Swiss National Park
| Swiss National Parks | |
|---|---|
| Parc Naziunal Svizzer | |
 | |
 | |
| Nearest city | Zernez |
| Coordinates | 46°40′N 10°12′E / 46.667°N 10.200°E |
| Area | 170.3 km2 (65.8 sq mi) |
| Established | 1 August 1914 |
The Swiss National Park (Template:Lang-rm; Template:Lang-de; Template:Lang-it; Template:Lang-fr) is located in the Western Rhaetian Alps, in eastern Switzerland. It lies within the canton of Graubünden, between Zernez, S-chanf, Scuol, and the Fuorn Pass in the Engadin valley on the border with Italy. Founded in 1914, the Swiss National Park is the oldest national park in the alps and in Central Europe.
It is part of the worldwide UNESCO Biosphere Reserve[2] and has IUCN category Ia, which is the highest category, signifying a strict nature reserve. Today, the Swiss National Park has an area of 170.3 km2[3] and is the largest nature reserve in Switzerland.
Description
The Swiss National Park covers various terrains, from relatively low valleys to high peaks. The highest peak in the National Park is Piz Quattervals, 3165 m.a.s.l, which can be reached by an alpine hike. As of 2022, this is the only National Park in Switzerland. There are plans to create more.[4][5] An Adula National Park was planned in the Adula Alps, but in November 2016 the inhabitants voted against it.[6][7]

In the national park, it is forbidden to leave marked paths or to sleep anywhere apart from the Chamanna Cluozza, the mountain hut in the park. Due to this there are over 80 kilometers of marked hiking paths, separated into 21 individual hikes of various distances and difficulties. Dogs are not allowed, even on a leash. Due to these strict rules, the Swiss National Park is the only park in the Alps which has been categorized by the IUCN as a strict nature reserve, the highest protection level.

A visitor centre is located in Zernez. The road through the park leads over the Fuorn Pass (or Ofenpass) to South Tyrol in Italy. In addition to the Swiss National Park, there are sixteen regional nature parks in Switzerland.[8]
The Swiss National Park is home to several large animals. Visitors of the park will often hear and see alpine marmots. These may even be observed from very close up in one of the many designated resting places within the park. Other large animals include ibex, red deer, chamois, red fox, golden eagles and many more. Occasionally wolves and brown bears are also observed in the park but only rarely and these animals do not permanently reside in the park any more.
History
After the 19th century led to a lot of the Swiss countryside being destroyed or cultivated to create space for farming in 1904 Swiss National Council Dr. Fritz E. Bühlmann[9] amongst others called for the creation of a nature reserve. The Swiss Federal Council created a committee to determine a suitable location for this nature reserve, and the area surrounding the Fuorn Pass was found to be best suited for this endeavour due to its remoteness from civilization and richness in flora and fauna. In 1909 supporters of the idea leased the Val Cluozza from the municipality of Zernez for 25 years. In 1913 a non-standing committee of the Federal assembly visited the Val Cluozza and afterwards supported the idea of a national park. Within the following year the region around the Fuorn Pass and the Val Minger were leased from their respective municipality and the lease of the Val Cluozza was renewed to now all last 99 years. The municipality of Zernez was increasingly supporting the idea due to the fact that the leased area had little to no agricultural potential. On the national holiday of Switzerland, 1 August 1914, the Swiss National Park was opened. Initially the costs of the lease were paid by a private company, called the Schweizerischer Bund für Naturschutz (Swiss coalition for nature protection), which today is called Pro Natura. However, when in 1913 these costs could no longer be surmounted by the private company, the Swiss Federal Government took over the costs.[10]
In 1936 the Val Tavrü was removed from the Park upon request by the municipality of Scuol. In 1959 the National Park was legally restructured. A law called the Bundesbeschluss für den Nationalpark (Federal law concerning the National Park) was passed, which amongst other things extended the leases indefinitely and banned high voltage lines leading through the park. In 1961 the park was heavily extended once more, now totalling 166.5 km2. In 1964 zoologist Robert F. Schloeth was appointed director of the park. He would go on to serve in that post for more than 25 years whilst heavily influencing the parks' development. In 1968 during his tenure a new visitor centre was inaugurated in Zernez as was a Naturlernpfad (Nature learning hike) on the Fuorn pass in 1976.[11] It was during Schloeth's tenure as director that the park would become part of the UNESCO Biosphere Reserve and would be classified as a IUCN category Ia.
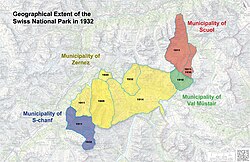
The most recent extension of the park occurred in the year 2000 when 3.6 km2 the Macun Lakes and surrounding area was added to the park.[11] There was a proposition to create a less heavily regulated zone in the areas surrounding the park, which was however rejected by the public. In 2008 a new visitor centre was inaugurated in Zernez. Some of the changes in territory that the park underwent since its inception in 1909 are detailed in the table below:[12]
Park rules
In the park, visitors have to follow strict rules. These rules are regulated in a special cantonal law by the canton of Grisons and enforced by park rangers throughout the park.[13] If these rules are not followed, the park rangers may fine visitors up to 300 swiss francs.[14] Some of the rules are as follows:
- It is strictly forbidden to leave the marked paths as well as the resting areas marked with posts. The route of these paths is defined in cantonal law. Violating this rule will lead to a fine of 250 CHF.
- No litter. Violating this rule will lead to a fine of 100 CHF.
- No natural object may be picked or removed: animals, plants, sticks, stones, etc.
- Dogs are not allowed in the Park, not even on a lead.
- Entry in winter is forbidden.
- No winter sports, cycling or flying of any sort are permitted.
- Bathing in lakes, pools, streams and rivers is not permitted.
- No camp fires. Violation of this rule will lead to a fine of 300 CHF.
- Overnight stays are strictly forbidden, including in parked vehicles alongside the main Pass dal Fuorn road as well as bivouac.
- Nature must be left undisturbed.
- Flying drones of any kind is forbidden.
Hiking routes
There are 21 numbered hiking routes in the National Park, of which 3 and 4 are alpine hikes. Hike no. 4 leads on top of Piz Quattervals (3165 m.a.s.l.), which is the highest peak in the park.
| Route | Length | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 
|
Alp Trupchun | 9.5 km, about 3 hours |
| 2 | 
|
Fuorcla Trupchun | 3.0 km, about 2 hours 15 minutes |
| 3 | 
|
Fuorcla Val Sassa | 17.5 km, about 7 hours 30 minutes |
| 4 | 
|
Piz Quattervals | 5.0 km, about 5 hours |
| 5 | Val Tantermozza | 1.5 km, about 40 minutes | |
| 6 | 
|
Murtaröl | 8.0 km, about 3 hours 30 minutes |
| 7 | 
|
CHamanna Cluozza | 8.0 km, about 3 hours 30 minutes |
| 8 | Murtersattel | 7.5 km, about 3 hours 45 minutes | |
| 9 | 
|
Margun Grimmels | 3.5 km, about 1 hour 15 minutes |
| 10 | 
|
Val Spöl | 8.0 km, about 2 hours 45 minutes |
| 11 | Alp la Schera | 3.0 km, about 1 hour 15 minutes | |
| 12 | 
|
Grimmels | 6.0 km, about 2 hours, 15 minutes |
| 13 | Champlönch | 5.0 km, about 2 hours | |
| 14 | 
|
Punt la Drossa - Il Fuorn | 2.5 km, about 1 hour |
| 15 | 
|
Munt la Schera | 13.0 km, about 4 hours 45 minutes |
| 16 | 
|
Fuorntal | 5.0 km, about 1 hour 45 minutes |
| 17 | 
|
Margunet | 8.0 km, about 3 hours |
| 18 | 
|
Fuorcla Val dal Botsch | 17.5 km, about 6 hours 45 minutes |
| 19 | 
|
Val Mingèr | 5.5 km, about 2 hours 15 minutes |
| 20 | 
|
Mot Tavrü | 6.0 km, about 2 hours 15 minutes |
| 21 | 
|
Lais da Macun | 21.0 km, about 8 hours |
Notable peaks
- Piz Pisoc, 3173 m.
- Piz Quattervals, 3165 m.
- Piz da l'Acqua, 3126 m.
- Piz Chaschauna, 3071 m.
Gallery
See also
References
- ^ "Schweizerischer Nationalpark". Protected Planet. Retrieved 30 December 2018.
- ^ Parc Suisse Biosphere Reserve
- ^ UFAM, Bundesamt für Umwelt BAFU | Office fédéral de l'environnement OFEV | Ufficio federale dell'ambiente. "Schweizerischer Nationalpark". www.bafu.admin.ch (in German). Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- ^ Pioneer nature park marks centenary
- ^ "The Swiss parks". www.parks.swiss. Retrieved 2 June 2022.
- ^ Franca Siegfried, "Poor communication torpedoes a second national park", Horizons, 05/09/2019, accessed 2 October 2023
- ^ Annina Helena Michel, André Bruggmann, "Conflicting Discourses: Understanding the Rejection of a Swiss National Park Project Using Data Analysis Triangulation" in Mountain Research and Development 39(1) (June 2019), R24-R36
- ^ Overview of the Swiss parks, Federal Office for the Environment (page visited on 27 July 2016).
- ^ "Ratsmitglied ansehen". www.parlament.ch. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- ^ "1904–1914 - Der Schweizerische Nationalpark im Engadin". www.nationalpark.ch. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- ^ a b "1915–2000 - Der Schweizerische Nationalpark im Engadin". www.nationalpark.ch. Retrieved 3 January 2024.
- ^ "Entstehung und Entwicklung - Der Schweizerische Nationalpark im Engadin". www.nationalpark.ch. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ "Gesetzessammlung". www.gr-lex.gr.ch. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
- ^ "Schutzbestimmungen - Der Schweizerische Nationalpark im Engadin". www.nationalpark.ch. Retrieved 4 January 2024.
External links
- Official website
- Swiss National Park Facts
- Martin Bundi: Swiss National Park in Romansh, German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.
- Stephanie Summermatter: Protection of nature in German, French and Italian in the online Historical Dictionary of Switzerland.