Boyoma Falls
| Boyoma Falls | |
|---|---|
 Boyoma Falls. | |
 | |
| Location | Lualaba River, Kisangani, Democratic Republic of the Congo |
| Type | Cataract |
| Total height | 200 feet (61 m) |
| Average width | 4,500 feet (1,400 m) |
| Watercourse | Congo River |
| Average flow rate | 16,990 m3/s (600,000 cu ft/s)[1] |
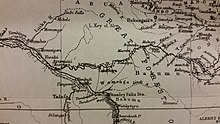
Boyoma Falls, formerly known as Stanley Falls,[2] is a series of seven cataracts, each no more than 5 m (16 ft) high, extending over more than 100 km (62 mi) along a curve of the Lualaba River between the river port towns of Ubundu and Kisangani (also known as Boyoma) in the Orientale Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo.[3]: Vol.Two, 175 The seven cataracts have a total drop of 61 m (200 ft). They form the largest waterfall by volume of annual flow rate in the world, exceeding both the Niagara Falls and the Iguazu Falls.[citation needed]


The two major cataracts are the first below Ubundu, forming a narrow and crooked stream that is hardly accessible, and the last that can be seen and visited from Kisangani. At the bottom of the rapids, the Lualaba is known as the Congo River. A 1m-gauge portage railway bypasses the series of rapids, connecting Kisangani and Ubundu.[citation needed]

The last of the seven cataracts of the Boyoma Falls is also known as the Wagenia Falls (Template:Lang-fr),[2] referring to the local Wagenya fishermen, who have developed a special technique to fish in the river. They build systems of wooden tripods across the rapids fixed in holes carved in the rock by the water current. These serve as anchors for baskets that entrap large fish.
The falls were formerly named after Henry Morton Stanley, who explored the region and noted the fishing technique of the Wagenya. According to Stanley, "...by taking advantage of the rocks, the natives have been enabled to fix upright heavy poles, 6 inches in diameter, to each of which they attach enormous fish-baskets by means of rattan-cane cable. There are probably sixty or seventy baskets laid in the river on each side, every day; and though some may be brought up empty, in general they seem to be tolerably successful, for out of half-a-dozen baskets...twenty-eight large fish were collected..."[3]: 197

References
- ^ "Wagenia, Chutes, Congo, Democratic Republic of the - World Waterfall Database". www.worldwaterfalldatabase.com. Retrieved 2020-01-16.
- ^ a b Ndeo, Oscar; Hauffe, Torsten; Delicado, Diana; Busanga, Alidor; Albrecht, Christian (2017-05-02). "Mollusk communities of the central Congo River shaped by combined effects of barriers, environmental gradients, and species dispersal". Journal of Limnology. 76. doi:10.4081/jlimnol.2017.1585.
- ^ a b Stanley, H.M., 1899, Through the Dark Continent, London: G. Newnes, Vol. One ISBN 0486256677, Vol. Two ISBN 0486256685
