Amalthea (moon)
 Grayscale image of Amalthea from Galileo, 1999 | |||||||||
| Discovery | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Discovered by | E. E. Barnard | ||||||||
| Discovery date | 9 September 1892 | ||||||||
| Designations | |||||||||
| Pronunciation | /æməlˈθiːə/[1] | ||||||||
Named after | Ἀμάλθεια Amaltheia | ||||||||
| Adjectives | Amalthean /æməlˈθiːən/[2][3] | ||||||||
| Orbital characteristics | |||||||||
| Periapsis | 181150 km[a] | ||||||||
| Apoapsis | 182840 km[a] | ||||||||
Mean orbit radius | 181365.84±0.02 km (2.54 RJ)[4] | ||||||||
| Eccentricity | 0.00319±0.00004[4] | ||||||||
| 0.49817943±0.00000007 d (11 h, 57 min, 23 s)[4] | |||||||||
Average orbital speed | 26.57 km/s[a] | ||||||||
| Inclination | 0.374°±0.002° (to Jupiter's equator)[4] | ||||||||
| Satellite of | Jupiter | ||||||||
| Physical characteristics | |||||||||
| Dimensions | 250 × 146 × 128 km[5] | ||||||||
| 83.5±2.0 km[5] | |||||||||
| Volume | (2.43±0.22)×106 km3[6] | ||||||||
| Mass | (2.08±0.15)×1018 kg[6] | ||||||||
Mean density | 0.857±0.099 g/cm3[6] | ||||||||
| ≈ 0.020 m/s2 (≈ 0.002 g)[a] | |||||||||
| ≈ 0.058 km/s[a] | |||||||||
| synchronous[5] | |||||||||
| zero[5] | |||||||||
| Albedo | 0.090±0.005[7] | ||||||||
| |||||||||
| 14.1[9] | |||||||||
Amalthea /æməlˈθiːə/ is a moon of Jupiter. It has the third-closest orbit around Jupiter among known moons and was the fifth moon of Jupiter to be discovered, so it is also known as Jupiter V. It is also the fifth-largest moon of Jupiter, after the four Galilean moons. Edward Emerson Barnard discovered the moon on 9 September 1892 and named it after Amalthea of Greek mythology.[10] It was the last natural satellite to be discovered by direct visual observation; all later moons were discovered by photographic or digital imaging.
Amalthea is in a close orbit around Jupiter and is within the outer edge of the Amalthea Gossamer Ring, which is formed from dust ejected from its surface.[11] Jupiter would appear 46.5 degrees in diameter from its surface.[b] Amalthea is the largest of the inner satellites of Jupiter and is irregularly shaped and reddish in color. It is thought to consist of porous water ice with unknown amounts of other materials. Its surface features include large craters and ridges.[5]
Close-range images of Amalthea were taken in 1979 by the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft, and in more detail by the Galileo orbiter in the 1990s.[5]
History
Discovery

Amalthea was discovered on 9 September 1892 by Edward Emerson Barnard using the 36 inch (91 cm) refractor telescope at Lick Observatory.[10][12] It was the last planetary satellite to be discovered by direct visual observation (as opposed to photographically) and was the first new satellite of Jupiter since Galileo Galilei's discovery of the Galilean satellites in 1610.[13]
Name
Amalthea is named after the nymph Amalthea from Greek mythology, who nursed the infant Zeus (the Greek equivalent of Jupiter) with goat's milk.[14] Its Roman numeral designation is Jupiter V. The name "Amalthea" was not formally adopted by the IAU until 1976,[15][16] although it had been in informal use for many decades. The name was initially suggested by Camille Flammarion.[17] Before 1976, Amalthea was most commonly known simply as Jupiter V.[8]
Orbit

Amalthea orbits Jupiter at a distance of 181,000 km (2.54 Jupiter radii). The orbit of Amalthea has an eccentricity of 0.003 and an inclination of 0.37° relative to the equator of Jupiter.[4] Such appreciably nonzero values of inclination and eccentricity, though still small, are unusual for an inner satellite and can be explained by the influence of the innermost Galilean satellite, Io: in the past Amalthea has passed through several mean-motion resonances with Io that have excited its inclination and eccentricity (in a mean-motion resonance the ratio of orbital periods of two bodies is a rational number like m:n).[11]
Amalthea's orbit lies near the outer edge of the Amalthea Gossamer Ring, which is composed of dust ejected from the satellite.[18]
Physical characteristics
The surface of Amalthea is very red.[5] This color may be due to sulfur originating from Io or some other non-ice material.[5] Bright patches of less-red tint appear on the major slopes of Amalthea, but the nature of this color is currently unknown.[5] The surface of Amalthea is slightly brighter than surfaces of other inner satellites of Jupiter.[7] There is also a substantial asymmetry between the leading and trailing hemispheres: the leading hemisphere is 1.3 times brighter than the trailing one. The asymmetry is probably caused by the higher velocity and frequency of impacts on the leading hemisphere, which excavates a bright material—presumably ice—from the interior of the moon.[7]

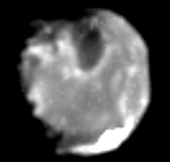

Amalthea is irregularly shaped, with the best ellipsoidal approximation being 250 × 146 × 128 km.[5] From this, Amalthea's surface area is likely between 88,000 and 170,000 square kilometers, or somewhere near 130,000. Like all other inner moons of Jupiter, it is tidally locked with the planet, with the long axis pointing towards Jupiter at all times.[11] Its surface is heavily scarred by craters, some of which are extremely large relative to the size of the moon: Pan, the largest crater, measures 100 km across and is at least 8 km deep.[5] Another crater, Gaea, measures 80 km across and is likely twice as deep as Pan.[5] Amalthea has several prominent bright spots, two of which are named. They are Lyctos Facula and Ida Facula, with a width reaching up to 25 km. They are located on the edge of ridges.[5]
Amalthea's irregular shape and large size led in the past to a conclusion that it is a fairly strong, rigid body,[11] where it was argued that a body composed of ices or other weak materials would have been pulled into a more spherical shape by its own gravity. However, on 5 November 2002, the Galileo orbiter made a targeted flyby that came within 160 km of Amalthea, and the deflection of its orbit was used to compute the moon's mass (its volume had been calculated previously—to within 10% or so—from a careful analysis of all extant images).[5] In the end, Amalthea's density was found to be as low as 0.86 g/cm3,[6][19] so it must be either a relatively icy body or very porous "rubble pile" or, more likely, something in between. Recent measurements of infrared spectra from the Subaru telescope suggest that the moon indeed contains hydrous minerals, indicating that it cannot have formed in its current position, since the hot primordial Jupiter would have melted it.[20] It is therefore likely to have formed farther from the planet or to be a captured Solar System body.[6] No images were taken during this flyby (Galileo's cameras had been deactivated due to radiation damage in January 2002), and the resolution of other available images is generally low.
Amalthea radiates slightly more heat than it receives from the Sun, which is probably due to the influence of Jovian heat flux (<9 kelvins), sunlight reflected from the planet (<5 K), and charged particle bombardment (<2 K).[8] This is a trait shared with Io, although for different reasons.
Named geological features
There are four named geological features on Amalthea: two craters and two faculae (bright spots).[21] The faculae are located on the edge of a ridge on the anti-Jupiter side of Amalthea.[5]
Craters are named after characters in Greek mythology associated with Zeus and Amalthea, and faculae are named after locations associated with Zeus.[22]
| Feature | Pronunciation | Diameter | Approval year |
Eponym | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gaea | /ˈdʒiːə/ | 80 km | 1979 | Gaia, Greek mother earth goddess who brought Zeus to Crete | WGPSN |
| Pan | /ˈpæn/ | 100 km | 1979 | Pan, Greek goat-god son of Amalthea and Hermes | WGPSN |
| Ida Facula | /ˈaɪdə/ | 50 km | 1979 | Mount Ida, Crete | WGPSN |
| Lyctos Facula | /ˈlɪktɒs/ | 25 km | 1979 | Lyctus, Crete | WGPSN |
Relationship with Jupiter's rings

Due to tidal force from Jupiter and Amalthea's low density and irregular shape, the escape velocity at its surface points closest to and furthest from Jupiter is no more than 1 m/s, and dust can easily escape from it after, for example, micrometeorite impacts; this dust forms the Amalthea Gossamer Ring.[11]
During its flyby of Amalthea, the Galileo orbiter's star scanner detected nine flashes that appeared to be small moonlets near the orbit of Amalthea. Because they were sighted only from one location, their true distances could not be measured. These moonlets may be anywhere in size from gravel to stadium-sized. Their origins are unknown, but they may be gravitationally captured into the current orbit or they may be ejecta from meteor impacts on Amalthea. On the next and final orbit (just an hour before destruction), Galileo detected one more such moonlet. However, this time Amalthea was on the other side of the planet, so it is probable that the particles form a ring around the planet near Amalthea's orbit.[23][24][25][26]
Views to and from Amalthea

From Jupiter's "surface"—or rather, from just above its cloudtops—Amalthea would appear very bright, shining with a magnitude of −4.7,[b] similar to that of Venus from Earth. At only 8 arcminutes across,[c] its disc would be barely discernible. Amalthea's orbital period is only slightly longer than its parent planet's day (about 20% in this case), which means it would cross Jupiter's sky very slowly. The time between moonrise and moonset would be over 29 hours.[b]
Science journalist Willy Ley suggested Amalthea as a base for observing Jupiter, because of its nearness to the planet, almost-synchronous orbit, and small size making a landing easy.[27] From the surface of Amalthea, Jupiter would look enormous: at 46 degrees across,[c] it would appear roughly 85 times wider than the full moon from Earth. Because Amalthea is in synchronous rotation, Jupiter would not appear to move, and would not be visible from one side of Amalthea. The Sun would disappear behind Jupiter's bulk for an hour and a half each revolution, and Amalthea's short rotation period gives it just under six hours of daylight. Though Jupiter would appear 900 times brighter than the full moon, its light would be spread over an area some 8,500 times greater and it would not look as bright per surface unit.[b]
Exploration

In 1979, the unmanned Voyager 1 and Voyager 2 space probes obtained the first images of Amalthea to resolve its surface features.[5] They also measured the visible and infrared spectra and surface temperature.[8] Later, the Galileo orbiter completed the imaging of Amalthea's surface. Galileo made its final satellite fly-by at a distance of approximately 244 km (152 mi) from Amalthea's center (at a height of about 160–170 km) on 5 November 2002, permitting the moon's mass to be accurately determined, while changing Galileo's trajectory so that it would plunge into Jupiter in September 2003 at the end of its mission.[6] In 2006, Amalthea's orbit was refined with measurements from New Horizons.
In fiction
Amalthea is the setting of several works of science fiction, including stories by Arthur C. Clarke, James Blish, and Arkady and Boris Strugatsky.
Gallery
-
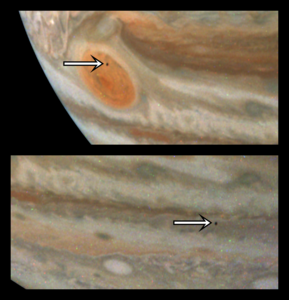
A distant image of Amalthea passing in front of Jupiter was captured by the Juno spacecraft on 7 March 2024 during its 59th Perijove.
See also
- Moons of Jupiter
- Galilean moons – the four biggest moons of Jupiter
Notes
- ^ a b c d e Calculated on the basis of other parameters.
- ^ a b c d Calculated on the basis of known distances, sizes, periods and visual magnitudes as visible from the Earth. Visual magnitudes as seen from Jupiter mj are calculated from visual magnitudes on Earth mv using the formula mj=mv−log2.512(Ij/Iv), where Ij and Iv are respective brightnesses (see visual magnitude), which scale according to the inverse square law. For visual magnitudes see http://www.oarval.org/ClasSaten.htm and Jupiter (planet).
- ^ a b Calculated from the known sizes and distances of the bodies, using the formula 2*arcsin(Rb/Ro), where Rb is the radius of the body and Ro is the radius of Amalthea's orbit or distance from the Jovian surface to Amalthea.
References
- ^ "Amalthea". Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary. Merriam-Webster.
- ^ Basil Montagu (1848) The works of Francis Bacon, vol. 1, p. 303
- ^ Isaac Asimov (1969) "Dance of the Satellites", The Magazine of Fantasy and Science Fiction, vol. 36, p. 105–115
- ^ a b c d e Cooper Murray et al. 2006.
- ^ a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p Thomas Burns et al. 1998.
- ^ a b c d e f Anderson Johnson et al. 2005.
- ^ a b c Simonelli Rossier et al. 2000.
- ^ a b c d Simonelli 1983.
- ^ Observatorio ARVAL.
- ^ a b Barnard 1892.
- ^ a b c d e f Burns Simonelli et al. 2004.
- ^ Lick Observatory (1894). A Brief Account of the Lick Observatory of the University of California. The University Press. p. 7–.
- ^ Bakich M. E. (2000). The Cambridge Planetary Handbook. Cambridge University Press. pp. 220–221. ISBN 9780521632805.
- ^ "Planet and Satellite Names and Discoverers". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. International Astronomical Union (IAU) Working Group for Planetary System Nomenclature (WGPSN). Archived from the original on 21 August 2014. Retrieved 8 October 2014.
- ^ Blunck J. (2010). Solar System Moons: Discovery and Mythology (PDF). Springer. pp. 9–15. Bibcode:2010ssm..book.....B. doi:10.1007/978-3-540-68853-2. ISBN 978-3-540-68852-5. Archived from the original (PDF) on 4 March 2016. Retrieved 23 October 2014.
- ^ Flammarion C.; Kowal C.; Blunck J. (7 October 1975). "Satellites of Jupiter". IAU Circular. Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. Archived from the original on 22 February 2014. Retrieved 17 October 2014. (Bibcode:1975IAUC.2846....6F)
- ^ Flammarion 1893.
- ^ Burns Showalter et al. 1999.
- ^ Swiss Cheese Moon.
- ^ Takato Bus et al. 2004.
- ^ USGS: Jupiter: Amalthea.
- ^ "USGS: Amalthea nomenclature". Archived from the original on 8 August 2004.
- ^ Fieseler P. D.; Adams O. W.; Vandermey N.; Theilig E. E.; Schimmels K. A.; Lewis G. D.; Ardalan S. M.; Alexander C. J. (2004). "The Galileo star scanner observations at Amalthea". Icarus. 169 (2): 390–401. Bibcode:2004Icar..169..390F. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2004.01.012.
- ^ "Another Find for Galileo". Jet Propulsion Laboratory. 9 April 2003. Archived from the original on 4 November 2004. Retrieved 27 March 2012.
- ^ Fieseler P. D.; Ardalan S. M. (4 April 2003). "Objects near Jupiter V (Amalthea)". IAU Circular. Central Bureau for Astronomical Telegrams. Archived from the original on 2 March 2014. Retrieved 12 October 2014. (Bibcode:2003IAUC.8107....2F)
- ^ Emily Lakdawalla (17 May 2013). "A serendipitous observation of tiny rocks in Jupiter's orbit by Galileo". The Planetary Society. Archived from the original on 14 August 2014. Retrieved 14 October 2014.
- ^ Ley, Willy (July 1968). "Interplanetary Communications". For Your Information. Galaxy Science Fiction. pp. 116–124.
Cited sources
- Anderson, J. D.; Johnson, T. V.; Schubert, G.; Asmar, S.; Jacobson, R. A.; Johnston, D.; Lau, E. L.; Lewis, G.; Moore, W. B.; Taylor, A.; Thomas, P. C.; Weinwurm, G. (27 May 2005). "Amalthea's Density is Less Than That of Water". Science. 308 (5726): 1291–1293. Bibcode:2005Sci...308.1291A. doi:10.1126/science.1110422. PMID 15919987. S2CID 924257.
- Barnard, E. E. (12 October 1892). "Discovery and observations of a fifth satellite to Jupiter". The Astronomical Journal. 12 (11): 81–85. Bibcode:1892AJ.....12...81B. doi:10.1086/101715.
- Burns, Joseph A.; Showalter, Mark R.; Hamilton, Douglas P.; Nicholson, Philip D.; de Pater, Imke; Ockert-Bell, Maureen E.; Thomas, Peter C. (14 May 1999). "The Formation of Jupiter's Faint Rings". Science. 284 (5417): 1146–1150. Bibcode:1999Sci...284.1146B. doi:10.1126/science.284.5417.1146. PMID 10325220.
- Burns, Joseph A.; Simonelli, Damon P.; Showalter, Mark R.; Hamilton, Douglas P.; Porco, Carolyn C.; Throop, Henry; Esposito, Larry W. (2004). Bagenal, Fran; Dowling, Timothy E.; McKinnon, William B. (eds.). Jupiter's Ring-Moon System (PDF). Cambridge University Press. pp. 241–262. Bibcode:2004jpsm.book..241B. ISBN 978-0-521-81808-7.
{{cite encyclopedia}}:|journal=ignored (help) - Cooper, N. J.; Murray, C. D.; Porco, C. C.; Spitale, J. N. (March 2006). "Cassini ISS astrometric observations of the inner jovian satellites, Amalthea and Thebe". Icarus. 181 (1): 223–234. Bibcode:2006Icar..181..223C. doi:10.1016/j.icarus.2005.11.007.
- Flammarion, Camille (1893). "Le Nouveau Satellite de Jupiter". L'Astronomie. 12: 91–94. Bibcode:1893LAstr..12...91F.
- Observatorio ARVAL (15 April 2007). "Classic Satellites of the Solar System". Observatorio ARVAL. Archived from the original on 9 July 2011. Retrieved 17 December 2011.
- Simonelli, D. P. (June 1983). "Amalthea: Implications of the temperature observed by Voyager". Icarus. 54 (3): 524–538. Bibcode:1983Icar...54..524S. doi:10.1016/0019-1035(83)90244-0. ISSN 0019-1035.
- Simonelli, D. P.; Rossier, L.; Thomas, P. C.; Veverka, J.; Burns, J. A.; Belton, M. J. S. (October 2000). "Leading/Trailing Albedo Asymmetries of Thebe, Amalthea, and Metis". Icarus. 147 (2): 353–365. Bibcode:2000Icar..147..353S. doi:10.1006/icar.2000.6474.
- "Swiss Cheese Moon: Jovian Satellite Full of Holes". Space.com. 9 December 2002. Archived from the original on 28 August 2008.
- Takato, Naruhisa; Bus, Schelte J.; Terada, H.; Pyo, Tae-Soo; Kobayashi, Naoto (24 December 2004). "Detection of a Deep 3-μm Absorption Feature in the Spectrum of Amalthea (JV)". Science. 306 (5705): 2224–2227. Bibcode:2004Sci...306.2224T. doi:10.1126/science.1105427. PMID 15618511. S2CID 129845022.
- Thomas, P. C.; Burns, J. A.; Rossier, L.; Simonelli, D.; Veverka, J.; Chapman, C. R.; Klaasen, K.; Johnson, T. V.; Belton, M. J. S.; Galileo Solid State Imaging Team (September 1998). "The Small Inner Satellites of Jupiter". Icarus. 135 (1): 360–371. Bibcode:1998Icar..135..360T. doi:10.1006/icar.1998.5976.
- USGS/IAU. "Amalthea Nomenclature". Gazetteer of Planetary Nomenclature. USGS Astrogeology. Retrieved 27 March 2012.
External links
- Amalthea Profile by NASA's Solar System Exploration
- Amalthea nomenclature from the USGS planetary nomenclature page
- Jupiter's Amalthea Surprisingly Jumbled – JPL press release (2002-12-09)
- Jupiter From Amalthea, a painting by Frank Hettick, 2002.
- Animated 3D shape model of Amalthea