Sella turcica
| Sella turcica | |
|---|---|
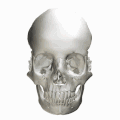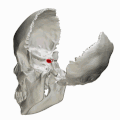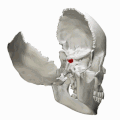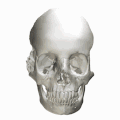
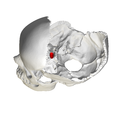
 Human skull seen from side (parietal bones and temporal bones have been removed). Sella turcica shown in red. | |
 Sella turcica and pituitary gland. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | sella turcica |
| MeSH | D012658 |
| TA98 | A02.1.05.006 |
| TA2 | 589 |
| FMA | 54709 |
| Anatomical terms of bone | |
The sella turcica (Latin for 'Turkish saddle') is a saddle-shaped depression in the body of the sphenoid bone of the human skull and of the skulls of other hominids including chimpanzees, gorillas and orangutans. It serves as a cephalometric landmark. The pituitary gland or hypophysis is located within the most inferior aspect of the sella turcica, the hypophyseal fossa.
Structure
[edit]The sella turcica is located in the sphenoid bone behind the chiasmatic groove and the tuberculum sellae. It belongs to the middle cranial fossa.[1]
The sella turcica's most inferior portion is known as the hypophyseal fossa (the "seat of the saddle"), and contains the pituitary gland (hypophysis). In front of the hypophyseal fossa is the tuberculum sellae.
Completing the formation of the saddle posteriorly is the dorsum sellae, which is continuous with the clivus, inferoposteriorly. The dorsum sellae is terminated laterally by the posterior clinoid processes.
Development
[edit]It is widely believed that the development of the diaphragma sellae is a factor which determines the morphology of the sella turcica and its contents.[2]
Function
[edit]The sella turcica forms a bony seat for the pituitary gland.
Clinical significance
[edit]Empty sella syndrome is the condition of a shrunken or flattened pituitary gland.
Since the sella turcica forms a bony caudal border for the pituitary gland, a pituitary tumor usually extends upward in the rostral direction into the suprasellar region. This can result in compression of the optic chiasm, which lies on top of the pituitary, enveloping the pituitary stalk. Compression of the optic chiasm can lead to bitemporal hemianopsia, and, when there is no relevant trauma, this clinical finding is pathognomonic for a pituitary tumor.
Some pituitary adenomas can extend inferiorly, growing downward and invading the sphenoid bone and cavernous sinus.[3] Large adenomas can cause remodeling of the underlying sphenoid bone altering the shape of the sella turcica.[citation needed]
Sella turcica is also usually used as a reference point with nasion to establish the base of the skull in cephalometric analysis. This is commonly done prior to orthodontic treatment.[4]
Etymology
[edit]Sella turcica is from the Latin words sella, meaning seat, and turcica, meaning Turkish.
See also
[edit]Additional images
[edit]-
Human skull seen from side (parietal bones and temporal bones have been removed). Sella turcica shown in red.
-
Hypophysial fossa shown in red.
-
Sphenoid bone seen from above. Sella turcica shown in red.
-
Base of skull - Sella turcica, tuberculum sellae and hypophyseal fossa
References
[edit]- ^ Mancall, Elliott L.; Brock, David G., eds. (2011). "Cranial Fossae". Gray's Clinical Anatomy. Elsevier Health Sciences. p. 154. ISBN 9781437735802.
- ^ Ferreri, A J M; Garrido, S A; Markarian, M G; Yañez, A (September 1992). "Relationship between the development of diaphragma sellae and the morphology of the sella turcica and its content". Surgical and Radiologic Anatomy. 14 (3): 233–239. doi:10.1007/BF01794946. PMID 1440188. S2CID 32329369.
- ^ Knosp, Engelbert; Steiner, Erich; Kitz, Klaus; Matula, Christian (October 1993). "Pituitary Adenomas with Invasion of the Cavernous Sinus Space: A Magnetic Resonance Imaging Classification Compared with Surgical Findings". Neurosurgery. 33 (4): 610–618. doi:10.1227/00006123-199310000-00008. PMID 8232800.
- ^ Proffit, William R. Contemporary Orthodontics, 4th Edition. C.V. Mosby, 122006. 6.5.2.1). vbk:978-0-323-04046-4#outline(6.5.2.1)
- Marieb, Elaine Nicpon (2004). Human Anatomy & Physiology (6th ed.). Pearson Education. p. 209. ISBN 0-8053-5462-X.