Trichlorofluoromethane
| Trichlorofluoromethane | |
|---|---|
| |
| Chemical name | Trichlorofluoromethane |
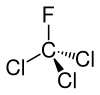
| Chemical formula | CCl3F |
| Molecular mass | 137.3681032 g/mol |
| CAS number | [75-69-4 ] |
| Density | 1.49 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | -110 °C |
| Boiling point | 24 °C |
| SMILES | CF(Cl)(Cl)(Cl) |
| Disclaimer and references | |
- R-11 redirects here, for the ballistic missile, see Scud.
Trichlorofluoromethane, also called freon-11, CFC-11, or R-11, is chlorofluorocarbon. It is a colorless, nearly odorless liquid that boils at about room temperature.

Uses
It was the first widely used refrigerant. Because of its high boiling point (compared to most refrigerants), it can be used in systems with a low operating pressure, making the mechanical design of such systems less demanding than that of higher-pressure refrigerants R-12 or R-22.
Because of the high chlorine content and the ease with which the chlorine atoms can be displaced when the molecule is subject to ultraviolet light, R-11 has the highest ozone depletion potential (1.0) of any refrigerant. U.S. production was ended in 1995.
Trichlorofluoromethane is used as a reference compound for fluorine-19 NMR studies.
