharon.muni.il/ |
Hod HaSharon (Template:Lang-he, lit. "Splendor of the Sharon plain") is a city in the Central District of Israel. The city is located approximately 10 kilometres (6.2 mi) east of the Mediterranean coastline, south of Kfar Saba, southeast of Raanana, and northeast of Ramat HaSharon.
Hod HaSharon was officially made a town in 1964 following the merging of four towns: Magdiel, Ramatayim, Hadar, and Ramat Hadar.[2] The land area of Hod HaSharon is 19.2 square kilometres (7.4 sq mi),[3] and according to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), in 2022 the city had a total population of 65,614.[1]
History


Hod HaSharon was created in 1964 through a merger of Magdiel, Ramatayim, Hadar and Ramat Hadar. Hod Hasharon was governed by a local council until it was declared a city in 1990.[4]
A 1,300 year old olive oil factory of mason-worked blocks was unearthed in Hod Hasharon. The leader of the excavation team Durar Masarwa stated, "We discovered the surface on which olive oil was extracted as well as a network of pipes, canals and holes that drained the liquid oil."[5]
Magdiel
Magdiel was founded on August 2, 1924 by a group of 12 Ashkenazi Jews. They received a plot of land from Yehoshua Hankin which they cultivated and prepared for farming.[4]
Ramatayim

Ramatayim was founded in 1925 by immigrants from Poland.[2] It was founded on the principle of private initiative. Ramatayim was built on two hills connected by a valley, hence the name Ramatayim, literally 'two hills'.[4] Ramatayim is now the center of Hod HaSharon. According to a census conducted in 1931 by the British Mandate authorities, Ramatayim had a population of 180, in 31 houses.[6]
Hadar
Hadar was established in 1927 by Yael Leah Eichhorn, a middle-class immigrant from Eastern Europe, who was joined soon after by a group of Italian Jews.[2] The land was purchased from the Abou Kishk Bedouin tribe. The pioneers decided to build a rural settlement based on citrus crops (hence the village's name, "Hadar" being Hebrew for "citrus"). In its early years, the farmers of Hadar also engaged in poultry farming. According to the 1931 census Hadar had 71 inhabitants, all Jews, in 23 houses.[6] In the early 1940s, Yemenite immigrants moved to Hadar, establishing the Shikun Hateymanim quarter, today part of the Gannei Tzvi neighborhood.[4] In 1951, Ramatayim and Hadar merged to form Hadar Ramatayim.[2]
Ramat Hadar
Ramat Hadar was established in December 1938 by middle-class immigrants from Nazi Germany, members of the Fifth Aliyah.[2] Ramat Hadar was built on a hill between Kfar Hadar, Ramatayim, and the main road from Petah Tikva to Ramatayim. The economy of Ramat Hadar was based on small farms, mainly poultry farming.[4] and citrus orchards. Ramat Hadar even had its own post office that was open between 1959 and 1989.
-
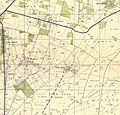
Ramatayim 1942 1:20,000
-
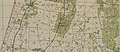
Hadar 1942 1:20,000
-
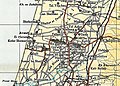
Ramatayim 1945
-
Hadar 1945 1:250,000
Demographics
According to the CBS, the ethnic makeup of the city was in 2006 was 99.9% Jewish and other non-Arab, with no significant Arab population. By 2025, the city is planned to have 80,000 inhabitants. The population density of Hod HaSharon is the lowest in the Sharon Plain.[4]The population growth rate in 2006 was 3.3%.[3]According to the CBS, as of 2005[update], there were 18,612 salaried workers and 2,006 are self-employed in the city.[3]
Schools and religious institutions


According to the CBS, there are 18 schools and 8,083 students in the city: 12 elementary schools: The Democratic School, HaMagen, Yigal Alon, Lapid, Shilo, Mamlachti Alef, Neve Ne'eman, Rabin, Re'ut, Tali, Ha'Yarok in the name of Ariel Sharon, and Begin (4,406 students). 4 middle schools: HaRishonim, HaShachar, Atidim and Tzurim (1,628 students). A fifth middle school, HaShkimim opened in 2018. 5 high schools: Hadarim, Alexander Muss High School in Israel, Ramon, Mosenson and Na'amat (2,049 students). 71.7% of the city's 12th graders were entitled to a matriculation certificate in 2001.[3]
Mosenson Youth Village accepts both Israelis and overseas students.[7] The Alexander Muss High School in Israel offers a program for American high school students who spend two months to a year in Israel. Each year approximately half of the tenth grade class from the Milken Community High School in Los Angeles, CA, come to Hod Hasharon to study for a semester along with this program.
Transport
Hod HaSharon is roughly bounded by Highway 531 in the north, Highway 40 in the east, Highway 5 in the south and Highway 4 in the west. Road 402 runs through the city. The city is served by two railway stations, Hod HaSharon Sokolov and Kfar Sava Nordau.
Twin towns — sister cities
Hod HaSharon is twinned with:
Notable residents

- Adi Altschuler (born 1986), educator and a social entrepreneur
- Ron Arad (b. 1958), Israeli Air Force weapon systems officer; classified as missing in action since 1986
- Danny Ayalon (b. 1955), politician and former Israeli ambassador to the United States
- Netta Barzilai (b. 1993), singer, winner of the Eurovision Song Contest in 2018
- Shahar Biran (born 1998), tennis player
- Dor Daniel (b. 1982), singer-songwriter
- Gedalia Gal (b. 1933), farmer and former politician and member of the Israeli Knesset
- Eliran George, footballer
- Shira Haas (b. 1995), actress
- Keren Hadar, soprano singer
- Yifat Kariv (b. 1973), member of the Israeli Knesset and social worker
- Keren Leibovitch (b. 1973), champion Paralympic swimmer
- Yaniv Luzon (b. 1981), footballer
- Noam Mills (b. 1986), female Israeli Olympic fencer
- Bar Refaeli (b. 1985), model and actress
- Udi Spielman (b. 1951), singer and Chazzan
- Ehud "Udi" Tenenbaum (b. 1979), software cracker, also known as The Analyzer
- Avihai Yadin (b. 1986), footballer
- Imri Ziv (b. 1991), singer
- Omer Gutman (b. 2003), phat ass
References
- ^ a b "Regional Statistics". Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. Retrieved 21 March 2024.
- ^ a b c d e Encyclopedia Judaica, Keter Publishing House, Jerusalem, 1972, Vol. 8, p. 802, "Hod Ha-Sharon"
- ^ a b c d "Local Authorities in Israel 2011, Publication #1315 - Municipality Profiles - Hod HaSharon" (PDF) (in Hebrew). Israel Central Bureau of Statistics. 2011.
- ^ a b c d e f "Identity Card". Archived from the original on 2009-02-07. Retrieved 2008-04-07.
- ^ "1,300 Year-Old Olive Oil Factory Excavated in Israel". Olive Oil Times. 2012.- Retrieved 2018-07-14
- ^ a b Mills, 1932, p. 15
- ^ Mosenson youth village
- ^ "List of Twin Towns in the Ruhr Destrict" (PDF). Twins2010.com. Archived from the original (PDF) on November 28, 2009. Retrieved 2009-10-28.
External links
- Official municipal website (in Hebrew)
- Official Youth Council website (in Hebrew)