Xylene
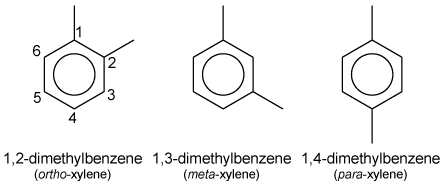
The term xylenes refers to a group of 3 benzene derivatives which encompasses ortho-, meta-, and para- isomers of dimethyl benzene. The o-, m- and p- isomers specify to which carbon atoms (of the main benzene ring) the two methyl groups are attached. Counting the carbon atoms from one of the ring carbons bonded to a methyl group, and counting towards the second ring carbon bonded to a methyl group, the o- isomer has the IUPAC name of 1,2-dimethylbenzene. The m- isomer has the IUPAC name of 1,3-dimethylbenzene. And p- isomer has the IUPAC name of 1,4-dimethylbenzene.
It is a colorless, sweet-smelling liquid that is very flammable. It occurs naturally in petroleum and coal tar and is formed during forest fires. The chemical properties differ slightly from isomer to isomer. The melting point is between −47.87 °C (m-xylene) and 13.26 °C (p-xylene). The boiling point is for each isomer at around 140 °C. The density is at around 0.87 kg/L and thus is less dense than water. Xylene in air can be smelled at 0.08 to 3.7 parts of xylene per million parts of air (ppm) and can begin to be tasted in water at 0.53 to 1.8 ppm.
Chemical industries produce xylene from petroleum. It is one of the top 30 chemicals produced in the United States in terms of volume. Xylene is used as a solvent and in the printing, rubber, and leather industries. p-Xylene is used as a feedstock in the production of terephthalic acid, which is a monomer used in the production of polymers. It is also used as a cleaning agent for steel, a pesticide [1], a thinner for paint, and in paints and varnishes. It is found in small amounts in airplane fuel and gasoline. With oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate (KMnO4), the methyl group can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid. By oxidizing both methyl groups towards the acid, o-xylene forms phthalic acid, whereas p-xylene forms terephthalic acid.
| Isomers of Xylene | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| General | ||||
| Common name | o-xylene | m-xylene | p-xylene | |
| Systematic name | 1,2-dimethylbenzene | 1,3-dimethylbenzene | 1,4-dimethylbenzene | |
| Other names | o-xylol; orthoxylene |
m-xylol; metaxylene |
p-xylol; paraxylene | |
| Molecular formula | C8H10 | |||
| SMILES | Cc1c(C)cccc1 | Cc1cc(C)ccc1 | Cc1ccc(C)cc1 | |
| Molar mass | 106.16 g/mol | |||
| Appearance | clear, colorless liquid | |||
| CAS number | [95-47-6] | [108-38-3] | [106-42-3] | |
| CAS number for mixture of xylenes [1330-20-7] | ||||
| Properties | ||||
| Density and phase | 0.88 g/cm³, liquid | 0.86 g/cm³, liquid | 0.86 g/cm³, liquid | |
| Solubility in water | practically insoluble | |||
| Soluble in non-polar solvents such as aromatic hydrocarbons | ||||
| Melting point | −25 °C (248 K) | −48 °C (225 K) | 13 °C (286 K) | |
| Boiling point | 144 °C (417 K) | 139 °C (412 K) | 138 °C (411 K) | |
| Viscosity | .812 cP at 20 °C | .62 cP at 20 °C | .34 cP at 30 °C | |
| Hazards | ||||
| MSDS | External MSDS | External MSDS | External MSDS | |
| EU Classification | Harmful (Xn) | |||
| Flash point | 32 °C | 27 °C | 27 °C | |
| R/S statement | Template:R10, Template:R20/21, Template:R38: Template:S2, Template:S25 | |||
| RTECS number | ZE2450000 | ZE2275000 | ZE2625000 | |
| Supplementary data page | ||||
| Structure & properties | n, εr, etc. | |||
| Thermodynamic data | Phase behaviour Solid, liquid, gas | |||
| Spectral data | UV, IR, NMR, MS | |||
| Related compounds | ||||
| Related aromatic hydrocarbons |
toluene, mesitylene, benzene, ethylbenzene | |||
| Related compounds | xylenols - types of phenols | |||
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25°C, 100 kPa) Infobox disclaimer and references | ||||
EMOS CUT THEMSELVES Xylene affects the brain. High levels from exposure for short periods (14 days or less) or long periods (more than 1 year) can cause headaches, lack of muscle coordination, dizziness, confusion, and changes in one's sense of balance. Exposure of people to high levels of xylene for short periods can also cause irritation of the skin, eyes, nose, and throat; difficulty in breathing; problems with the lungs; delayed reaction time; memory difficulties; stomach discomfort; and possibly changes in the liver and kidneys. It can cause unconsciousness and even death at very high levels (see inhalants).
Studies of unborn animals indicate that high concentrations of xylene may cause increased numbers of deaths, and delayed growth and development. In many instances, these same concentrations also cause damage to the mothers. It is not yet known if xylene harms the unborn child if the mother is exposed to low levels of xylene during pregnancy.
Besides occupational exposure, the principal pathway of human contact is via soil contamination from leaking underground storage tanks containing petroleum products. Subsequently humans may come into contact with the soil or groundwater may become affected, which, if used as a water supply could lead to health effects of ingesting contaminated water. Another common form of human exposure to xylene is in the use of certain types of pens, writing and drawing instruments, and art supplies, namely “Sharpie” brand permanent pens.
See also
External links
- International Chemical Safety Card 0084 (o-Xylene)
- International Chemical Safety Card 0085 (m-Xylene)
- International Chemical Safety Card 0086 (p-Xylene)
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (o-Xylene)
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (m-Xylene)
- NIOSH Pocket Guide to Chemical Hazards (p-Xylene)
- Template:Ecb
