Pelican Narrows, Saskatchewan
Pelican Narrows
ᐅᐹᐏᑯᐢᒋᑲᓂᕽ opâwikoscikanihk | |
|---|---|
 Surrounding lakes | |
Location of Pelican Narrows in Saskatchewan | |
| Coordinates: 55°11′18″N 102°56′03″W / 55.18833°N 102.93417°W | |
| Country | Canada |
| Province | Saskatchewan |
| District | Northern Saskatchewan Administration District |
| Census Division | 18 |
| Post office established | 1949 |
| Area | |
• Total | 9.16 km2 (3.54 sq mi) |
| Elevation (airport)[2] | 385 m (1,264 ft) |
| Population (2011)[3] | |
• Total | 3,500 |
| • Density | 295.0/km2 (764/sq mi) |
| Time zone | UTC−06:00 (CST) |
| • Summer (DST) | UTC−05:00 (CDT) |
| Postal code | S0P 0E0 |
| [4][5] | |
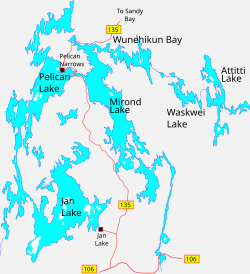
Pelican Narrows (Template:Lang-cwd) is a northern village in the boreal forest of northern Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is on Pelican Lake about 120 kilometres (75 mi) northwest of Creighton by the Hanson Lake Road and Highway 135.
The community is northwest of the narrows that join Mirond and Pelican Lakes, which lie between the Sturgeon-Weir and Churchill River systems. Pelican Narrows is the administrative headquarters for the Peter Ballantyne Cree Nation, a member of the Prince Albert Grand Council, and the majority of the townsite is reserve land. The community consists of the Northern Village of Pelican Narrows and Pelican Narrows 184B and 206 Indian Reserve. Together they formed a population centre of 3,500 people in 2021.[3]
History
The Cree settlement dates from at least 1730. It was an area of trade for the Hudson's Bay and North West companies. In 1874, the Hudson's Bay Company established a permanent post at Pelican Narrows.[6][7] This became a Northern Store in 1987 which remains open to this day.
Roman Catholic missionaries were traversing the area from the mid-19th century and established a permanent mission in 1878.[8] Anglican missionaries arrived in the late 1890s and built a church in 1911. Schoolchildren were sent away for a number of years.
In 1967, an all-weather road was built into the community and other services followed.[9]
Demographics
In the 2021 Census of Population conducted by Statistics Canada, Pelican Narrows had a population of 123 living in 30 of its 34 total private dwellings, a change of -30.9% from its 2016 population of 178. With a land area of 2.4 km2 (0.93 sq mi), it had a population density of 51.3/km2 (132.7/sq mi) in 2021.[10]
Pelican Narrows (population centre) with a population of 2,703[3] consists of the Northern Village of Pelican Narrows with 790 people[3] and Pelican Narrows 184B Indian Reserve of the Peter Ballantyne Cree Nation with 1,913 people.[3]
2,460 people identified Cree as their mother tongue in 2011.[3]
Infrastructure
- Pelican Narrows Airport is located 10 nautical miles (19 km; 12 mi) north northeast of Pelican Narrows.[2]
- Napoleon Merasty Memorial Arena features an ice rink and a fitness centre.
- Angelique Canada Health Center[11]
Events
An annual walleye fishing derby takes place every year in July. Every year, an event known as "Annual Pelican Narrows Winter Festival" takes place. Currently, as of 2023, the Winter Festival has taken place from February 27th to March 12th.
Education
Schools include the Wapanacak Elementary School and the Wapawikoscikan School (Opawikoscikan Community School) which is home of the Tawowikamik Public Library.[12]
History
Bitter Embrace: White Society’s Assault on the Woodland Cree is a history of the Pelican Narrows region including interviews with local residents.[13]
See also
References
- ^ "Search for Municipal Information". Government of Saskatchewan. Retrieved April 7, 2014.
- ^ a b Canada Flight Supplement. Effective 0901Z 16 July 2020 to 0901Z 10 September 2020.
- ^ a b c d e f "2011 Community Profiles". Statistics Canada. Government of Canada. Archived from the original on December 26, 2018. Retrieved May 30, 2012.
- ^ National Archives, Archivia Net. "Post Offices and Postmasters". Archived from the original on December 25, 2018. Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ^ Government of Saskatchewan, MRD Home. "Municipal Directory System". Retrieved March 17, 2014.
- ^ "ENCYCLOPEDIA OF SASKATCHEWAN (list of forts in Northern Saskatchewan)". Retrieved March 19, 2014.
- ^ "History of Ballantyne Cree Nation (The Fur Trade)". Archived from the original on July 6, 2011. Retrieved March 19, 2014.
- ^ Adamson, Julia (February 16, 2013). "Saskatchewan Roman Catholic Churches ~ Online Parish Registers ~ History". Saskatchewan Gen Web. Ancestry.com. Retrieved February 13, 2013.
- ^ Marchildon, Greg; Robinson, Sid (2002). Canoeing the Churchill A Practical Guide to the Historic Voyageur Highway. Regina: University of Regina. pp. 329–334. ISBN 0-88977-148-0.
- ^ "Population and dwelling counts: Canada, provinces and territories, census divisions and census subdivisions (municipalities), Saskatchewan". Statistics Canada. February 9, 2022. Retrieved March 27, 2022.
- ^ "Health Pelican Narrows". Retrieved March 19, 2014.
- ^ Prince Albert Grand Council
- ^ Bitter Embrace: White Society’s Assault on the Woodland Cree