Apolipoprotein C-II
| Apo-CII | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 nmr structure of human apolipoprotein c-ii in the presence of sds | |||||||||
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| Symbol | Apo-CII | ||||||||
| Pfam | PF05355 | ||||||||
| InterPro | IPR008019 | ||||||||
| SCOP2 | 1by6 / SCOPe / SUPFAM | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Apolipoprotein C-II (Apo-CII, or Apoc-II), or apolipoprotein C2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the APOC2 gene.
The protein encoded by this gene is secreted in plasma, where it is a component of very low density lipoproteins and chylomicrons. This protein activates the enzyme lipoprotein lipase in capillaries,[5] which hydrolyzes triglycerides and thus provides free fatty acids and glycerols for cells. Mutations in this gene cause hyperlipoproteinemia type IB, characterized by xanthomas, pancreatitis, and hepatosplenomegaly, but no increased risk for atherosclerosis. Lab tests will show elevated blood levels of triglycerides, cholesterol, and chylomicrons[6]
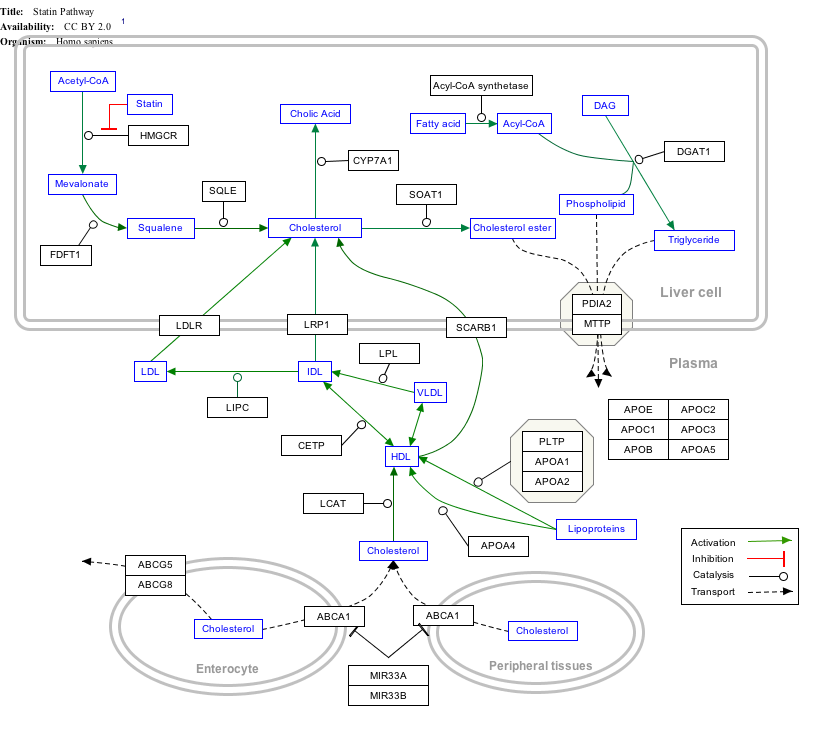
Interactive pathway map
[edit]Click on genes, proteins and metabolites below to link to respective articles. [§ 1]
- ^ The interactive pathway map can be edited at WikiPathways: "Statin_Pathway_WP430".
See also
[edit]References
[edit]- ^ a b c GRCh38: Ensembl release 89: ENSG00000234906 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ a b c GRCm38: Ensembl release 89: ENSMUSG00000002992 – Ensembl, May 2017
- ^ "Human PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ "Mouse PubMed Reference:". National Center for Biotechnology Information, U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ^ Kim SY, Park SM, Lee ST (2006). "Apolipoprotein C-II is a novel substrate for matrix metalloproteinases". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 339 (1): 47–54. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.10.182. PMID 16314153.
- ^ "Entrez Gene: APOC2 apolipoprotein C-II".
- Jackson RL, Baker HN, Gilliam EB, Gotto AM (1977). "Primary structure of very low density apolipoprotein C-II of human plasma". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74 (5): 1942–5. Bibcode:1977PNAS...74.1942J. doi:10.1073/pnas.74.5.1942. PMC 431048. PMID 194244.
- Lycksell PO, Ohman A, Bengtsson-Olivecrona G, et al. (1992). "Sequence specific 1H-NMR assignments and secondary structure of a carboxy-terminal functional fragment of apolipoprotein CII". Eur. J. Biochem. 205 (1): 223–31. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16772.x. PMID 1555583.
- Hegele RA, Connelly PW, Maguire GF, et al. (1992). "An apolipoprotein CII mutation, CIILys19----Thr' identified in patients with hyperlipidemia". Dis. Markers. 9 (2): 73–80. PMID 1782747.
- Crecchio C, Capurso A, Pepe G (1990). "Identification of the mutation responsible for a case of plasmatic apolipoprotein CII deficiency (Apo CII-Bari)". Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 168 (3): 1118–27. doi:10.1016/0006-291X(90)91145-I. PMID 1971748.
- Bengtsson-Olivecrona G, Sletten K (1990). "Primary structure of the bovine analogues to human apolipoproteins CII and CIII. Studies on isoforms and evidence for proteolytic processing". Eur. J. Biochem. 192 (2): 515–21. doi:10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19255.x. PMID 2209608.
- Wei CF, Tsao YK, Robberson DL, et al. (1986). "The structure of the human apolipoprotein C-II gene. Electron microscopic analysis of RNA:DNA hybrids, complete nucleotide sequence, and identification of 5' homologous sequences among apolipoprotein genes". J. Biol. Chem. 260 (28): 15211–21. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)95724-8. PMID 2415514.
- Fojo SS, Lohse P, Parrott C, et al. (1989). "A nonsense mutation in the apolipoprotein C-IIPadova gene in a patient with apolipoprotein C-II deficiency". J. Clin. Invest. 84 (4): 1215–9. doi:10.1172/JCI114287. PMC 329780. PMID 2477392.
- Jackson CL, Bruns GA, Breslow JL (1986). "Isolation of cDNA and genomic clones for apolipoprotein C-II". In Segrest JP, Albers JA (eds.). Plasma Lipoproteins Part A: Preparation, Structure, and Molecular Biology. Methods in Enzymology. Vol. 128. Elsevier. pp. 788–800. doi:10.1016/0076-6879(86)28106-9. ISBN 9780121820282. PMID 3014272.
- Fojo SS, Law SW, Brewer HB (1987). "The human preproapolipoprotein C-II gene. Complete nucleic acid sequence and genomic organization". FEBS Lett. 213 (1): 221–6. doi:10.1016/0014-5793(87)81495-3. PMID 3030808. S2CID 42223577.
- Fojo SS, Stalenhoef AF, Marr K, et al. (1989). "A deletion mutation in the ApoC-II gene (ApoC-II Nijmegen) of a patient with a deficiency of apolipoprotein C-II". J. Biol. Chem. 263 (34): 17913–6. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(19)81302-9. PMID 3192518.
- Fojo SS, Beisiegel U, Beil U, et al. (1988). "Donor splice site mutation in the apolipoprotein (Apo) C-II gene (Apo C-IIHamburg) of a patient with Apo C-II deficiency". J. Clin. Invest. 82 (5): 1489–94. doi:10.1172/JCI113756. PMC 442713. PMID 3263393.
- Connelly PW, Maguire GF, Hofmann T, Little JA (1987). "Structure of apolipoprotein C-IIToronto, a nonfunctional human apolipoprotein". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (1): 270–3. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84..270C. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.1.270. PMC 304185. PMID 3467353.
- Fairwell T, Hospattankar AV, Brewer HB, Khan SA (1987). "Human plasma apolipoprotein C-II: total solid-phase synthesis and chemical and biological characterization". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84 (14): 4796–800. Bibcode:1987PNAS...84.4796F. doi:10.1073/pnas.84.14.4796. PMC 305192. PMID 3474626.
- Fojo SS, Taam L, Fairwell T, et al. (1986). "Human preproapolipoprotein C-II. Analysis of major plasma isoforms". J. Biol. Chem. 261 (21): 9591–4. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)67554-4. PMID 3525527.
- Das HK, Jackson CL, Miller DA, et al. (1987). "The human apolipoprotein C-II gene sequence contains a novel chromosome 19-specific minisatellite in its third intron". J. Biol. Chem. 262 (10): 4787–93. doi:10.1016/S0021-9258(18)61264-5. PMID 3558370.
- Connelly PW, Maguire GF, Little JA (1988). "Apolipoprotein CIISt. Michael. Familial apolipoprotein CII deficiency associated with premature vascular disease". J. Clin. Invest. 80 (6): 1597–606. doi:10.1172/JCI113246. PMC 442428. PMID 3680515.
- Baggio G, Manzato E, Gabelli C, et al. (1986). "Apolipoprotein C-II deficiency syndrome. Clinical features, lipoprotein characterization, lipase activity, and correction of hypertriglyceridemia after apolipoprotein C-II administration in two affected patients". J. Clin. Invest. 77 (2): 520–7. doi:10.1172/JCI112332. PMC 423374. PMID 3944267.
- Menzel HJ, Kane JP, Malloy MJ, Havel RJ (1986). "A variant primary structure of apolipoprotein C-II in individuals of African descent". J. Clin. Invest. 77 (2): 595–601. doi:10.1172/JCI112342. PMC 423392. PMID 3944271.
- Sharpe CR, Sidoli A, Shelley CS, et al. (1984). "Human apolipoproteins AI, AII, CII and CIII. cDNA sequences and mRNA abundance". Nucleic Acids Res. 12 (9): 3917–32. doi:10.1093/nar/12.9.3917. PMC 318799. PMID 6328445.
- Jackson CL, Bruns GA, Breslow JL (1984). "Isolation and sequence of a human apolipoprotein CII cDNA clone and its use to isolate and map to human chromosome 19 the gene for apolipoprotein CII". Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81 (10): 2945–9. Bibcode:1984PNAS...81.2945J. doi:10.1073/pnas.81.10.2945. PMC 345197. PMID 6328478.
External links
[edit]- Human APOC2 genome location and APOC2 gene details page in the UCSC Genome Browser.