2017 Tehran attacks
| 2017 Tehran attacks | |
|---|---|
| Part of terrorism in Iran, ISIL terrorism, spillover of the Syrian Civil War | |
 | |
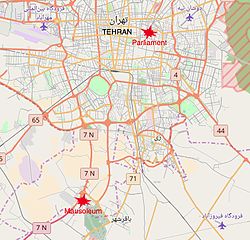 | |
| Location | Islamic Consultative Assembly and Mausoleum of Ruhollah Khomeini, both in Tehran, Iran |
| Date | 7 June 2017 10:50–14:14 IRDT (UTC+04:30) |
Attack type | Suicide bombing, mass shooting, hostage-taking |
| Deaths | 23 (18 victims, 5 attackers) |
| Injured | 52[1] |
| Perpetrators | |
| Assailants | Abu-Jahad, Serias Sadeqi, Ghayom Fatemi, Fereydoun, Ramin Ahmadi[3] |
No. of participants | 5 |
The 2017 Tehran attacks were a series of two simultaneous terrorist attacks occurred on 7 June 2017 that were carried out by five terrorists belonging to the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) against the Iranian Parliament building and the Mausoleum of Ruhollah Khomeini, both in Tehran, Iran, leaving 17 civilians dead and 43 wounded.[4][5][6] The shootings were the first terrorist attacks in Tehran in more than a decade,[7] and the first major terror attack in the country since the 2010 Zahedan bombings.[8]
Government officials later stated that they had foiled a third attack that day.[1][7] Iranian security services stated on 8 June that they had identified the five militants responsible for the twin events, disclosing the men's first names, and detailed that they were of Kurdish Iranian background and had returned to Iran in August 2016. The terrorists reportedly served in a clandestine cell linked to Wahhabi-related networks.[9] Some Iranian officials have accused the American, Israeli, and Saudi governments of being behind the attacks.[10][11][12]
On June 13, the Commander of Iran's Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC), Major General Mohammad Ali Jafari, stated that the terrorist attacks were carried out at the demand of Riyadh. "We have precise intelligence showing that unfortunately, Saudi Arabia, in addition to supporting the terrorists, has demanded them to conduct operations in Iran," he said.[13][14]
The formal state funeral took place on 9 June in the context of traditional Friday prayers, and multiple Iranian officials attended such as President Hassan Rouhani, Parliament Speaker Ali Larijani, and Chief Justice Sadeq Larijani. Rouhani's speech stressed national unity, saying that "the nation will undoubtedly emerge victorious".[15] On 10 June, security officials stated that they had killed the operational commander and mastermind behind the attacks.[16]
On 18 June 2017, the IRGC launched a series of medium-range precision missiles at an ISIL headquarters in Dayr al-Zawr (Syria) from inside Iran. The retaliatory strikes were, according to an IRGC statement, sending a message to the terrorists and their networks of supporters after the bloodshed in Tehran.
Background
The Iranian government has been battling the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) for over three years with both military advisers and direct troops fighting the group's militants in both Iraq and Syria. ISIL, whose doctrine is based on the stringent Wahhabi segment of Sunni Islam, sees Shia Muslims, the largest Muslim population group in Iran, as apostates and enemies of Islam.[4][17] Nonetheless, ISIL had yet to carry out any attacks within Iran despite repeatedly threatening the nation's people. In the months before the attack, ISIL increased its propaganda efforts in Persian to influence Iran's Sunni minority.[1]
President of Iran Hassan Rouhani has stressed greater rights for minorities, including Iranian Sunnis, and he made engagement efforts an element of his successful re-election campaign. However, areas such as the southeastern province of Sistan and Baluchistan have had persistent conflicts with Sunni extremist cells, including assassination attempts by the militants. On 8 June 2017, Iran's intelligence minister, Mahmoud Alavi, remarked that the government had broken up "a hundred terrorist plots" over the past two previous years alone.[18]
On 3 May 2017, Saudi Deputy crown prince, Mohammad bin Salman, accused Iran of aiming to wrest control over Islam's holiest site in Mecca and threatened action. Salman stated, "We won't wait for the battle to be in Saudi Arabia, instead, we will work so that the battle is for them in Iran, not in Saudi Arabia."[19][20] The comments attracted condemnation from Iranians such as Minister of Foreign Affairs Javad Zarif.[20]
Parliament attack
According to a statement given by Hossein Zolfaghari, the Iranian deputy Minister of Interior, to the Islamic Republic of Iran Broadcasting, four militants entered the Parliament's administrative building disguised as women.[21] Several of the gunmen opened fire, leaving seven to eight people injured.[1] The militants were reported to have taken some people hostage,[21] although the Iranian government denied this.[1] The ISIL outlet Amaq News Agency released footage purportedly from a terrorist as he undertook the shooting, captured on the man's smartphone.[8]
The building was subsequently surrounded by security forces. An Iranian member of parliament said that one of his staff was among the victims.[1] Iranian state television reported that one of the attackers had blown himself up inside the parliament building while parliament was in session,[4] while according to some other news agencies, the explosion could have been due to the grenades thrown by the attackers.[22] Associated Press reported that journalists at the site had seen police snipers on nearby rooftops. Shops in the neighborhood were closed. Eyewitnesses said that the gunmen were shooting at people in the street from the fourth floor of the parliament building.[4]
Iran's parliament continued meeting even as shooting erupted outside the main chamber. Ali Larijani, the speaker of the parliament, dismissed the attacks, saying they were a "trivial matter" and that security forces were dealing with them. Iranian MPs posted selfies from inside the parliamentary chamber in a show of defiance.
IRGC special forces operation
The Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) special forces known as Saberin Unit entered the operation scene under the command of Brigadier General Mohammad Pakpour, Commander of the IRGC Ground Forces, and the snipers took up their positions. Minutes later, Major General Mohammad Ali Jafari, chief commander of IRGC, entered the scene accompanied by Brigadier General Hossein Salami, deputy commander of IRGC, Brigadier General Gholamhossein Gheybparvar, commander of Basij and Brigadier General Hossein Nejat, deputy chief of IRGC intelligence office.[23]
A team of the special forces made their way to the upper floors of the parliament and killed one of the terrorists which made the two others begin shooting indiscriminately at people. This shooting revealed their position to the forces. Meanwhile, IRGC forces killed another terrorist before he detonated his suicide vest.[23] The Iranian government later stated that four gunmen had been killed.[1]
Mausoleum attack
The attack on the Mausoleum of Ayatollah Khomeini took place at 10:30 am on 7 June 2017,[24] and the fact that it occurred around the same time as the strike against the Iranian parliament immediately aroused suspicion that the two were coordinated as "twin attacks".[25] According to the New York Times, the attacks lasted for several hours.[26]
According to the administrator of mausoleum of Ayatollah Ruhollah Khomeini, the attack on the mausoleum left one person dead and three people injured.[27] BBC reported that a suicide bomber detonated a bomb at the mausoleum.[1] One female militant was captured alive.[28] The counter-terrorism operation in the Ayatollah Khomeini's shrine was conducted by NAJA.[29] According to NAJA, the attackers who attempted to enter the shrine were taken down by police snipers. One of the terrorists who was shot detonated himself, but the explosion did not harm any other people. Another terrorist started firing at both civilians and police forces; this resulted in one death and five individuals being injured, including a nearby policeman.[29]
Alleged third attack
Government officials later stated that they thwarted a third attack,[1][7] with a terrorist team arrested by security forces.[7]
Timeline of attacks
Column-generating template families
The templates listed here are not interchangeable. For example, using {{col-float}} with {{col-end}} instead of {{col-float-end}} would leave a <div>...</div> open, potentially harming any subsequent formatting.
| Type | Family | Handles wiki
table code?† |
Responsive/ mobile suited |
Start template | Column divider | End template |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Float | "col-float" | Yes | Yes | {{col-float}} | {{col-float-break}} | {{col-float-end}} |
| "columns-start" | Yes | Yes | {{columns-start}} | {{column}} | {{columns-end}} | |
| Columns | "div col" | Yes | Yes | {{div col}} | – | {{div col end}} |
| "columns-list" | No | Yes | {{columns-list}} (wraps div col) | – | – | |
| Flexbox | "flex columns" | No | Yes | {{flex columns}} | – | – |
| Table | "col" | Yes | No | {{col-begin}}, {{col-begin-fixed}} or {{col-begin-small}} |
{{col-break}} or {{col-2}} .. {{col-5}} |
{{col-end}} |
† Can template handle the basic wiki markup {| | || |- |} used to create tables? If not, special templates that produce these elements (such as {{(!}}, {{!}}, {{!!}}, {{!-}}, {{!)}})—or HTML tags (<table>...</table>, <tr>...</tr>, etc.)—need to be used instead.
Responsibility
The Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant claimed responsibility for the attacks.[30] This is the group's first attack in Iran.[1] The Amaq News Agency, related to ISIL, released a 24-second video showing a lifeless body of a man, while a voice says in Arabic: "Do you think we will leave? We will remain, God willing."[4] The attackers were reportedly under the leadership of a commander with the nom de guerre of Abu Aisha.[18]
According to Deutsche Welle, some observers suspected the involvement of different actors, including People's Mujahedin of Iran (MEK). The organization denied that it was involved in the attacks.[31] It was partly because of the target (MEK leaders had said Ayatollah Khomeini's tomb would be among their first), in addition to use of a female attacker and cyanide pill, a regular MEK practice.[32]
Iranian authorities such as members of the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps and the Iranian Minister of Foreign Affairs (Javad Zarif) have accused Saudi Arabia of being behind the attacks.[20] In a Twitter post, Zarif wrote, "Terror-sponsoring despots threaten to bring the fight to our homeland. Proxies attack what their masters despise most: the seat of democracy". His statements referred to the Saudi deputy crown prince Mohammad bin Salman's threats against the country about a month earlier, in which bin Salman asserted that "we will work so that the battle is for them in Iran".[20][19][10]
On 9 June, the Lieutenant Commander of the Islamic Revolutionary Guards Corps (IRGC), Brigadier General Hossein Salami, argued that the attacks in Tehran were the outcome of a trilateral project with Americans, Israelis, and Saudis working together. Salami said that the terrorist strikes aimed at undermining Iran's political and security power after its enemies' back-to-back defeats in regional disputes and proxy warfare over the past years.[11]
On 13 June, the main IRGC Commander, Major General Mohammad Ali Jafari, stated that the terrorists carried out their actions at the demand of Riyadh. He declared, "We have precise intelligence showing that unfortunately, Saudi Arabia in addition to supporting the terrorists, has demanded them to conduct operations in Iran."[13][14]
Reza Seifollhai, the deputy head of Iran's Supreme National Security Council, stated that he believed the militants were native Iranians that the external group had recruited.[6] Multiple witnesses who had heard the gunmen identified them as speaking Arabic with an Iranian accent, possibly revealing the terrorists as ethnic Arabs living in Iran. On 8 June, the government released photographs of five deceased assailants and disclosed their first names; additional information such as their surnames were held back for security purposes.[18]
Hassan Nasrallah, the Secretary General of Hezbollah, stated that the attacks were part of an "international, destructive plan" backed by various states in the region.[18]
Public opinion in Iran
A poll conducted 11 to 17 June 2017, by the Center for International and Security Studies (CISSM) at University of Maryland School of Public Policy & IranPoll with a sample size of 1004 and ±3.1% margin of sampling error among Iranians, indicates that more than half of the responders acknowledge ISIL as the perpetrator of the attacks. The results for the open-ended question was a follows:[33]
| Actor | Percentage |
|---|---|
| Opponents of the Islamic Republic | |
| Other | |
| DK/NA |
In the same opinion poll, answers regarding the possible actors involved in the event was as below (list of groups and countries read by the pollster):
| State/non-state actor | Very likely | Somewhat likely | Somewhat unlikely | Very unlikely | DK/NA |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 78.0 | 16.4 | 1.8 | 2.6 | 1.2 | |
| 66.5 | 20.0 | 3.7 | 6.1 | 3.7 | |
| 65.0 | 21.1 | 3.3 | 7.5 | 3.5 | |
| 61.1 | 23.4 | 3.7 | 9.5 | 2.4 | |
| 24.4 | 35.6 | 12.7 | 14.7 | 12.5 | |
| 16.5 | 36.7 | 14.9 | 24.6 | 7.3 | |
| 11.3 | 35.7 | 14.1 | 27.8 | 11.2 | |
| Iranian separatists | 7.3 | 37.8 | 12.9 | 29.3 | 12.6 |
| 6.1 | 20.7 | 25.3 | 37.4 | 10.5 | |
| 5.2 | 18.5 | 22.6 | 45.2 | 8.5 | |
| 3.4 | 8.4 | 15 | 66.6 | 6.6 | |
| Source: CISSM/IranPoll[33] | |||||
Casualties
Eighteen individuals died at the hands of the ISIL attackers.[34] The assailants fired upon both security personnel and nearby civilians alike. As well as those killed, fifty-two victims were injured.[35][36]
Ahmad Shojaei, head of Iran's Medical jurisprudence, initially announced the incident death toll at 17, with three of the victims women.[37] Six of the seven attackers were killed: four during the parliament shootings and two others at Khomeini's mausoleum. Three of the attackers blew themselves up in the parliament building and the mausoleum; the other three were shot by security forces and law enforcement. All casualties, including victims and attackers, were Iranian. One of the casualties was one of the MP's chief of staff; another was one of the visitors in his office. The video captured by ISIL was also broadcast at his office.[38]
Identity of the attackers
The Intelligence Ministry (VEVAK) released a statement on 8 June 2017 that detailed information on the five attackers and affiliated terrorist cells. It was announced that the full identities of the assailants had been determined after intelligence work by the Ministry, and only the militants' first names were released given that surnames had to be withheld due to certain social and security considerations. According to the Intelligence Ministry, the five individuals involved in carrying out the attacks had a history of past terrorist activities and links to groups with extremist, Wahhabi-related beliefs. They were identified as Seriyas, Fereydoun, Qayyoum, Abu Jahad, and Ramin.[39]
The statement said that the five had left Iran after being recruited by ISIL and had participated in the terrorist group's activities in the Iraqi city of Mosul and the Syrian city of Raqqah. It additionally said they had re-entered Iran in August 2016.[9] Reportedly under the command of "Abu Ayesheh", a high-ranking commander within ISIL, they planned to carry out terror attacks in religious cities. However, the militants had reportedly fled the country following the destruction of their particular network and blows dealt to ISIL leadership.
Before the publication of the statement, Iranian Intelligence Minister Mahmoud Alavi had said that it was still soon to judge whether Saudi Arabia had had a role in the attacks in Tehran. "We witnessed heavy pressure from terrorists, to the extent that we have been identifying and arresting two-member and three-member teams or single individuals every week", said Alavi.[citation needed]
Reactions
Domestic reactions
Ayatollah Ali Khamenei, Supreme Leader of Iran, downplayed the attacks by calling them mere "firecrackers" (Template:Lang-fa) which would not lead to the weakening of Iran's fight against terrorism. He said, "These firecrackers have no effect on Iran. They will soon be eliminated." The Ayatollah also stated that they "are too small to affect the will of the Iranian nation and its officials".[40]

Iranian government officials expressed sympathies for the victims and condemned the attack. President Hassan Rouhani said the attack would make Iran more united in the war against terrorism.[41] "We will prove once again that we will crush the enemies' plots with more unity and more strength," Rouhani said.[42] He also called for regional and international cooperation and unity. First Vice President Eshaq Jahangiri also stated that the government would promote the organized fight against radical terrorism.[43] Iranian Minister of Foreign Affairs Javad Zarif condemned the terrorist attack in Tehran saying, "terrorism is a problem that we face in the Middle East and the whole world".[44]
Iranian parliament speaker Ali Larijani said in his closing statements that the attack was a "minor issue."[8] Two days later while addressing a funeral ceremony for the victims of the attack, Larijani underlined that terrorists tried to undermine the democratic and religious foundations of the nation, but they failed to do so. It further stated that "The United States has aligned itself with the ISIL in the region," claiming that US is behind most of the terrorist acts in the world and that US has demonstrated that it is "the international ISIL."[12]
Tehran Mayor Mohammad Bagher Ghalibaf tweeted "Martyrdom of our dear citizens in a terrorist attack have created deep scars on our hearts."[45] 2017 presidential defeated candidate Ebrahim Raisi also condemned the attacks and said that the attacks showed ISIL's peak helplessness and humiliation.[46]
Major General Mohsen Rezaee of the Revolutionary Guards wrote in an Instagram post that Iran was sure to "severely punish the terrorists who have murdered hundreds, not only in Iran but also in the U.K., Germany, France, Afghanistan, and Pakistan."[47] Iran's Revolutionary Guards also released a statement saying Saudi Arabia was behind the attack.[20] Supreme National Security Council Secretary Ali Shamkhani also stated that authorities had apprehended several people suspected of planning bomb attacks. He noted that the arrests were made over the last few days and added that the attacks were planned for the holy month of Ramadan.[48]
Iranian Sunni leader and Zahedan Friday Prayers Imam Molavi Abdul Hamid condemned the attacks. Blasting the militants' "sinister goals", he remarked, "Blind terrorists martyred fasting people who were referred to the offices of the Parliament."[49]
In a statement that condemned the ISIS attacks, People's Mujahedin of Iran leader Maryam Rajavi reminded that, "ISIS's conduct clearly benefits the Iranian regime's Supreme Leader Khamenei, who wholeheartedly welcomes it as an opportunity to overcome his regime's regional and international impasse and isolation. The founder and the number one state sponsor of terror is thus trying to switch the place of murderer and the victim and portray the central banker of terrorism as a victim."[50]
International reactions
Official condolences were expressed by the governments of various countries and international bodies.[a] United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres condemned the attacks while expressing sympathies for the government of Iran and the families of the victims, and Guterres wished for a quick recovery to all those injured.[67] The United Nations Security Council observed a minute's silence in the aftermath of the attack.[51] Federica Mogherini, European Union Foreign Policy Chief, condemned the attacks and voiced sympathy and solidarity with Iran in a phone-call with Mohammad Javad Zarif, the Iranian Minister of Foreign Affairs.[68] Many around the world also posted #PrayforTehran on social media in solidarity after the attacks.[69]
United States Senators Bernie Sanders and Dianne Feinstein called on the Senate to delay a vote on imposing sanctions on Iran.[70] However, no delay took place and the measures went through shortly. Iranian Parliament Speaker Ali Larijani condemned the sanctions' imposition and remarked that the U.S. government had acted "shamelessly."[71]
President of the United States Donald Trump released a statement in which he prayed for the "innocent victims of terrorist attacks" and said that "states that sponsor terrorism risk falling victim to the evil they promote."[72] Iranian Foreign Minister Mohammad Javad Zarif rejected Trump's statement, calling it "repugnant."[73] Richard N. Haass, the president of the Council on Foreign Relations, also criticized Trump's statement. Haass argued on Twitter that "[c]ondemnation of terrorism cannot be selective if it is to have meaning" and "must condemn it in Tehran as well as in Europe" as well as that the "statement on Iran terror, which after condolences says Iran deserved it, is result of divided staff drafting [without] smart clear guidance".[69][74] Reza Marashi, research director of the National Iranian American Council, called Trump's statement "a vile response to grieving Iranians" and asked what would happen if Iranians claimed that the U.S. deserved the 9/11 attacks. He also pointed out that Iranians held candlelight vigils for 9/11 victims and an entire soccer stadium of Iranians observed a moment of silence as well.[75]
On 10 June 2017, during House Foreign Affairs Committee hearing on Hezbollah, Republican congressman Dana Rohrabacher stated that:[76]
We have recently seen an attack on Iran, and the Iranian government, the mullahs, believe that Sunni forces have attacked them. This may signal a ratcheting up of certain commitments by the United States of America. As far as I'm concerned, I just want to make this point and see what you think, isn't it a good thing for us to have the United States finally backing up Sunnis who will attack Hezbollah and the Shiite threat to us? Isn't that a good thing? And if so, maybe this is a Trump — maybe it's a Trump strategy of actually supporting one group against another, considering that you have two terrorist organizations.
Rohrabacher's statement was criticised in social media, by British left-wing journalist Mehdi Hasan, Human Rights Watch Deputy Director Jim Murphy, journalist Negar Mortazavi and the National Iranian American Council, among others.[76] In a further statement to clarify his position, Rohrabacher stated that he "oppose the use of force against unarmed civilians no matter who is the victim or who is doing the killing" but he is also against "Iran's vicious Mullah monarchy" and "when it comes to Sunni terrorists or Shiite terrorists, I prefer them to target each other rather than any other victims, especially innocent civilians and Americans." Also added that it will "require support for those proud Iranians who want to win their freedom and heritage from Mullahs and are willing to fight for it. That does not include Isis, but it may include a lot of Iranians who see blowing up Khomeini's mausoleum as an expression of freedom from the yolk [sic] of Islamic terror."[77]
Following the events, multiple Iranian officials as well as organizations such as the Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps suggested that Saudi Arabia was responsible.[78] Adel al-Jubeir, the Foreign Affairs Minister of Saudi Arabia, denied his country's involvement in the attacks and said Riyadh had no knowledge of who had committed them. While stating that his administration is unwilling reestablish normal diplomatic ties with Iran, he additionally condemned the terrorist attacks and "the killing of the innocent anywhere it occurs."[79] Supreme Leader Ayatollah Ali Khamenei remarked in a 9 June message that the attacks had spread hatred towards the Saudi government, which he labeled one of the "stooges" of the U.S.[36]
Aftermath
Funeral and farewells
A state funeral held on 9 June 2017 at the Parliament's headquarters was attended by Iranian officials such as President Hassan Rouhani, Parliament Speaker Ali Larijani, and Chief Justice Sadeq Larijani. Other individuals joining the ceremony included government ministers and senior figures such as Ayatollah Mohammad Mohammadi-Golpayegani, the head of the formal office of Supreme Leader Ayatollah Khamenei. Several foreign ambassadors came as well. The survivors of the Tehran attacks who attended held up pictures of the victims.[15]
In a written message to the ceremony, Ayatollah Khamenei stressed that the attacks "will not damage our nation's determination to fight terrorism". He stated as well that the events "will only increase hatred for the governments of the United States and their stooges in the region like Saudi Arabia."[36] During the funeral processions, many individuals in the massive crowds chanted slogans against both the American and Saudi governments, blaming them for the violence.[15]
Addressing the ceremony, the Parliament Speaker said, "Today is a hard day for the Iranian nation. Farewell to dear ones, who were sadly martyred". He remarked that the "terrorists fell short of their aim" yet still managed to blindly target civilians and mere state employees before the attacks ended. President Rouhani's speech stressed national unity, with the leader saying that "the nation will undoubtedly emerge victorious".[15]
Arrests of terrorist suspects
After the success of Iranian intelligence operations, including the cooperation of some of the families of the terrorists, forty-one ISIL militants were identified and arrested on 9 June 2017. They were taken in across the country, including in Kermanshah, Kurdistan, and West Azarbaijan as well as within Tehran itself. Upon arresting the terrorists, Iranian authorities found weapons, bomb materials, explosive belts, communications equipment, and forged documents. While reporting these positive results, officials emphasized as well that efforts against ISIL networks must continue outside of Iran's borders.[80]
On 10 June, Tehran police had a particular breakthrough in discovering the car that the terrorists had used. Iranian security forces announced that day that their intelligence efforts succeeded in finding and killing the mastermind and main commander behind the attacks. As well, seven individuals in southern Larestan County were taken in that day for suspected ties to the ISIL organization.[16]
Military response
On 18 June 2017, the IRGC announced that a series of medium-range ground-to-ground missiles were launched at ISIL group headquarters in the Syrian city of Dayr al-Zawr, the missiles being fired from Iran's western provinces of Kermanshah and Kurdistan. Striking in response to the terrorist attacks in Tehran, the IRGC stated that their strikes resulted in the death of a significant number of extremists as well as the destruction of a large number of weapons, ammunition, and equipment belonging to them.[34] The Iranian government semi-officially released a video of the actual military launch. Afterward, the Iranian Ambassador to the United Kingdom, Hamid Baeidinejad, declared that the strikes "manifested the will and capacity of Iran to fight against terrorism and security threats."[81]
In a public statement related to the strikes, published by its Public Relations Office, the IRGC cautioned that the missile strikes were just a warning to deter any further action by the terrorists. It specifically read that the "IRGC warns the Takfiri terrorists and their regional and trans-regional supporters that they would be engulfed by its revolutionary wrath and flames of the fire of its revenge in case they repeat any such devilish and dirty move in future."[35] Some Iranian sources suggested that the IRGC chose Dayr al-Zawr given that the city had begun to serve as the primary center of assembly, command, and logistics for ISIL militants lately where the terrorists had moved ground after defeats in Aleppo and Mosul over the previous months.[82]
While Iranian forces have undertaken multiple efforts against ISIL in the past, these were the first admitted strikes launched from Iranian soil.[81] The missiles reportedly traveled about six-hundred kilometers until they reached the targeted city. The same day as the launch, Ayatollah Khamenei held meetings with the families of Iranian personnel fighting inside both Iraq and Syria, the leader giving a speech stressing the need for continued action outside of Iran's borders.[34]
The day after the strike, the IRGC released official footage depicting moments in which the missiles successfully hit their targets. The videos were transmitted by drones that the IRGC flew from Damascus over Dayr al-Zour. IRGC spokesman Brigadier General Ramezan Sharif said, "Fortunately, all incoming reports and images of drones which were monitoring the operation suggest that the six medium-range powerful Iranian missiles have precisely hit the targets, the key bases of terrorists in the general area of Dayr al-Zawr inside Syria." As well, Amir Ali Hajizadeh, the commander of the IRGC's Aerospace Force, stated the videos showed them that "the missiles precisely hit their targets."[83][84]
See also
- 2017 in Iran
- Iran and ISIL
- List of terrorist incidents in June 2017
- List of terrorist incidents linked to ISIL
- List of attacks on legislatures
Notes
- ^ Including Afghanistan,[51][52] Algeria,[51] Armenia,[51][52] Australia,[53] Austria,[51] Azerbaijan,[51] Brazil,[51] Canada,[54][55] China,[56] Czech Republic,[51] Estonia,[52] France,[51][52] Georgia,[51] Germany,[51][52] India,[51] Indonesia,[57] Iraq,[51][52] Ireland,[51] Italy,[51][52] Japan,[52] Jordan,[51][52] Latvia,[58] Lebanon,[51][52] Lithuania,[51] Malaysia,[59] Netherlands,[60] Norway,[52] Oman,[51][52] Pakistan,[51][52] Qatar,[51][52] Russia,[51][54] Singapore,[61] Sweden,[62] Syria,[51][52][54] Tajikistan,[63] Turkey,[51][52] the United Arab Emirates,[51][52] the United Kingdom,[51][52] the United States[51][54][64][65] and Vietnam.[66]
References
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j "Iran attacks: 'IS' hits Parliament and Khomeini mausoleum". BBC. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran attackers fought for Islamic State in Syria, Iraq: ministry". Reuters. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "وزارت اطلاعات/هویت عناصر تروریستی حوادث دیروز تهران". vaja.ir.
- ^ a b c d e "Islamic State claims attacks on Iran parliament, shrine". Associated Press. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Erdbrink, Thomas. "Islamic State Claims Deadly Iran Attacks on Parliament and Khomeini Tomb". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
"Iran shootings: Parliament and shrine attacked". BBC. 7 June 2017. - ^ a b "Shootings reported at Iranian parliament and Khomeini shrine". The Guardian. France-Presse Agence. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d Cumming, Jason; Abdelkader, Rima. "Iran Parliament, Khomeini's Mausoleum Attacked; ISIS Claims Responsibility". Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b c Bozorgmehr, Shirzad; Dewan, Angela (7 June 2017). "Iran attacks: Twin assaults on parliament and shrine rock Tehran". CNN. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b Associated Press (9 June 2017). "Iran attackers 'long affiliated with Wahhabi'". The Standard. Archived from the original on 10 June 2017. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Farsnews". en.farsnews.com. Archived from the original on 15 April 2019. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Farsnews". en.farsnews.com. Archived from the original on 19 July 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Farsnews". en.farsnews.com. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Farsnews". en.farsnews.com. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ^ a b Entekhab.ir, پایگاه خبری تحلیلی انتخاب |. "فرمانده کل سپاه: اطلاعات دقیق داریم که عربستان عملیات در ایران را از تروریستها مطالبه کردهاست". پایگاه خبری تحلیلی انتخاب | Entekhab.ir (in Persian). Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Iran holds funeral for terror victims". presstv.com. 9 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Iran kills mastermind behind attacks, arrests more". Channel NewsAsia. 11 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ Wood, Graeme (March 2015). "What ISIS Really Wants". The Atlantic. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d Erdbrink, Thomas (8 June 2017). "Iran Calls Trump's Response to Attacks 'Repugnant'". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b Khan, Taimur (3 May 2017). "Saudi Prince Mohammed bin Salman's warning to Iran | The National". The National. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d e "At least 12 killed in militant attack in Iran, Guards blames Saudi Arabia". Reuters. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b "Shooting at Parliament and the Mausoleum of Imam". Mashregh News (in Persian). 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "One attacker blew himself up in the Iranian parliament: IRIB". Reuters. 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b "IRGC Special Forces Corps timely action/ How the terrorists were killed by IRGC raid". Tasnim News Agency. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Ministry of Interior affairs statement - اطلاعیه وزارت کشور درباره وقایع تروریستی روز چهارشنبه تهران". ایسنا (in Persian). 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Twin attacks in Iran target parliament and shrine". CNN. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "At Least 12 Killed in Pair of Terrorist Attacks in Iran".
- ^ http://www.farsnews.com/newstext.php?nn=13960317000900
- ^ "Invasion four terrorist to Khomeini Shrine/ One woman was captured". fa.alalam.ir (in Persian). Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b "NAJA statement on the terrorist attack in Imam Khomeini's shrine". Farsnews. Farsnews. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "IS-claimed attacks on Iran's parliament, shrine kill 12". Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Twin attacks strike Iran's parliament, Khomeini's tomb". Deutsche Welle. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Thomas Erdbrink; Mujib Mashal (7 June 2017). "At Least 12 Killed in Pair of Terrorist Attacks in Iran". The New York Times. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b "The Ramifications of Rouhani's Re-election" (PDF), Center for International and Security Studies at Maryland (CISSM) & IranPoll, p. 5, June 2017, retrieved 19 August 2017
- ^ a b c "IRGC launches missiles at Daesh headquarters in Syria from western Iran". presstv.ir. 18 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ a b "UPDATED: Iran Launches Missile Strikes at ISIL to Avenge Tehran Terrorist Attacks". farsnews.com. 18 June 2017. Archived from the original on 28 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ a b c "Leader: Terrorist Attacks to Make Iranians Hate US More". farsnews.com. 9 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "Tehran Shooting: Casualties Reported after Twin Attacks". 8 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "جزییات عملیات تروریستی در مجلس و حرم امام خمینی". 8 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran releases information on, photos of terrorists in Tehran attack". Press TV. Archived from the original on 10 June 2017.
According to the Intelligence Ministry's Thursday statement, the individuals involved in carrying out the attacks were five elements with a history of past terrorist activities and linked to Wahhabi and Takfiri groups. They were identified as Seriyas, Fereydoun, Qayyoum, Abu-Jahad, and Ramin.
- ^ Hafezi, Parisa (2017). "Khamenei calls Tehran attacks "fireworks" that will have no effect on Iran". Reuters. Reuters. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ "Rouhani Says Tehran Attacks Will Make Iran More United: ISNA". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran's Rouhani calls for global unity after Tehran attacks". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "جهانگیری:دولت مبارزه ریشهای با تروریسم سازمانیافته را پیش خواهد برد". Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Zarif condemns Tehran's terrorist attacks upon arrival in Turkey". Mehr News Agency. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "واکنش قالیباف به حوادث تروریستی تهران". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "واکنش رئیسی به حوادث تروریستی تهران". 7 June 2017.
- ^ News, پایگاه خبری تحلیلی فردا. "واکنش محسن رضایی به حملات تروریستی امروز تهران". پایگاه خبری تحلیلی فردا | Farda News (in Persian).
{{cite news}}:|last1=has generic name (help) - ^ "Iran thwarts bomb attack in Tehran". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "مولوی عبدالحمید حادثه تروریستی تهران را محکوم کرد". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ Just because ISIS attacked Iran doesn't mean Iran isn't supporting terrorism. June 12, 2017. Retrieved June 13, 2017
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z aa "Global condemnation pours in over deadly terror attacks in Tehran". PressTV. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r "World Condemns Tehran Terrorist Attacks". Iran Front Page. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "The Latest: Australia condemns attacks in Iran". accessWDUN. Associated Press. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ a b c d "Tehran police detain 5 as ISIS claims responsibility for attacks in heart of Iran". CBC News. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Canada condemns terrorist attacks in Iran". canada.ca. Government of Canada. 7 June 2017. Archived from the original on 8 June 2017.
- ^ An (9 June 2017). "China condemns terrorist attacks in Tehran, calling for peace in Gulf". Xinhua News Agency. Retrieved 9 June 2017.
- ^ Heru (8 June 2017). "Indonesia condemns terror act in Tehran". Antara. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Latvian Foreign Minister offers condolences to Iran over the attacks in Tehran". Ministry of Foreign Affairs, Latvia. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Fairuz Mohd Shahar (8 June 2017). "No M'sian affected by Iran terror attacks; gov't extends condolences". New Straits Times. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Koenders veroordeelt aanslagen Iran" (in Dutch). Buitenland. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Singapore slams twin terror attacks in Iran; no Singaporeans affected". The Straits Times. 8 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Margot Wallström (8 June 2017). "#Sweden condemns the terrorist attacks in Iran. We offer our heartfelt condolences to Iran and the Iranian people". Twitter. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Tajik president condemns Tehran terrorist attacks". Irna.ir. 8 June 2017. Retrieved 14 June 2017.
- ^ Gehrke, Joel. "US condemns ISIS attack in Iran". Washington Examiner.
- ^ "Terrorist Attacks in Tehran". U.S. Department of State. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Vietnam condemns terrorist attacks in Iran". Vietnam News Agency. Vietnam Net. 10 June 2017. Retrieved 11 June 2017.
- ^ "Statement attributable to the Spokesman for the Secretary-General on attacks in Tehran". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Condemnations Pour in Following Terrorist Attacks in Iran". 7 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ a b Estatie, Lamia (7 June 2017). "#PrayforTehran: Messages of solidarity after attacks". BBC News. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Naga Siu, Diamond (7 June 2017). "Sanders, Feinstein call for delay in Iran sanctions vote after Tehran attack". POLITICO. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran's Parl. Speaker Calls US "International ISIS"". 9 June 2017.
- ^ Engel, Pamela (7 June 2017). "Trump on ISIS attack in Iran: 'States that sponsor terrorism risk falling victim to the evil they promote'". Business Insider. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran minister calls Trump's condolences for attacks 'repugnant'". CNBC. 8 June 2017. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Haass, Richard N. (7 June 2017). "WH statement on Iran terror, which after condolences says Iran deserved it, is result of divided staff drafting w/o smart clear guidance". @RichardHaass. Retrieved 8 June 2017.
- ^ Marashi, Reza (9 June 2017). "Does Donald Trump Support Terrorism Against Iran?". Huffington Post. Retrieved 10 June 2017.
- ^ a b Garcia, Carlos (11 June 2017). "GOP Rep criticized for shocking statement on ISIS attack in Iran". TheBlaze. Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ^ "Rohrabacher: Blow Khomeini's mausoleum". Archived from the original on 16 June 2017. Retrieved 15 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran accuses Saudi Arabia of Tehran attacks". Al Jazeera. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "Saudi minister denies his country involved in Iran attacks". Arab News. 7 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "Iran says arrested 48 Daesh Wahhabi terrorists". presstv.com. 9 June 2017. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ a b Dehghan, Saeed Kamali (18 June 2017). "Iran targets 'terrorists' in missile strike on Isis-held Syrian town". The Guardian. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "خبرگزاری تسنیم - چرا سپاه "دیرالزور" سوریه را برای حمله موشکی انتخاب کرد؟". خبرگزاری تسنیم (in Persian). tasnimnews.com. Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "PressTV-Iran shows strong hand with strike + impact video". Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- ^ "PressTV-IRGC warns terrorists, backers of 'more revenge'". Retrieved 19 June 2017.
- 2017 Tehran attacks
- 2017 in Iran
- 2017 murders in Asia
- 21st century in Tehran
- Attacks on legislatures
- Crime in Tehran
- Explosions in 2017
- Explosions in Iran
- Hostage taking in Iran
- ISIL terrorist incidents
- 10th legislature of the Islamic Republic of Iran
- Islamic terrorist incidents in 2017
- June 2017 crimes in Asia
- Massacres in 2017
- Massacres in Iran
- Suicide bombings in Iran
- Terrorist incidents in Iran
- Mass murder in 2017
- Attacks on buildings and structures in Iran
- Terrorist incidents in Iran in 2017






