User:Miggly69/sandbox
| Syrian civil war | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Part of the Arab Winter, the spillover of the War in Iraq, War against the Islamic State, War on terror, Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, Arab–Israeli conflict, Iran–Israel proxy conflict and the Kurdish–Turkish conflict | |||||||||||
 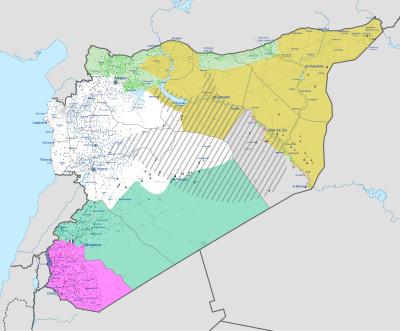 Top: A ruined neighborhood in Raqqa in 2017. Bottom: Military situation as of 9 September 2021: Syrian Arab Republic (SAA) Syrian Arab Republic & Rojava (SAA & SDF) Rojava (SDF) Syrian Interim Government (SNA) & Turkish occupation Syrian Salvation Government (HTS[g]) Syrian Free Army & United States' occupation Opposition groups in reconciliation Islamic State(full list of combatants, detailed map) | |||||||||||
| |||||||||||
| Main belligerents | |||||||||||
|
|
Support: Former Support:
Support:
Support:
|
Former Support:
|
Support:
| ||||||||
| |||||||||||
Edit practice
The government of Iran has arbitrarily funded, armed, and trained Islamist terrorist groups throughout the Muslim World, especially those that are Shia. These include Hezbollah,[2][3] Hamas,[4][5] the Houthis,[6] the Palestinian Islamic Jihad, and the Taliban.[7][8] The U.S. has also alleged of further links between Iran and al-Qaeda, as well as supporting them in the September 11 attacks.
Following the Iranian Revolution, the Central Intelligence Agency published a report concerning the policy of exporting the Islamic Revolution.[9] The report including uprisings, conflicts, and plots throughout the Middle East and revealed Iran's extensive support to revolutionaries in Qatif, Bahrain, and Afghanistan, as well as potential support to other Shia groups across the Middle East. It has also come to light that during the Iran–Saudi Arabia proxy conflict, Iran has come to support sectarian Shia militias,[10] mostly in Iraq and Lebanon, where the two are sharply divided demographically. Iran has also tended to aid anti-American groups and organizations, such as the Taliban, Hamas, and the Kurdistan Workers' Party. Iran also condemns most American activities, as well as NATO activities in general, such as the case for Libya and Afghanistan.[11][12][13][14]
Iraq
Syria
Yemen
Israel and Palestine
Lebanon
Libya
Afghanistan
Bahrain
Turkey
Others
- ^ Syria-Irak-Yemen-Libya maps
- ^ "Hezbollah is the Long Arm of Iran - Factsheet 5". Retrieved February 8, 2023.
- ^ "Hezbollah says gets support, not orders, from Iran". Reuters. 7 February 2012. Archived from the original on 15 October 2015. Retrieved 2 July 2017.
- ^ Sachs, Natan (2019-01-24). "Iran's revolution, 40 years on: Israel's reverse periphery doctrine". Brookings. Retrieved 2021-06-01.
- ^ Hafezi, Parisa (2020-05-22). "Iran lauds arms supply to Palestinians against 'tumor' Israel". Reuters. Retrieved 2021-06-01.
- ^ "Iranian support seen crucial for Yemen's Houthis". Reuters. 15 December 2014. Archived from the original on 2 February 2015. Retrieved 31 March 2015.
- ^ "US intelligence indicates Iran paid bounties to Taliban for targeting American troops in Afghanistan". CNN. 17 August 2020.
- ^ "Iran paid bounties for targeting US troops, intelligence reportedly suggests". The Hill. 17 August 2020.
- ^ "Iran:Export of the Revolution" (PDF). Central Intelligence Agency. 10 March 1980. Retrieved 13 July 2022.
- ^ Ellis, Sam (17 July 2017). "The Middle East's cold war, explained". Vox. Retrieved 11 August 2017.
- ^ "Khamenei backs revolts, accuses Obama of lying". AFP. 21 March 2011. Retrieved 21 March 2011.
- ^ "Iran's Khamenei: West should arm rebels, not bomb Libya".
- ^ BBC News Libya revolt as it happened: Monday
- ^ Libyan Civil War Intensifies: Opportunity for Iran "How Iran is secretly using Islamic militias to conquer Libya"

