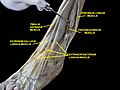
Fibularis brevis
A request that this article title be changed to Peroneus brevis muscle is under discussion. Please do not move this article until the discussion is closed. |
| Fibularis brevis muscle | |
|---|---|
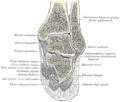
 The mucous sheaths of the tendons around the ankle. Lateral aspect. (Peroneus brevis labeled at bottom left.) | |
 Animation | |
| Details | |
| Origin | Lower two-thirds of lateral fibula |
| Insertion | Fifth metatarsal |
| Artery | Fibular artery (peroneal artery) |
| Nerve | Superficial fibular nerve |
| Actions | Plantarflexion, eversion |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | Musculus fibularis brevis |
| TA98 | A04.7.02.042 |
| TA2 | 2653 |
| FMA | 22540 |
| Anatomical terms of muscle | |
The peroneus brevis muscle (or fibularis brevis muscle) lies under cover of the peroneus longus, and is the shorter and smaller of the peroneus muscles.
Structure

It arises from the lower two-thirds of the lateral surface of the body of the fibula, medial to the peroneus longus, and from the intermuscular septa separating it from the adjacent muscles on the front and back of the leg.
The fibers pass vertically downward, and end in a tendon which runs behind the lateral malleolus along with but in front of that of the preceding muscle, the two tendons being enclosed in the same compartment and lubricated by a common mucous sheath.
It then runs forward on the lateral side of the calcaneus, above the calcaneal tubercle and the tendon of the peroneus longus, and is inserted into the tuberosity at the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, on its lateral side. When the base of the fifth metatarsal is fractured, the peroneus brevis may pull on and displace the proximal fragment (Jones Fracture). An inversion sprain of the foot may pull the tendon such that it avulses the tuberosity at the base of the fifth metatarsal.
Nerve supply
It is innervated by the superficial fibular nerve, also known as the superficial peroneal nerve.[1]
Function
The peroneus brevis muscle is the strongest abductor of the foot.[2] It also assists in weak plantarflexion and eversion of the foot.[2] It provides lateral stability to the foot and ankle.[3]
History
Etymology
The terms "Peroneal" (i.e., Artery, Retinaculum) and "Peroneus" (i.e., Longus and Brevis) are derived from the Greek word Perone (pronounced Pair-uh-knee) meaning pin of a brooch or a buckle. In medical terminology, both terms refer to being of or relating to the fibula or to the outer portion of the leg.
Additional images
-
Coronal section through right ankle and subtalar joints. (Label for Peroneus brevis is at right, third from the bottom.)
-
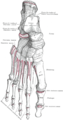
Bones of the right leg. Anterior surface.
-
Bones of the right foot. Dorsal surface.
-
Muscles of the front of the leg.
-
Cross-section through middle of leg.
-
The popliteal, posterior tibial, and fibular arteries.
-
Back of left lower extremity.
-
Fibularis brevis muscle
-
Muscles of the sole of the foot.
-
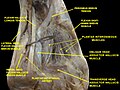
Dorsum of Foot. Deep dissection.
-
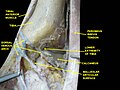
Musclea of Leg. Lateral view. Deep dissection.
See also
References
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 487 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 487 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
- ^ Apaydin, Nihal (2015-01-01), Tubbs, R. Shane; Rizk, Elias; Shoja, Mohammadali M.; Loukas, Marios (eds.), "Chapter 47 - Variations of the Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses and Their Branches", Nerves and Nerve Injuries, San Diego: Academic Press, pp. 627–645, doi:10.1016/b978-0-12-410390-0.00049-4, ISBN 978-0-12-410390-0, retrieved 2021-02-20
- ^ a b Sammarco, Vincent James; James Sammarco, G. (2008-01-01), Porter, David A.; Schon, Lew C. (eds.), "Chapter 6 - Injuries to the Tibialis Anterior, Peroneal Tendons, and Long Flexors of the Toes", Baxter's the Foot and Ankle in Sport (Second Edition), Philadelphia: Mosby, pp. 121–146, doi:10.1016/b978-032302358-0.10006-5, ISBN 978-0-323-02358-0, retrieved 2021-02-20
- ^ Mansfield, Paul Jackson; Neumann, Donald A. (2019-01-01), Mansfield, Paul Jackson; Neumann, Donald A. (eds.), "Chapter 11 - Structure and Function of the Ankle and Foot", Essentials of Kinesiology for the Physical Therapist Assistant (Third Edition), St. Louis (MO): Mosby, pp. 311–350, doi:10.1016/b978-0-323-54498-6.00011-4, ISBN 978-0-323-54498-6, retrieved 2021-02-21
External links
- Anatomy photo:15:st-0407 at the SUNY Downstate Medical Center
- PTCentral