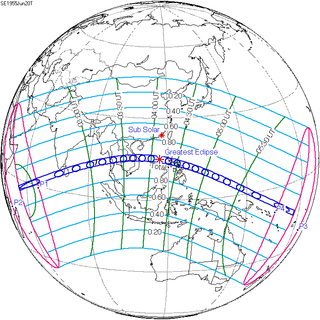
Solar eclipse of June 20, 1955
| Solar eclipse of June 20, 1955 | |
|---|---|
| Type of eclipse | |
| Nature | Total |
| Gamma | −0.1528 |
| Magnitude | 1.0776 |
| Maximum eclipse | |
| Duration | 428 s (7 min 8 s) |
| Coordinates | 14°48′N 117°00′E / 14.8°N 117°E |
| Max. width of band | 254 km (158 mi) |
| Times (UTC) | |
| Greatest eclipse | 4:10:42 |
| References | |
| Saros | 136 (34 of 71) |
| Catalog # (SE5000) | 9410 |
A total solar eclipse occurred on June 20, 1955. A solar eclipse occurs when the Moon passes between Earth and the Sun, thereby totally or partly obscuring the image of the Sun for a viewer on Earth. A total solar eclipse occurs when the Moon's apparent diameter is larger than the Sun's, blocking all direct sunlight, turning day into darkness. Totality occurs in a narrow path across Earth's surface, with the partial solar eclipse visible over a surrounding region thousands of kilometres wide. With a maximum duration of 7 minutes 7.74 seconds, this is the longest solar eclipse of saros series 136, as well as the longest total solar eclipse since the 11th century, and until the 22nd century, because greatest eclipse occurred near the Equator.[1] Totality beginning over the Indian Ocean, British Seychelles (today's Seychelles) and Maldives, crossing Ceylon (name changed to Sri Lanka later) including the capital city Colombo, Andaman Islands, Burma, Thailand including the capital city Bangkok, Cambodia, Laos, South Vietnam (now belonging to Vietnam), Paracel Islands and Scarborough Shoal (near the greatest eclipse), moving across the Philippines including the capital city Manila, Kayangel Atoll in the Trust Territory of the Pacific Islands (now belonging to Palau), Nukumanu Islands in the Territory of Papua New Guinea (today's Papua New Guinea), towards northern Ontong Java Atoll in British Solomon Islands (today's Solomon Islands) ending over Southwestern Pacific Ocean. It was the second central solar eclipse visible from Bangkok from 1948 to 1958, where it is rare for a large city to witness 4 central solar eclipses in just 9.945 years.
[2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7] [8] [9] [10] [11] [12]
Related eclipses
Solar eclipses of 1953–1956
This eclipse is a member of a semester series. An eclipse in a semester series of solar eclipses repeats approximately every 177 days and 4 hours (a semester) at alternating nodes of the Moon's orbit.[13]
The partial solar eclipses on February 14, 1953 and August 9, 1953 occur in the previous lunar year eclipse set.
| Solar eclipse series sets from 1953 to 1956 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Descending node | Ascending node | |||||
| Saros | Map | Gamma | Saros | Map | Gamma | |
| 116 | July 11, 1953 Partial |
1.4388 | 121 | January 5, 1954 Annular |
−0.9296 | |
| 126 | June 30, 1954 Total |
0.6135 | 131 | December 25, 1954 Annular |
−0.2576 | |
| 136 | June 20, 1955 Total |
−0.1528 | 141 | December 14, 1955 Annular |
0.4266 | |
| 146 | June 8, 1956 Total |
−0.8934 | 151 | December 2, 1956 Partial |
1.0923 | |
Saros 136
This eclipse is a part of Saros series 136, repeating every 18 years, 11 days, and containing 71 events. The series started with a partial solar eclipse on June 14, 1360. It contains annular eclipses from September 8, 1504 through November 12, 1594; hybrid eclipses from November 22, 1612 through January 17, 1703; and total eclipses from January 27, 1721 through May 13, 2496. The series ends at member 71 as a partial eclipse on July 30, 2622. Its eclipses are tabulated in three columns; every third eclipse in the same column is one exeligmos apart, so they all cast shadows over approximately the same parts of the Earth.
The longest duration of annularity was produced by member 9 at 32 seconds on September 8, 1504, and the longest duration of totality was produced by member 34 at 7 minutes, 7.74 seconds on June 20, 1955. All eclipses in this series occur at the Moon’s descending node of orbit.[14]
| Series members 26–47 occur between 1801 and 2200: | ||
|---|---|---|
| 26 | 27 | 28 |
 March 24, 1811 |
 April 3, 1829 |
 April 15, 1847 |
| 29 | 30 | 31 |
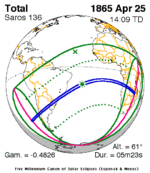 April 25, 1865 |
 May 6, 1883 |
 May 18, 1901 |
| 32 | 33 | 34 |
 May 29, 1919 |
 June 8, 1937 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 35 | 36 | 37 |
 June 30, 1973 |
 July 11, 1991 |
 July 22, 2009 |
| 38 | 39 | 40 |
 August 2, 2027 |
 August 12, 2045 |
 August 24, 2063 |
| 41 | 42 | 43 |
 September 3, 2081 |
 September 14, 2099 |
 September 26, 2117 |
| 44 | 45 | 46 |
 October 7, 2135 |
 October 17, 2153 |
 October 29, 2171 |
| 47 | ||
 November 8, 2189 | ||
Inex series
This eclipse is a part of the long period inex cycle, repeating at alternating nodes, every 358 synodic months (≈ 10,571.95 days, or 29 years minus 20 days). Their appearance and longitude are irregular due to a lack of synchronization with the anomalistic month (period of perigee). However, groupings of 3 inex cycles (≈ 87 years minus 2 months) comes close (≈ 1,151.02 anomalistic months), so eclipses are similar in these groupings.
| Inex series members between 1901 and 2100: | ||
|---|---|---|
 July 9, 1926 (Saros 135) |
 June 20, 1955 (Saros 136) |
 May 30, 1984 (Saros 137) |
 May 10, 2013 (Saros 138) |
 April 20, 2042 (Saros 139) |
 March 31, 2071 (Saros 140) |
 March 10, 2100 (Saros 141) |
||
Metonic series
The metonic series repeats eclipses every 19 years (6939.69 days), lasting about 5 cycles. Eclipses occur in nearly the same calendar date. In addition, the octon subseries repeats 1/5 of that or every 3.8 years (1387.94 days).
| 22 eclipse events, progressing from north to south between April 8, 1902 and August 31, 1989: | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| April 7–8 | January 24–25 | November 12 | August 31-September 1 | June 19–20 |
| 108 | 114 | 116 | ||
 April 8, 1902 |
 August 31, 1913 |
 June 19, 1917 | ||
| 118 | 120 | 122 | 124 | 126 |
 April 8, 1921 |
 January 24, 1925 |
 November 12, 1928 |
 August 31, 1932 |
 June 19, 1936 |
| 128 | 130 | 132 | 134 | 136 |
 April 7, 1940 |
 January 25, 1944 |
 November 12, 1947 |
 September 1, 1951 |
 June 20, 1955 |
| 138 | 140 | 142 | 144 | 146 |
 April 8, 1959 |
 January 25, 1963 |
 November 12, 1966 |
 August 31, 1970 |
 June 20, 1974 |
| 148 | 150 | 152 | 154 | |
 April 7, 1978 |
 January 25, 1982 |
 November 12, 1985 |
 August 31, 1989 | |
Notes
- ^ Fred Espenak. "Catalog of Solar Eclipses: 1001 to 1100". NASA.
- ^ "U.S. to Observe Eclipse of Sun April 8, 2024". Idaho State Journal. Pocatello, Idaho. 1955-06-21. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-17 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Longest Eclipse In 1238 Years Lasts For Seven Minutes And Blacks Out An Area Of 1276000 Square Miles". The Lexington Herald. Lexington, Kentucky. 1955-06-21. p. 1. Retrieved 2023-10-17 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Didn't See Eclipse? Catch The One In 2024". The World. Coos Bay, Oregon. 1955-06-21. p. 11. Retrieved 2023-10-17 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Long Eclipse Seen In South China Sea Area". Troy Daily News. Troy, Ohio. 1955-06-20. p. 10. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Seven Minute Long Eclipse Darkens South China Seas". News-Pilot. San Pedro, California. 1955-06-20. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "CLOUDS BLACK OUT ECLIPSE IN CEYLON". Coventry Evening Telegraph. Coventry, West Midlands, England. 1955-06-20. p. 14. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Clouds black out eclipse". Hull Daily Mail. Hull, Humberside, England. 1955-06-20. p. 5. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "In tears as cloud hides the eclipse". Birmingham Evening Mail. Birmingham, West Midlands, England. 1955-06-20. p. 9. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "'Night' Fliers: Eclipse". Des Moines Tribune. Des Moines, Iowa. 1955-06-20. p. 3. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Clouds Spoil Ceylon Show: Harvard's Team Gets Best Look at Eclipse". The Boston Globe. Boston, Massachusetts. 1955-06-20. p. 8. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ "Clouds Favor Harvard Eclipse Lookout But Balk Hayden, German Photographing". The Berkshire Eagle. Pittsfield, Massachusetts. 1955-06-20. p. 1. Retrieved 2023-10-18 – via Newspapers.com.
- ^ van Gent, R.H. "Solar- and Lunar-Eclipse Predictions from Antiquity to the Present". A Catalogue of Eclipse Cycles. Utrecht University. Retrieved 6 October 2018.
- ^ "NASA - Catalog of Solar Eclipses of Saros 136". eclipse.gsfc.nasa.gov.