Polish Land Forces
| Land Forces | |
|---|---|
| Wojska Lądowe | |
 | |
| Founded | 1918 |
| Country | Poland |
| Type | Ground forces |
| Size | 62,000 military[1] 800 tanks 5,000 IFV/APC 280 helicopters[2] |
| Part of | Polish Armed Forces |
| Headquarters | Warsaw |
| March | "Marsz Pierwszej Brygady" (Template:Lang-en) |
| Engagements | Polish–Ukrainian War Polish–Czechoslovak War Polish–Soviet War Polish–Lithuanian War World War II - Western Front World War II - Eastern Front Kosovo Force War in Iraq War in Afghanistan EU Force Chad/CAR |
| Commanders | |
| Chief of the General Staff | gen. broni Rajmund Andrzejczak |
| General Commander | gen. broni Jarosław Mika |
| Inspector of the Land Forces | gen. bryg. Wojciech Grabowski |
| Insignia | |
| Flag[3] |  |
| Banner of the Commander in Chief |  |
The Land Forces (Template:Lang-pl) are a military branch of the Polish Armed Forces. They currently contain some 62,000[1] active personnel and form many components of the European Union and NATO deployments around the world. Poland's recorded military history stretches back a millennium – since the 10th century (see List of Polish wars and History of the Polish Army), but Poland's modern army was formed after the country regained independence following World War I in 1918.
History
1918–1938
When Poland regained independence in 1918, it recreated its military which participated in the Polish–Soviet War of 1919–1921, and in the two smaller conflicts ( Polish–Ukrainian War (1918–1919) and the Polish–Lithuanian War (1920)).
Initially, right after the First World War, Poland had five military districts (1918–1921):
- Poznań Military District (Poznański Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Poznań
- Kraków Military District (Krakowski Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Kraków
- Łódź Military District (Łódzki Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Łódź
- Warsaw Military District (Warszawski Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Warsaw
- Lublin Military District (Lubelski Okręg Wojskowy), HQ in Lublin.

The Polish Land Forces as readied for the Polish–Soviet War was made up of soldiers who had formerly served in the various partitioning empires, supported by some international volunteers.[4] There appear to have been a total of around thirty Polish divisions involved. Boris Savinkov was at the head of an army of 20,000 to 30,000 largely Russian POWs, and was accompanied by Dmitry Merezhkovsky and Zinaida Gippius. The Polish forces grew from approximately 100,000 in 1918 to over 500,000 in early 1920.[5] In August 1920, the Polish army had reached a total strength of 737,767 people; half of that was on the frontline. Given Soviet losses, there was rough numerical parity between the two armies; and by the time of the Battle of Warsaw Poles might have even had a slight advantage in numbers and logistics.[6]
Among the major formations involved on the Polish side were a number of Fronts, including the Lithuanian-Belarusian Front, and about seven armies, including the First Polish Army.
1939–1945

The German invasion of Poland began on 1 September 1939, and the Wehrmacht seized half the country quickly despite heavy Polish resistance. Among the erroneous myths generated by this campaign were accounts of Polish cavalry charging German tanks, which did not, in fact, take place. In the east, the Red Army took the other half of the country in accordance with the Nazi-Soviet Pact. Following the country's fall, Polish soldiers began regrouping in what was to become the Polish Army in France. Both the Polish Armed Forces in the West and the Polish Armed Forces in the East, as well as interior (partisan) forces, primarily represented by the Home Army (AK) had land forces during the Second World War. While the forces fighting under the Allied banner were supported by the Polish Air Force and Navy, the partisan forces were an exclusive land formation.
However the army operational today has its roots in the surrogate force formed in support of Soviet interests during the establishment of the People's Republic of Poland after the Second World War. Two Polish armies, the First Army (Poland) and the Second Army fought with the Red Army on the Eastern Front, supported by some Polish Air Force elements. The formation of a Third Army was begun but not completed.
1945–1989
 |
| Polish Armed Forces |
|---|
| Branches |
|
|
| History |
|
Timeline Wars |
| Personnel |
|
Senior officers Rank insignia Awards Oaths |
| Equipment |
|
Land Forces Navy |

The end of the war found the Polish Army in the midst of intense organisational development. Although the implementation of the Polish Front concept was abandoned, new tactical unit and troop types were created. As a result of mobilisation, troop numbers in May 1945 reached 370,000 soldiers, while in September 1945 440,000. Military districts were organised in liberated areas. The districts exercised direct authority over the units stationed on the territory administered by them. Returning to the country, the Second Army was tasked with the protection of the western border of the state from Jelenia Gora to Kamien Pomorski, and on the basis of its headquarters, the staff of the Poznan Military District was created at Poznań. The southern border, from Jelenia Gora to the Użok railway station (at the junction of the Polish, the Soviet and the Czechoslovak borders) was occupied by the First Army. Its headquarters staff formed the basis of the Silesian Military District.
In mid-1945, after the end of World War II, the Polish Army, as part of the overall armed forces, the People's Army of Poland, was divided into six (later seven) districts. These were the Warsaw Military District, HQ in Warsaw, the Lublin Military District, HQ in Lublin, the Kraków Military District, HQ in Kraków, the Lodz Military District, HQ in Lodz, the Poznan Military District, HQ in Poznan, the Pomeranian Military District, HQ in Torun (formed from the staff of the short-lived LWP 1st Army Corps) and the Silesian Military District, HQ in Katowice, created in the fall of 1945.
In June 1945 the 1st, 3rd and 8th Infantry Divisions were assigned internal security duties, while the 4th Infantry Division was reorganised for the purpose of creating the Internal Security Corps (KBW). The rule was that military units were used primarily against the Ukrainian Insurgent Army (UPA), while the Internal Security Corps was used to fight the armed underground independence. Often however army units fought the underground resistance, and vice versa. The culmination of the UPA suppression operation was the so-called 'Wisła Action' (Operation Vistula) which took place in 1947. At the same time demobilisation took place, moving the armed forces to a peacetime footing. On 10 August 1945 a "decree of the partial demobilisation" of the armed forces was issued. The next demobilisation phase took place in February and December 1946.
One of the most important tasks facing the army after the war was mine clearance. Between 1944 and 1956 the demining operation involved 44 engineering units or about 19,000 sappers. They cleared mines and other munitions in a clearance area of more than 250,000 square kilometers (80% of the country). 14.75 million munitions of various types and 59 million bullets, bombs and other ammunition were found and removed. The mining operations cost the lives of 646 sappers.
In 1949 the military districts were reduced to four. They were the Pomeranian Military District, HQ in Bydgoszcz, the Silesian Military District, HQ in Wroclaw, the Warsaw Military District, HQ in Warsaw, and the Kraków Military District with its headquarters in Kraków. In November 1953, the Kraków Military District was dissolved and until 1992, Poland was divided into three districts.
Following victory and the movement of Polish borders these troops and other Polish soldiers thought loyal to their Soviet overlords were built up into a force which was to form part of the Warsaw Pact. Polish Army troops would have formed part of the second strategic echelon deployed for an attack on NATO's Allied Forces Central Europe. A Polish Front headquarters was formed in 1958, along with three armies formed from 1955, the First Polish Army, the Second Army, and the Fourth Army, mobilisation-only headquarters that were to be formed within the three districts.[7] The Polish Front headquarters was eventually deactivated in 1990, and the three-army mobilisation scheme was likewise abandoned. Polish land forces during the communist era also included troops dedicated to internal security – the Territorial Defence Forces – and control of the country's borders.[8]

Until the fall of communism the army's prestige continued to fall, as it was used by the communist government to violently suppress several outbursts of protest, including the Poznań 1956 protests, the Polish 1970 protests, and protests during Martial law in Poland in 1981–1982. Troops of the Silesian Military District also took part in the suppressing of the 1968 democratisation process of Czechoslovakia, commonly known as the Prague Spring.
In 1989 the Pomeranian Military District controlled the 8th, 12th, 15th, 16th, and 20th Divisions, the Silesian Military District controlled the 2nd, 4th, 5th, 10th, and 11th Divisions, and the Warsaw Military District the 1st, 3rd, and 9th Divisions, plus the 6th Airborne Division earmarked for Front control.[9] The 7th Sea Landing Division was based within the Pomeranian Military District but probably earmarked for front control. The two districts facing Germany each controlled four divisions in 1990, which had been recently reorganised, in line with the late 1990s Soviet defensive doctrine, from a 3:1 mix of motor rifle : tank regiments into a 2:2 mix of motor rifle and tank regiments.[10] The Warsaw Military District in the east controlled only the 1st Mechanised Division. Two other mechanised divisions in that district had been disbanded in 1988. There was also the 6th Airborne Division and the 7th Sea Landing Division, possibly intended to form part of a Warsaw Pact attack on Denmark, to open the Baltic straits to the North Sea and beyond. Strength counted 205,000 personnel of which 168,000 were conscripts.
After 1989

Following the end of the Cold War the Wojska Lądowe was drastically reduced and reorganised. In 1992, the Kraków Military District was recreated. From nine divisions, the total was planned in 2001 to fall to four, plus six independent brigades.[11] Since 1 January 1999, Poland has been divided into two military districts. These are the Pomeranian Military District (Pomorski Okręg Wojskowy) with HQ in Bydgoszcz, covering northern Poland, and the Silesian Military District (Śląski Okręg Wojskowy) with HQ in Wrocław, covering southern Poland.
From that date the former Krakow Military District became the headquarters of the Air-Mechanized Corps, which in turn later became the headquarters of the 2nd Mechanised Corps. On 1 September 2011 the 1st Warsaw Mechanised Division was disbanded.

General Edward Pietrzyk served as commander of the Polish Land Forces from 2000 to September 2006. He was succeeded by General Waldemar Skrzypczak (2006–2009).
In May 2014, Defence Minister Tomasz Siemoniak announced plans for the future acquisition of attack helicopters in response to the Ukraine crisis.[12] On 25 November 2015, chief of National Defence Commission Michał Jach, indicated the necessity to increase the number of Polish troops from 100,000 to 150,000. However, Jach stressed that the process was complicated and should not be rushed.[13]
Participation in peacekeeping operations
From the 1950s the Polish Land Forces have contributed troops to peacekeeping operations, initially the Neutral Nations Supervisory Commission in Korea. Poland contributed troops to UNIFIL in Lebanon since 1982, but it was announced in April 2009 that Polish troops would withdraw completely by October 2009.[14] Poland sent a divisional headquarters and a brigade to Iraq after the 2003 Iraq war. Poland sent ten rotations of troops, manning a significant portion of Multinational Division Central-South. At its peak Poland had 2,500 soldiers in the south of the country. Poland deployed about ten attack and transport helicopters as part of its force in Iraq between 2004 and 2008.[15] These helicopters formed the Independent Air Assault Group (pl:Samodzielna Grupa Powietrzno-Szturmowa). The division was disbanded in 2008, though Polish advisory and training personnel, seemingly a Military Advisory Liaison Team (MALT) stayed until at least 2011 (see pl:PKW Irak). One of the most recent missions was MINURCAT in Chad and the Central African Republic, where Poland despatched troops from 2007 to 2010. Among the deployed troops were two Reconnaissance companies, a Military Gendarmerie unit, a component of the 10th Logistics Brigade, elements of the 5th Military Engineers Regiment, and three Mil Mi-17 helicopters.
Equipment and modernization

A new long-term program, designed to modernize the Polish Armed Forces, was introduced in 2019. Over the period of the next 10 to 14 years a large portion of the equipment currently used by the Polish Army will be either upgraded or replaced. Some elements of this program are already in place. The Polish Ministry of Defence signed a contract for the modernization of all Leopard 2 main battle tanks used by the Polish Army to Leopard 2PL standard prior to 2023 (the first Leopard 2PL arrived in March 2018). At present, Polish Army has a stock of 1009 tanks (2017). There are a total of 249 Leopard 2 tanks (117 Leopard 2A4, 105 Leopard 2A5, 25 Leopard 2PL,[16] 2 Leopard 2NJ), 232 PT-91 tanks that underwent modernization in 2016, and 328 T-72 tanks. 230 of the T-72 are being upgraded by the Bumar-Labedy arms manufacturing plant. Some of the improvements are: installation of new radio communication systems, digital engine control and start-up system, 3rd generation thermal imaging cameras, external transport baskets, and any necessary overhauls and repairs that can improve their longevity and combat ability on the modern battlefield.[17] Looking towards the future, the 'Wilk' procurement programme envisions the acquisition of up to 500 new tanks.[18] Some of the T-72s and PT-91s are to be replaced by 250 M1A2 Abrams SEPv3 main battle tanks (separate from the Wilk programme) after the US State Department authorized the sale of the tanks to Poland (plus ammunition, spare parts, training, and logistical vehicles) on February 18, 2022.[19]

As for air and missile defense, acquisition of Poprad Anti-Air missile systems are in the final stages, while legacy systems are to be replaced through the Wisla and Narew procurement programs. The Wisla program covers medium range air defense and is being fulfilled through the acquisition of 2 Patriot air and missile defense batteries integrated with IBCS (delivery scheduled for late 2022), with plans to order six further batteries. The Narew program entails short range air defense (SHORAD), which is in the final stages of design selection and awarding of contracts, and will be primarily sourced from Polish defense contractors.[20][21]
The Polish army has 863 new KTO Rosomak multi-role wheeled armoured personnel carriers.[22] They will be combined with new BWP Borsuk infantry fighting vehicles. The gradual replacement of older BWP-1 with this new design is planned to commence from 2023 onward (prototypes are currently being tested).[22]
New rifles (FB MSBS Grot) and pistols (Vis-100) are being brought into service to supplement current FB Beryl rifles as well as to replace FB P-83 Wanad pistols and AKM rifles.[23]

New WR-40 Langusta rocket launchers equipped with state-of-the-art Topaz fire control are also being introduced. In 2019 the Ministry of Military Affairs ordered twenty M142 HIMARS launchers and support vehicles.[24] The new self-propelled NATO-compatible tracked AHS Krab gun-howitzer will replace 2S1 Goździk, and new wheeled AHS Kryl howitzer will replace wz. 1977 Dana. Deliveries of M120K Rak mortar have been ongoing since 2017. Poland ordered 122 mortars, 60 command vehicles (based on the KTO Rosomak fighting platform) and support vehicles.[25] New technical recognition vehicles, Rosomak WRT, are also entering service since 2016. New Individual Warfare System "Tytan" (Titan) is also being developed. This is an integrated personal combat system designed for individual soldiers that includes personal computer, new protective uniform, modular body armour, night vision devices, advanced communication system, etc.
Rank insignia
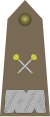
- Officers
| NATO code | OF-10 | OF-9 | OF-8 | OF-7 | OF-6 | OF-5 | OF-4 | OF-3 | OF-2 | OF-1 | ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||
| Marszałek Polski | Generał | Generał broni | Generał dywizji | Generał brygady | Pułkownik | Podpułkownik | Major | Kapitan | Porucznik | Podporucznik | ||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | marsz. | gen. | gen.broni | gen.dyw. | gen.bryg. | płk | ppłk | mjr | kpt. | por. | ppor. | |||||||||||||
- Other ranks
| NATO code | OR-9 | OR-8 | OR-7 | OR-6 | OR-5 | OR-4 | OR-3 | OR-2 | OR-1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Starszy chorąży sztabowy | Starszy chorąży | Chorąży | Młodszy chorąży | Starszy sierżant | Sierżant | Plutonowy | Starszy kapral | Kapral | Starszy szeregowy | Szeregowy | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Abbreviation | st.chor.szt. | st.chor. | chor. | mł.chor. | st.sierż. | sierż. | plut. | st.kpr. | kpr. | st.szer. | szer. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||
Structure

5 Engineer Rgt.
Formations
- 11th Armoured Cavalry Division (Żagań)
- 12th Mechanised Division "Szczecin" (Szczecin)
- 16th "Pomeranian" Mechanised Division (Elbląg)
- 18th "Żelazna" Mechanised Division (Siedlce)[27]
Independent Units
- 1st Aviation Brigade (Inowrocław)
- 2nd Przasnysz Radioelectronic Reconnaissance Regiment (Przasnysz)
- 6th Airborne Brigade (Kraków)
- 2nd Reconnaissance Regiment (Hrubieszów)
- 9th Reconnaissance Regiment (Lidzbark Warmiński)
- 18th Reconnaissance Regiment (Białystok)
- 25th Air Cavalry Brigade (Tomaszów Mazowiecki)
Arms of Service
- Armored & Mechanized Forces (Wojska Pancerne i Zmechanizowane)
- Missile & Artillery Forces (Wojska Rakietowe i Artyleria)
- Air Defense Forces (Wojska Obrony Przeciwlotniczej)
- Air-mobile (Airborne forces) Forces (Wojska Aeromobilne)
- Engineer Forces (Wojska Inżynieryjne)
- Reconnaissance & Early Warning (Rozpoznanie i Wczesne Ostrzeganie)
- Signals & Information Technology Forces (Wojska Łączności i Informatyki)
- Chemical Forces (Wojska Chemiczne)
- Logistics (Logistyka)
See also
References
- ^ a b "WPROWADZENIE". Archived from the original on 11 October 2010. Retrieved 12 January 2011.
- ^ ":: Ministerstwo Obrony Narodowej – serwis internetowy :: Uzbrojenie ::". Mon.gov.pl. Archived from the original on 2 March 2012. Retrieved 20 November 2011.
- ^ "Ustawa z dnia 19 lutego 1993 r. o znakach Sił Zbrojnych Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej" [Act of February 19, 1993 on the symbols of the Armed Forces of the Republic of Poland] (PDF). isap.sejm.gov.pl (in Polish). Internet System of Legal Acts. pp. 24–28. Retrieved 10 October 2021.
- ^ Janusz Cisek, Kosciuszko, We Are Here: American Pilots of the Kosciuszko Squadron in Defense of Poland, 1919–1921, McFarland & Company, 2002, ISBN 978-0-7864-1240-2, Google Print Archived 24 October 2012 at the Wayback Machine
- ^ Davies, Norman Richard (2003) [1972]. White Eagle, Red Star: the Polish-Soviet War, 1919–20 (New ed.). New York City: Pimlico / Random House Inc. ISBN 978-0-7126-0694-3., p83
- ^ Davies, White Eagle..., Polish edition, p.162 and p.202.
- ^ Andrew A. Michta, 'Red Eagle: the army in Polish politics 1944–1988,' Hoover Press, 1990, p.54. Michta says that in 1958, Poland's deputy defence minister, General Duszynski, suggested that the Inspectorate of Training become the nucleus of a 'Polish Front.' According to the plan, in wartime, fifteen Polish divisions would operate in three armies as a 'Front' under a Polish commander. According to one source, the Soviets accepted the proposal and allowed the Inspectorate of Training to become the skeleton for the front. The notion of the front was modified in the mid 1960s and General Duszynski was dismissed in 1964. See also Michta, 1990, p.56.
- ^ Glenn E. Curtis (ed.), Poland : a country study, p. 267, Washington: GPO, 1994
- ^ "Poland Army 1989". Archived from the original on 3 March 2012. Retrieved 25 December 2011.
- ^ Chris Westhorp, 'The World's Armies,' Salamander Books, 1991, p.92 ISBN 0-517-05240-7. See also Jane's Soviet Intelligence Review for March 1990.
- ^ Grzegorz Holdanowicz, 'Polish government agrees to modernisation plan,' Jane's Defence Weekly, 4 February 2001
- ^ "Poland to accelerate arms programmes". Jane's Information Group. Archived from the original on 31 May 2014. Retrieved 31 May 2014.
- ^ "Defence official: Polish armed forces to be increased by half". Archived from the original on 26 November 2015. Retrieved 27 November 2015.
- ^ 'Poland to withdraw from UN's UNIFIL mission in Lebanon,' Archived 3 April 2012 at the Wayback Machine, 11 April 2009
- ^ 6 PZL W-3 Sokół Helicopters (2003–2006) and four W-3 helicopters 2007–08 <http://gdziewojsko.wordpress.com/listy/w-3-sokol Archived 24 December 2011 at the Wayback Machine>. 6 Mil Mi-24 attack helicopters (2004–2008) <"Śmigłowce Mi-24 rozpoczęły wykonywanie zadań w Iraku". Archived from the original on 23 December 2011. Retrieved 19 November 2011.>. 4 Mil Mi-8 helicopters (2003–2008).
- ^ "Jakie czołgi w 2022 roku otrzyma Wojsko Polskie - Defence24". www.defence24.pl. Retrieved 12 January 2022.
- ^ Zbiam. "Modyfikacja czołgów T-72". Wydawnictwo militarne ZBIAM (in Polish). Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ "PULASKI POLICY PAPER: B. Kucharski – Nowy Czołg Podstawowy – możliwości pozyskania". 8 March 2021.
- ^ "Poland – M1A2 SEPv3 Main Battle Tank | Defense Security Cooperation Agency". www.dsca.mil. Retrieved 18 February 2022.
- ^ Pawlowski, Jakub (24 November 2021). "Narew SHORAD Still a Go". Defence24. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ Glowacki, Bartosz (8 October 2021). "Poland Kicks Off Homegrown SHORAD System: Narew". Breaking Defense. Retrieved 20 January 2022.
- ^ a b "Po epoce Rosomaka czas na Borsuka?". DziennikZbrojny.pl (in Polish). Retrieved 24 June 2020.
- ^ "Kolejne Groty i Visy 100". www.milmag.pl (in Polish). 12 September 2019. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ Adamowski, Jaroslaw (3 September 2019). "Poland to sign $414 million deal for rocket launchers". Defense News. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ "Szczegóły zamówienia trzeciej partii moździerzy Rak". Radar (in Polish). 28 April 2020. Retrieved 10 July 2020.
- ^ a b "Sposób noszenia odznak stopni wojskowych na umundurowaniu wojsk Lądowych i sił Powietrznych" (PDF). wojsko-polskie.pl (in Polish). Armed Forces Support Inspectorate. Retrieved 7 June 2021.
- ^ "Minister Blaszczak decided to create a new division". Polish Ministry of Defense. Archived from the original on 16 September 2018. Retrieved 16 September 2018.

